浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2325-2339.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250055
加拿大一枝黄花入侵对温州沿海区域植物群落结构的影响
应碧旷1,2( ), 刘宇2, 魏馨2, 李晶2, 王金旺2,*(
), 刘宇2, 魏馨2, 李晶2, 王金旺2,*( )
)
- 1.浙江农林大学 林业与生物技术学院,浙江 杭州 311300
2.浙江省亚热带作物研究所,浙江 温州 325005
-
收稿日期:2025-01-17出版日期:2025-11-25发布日期:2025-12-08 -
作者简介:应碧旷(1998—),男,浙江台州人,硕士研究生,主要从事林业生态研究。E-mail:18857615869@163.com -
通讯作者:*王金旺,E-mail: kingwwang@163.com -
基金资助:农业农村部政府购买服务项目(13230119)
Impacts of Solidago canadensis invasion on plant community structure in coastal region of Wenzhou, China
YING Bikuang1,2( ), LIU Yu2, WEI Xin2, LI Jing2, WANG Jinwang2,*(
), LIU Yu2, WEI Xin2, LI Jing2, WANG Jinwang2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Zhejiang Institute of Subtropical Crops, Wenzhou 325005, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2025-01-17Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
摘要: 加拿大一枝黄花(Solidago canadensis)是被列入《中国第二批外来入侵物种名单》的植物,于2003年在温州发现有分布。选择沿海典型生境,基于温州市40个样方调查数据,开展加拿大一枝黄花在不同入侵程度与不同生境中对群落结构、物种多样性的影响研究,探讨其入侵特征与机制。结果表明:温州市沿海典型生境中,加拿大一枝黄花入侵的群落包含维管植物13科28属34种,其中,外来入侵植物的物种数占26.5%。随着加拿大一枝黄花入侵程度的增强,群落内的物种数逐渐降低,外来入侵植物的种类占比逐渐增加,且外来入侵植物的重要值之和逐渐增加。在供试样方中,加拿大一枝黄花的重要值与生态位宽度在各类入侵群落中均最高,且其他外来入侵植物的重要值与生态位宽度也多位于各样方前列。加拿大一枝黄花重度入侵群落的多样性指数显著(p<0.05)低于轻、中度入侵群落。加拿大一枝黄花的相对多度与其他外来入侵植物、本土植物呈负相关关系,且其相关性随入侵程度的增强而增强。生态位重叠指数分析进一步明确,在中、重度入侵群落中,加拿大一枝黄花与其他外来入侵植物、本土植物之间逐渐增强的竞争关系是导致以上结果的重要原因。在各地类中,园地与交通用地有利于外来入侵植物扩散,而耕地有利于防止外来植物入侵。
中图分类号:
引用本文
应碧旷, 刘宇, 魏馨, 李晶, 王金旺. 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对温州沿海区域植物群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2325-2339.
YING Bikuang, LIU Yu, WEI Xin, LI Jing, WANG Jinwang. Impacts of Solidago canadensis invasion on plant community structure in coastal region of Wenzhou, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2325-2339.
| 科名 Family | 种名 Species | 科名 Family | 种名 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 桑科Moraceae | 葎草Humulus scandens | 大戟科Euphorbiaceae | 铁苋菜Acalypha australis |
| 蓼科Polygonaceae | 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | |
| 苋科Amaranthaceae | 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides◆ | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 禾本科Poaceae | 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 硕苞蔷薇Rosa bracteata | 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | |
| 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata◆ | 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | |
| 菊科Asteraceae | 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis◆ | 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum◆ | 假稻Leersia japonica | ||
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | ||
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | 铺地黍Panicum repens◆ | ||
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | ||
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba◆ | 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | ||
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa◆ | 结缕草Zoysia japonica | ||
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis◆ | 莎草科Cyperaceae | 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis◆ | 爵床科Acanthaceae | 爵床Justicia procumbens | |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 茜草科Rubiaceae | 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens |
表1 调查地植物名录
Table 1 List of plants in survey site
| 科名 Family | 种名 Species | 科名 Family | 种名 Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 桑科Moraceae | 葎草Humulus scandens | 大戟科Euphorbiaceae | 铁苋菜Acalypha australis |
| 蓼科Polygonaceae | 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | |
| 苋科Amaranthaceae | 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides◆ | 葡萄科Vitaceae | 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 禾本科Poaceae | 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 硕苞蔷薇Rosa bracteata | 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | |
| 酢浆草科Oxalidaceae | 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata◆ | 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | |
| 菊科Asteraceae | 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis◆ | 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum◆ | 假稻Leersia japonica | ||
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | ||
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | 铺地黍Panicum repens◆ | ||
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | ||
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba◆ | 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | ||
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa◆ | 结缕草Zoysia japonica | ||
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis◆ | 莎草科Cyperaceae | 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis◆ | 爵床科Acanthaceae | 爵床Justicia procumbens | |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 茜草科Rubiaceae | 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens |
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 入侵强度 Invasion intensity | 样方数量 Number of quadrats | 科数量 Number of family | 属数量 Number of genus | 植物物种数 Number of plant species | 入侵植物种数 Number of invasive plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城镇用地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 2 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 3 |
| Urban land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 5 | 3 | 13 | 13 | 5 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 交通用地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Transportation land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 2 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| 耕地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 3 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 6 |
| Cultivated land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 2 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 5 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 5 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 | |
| 园地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Garden land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 2 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 7 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
表2 不同生境加拿大一枝黄花入侵群落的物种组成
Table 2 Species composition of invaded communities by Solidago canadensis in different habitats
| 生境类型 Habitat type | 入侵强度 Invasion intensity | 样方数量 Number of quadrats | 科数量 Number of family | 属数量 Number of genus | 植物物种数 Number of plant species | 入侵植物种数 Number of invasive plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城镇用地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 2 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 3 |
| Urban land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 5 | 3 | 13 | 13 | 5 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | |
| 交通用地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Transportation land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 2 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| 耕地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 3 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 6 |
| Cultivated land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 2 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 5 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 5 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 | |
| 园地 | 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Garden land | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 2 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| 重度入侵Severe invasion | 7 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 物种 Species | 不同入侵强度下物种的重要值Importance values of species under invasion intensities | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 重度入侵Severe invasion | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis | 15.09 | 22.87 | 50.52 |
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis | 11.31 | 6.87 | 3.32 |
| 铺地黍Panicum repens | 5.31 | — | — |
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba | 4.90 | 3.32 | 9.15 |
| 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata | 3.28 | — | — |
| 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides | 2.31 | 20.51 | 4.15 |
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa | 1.69 | 1.20 | — |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis | 1.39 | 1.65 | 2.91 |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum | 0.70 | 7.42 | 2.03 |
| 入侵植物总和Sum of invasive plants | 45.98 | 63.84 | 72.08 |
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | 12.98 | 2.03 | — |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 12.10 | 4.70 | 7.89 |
| 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | 8.39 | 1.36 | — |
| 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | 3.19 | 2.18 | — |
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | 2.12 | — | 2.29 |
| 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica | 1.54 | — | — |
| 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | 1.51 | 3.00 | 3.96 |
| 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | 1.37 | — | — |
| 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | 1.26 | 1.62 | — |
| 假稻Leersia japonica | 1.24 | 4.32 | — |
| 铁苋菜Acalypha australis | 1.18 | — | 2.50 |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | 1.15 | — | 3.68 |
| 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | 0.82 | 6.46 | 4.30 |
| 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | 0.79 | 2.76 | — |
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 0.79 | 1.31 | 1.58 |
| 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | 0.67 | — | — |
| 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | 0.60 | — | — |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 0.60 | — | — |
| 葎草Humulus scandens | 0.53 | — | — |
| 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 0.60 | — | — |
| 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens | 0.57 | — | — |
| 结缕草Zoysia japonica | — | 3.19 | — |
| 爵床Justicia procumbens | — | 1.93 | — |
| 硕包蔷薇Rosa bracteata | — | — | 1.73 |
| 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | — | 1.26 | — |
| 本土植物总和Sum of native plants | 54.00 | 36.12 | 27.93 |
表3 不同入侵程度下植物群落的物种重要值(Ⅳ)
Table 3 Importance values (Ⅳ) of species in plant communities under different invasion intensities
| 物种 Species | 不同入侵强度下物种的重要值Importance values of species under invasion intensities | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度入侵Slight invasion | 中度入侵Moderate invasion | 重度入侵Severe invasion | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis | 15.09 | 22.87 | 50.52 |
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis | 11.31 | 6.87 | 3.32 |
| 铺地黍Panicum repens | 5.31 | — | — |
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba | 4.90 | 3.32 | 9.15 |
| 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata | 3.28 | — | — |
| 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides | 2.31 | 20.51 | 4.15 |
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa | 1.69 | 1.20 | — |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis | 1.39 | 1.65 | 2.91 |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum | 0.70 | 7.42 | 2.03 |
| 入侵植物总和Sum of invasive plants | 45.98 | 63.84 | 72.08 |
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | 12.98 | 2.03 | — |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 12.10 | 4.70 | 7.89 |
| 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | 8.39 | 1.36 | — |
| 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | 3.19 | 2.18 | — |
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | 2.12 | — | 2.29 |
| 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica | 1.54 | — | — |
| 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | 1.51 | 3.00 | 3.96 |
| 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | 1.37 | — | — |
| 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | 1.26 | 1.62 | — |
| 假稻Leersia japonica | 1.24 | 4.32 | — |
| 铁苋菜Acalypha australis | 1.18 | — | 2.50 |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | 1.15 | — | 3.68 |
| 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | 0.82 | 6.46 | 4.30 |
| 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | 0.79 | 2.76 | — |
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 0.79 | 1.31 | 1.58 |
| 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | 0.67 | — | — |
| 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | 0.60 | — | — |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 0.60 | — | — |
| 葎草Humulus scandens | 0.53 | — | — |
| 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 0.60 | — | — |
| 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens | 0.57 | — | — |
| 结缕草Zoysia japonica | — | 3.19 | — |
| 爵床Justicia procumbens | — | 1.93 | — |
| 硕包蔷薇Rosa bracteata | — | — | 1.73 |
| 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | — | 1.26 | — |
| 本土植物总和Sum of native plants | 54.00 | 36.12 | 27.93 |
| 物种 Species | 不同生境下物种的重要值Importance values of species under habitat types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Cultivated land | 城镇用地 Urban land | 交通用地 Transportation land | 园地 Garden land | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis | 20.44 | 27.79 | 43.20 | 54.83 |
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis | 3.38 | 24.20 | — | — |
| 铺地黍Panicum repens | — | — | — | 4.60 |
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba | 2.57 | — | — | 6.57 |
| 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata | — | — | 2.10 | — |
| 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides | 8.38 | 1.03 | 22.64 | 6.68 |
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa | 0.95 | — | — | — |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis | — | 0.86 | — | 5.84 |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum | 1.19 | 5.13 | — | — |
| 入侵植物总和Sum of invasive plants | 36.91 | 59.01 | 67.94 | 78.52 |
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | — | 2.95 | 18.22 | — |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 5.45 | 5.92 | — | 18.82 |
| 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | 12.44 | — | — | — |
| 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | 2.52 | — | — | — |
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | — | 2.63 | — | — |
| 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica | — | 3.54 | 9.27 | — |
| 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | 7.74 | 2.70 | — | — |
| 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | — | 3.46 | — | — |
| 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | — | 3.24 | — | — |
| 假稻Leersia japonica | 13.06 | — | — | — |
| 铁苋菜Acalypha australis | 5.24 | — | — | 2.66 |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | 3.57 | — | — | — |
| 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | 3.56 | — | — | — |
| 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | — | 4.44 | — | — |
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 2.59 | — | — | — |
| 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | — | 5.55 | — | — |
| 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | 0.69 | — | — | — |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 3.41 | — | — | — |
| 葎草Humulus scandens | — | — | 1.94 | — |
| 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 0.61 | — | — | — |
| 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens | 0.92 | — | — | — |
| 结缕草Zoysia japonica | — | 4.38 | — | — |
| 爵床Justicia procumbens | 1.26 | — | — | — |
| 硕包蔷薇Rosa bracteata | — | — | 2.64 | — |
| 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | — | 2.16 | — | — |
| 本土植物总和Sum of native plants | 63.06 | 40.97 | 32.07 | 21.48 |
表4 不同生境下植物群落物种的重要值
Table 4 Importance values of species in plant communities under different habitats
| 物种 Species | 不同生境下物种的重要值Importance values of species under habitat types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Cultivated land | 城镇用地 Urban land | 交通用地 Transportation land | 园地 Garden land | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花Solidago canadensis | 20.44 | 27.79 | 43.20 | 54.83 |
| 小蓬草Erigeron canadensis | 3.38 | 24.20 | — | — |
| 铺地黍Panicum repens | — | — | — | 4.60 |
| 白花鬼针草Bidens alba | 2.57 | — | — | 6.57 |
| 红花酢浆草Oxalis corniculata | — | — | 2.10 | — |
| 喜旱莲子草Alternanthera philoxeroides | 8.38 | 1.03 | 22.64 | 6.68 |
| 鬼针草Bidens pilosa | 0.95 | — | — | — |
| 香丝草Erigeron bonariensis | — | 0.86 | — | 5.84 |
| 钻叶紫菀Symphyotrichum subulatum | 1.19 | 5.13 | — | — |
| 入侵植物总和Sum of invasive plants | 36.91 | 59.01 | 67.94 | 78.52 |
| 野艾蒿Artemisia lavandulaefolia | — | 2.95 | 18.22 | — |
| 翅果菊Lactuca indica | 5.45 | 5.92 | — | 18.82 |
| 光头稗Echinochloa colonum | 12.44 | — | — | — |
| 荩草Arthraxon hispidus | 2.52 | — | — | — |
| 矮蒿Artemisia lancea | — | 2.63 | — | — |
| 乌蔹莓Causonis japonica | — | 3.54 | 9.27 | — |
| 糠稷Panicum bisulcatum | 7.74 | 2.70 | — | — |
| 大白茅Imperata cylindrica var. major | — | 3.46 | — | — |
| 大狗尾草Setaria faberi | — | 3.24 | — | — |
| 假稻Leersia japonica | 13.06 | — | — | — |
| 铁苋菜Acalypha australis | 5.24 | — | — | 2.66 |
| 金色狗尾草Setaria pumlia | 3.57 | — | — | — |
| 升马唐Digitaria ciliaris | 3.56 | — | — | — |
| 鸡眼草Kummerowia striata | — | 4.44 | — | — |
| 鳢肠Eclipta prostrata | 2.59 | — | — | — |
| 叶下珠Phyllanthus urinaria | — | 5.55 | — | — |
| 水蜈蚣Kyllinga brevifolia | 0.69 | — | — | — |
| 莲子草Alternanthera sessilis | 3.41 | — | — | — |
| 葎草Humulus scandens | — | — | 1.94 | — |
| 长鬃蓼Polygonum longisetum | 0.61 | — | — | — |
| 鸡矢藤Paederia scandens | 0.92 | — | — | — |
| 结缕草Zoysia japonica | — | 4.38 | — | — |
| 爵床Justicia procumbens | 1.26 | — | — | — |
| 硕包蔷薇Rosa bracteata | — | — | 2.64 | — |
| 红尾翎Digitaria radicosa | — | 2.16 | — | — |
| 本土植物总和Sum of native plants | 63.06 | 40.97 | 32.07 | 21.48 |
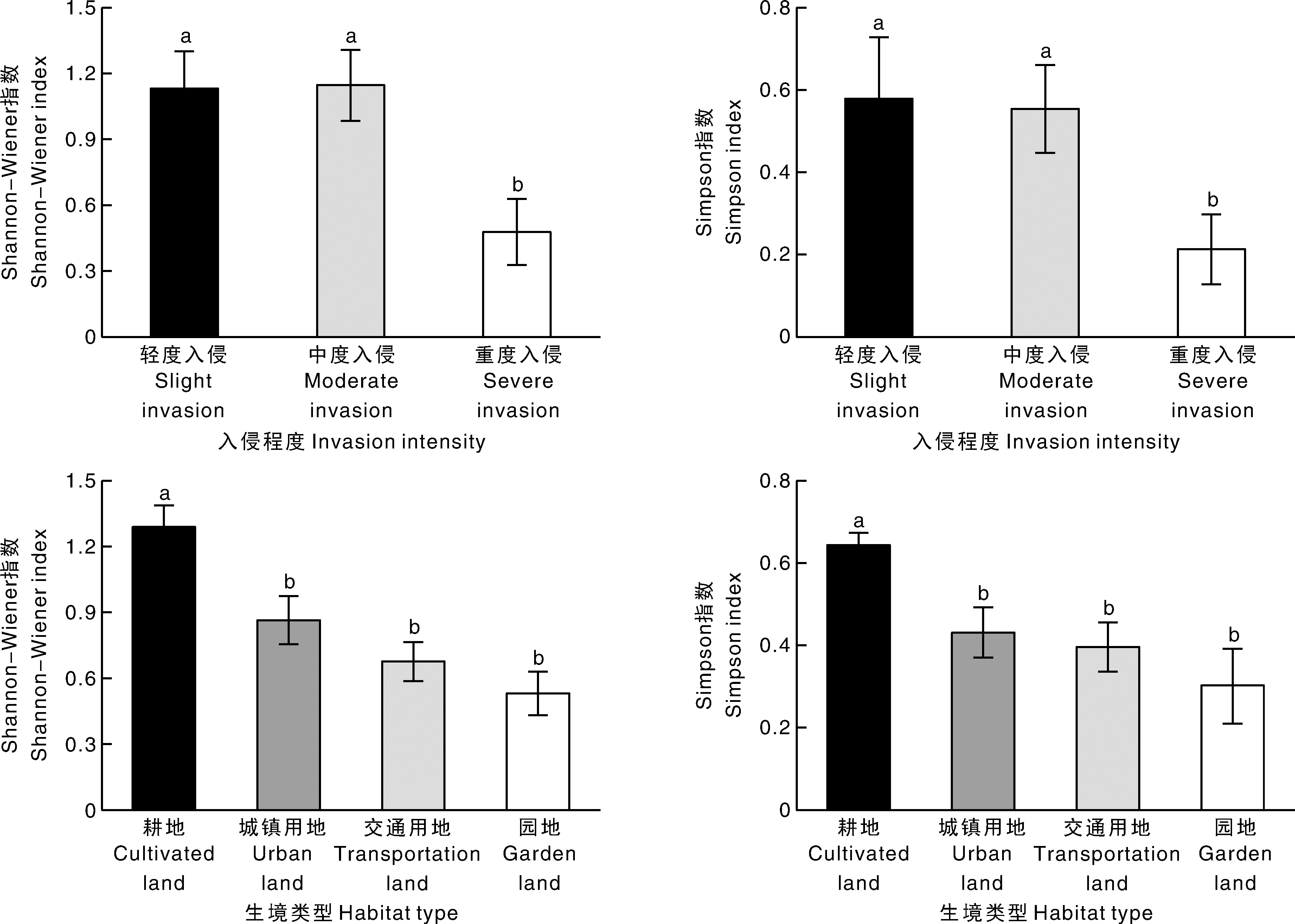
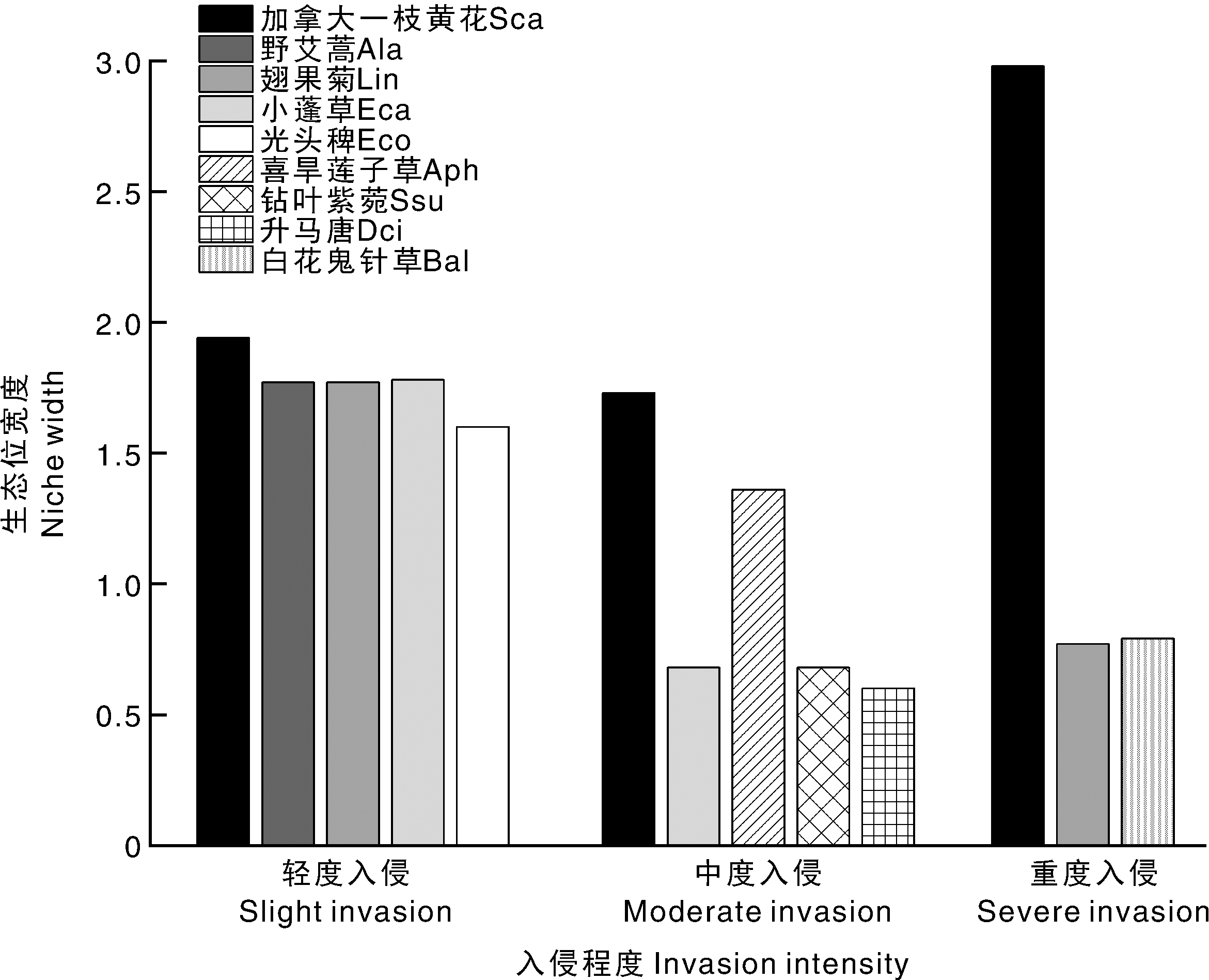
图1 加拿大一枝黄花群落的多样性指数 柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。
Fig.1 Diversity index of Solidago canadensis communities Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference at p<0.05.
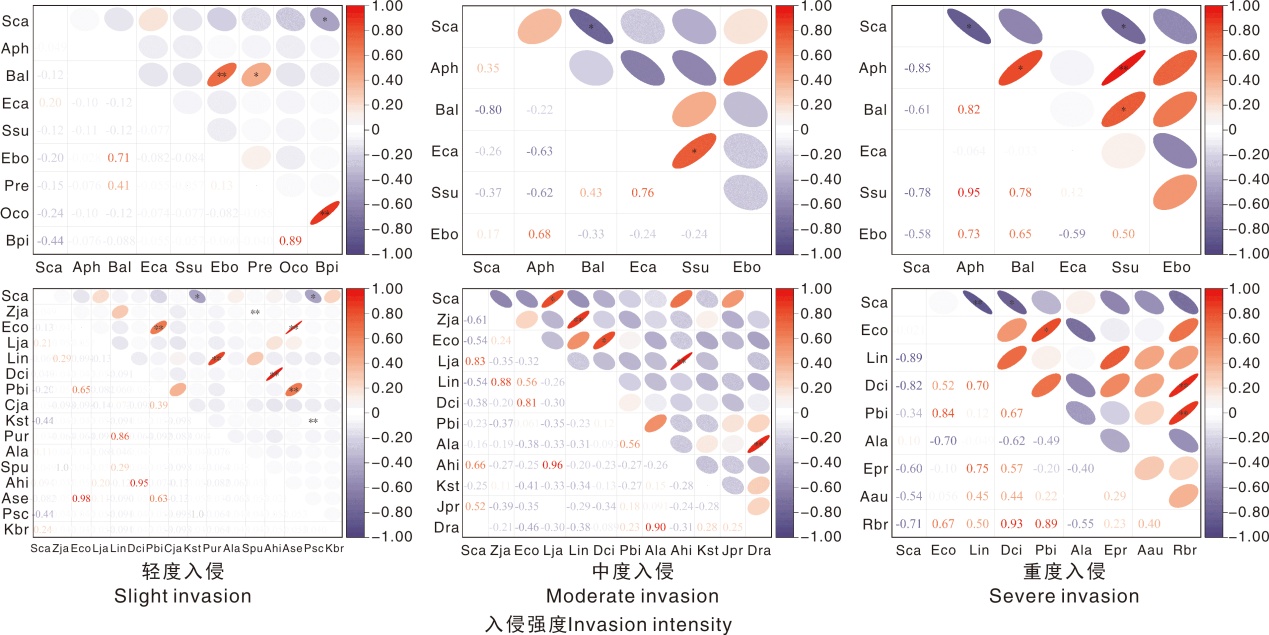
图2 不同入侵程度下加拿大一枝黄花与其他入侵植物(上行)、本土植物(下行)相对多度的相关性 Aph,喜旱莲子草;Ase,莲子草;Rbr硕苞蔷薇;Kst鸡眼草;Oco,红花酢浆草;Sca,加拿大一枝黄花;Ssu,钻叶紫菀;Epr,鳢肠;Ala,野艾蒿;Bal,白花鬼针草;Bpi,鬼针草;Eca,小蓬草;Ebo,香丝草;Lin,翅果菊;Aau,铁苋菜;Pur,叶下珠;Cja,乌蔹莓;Ahi,荩草;Dci,升马唐;Dra,红尾翎;Eco,光头稗;Lja,假稻;Pbi,糠稷;Pre,铺地黍;Spu,金色狗尾草;Zja,结缕草;Kbr,水蜈蚣;Jpr,爵床;Psc,鸡矢藤。标“*”和“**”的分别表示显著(p<0.05)和极显著(p<0.05)相关。下同。
Fig.2 Correlation of relative abundance of Solidago canadensis with other invasive (upper row) and native species (lower row) under different invasion intensities Aph, Alternanthera philoxeroides; Ase, Alternanthera sessilis; Rbr, Rosa bracteata; Kst, Kummerowia striata; Oco, Oxalis corniculata; Sca, Solidago canadensis; Ssu, Symphyotrichum subulatum; Epr, Eclipta prostrata; Ala, Artemisia lavandulaefolia; Bal, Bidens alba; Bpi, Bidens pilosa; Eca, Erigeron canadensis; Ebo, Erigeron bonariensis; Lin, Lactuca indica; Aau, Acalypha australis; Pur, Phyllanthus urinaria; Cja, Causonis japonica; Ahi, Arthraxon hispidus; Dci, Digitaria ciliaris; Dra, Digitaria radicosa; Eco, Echinochloa colonum; Lja, Leersia japonica; Pbi, Panicum bisulcatum; Pre, Panicum repens; Spu, Setaria pumila; Zja, Zoysia japonica; Kbr, Kyllinga brevifolia; Jpr, Justicia procumbens; Psc, Paederia scandens. “*” and “**” indicate significant correlation at p<0.05 and p<0.01 level, respectively.The same as below.
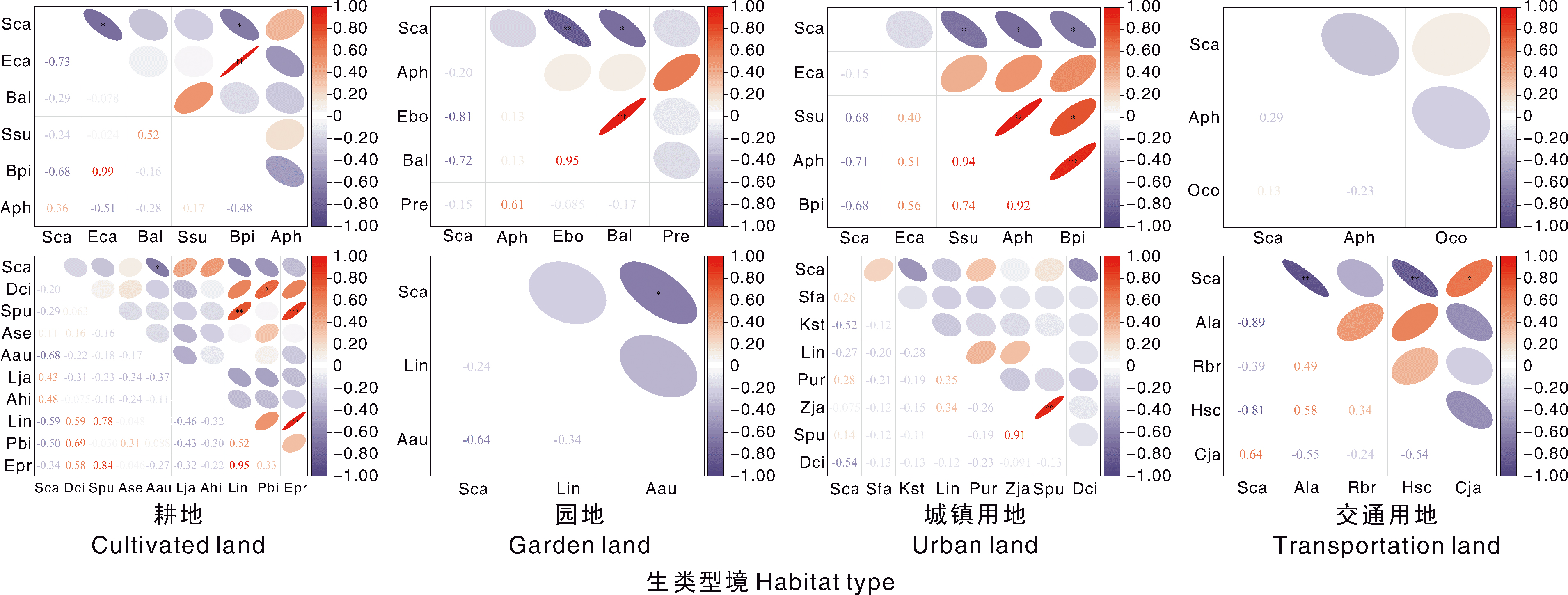
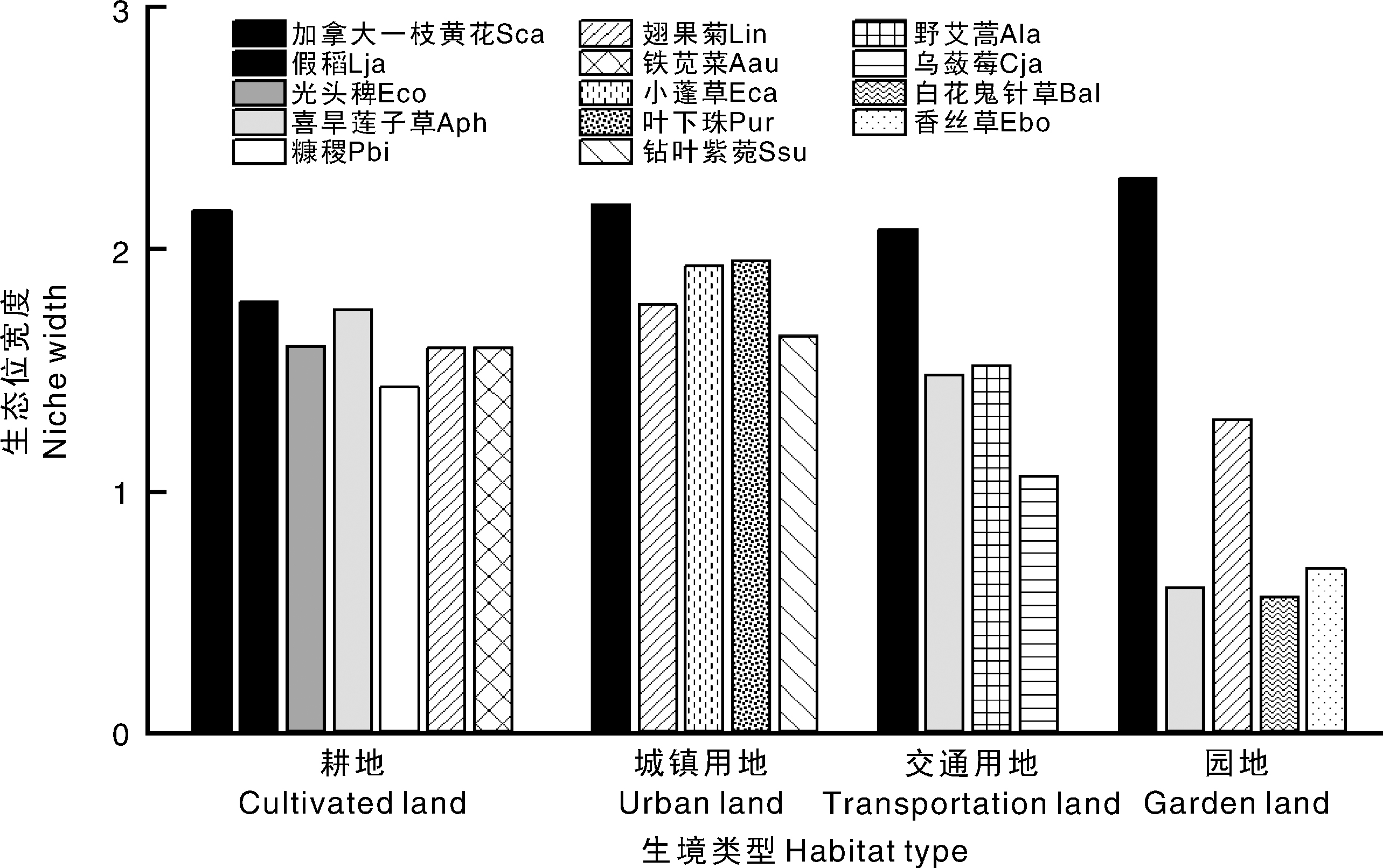
图3 不同生境加拿大一枝黄花与其他外来入侵植物(上行)、乡土植物(下行)相对多度的相关性 Hsc,葎草;Sfa,大狗尾草。
Fig.3 Correlation of relative abundance of Solidago canadensis with other invasive (upper row) and native species (lower row) under different habitat types Hsc, Humulus scandens; Sfa, Setaria faberi.
| 物种 species | 不同入侵强度下的生态位重叠指数 Niche overlap index under invasion intensities | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度入侵 Slight invasion | 中度入侵 Moderate invasion | 重度入侵 Severe invasion | |
| Eca | 0.45 | 0.68 | — |
| Lin | 0.61 | — | 0.81 |
| Eco | 0.53 | — | — |
| Ala | 0.55 | — | — |
| Aph | — | 0.63 | — |
| Dci | — | 0.41 | — |
| Ssu | — | 0.36 | — |
| Bal | — | — | 0.83 |
表5 不同入侵强度下加拿大一枝黄花与其他植物的生态位重叠指数
Table 5 Niche overlap index between Solidago canadensis and other plants under different invasion intensities
| 物种 species | 不同入侵强度下的生态位重叠指数 Niche overlap index under invasion intensities | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度入侵 Slight invasion | 中度入侵 Moderate invasion | 重度入侵 Severe invasion | |
| Eca | 0.45 | 0.68 | — |
| Lin | 0.61 | — | 0.81 |
| Eco | 0.53 | — | — |
| Ala | 0.55 | — | — |
| Aph | — | 0.63 | — |
| Dci | — | 0.41 | — |
| Ssu | — | 0.36 | — |
| Bal | — | — | 0.83 |
| 物种 Species | 不同生境的生态位重叠指数Niche overlap index under different habitat types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Cultivated land | 交通用地 Transportation land | 园地 Garden land | 城镇用地 Urban land | |
| Pbi | 0.22 | — | — | — |
| Eca | 0.36 | — | — | 0.27 |
| Aph | 0.35 | 0.85 | 0.84 | — |
| Lin | 0.47 | — | 0.87 | 0.54 |
| Lja | 0.37 | — | — | — |
| Aau | 0.22 | 0.66 | — | — |
| Ebo | — | — | 0.91 | — |
| Bal | — | — | 0.58 | — |
| Pur | — | — | — | 0.61 |
| Ssu | — | — | — | 0.38 |
| Cja | — | 0.77 | — | — |
表6 不同生境加拿大一枝黄花与其他植物的生态位重叠指数
Table 6 Niche overlap index between Solidago canadensis and other plants under different habitats
| 物种 Species | 不同生境的生态位重叠指数Niche overlap index under different habitat types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Cultivated land | 交通用地 Transportation land | 园地 Garden land | 城镇用地 Urban land | |
| Pbi | 0.22 | — | — | — |
| Eca | 0.36 | — | — | 0.27 |
| Aph | 0.35 | 0.85 | 0.84 | — |
| Lin | 0.47 | — | 0.87 | 0.54 |
| Lja | 0.37 | — | — | — |
| Aau | 0.22 | 0.66 | — | — |
| Ebo | — | — | 0.91 | — |
| Bal | — | — | 0.58 | — |
| Pur | — | — | — | 0.61 |
| Ssu | — | — | — | 0.38 |
| Cja | — | 0.77 | — | — |
| [1] | 李伟杰, 朱珣之, 罗会婷, 等. 南京市加拿大一枝黄花入侵地群落的物种组成与多样性特征研究[J]. 广西植物, 2023, 43(8): 1488-1500. |
| LI W J, ZHU X Z, LUO H T, et al. Species composition and diversity characteristics of invaded community of Solidago canadensis in Nanjing[J]. Guihaia, 2023, 43(8): 1488-1500. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | DAWSON W, MOSER D, VAN KLEUNEN M, et al. Global hotspots and correlates of alien species richness across taxonomic groups[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2017, 1: 186. |
| [3] | EARLY R, BRADLEY B A, DUKES J S, et al. Global threats from invasive alien species in the twenty-first century and national response capacities[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12485. |
| [4] | 陈菁. 中国外来入侵物种的分布格局及主要影响因素[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2022. |
| CHEN J. The distribution patterns and the major influencing factors of invasive alien species in China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 李炫榕, 章巧依, 金鑫杰, 等. 浙江入侵新记录种薇甘菊发生现状及危害预测[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2023, 43(3): 132-137. |
| LI X R, ZHANG Q Y, JIN X J, et al. A new invasive genus and species of Mikania micrantha in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 2023, 43(3): 132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 肖永康, 何健霄, 隋晓青, 等. 意大利苍耳入侵对本地植物群落物种多样性和稳定性的影响: 以乌鲁木齐市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(13): 5717-5725. |
| XIAO Y K, HE J X, SUI X Q, et al. Effects of Xanthium italicum invasion on the diversity and stability of native plant communities: a case study of Urumqi, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(13): 5717-5725. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | KOLAR C S, LODGE D M. Progress in invasion biology: predicting invaders[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2001, 16(4): 199-204. |
| [8] | GIORIA M, HULME P E, RICHARDSON D M, et al. Why are invasive plants successful[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2023, 74: 635-670. |
| [9] | WANG C Y, CHENG H Y, WU B D, et al. The functional diversity of native ecosystems increases during the major invasion by the invasive alien species, Conyza canadensis[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2021, 159: 106093. |
| [10] | LEVINE J M, ADLER P B, YELENIK S G. A meta-analysis of biotic resistance to exotic plant invasions[J]. Ecology Letters, 2004, 7(10): 975-989. |
| [11] | 柳晓燕, 朱金方, 李飞飞, 等. 豚草入侵对新疆伊犁河谷林下本地草本植物群落结构的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(24): 9613-9620. |
| LIU X Y, ZHU J F, LI F F, et al. Effect of invaded Ambrosia artemisiifolia on understory native plant community structure in Yili River Valley of Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(24): 9613-9620. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 吴晓雯, 罗晶, 陈家宽, 等. 中国外来入侵植物的分布格局及其与环境因子和人类活动的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2006, 30(4): 576-584. |
| WU X W, LUO J, CHEN J K, et al. Spatial patterns of invasive alien plants in China and its relationship with environmental and anthropological factors[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2006, 30(4): 576-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | WANG C, ZHOU J, LIU J, et al. Responses of the soil fungal communities to the co-invasion of two invasive species with different cover classes[J]. Plant Biology, 2018, 20(1): 151-159. |
| [14] | 綦顺英, 宫志锋, 杨宇航, 等. 加拿大一枝黄花入侵对地上植被及土壤种子库的影响[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2022, 49(3): 476-482. |
| QI S Y, GONG Z F, YANG Y H, et al. Effects of Solidago canadensis invasion on aboveground vegetation and soil seed banks[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2022, 49(3): 476-482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 强胜, 张欢. 中国农业生态系统外来植物入侵及其管理现状[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2022, 45(5): 957-980. |
| QIANG S, ZHANG H. Invasion and management of alien plants in agroecosystems in China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2022, 45(5): 957-980. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 张献瑞, 李欣迪, 陈瑜, 等. 加拿大一枝黄花入侵中国过程中的气候生态位变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(10): 2707-2714. |
| ZHANG X R, LI X D, CHEN Y, et al. Changes of climate niche of Solidago canadensis during its invasion in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(10): 2707-2714. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 黄华, 郭水良. 外来入侵植物加拿大一枝黄花繁殖生物学研究[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(11): 2795-2803. |
| HUANG H, GUO S L. Study on reproductive biology of the invasive plant Solidago canadensis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(11): 2795-2803. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 金樑. 外来入侵种加拿大一枝黄花的菌根生态学研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2005. |
| JIN L. Ecology of arbuscular mycorrhizal associations in Solidago canadensis, an invasive alien plant[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | YANG R Y, MEI L X, TANG J J. Allelopathic effects of invasive Solidago canadensis L. on germination and root growth of native Chinese plant species[J], Allelopathy Journal, 2007, 19(1): 241-248. |
| [20] | 袁亦文, 王映雪, 方吉, 等. 温州市加拿大一枝黄花发生现状及入侵成因分析[J]. 植物检疫, 2006, 20(4): 228-229. |
| YUAN Y W, WANG Y X, FANG J, et al. Occurrence status and invasion causes of Solidago canadensis in Wenzhou City[J]. Plant Quarantine, 2006, 20(4): 228-229. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 高末, 胡仁勇, 陈贤兴, 等. 干扰、地形和土壤对温州入侵植物分布的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(4): 424-431. |
| GAO M, HU R Y, CHEN X X, et al. Effects of disturbance, topography, and soil conditions on the distribution of invasive plants in Wenzhou[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2011, 19(4): 424-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 胡仁勇, 丁炳扬, 陈贤兴, 等. 温州地区外来入侵植物的种类组成及区系特点[J]. 温州大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 32(3): 18-25. |
| HU R Y, DING B Y, CHEN X X, et al. Study on species composition and flora characteristics of alien invasive plants in Wenzhou[J]. Journal of Wenzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2011, 32(3): 18-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 温州市林业志编辑委员会. 温州市林业志[S]. 北京: 中华书局, 2004:63-65. |
| [24] | 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. |
| FANG J Y, WANG X P, SHEN Z H, et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 张亚芬, 郑子洪, 陈旭波, 等. 入侵植物藿香蓟与常见伴生杂草的生态位特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(9): 3727-3737. |
| ZHANG Y F, ZHENG Z H, CHEN X B, et al. Niche characteristics of the invasive plant Ageratum conyzoides and its commonly associated weeds[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 3727-3737. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | MAGURRAN A E. Ecological diversity and its measurement[M]. Berlin: Springer Netherlands, 1988. |
| [27] | SIMPSON E H. Measurement of diversity[J]. Nature, 1949, 163(4148): 688. |
| [28] | JAMESON D L. Environmental evolution evolution in changing environments, some theoretical explorations[J]. BioScience, 1969, 19(7): 659-660. |
| [29] | PIANKA E R. The structure of lizard communities[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1973, 4: 53-74. |
| [30] | 马晓迪, 姜德刚, 刘子琳, 等. 平潭岛台湾相思群落优势种群生态位研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2022, 43(12): 2614-2625. |
| MA X D, JIANG D G, LIU Z L, et al. Niche of dominant plant populations of Acacia confusa community in Pingtan Island[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2022, 43(12): 2614-2625. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | KAMA R, JAVED Q, BO Y W, et al. Identity and diversity of invasive plant affecting the growth of native Lactuca indica[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(20): 17983-17991. |
| [32] | 杨博, 央金卓嘎, 潘晓云, 等. 中国外来陆生草本植物: 多样性和生态学特性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(6): 660-673. |
| YANG B, YANG J, PAN X Y, et al. Alien terrestrial herbs in China: diversity and ecological insights[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2010, 18(6): 660-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 宋煜, 单立山, 杨洁, 等. 生境异质性对典型荒漠植物群落多样性的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2023, 58(6): 136-144. |
| SONG Y, SHAN L S, YANG J, et al. Impact of habitat heterogeneity on plant community diversity in typical deserts[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2023, 58(6): 136-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 华茹婷, 单凯歌, 张太红, 等. 四川省青川县外来入侵植物现状及风险评估[J]. 生物安全学报(中英文), 2025, 34(2): 180-190. |
| HUA R T, SHAN K G, ZHANG T H, et al. Current status and risk assessment of invasivealien plants in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2025, 34(2): 180-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 李毅, 陈吕泽, 王春晓, 等. 琅岐岛公园外来入侵植物调查与风险评估[J]. 福建热作科技, 2024, 49(4): 1-5. |
| LI Y, CHEN L Z, WANG C X, et al. Investigation and risk assessment of invasive alien plants in Langqi Island Park[J]. Fujian Science & Technology of Tropical Crops, 2024, 49(4): 1-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 王冲勇, 胡明勇, 王少希, 等. 不同土地利用方式土壤肥力调查与评价: 以长沙市为例[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2024(4): 42-47. |
| WANG C Y, HU M Y, WANG S X, et al. Investigation and evaluation of soil fertility under different land use patterns: a case study of Changsha City[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2024(4): 42-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 葛结林, 何家庆, 孙晓方, 等. 入侵植物加拿大一枝黄花对土壤水分变化的生态学响应[J]. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(3): 575-585. |
| GE J L, HE J Q, SUN X F, et al. Ecological responses of the invasive alien plant Solidago canadensis to changes of soil water content[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(3): 575-585. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 张震, 曹亚蒙, 钟耀华, 等. 加拿大一枝黄花在安徽合肥的入侵生态因子分析[J]. 生物安全学报, 2019, 28(2): 133-139. |
| ZHANG Z, CAO Y M, ZHONG Y H, et al. Factors contributing to the spread of the invasive plant Solidago canadensis L. in Hefei, Anhui Province, China[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2019, 28(2): 133-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 张晓亮. 水生生物常见外来种的种间关系及其对乡土种的影响[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| ZHANG X L. The interspecific relationship and the effects on native species of common aquatic exotic species[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | SKÁLOVÁ H, JAROŠÍK V, DVOŘÁČKOVÁ Ś, et al. Effect of intra- and interspecific competition on the performance of native and invasive species of Impatiens under varying levels of shade and moisture[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(5): e62842. |
| [41] | LU X M, SIEMANN E, SHAO X, et al. Climate warming affects biological invasions by shifting interactions of plants and herbivores[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(8): 2339-2347. |
| [42] | LIU Y J, VAN KLEUNEN M. Responses of common and rare aliens and natives to nutrient availability and fluctuations[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2017, 105(4): 1111-1122. |
| [43] | 王金旺, 邹颖颖, 于丹. 瓯江流域水生植物多样性与生态位研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2015, 39(6): 1184-1197. |
| WANG J W, ZOU Y Y, YU D. The diversity, niche breadth, and niche overlap of aquatic plants in the Oujiang River[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2015, 39(6): 1184-1197. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | WANG C Y, CHENG H Y, WANG S, et al. Plant community and the influence of plant taxonomic diversity on community stability and invasibility: a case study based on Solidago canadensis L[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 768: 144518. |
| [45] | 江燕东, 彭正东, 徐琪, 等. 喜旱莲子草叶片、细根功能性状对异质生境的响应[J]. 植物研究, 2024, 44(3): 410-419. |
| JIANG Y D, PENG Z D, XU Q, et al. Responses of leaf and fine root functional traits of Alternanthera philoxeroides to heterogeneous habitats[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 410-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 黄乾龙, 王楚桃, 何永歆, 欧阳杰, 朱子超, 管玉圣, 蒋刚, 熊英, 李贤勇. 直播方式对重庆地区稻田杂草群落组成和生态位的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 383-390. |
| [2] | 牙克甫·艾散江, 吾玛尔·阿布力孜, 买尔旦·艾斯卡尔, 阿丽亚·司地克. 新疆7种微生境的土壤甲螨多样性特征[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(4): 696-704. |
| [3] | 董万鹏, 李安定, 张建利, 龙秀琴. 喀斯特峰丛洼地西番莲逸生生境和生态位特征[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(8): 1305-1311. |
| [4] | 朱宏, 周婷婷, 李欣, 阮宏华, 谢冬. 太湖沉水植物附生藻类群落对水盾草入侵能力的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(11): 1880-1887. |
| [5] | 吴昊. 陆生生境入侵植物空心莲子草群落数量分类与排序[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(3): 433-444. |
| [6] | 梁森苗;王勤红;倪国富;钱丽萍;赵贤生;戚行江;*. 杨梅园自然生草对土壤肥力及果实品质的影响[J]. , 2012, 24(5): 0-825. |
| [7] | 吴全聪;郑仕华. 浙西南山地桃园生境天敌昆虫相对丰盛度调查[J]. , 2010, 22(1): 0-95. |
| [8] | 陈再廖;许方程;吴永汉;陈小影. 浙南地区菜田蜘蛛自然种群消长动态及农药对其毒性[J]. , 2002, 14(2): 0-99. |
| [9] | 徐红星;俞晓平;吕仲贤;陈建明;郑许松;陶林勇;卜卫良. 水稻田和茭白田越冬代二化螟成虫习性研究[J]. , 2001, 13(03): 0-160. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||