浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 85-94.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241057
γ-聚谷氨酸配施化肥对党参生长的影响及其作用机制
施静1,2( ), 李建宏3,*(
), 李建宏3,*( ), 褚鹏星3, 余锐2, 姜明2, 陈光丽2, 赵小霞2, 冯莉1,*(
), 褚鹏星3, 余锐2, 姜明2, 陈光丽2, 赵小霞2, 冯莉1,*( )
)
- 1.中国矿业大学 化工学院,江苏 徐州 221116
2.六盘水职业技术学院 生物工程系,贵州 六盘水 553000
3.六盘水师范学院 生物科学与技术学院,贵州 六盘水 553004
-
收稿日期:2024-12-04出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:李建宏,E-mail:lijianhong123@126.com
冯莉,E-mail:cumthgfl@163.com;
施静,研究方向为土壤修复。E-mail:1093040619@qq.com -
通讯作者:李建宏,冯莉 -
基金资助:贵州省职业教育“技能贵州”行动计划项目(黔教函〔2025〕17号);贵州省职业教育“技能贵州”行动计划项目(黔教函〔2023〕100号);2024年贵州省教育科学规划课题暨粤黔专项课题(2024A018);六盘水市科技发展项目(52020-0-1-24);六盘水职业技术学院院级项目(Lyk2405);山地高原特色农产品技术创新中心(520202023018)
Effects and mechanism of γ-polyglutamic acid coupled with chemical fertilizer on growth of Codonopsis pilosula
SHI Jing1,2( ), LI Jianhong3,*(
), LI Jianhong3,*( ), CHU Pengxing3, YU Rui2, JIANG Ming2, CHEN Guangli2, ZHAO Xiaoxia2, FENG Li1,*(
), CHU Pengxing3, YU Rui2, JIANG Ming2, CHEN Guangli2, ZHAO Xiaoxia2, FENG Li1,*( )
)
- 1. School of Chemical Engineering & Technology, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, Jiangsu, China
2. Department of Biological Engineering, Liupanshui Vocational and Technical College, Liupanshui 553000, Guizhou, China
3. School of Biological Sciences and Technology, Liupanshui Normal University, Liupanshui 553004, Guizhou, China
-
Received:2024-12-04Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:LI Jianhong,FENG Li
摘要:
本研究以党参为试验材料,通过设置不同用量的化肥与γ-聚谷氨酸(γ-PGA)配施的处理,分析党参生长指标、土壤理化性质和微生物群落的变化,探讨γ-PGA与化肥配施对党参生长的影响及其可能的作用机制。 结果显示: 与不施用化肥和γ-PGA的对照(CK)相比,只施用γ-PGA的处理(T1)的党参株高、根直径、根长、根干重均无显著差异,但当γ-PGA与化肥配施后,党参的根干重和根冠比较T1处理显著(p<0.05)增加,增幅分别为4.10%~21.92%、2.45%~17.48%。γ-PGA与适量化肥配施显著提高了土壤的铵态氮、速效钾和有效磷含量,但会降低土壤的pH值。在土壤微生物方面,γ-PGA与适量化肥配施可显著增加土壤中的氨化细菌和好气性自生固氮菌的数量,增强土壤对有机氮的矿化作用和固氮能力。综上,我们认为,γ-PGA与适量化肥配施可通过改善土壤理化性状、促进有益微生物生长、改善根际土壤微生态环境等来促进党参生长。
中图分类号:
引用本文
施静, 李建宏, 褚鹏星, 余锐, 姜明, 陈光丽, 赵小霞, 冯莉. γ-聚谷氨酸配施化肥对党参生长的影响及其作用机制[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 85-94.
SHI Jing, LI Jianhong, CHU Pengxing, YU Rui, JIANG Ming, CHEN Guangli, ZHAO Xiaoxia, FENG Li. Effects and mechanism of γ-polyglutamic acid coupled with chemical fertilizer on growth of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 85-94.
| 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height/cm | 根直径/mm Root diameter/mm | 根长/cm Root length/cm | 地上部干重/g Shoot dry weight/g | 根干重/g Root dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 17.54±0.49 d | 2.67±0.05 b | 24.49±0.42 d | 0.262±0.003 a | 0.71±0.01 e | 2.71±0.02 g |
| T1 | 18.68±0.39 bcd | 2.84±0.12 ab | 25.01±0.56 cd | 0.255±0.004 ab | 0.73±0.01 e | 2.86±0.02 f |
| T2 | 18.57±0.51 cd | 2.75±0.03 ab | 25.90±0.73 bcd | 0.259±0.003 ab | 0.76±0.01 d | 2.93±0.01 e |
| T3 | 19.38±0.40 abc | 2.81±0.07 ab | 26.31±0.24 abc | 0.268±0.004 a | 0.81±0.01 c | 3.02±0.02 d |
| T4 | 19.26±0.28 abc | 2.83±0.05 ab | 26.73±0.28 ab | 0.267±0.004 a | 0.85±0.01 b | 3.18±0.03 c |
| T5 | 20.39±0.61 a | 2.90±0.04 a | 27.64±0.42 a | 0.265±0.003 a | 0.89±0.01 a | 3.36±0.02 a |
| T6 | 19.89±0.23 ab | 2.84±0.06 ab | 27.00±0.06 ab | 0.249±0.003 b | 0.82±0.01 c | 3.29±0.01 b |
| T7 | 19.60±0.58 abc | 2.84±0.02 ab | 26.28±0.92 abc | 0.235±0.004 b | 0.77±0.01 d | 3.28±0.01 b |
表1 不同处理下党参植株的生长状况
Table 1 Growth of Codonopsis pilosula under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 株高/cm Plant height/cm | 根直径/mm Root diameter/mm | 根长/cm Root length/cm | 地上部干重/g Shoot dry weight/g | 根干重/g Root dry weight/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 17.54±0.49 d | 2.67±0.05 b | 24.49±0.42 d | 0.262±0.003 a | 0.71±0.01 e | 2.71±0.02 g |
| T1 | 18.68±0.39 bcd | 2.84±0.12 ab | 25.01±0.56 cd | 0.255±0.004 ab | 0.73±0.01 e | 2.86±0.02 f |
| T2 | 18.57±0.51 cd | 2.75±0.03 ab | 25.90±0.73 bcd | 0.259±0.003 ab | 0.76±0.01 d | 2.93±0.01 e |
| T3 | 19.38±0.40 abc | 2.81±0.07 ab | 26.31±0.24 abc | 0.268±0.004 a | 0.81±0.01 c | 3.02±0.02 d |
| T4 | 19.26±0.28 abc | 2.83±0.05 ab | 26.73±0.28 ab | 0.267±0.004 a | 0.85±0.01 b | 3.18±0.03 c |
| T5 | 20.39±0.61 a | 2.90±0.04 a | 27.64±0.42 a | 0.265±0.003 a | 0.89±0.01 a | 3.36±0.02 a |
| T6 | 19.89±0.23 ab | 2.84±0.06 ab | 27.00±0.06 ab | 0.249±0.003 b | 0.82±0.01 c | 3.29±0.01 b |
| T7 | 19.60±0.58 abc | 2.84±0.02 ab | 26.28±0.92 abc | 0.235±0.004 b | 0.77±0.01 d | 3.28±0.01 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 铵态氮含量/(mg·kg-1) Ammonium nitrogen content/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/(mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/(mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/(mg·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.26±0.03 h | 71.78±0.02 f | 0.96±0.03 f | 6.41±0.01 a |
| T1 | 1.23±0.01 e | 150.60±0.02 c | 13.37±0.01 c | 6.31±0.01 b |
| T2 | 3.81±0.02 a | 71.70±0.01 g | 7.20±0.10 e | 5.02±0.01 e |
| T3 | 1.19±0.01 f | 172.10±0.01 a | 11.19±0.02 d | 6.14±0.01 d |
| T4 | 0.64±0.01 g | 64.32±0.02 h | 19.51±0.06 b | 6.31±0.05 b |
| T5 | 2.20±0.01 c | 136.45±0.05 d | 11.24±0.01 d | 6.20±0.02 c |
| T6 | 1.78±0.01 d | 159.63±0.05 b | 62.53±0.02 a | 6.48±0.04 a |
| T7 | 3.63±0.02 b | 114.27±0.06 e | 1.00±0.01 f | 6.33±0.03 b |
表2 不同处理下的土壤理化性质
Table 2 Soil physicochemical properties under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 铵态氮含量/(mg·kg-1) Ammonium nitrogen content/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/(mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/(mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/(mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/(mg·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.26±0.03 h | 71.78±0.02 f | 0.96±0.03 f | 6.41±0.01 a |
| T1 | 1.23±0.01 e | 150.60±0.02 c | 13.37±0.01 c | 6.31±0.01 b |
| T2 | 3.81±0.02 a | 71.70±0.01 g | 7.20±0.10 e | 5.02±0.01 e |
| T3 | 1.19±0.01 f | 172.10±0.01 a | 11.19±0.02 d | 6.14±0.01 d |
| T4 | 0.64±0.01 g | 64.32±0.02 h | 19.51±0.06 b | 6.31±0.05 b |
| T5 | 2.20±0.01 c | 136.45±0.05 d | 11.24±0.01 d | 6.20±0.02 c |
| T6 | 1.78±0.01 d | 159.63±0.05 b | 62.53±0.02 a | 6.48±0.04 a |
| T7 | 3.63±0.02 b | 114.27±0.06 e | 1.00±0.01 f | 6.33±0.03 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 氨化细菌数量/ (104 CFU·g-1) Quantity of ammonifiers/ (104 CFU·g-1) | 好气性自生固氮菌数量/ (103 CFU·g-1) Quantity of aerobic azotobacter/ (103 CFU·g-1) | 嫌气性自生固氮菌数量/ (106 CFU·g-1) Quantity of anaerobic azotobacter/ (106 CFU·g-1) | 硝化细菌数量/ (105 CFU·g-1) Quantity of nitrifying bacteria/ (105 CFU·g-1) | 反硝化细菌数量/ (106 CFU·g-1) Quantity of denitrifying bacteria/ (106 CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.54±0.04 d | 6.20±0.04 c | 0.16±0.01 d | 3.55±0.37 c | 3.58±0.31 d |
| T1 | 43.71±3.45 b | 8.79±0.30 c | 18.78±0.53 b | 31.72±0.11 a | 10.08±0.13 d |
| T2 | 12.92±0.16 d | 6.89±0.46 c | 19.96±0.15 b | 0.79±0.03 e | 192.59±2.11 a |
| T3 | 9.54±0.44 d | 2.91±0.06 c | 2.65±0.04 d | 2.05±0.04 d | 19.70±0.24 c |
| T4 | 3.40±0.35 e | 12.27±0.43 c | 10.54±0.49 c | 14.14±0.15 b | 7.73±0.55 d |
| T5 | 35.69±0.97 c | 11.39±0.61 c | 153.53±2.73 a | 0.28±0.01 e | 154.34±5.21 b |
| T6 | 2.09±0.05 e | 45.57±0.66 b | 13.07±0.59 c | 3.64±0.33 c | 5.84±0.09 d |
| T7 | 86.24±3.87 a | 74.95±9.98 a | 1.80±0.32 d | 3.95±0.34 c | 156.20±4.88 b |
表3 不同处理下土壤氮代谢相关菌群的数量
Table 3 Quantity of nitrogen metabolism related bacteria in soil under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 氨化细菌数量/ (104 CFU·g-1) Quantity of ammonifiers/ (104 CFU·g-1) | 好气性自生固氮菌数量/ (103 CFU·g-1) Quantity of aerobic azotobacter/ (103 CFU·g-1) | 嫌气性自生固氮菌数量/ (106 CFU·g-1) Quantity of anaerobic azotobacter/ (106 CFU·g-1) | 硝化细菌数量/ (105 CFU·g-1) Quantity of nitrifying bacteria/ (105 CFU·g-1) | 反硝化细菌数量/ (106 CFU·g-1) Quantity of denitrifying bacteria/ (106 CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.54±0.04 d | 6.20±0.04 c | 0.16±0.01 d | 3.55±0.37 c | 3.58±0.31 d |
| T1 | 43.71±3.45 b | 8.79±0.30 c | 18.78±0.53 b | 31.72±0.11 a | 10.08±0.13 d |
| T2 | 12.92±0.16 d | 6.89±0.46 c | 19.96±0.15 b | 0.79±0.03 e | 192.59±2.11 a |
| T3 | 9.54±0.44 d | 2.91±0.06 c | 2.65±0.04 d | 2.05±0.04 d | 19.70±0.24 c |
| T4 | 3.40±0.35 e | 12.27±0.43 c | 10.54±0.49 c | 14.14±0.15 b | 7.73±0.55 d |
| T5 | 35.69±0.97 c | 11.39±0.61 c | 153.53±2.73 a | 0.28±0.01 e | 154.34±5.21 b |
| T6 | 2.09±0.05 e | 45.57±0.66 b | 13.07±0.59 c | 3.64±0.33 c | 5.84±0.09 d |
| T7 | 86.24±3.87 a | 74.95±9.98 a | 1.80±0.32 d | 3.95±0.34 c | 156.20±4.88 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 各类微生物的FLPA含量FLPA content of different kinds of micrboes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏阳性菌 Gram-positive bacteria | 革兰氏阴性菌 Gram-negative bacteria | 细菌 Bacteria | 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 真菌 Fungi | 总计 Total | |
| CK | 5.38±3.26 b | 3.26±0.01 b | 14.80±1.14 b | 2.51±0.01 f | 4.31±0.01 a | 21.61±1.13 d |
| T1 | 5.41±3.25 b | 3.25±0.01 b | 15.34±1.17 b | 2.52±0.01 f | 4.25±0.01 ab | 22.77±0.02 c |
| T2 | 5.38±3.24 b | 3.24±0.01 b | 19.17±0.08 a | 3.52±0.01 e | 4.31±0.01 a | 24.06±0.04 b |
| T3 | 5.02±3.20 c | 3.20±0.05 c | 14.99±0.09 b | 6.65±0.11 a | 4.22±0.01 b | 25.85±0.19 a |
| T4 | 6.38±3.80 a | 3.80±0.01 a | 16.42±0.07 b | 5.28±0.02 b | 3.91±0.02 c | 25.61±0.12 a |
| T5 | 4.65±2.44 d | 2.44±0.02 d | 12.15±0.07 c | 4.74±0.01 c | 2.47±0.02 d | 19.37±0.07 e |
| T6 | 3.77±2.35 f | 2.35±0.01 e | 11.04±0.34 c | 3.95±0.03 d | 2.07±0.04 e | 17.06±0.41 f |
| T7 | 3.98±2.20 e | 2.20±0.01 f | 10.84±0.08 c | 3.85±0.11 d | 1.91±0.04 f | 16.60±0.12 f |
表4 不同处理下土壤中各类微生物的磷脂脂肪酸(PLFA)含量
Table 4 Phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) content of different kinds of microbes in soil under different treatments nmol·g-1
| 处理 Treatment | 各类微生物的FLPA含量FLPA content of different kinds of micrboes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏阳性菌 Gram-positive bacteria | 革兰氏阴性菌 Gram-negative bacteria | 细菌 Bacteria | 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 真菌 Fungi | 总计 Total | |
| CK | 5.38±3.26 b | 3.26±0.01 b | 14.80±1.14 b | 2.51±0.01 f | 4.31±0.01 a | 21.61±1.13 d |
| T1 | 5.41±3.25 b | 3.25±0.01 b | 15.34±1.17 b | 2.52±0.01 f | 4.25±0.01 ab | 22.77±0.02 c |
| T2 | 5.38±3.24 b | 3.24±0.01 b | 19.17±0.08 a | 3.52±0.01 e | 4.31±0.01 a | 24.06±0.04 b |
| T3 | 5.02±3.20 c | 3.20±0.05 c | 14.99±0.09 b | 6.65±0.11 a | 4.22±0.01 b | 25.85±0.19 a |
| T4 | 6.38±3.80 a | 3.80±0.01 a | 16.42±0.07 b | 5.28±0.02 b | 3.91±0.02 c | 25.61±0.12 a |
| T5 | 4.65±2.44 d | 2.44±0.02 d | 12.15±0.07 c | 4.74±0.01 c | 2.47±0.02 d | 19.37±0.07 e |
| T6 | 3.77±2.35 f | 2.35±0.01 e | 11.04±0.34 c | 3.95±0.03 d | 2.07±0.04 e | 17.06±0.41 f |
| T7 | 3.98±2.20 e | 2.20±0.01 f | 10.84±0.08 c | 3.85±0.11 d | 1.91±0.04 f | 16.60±0.12 f |
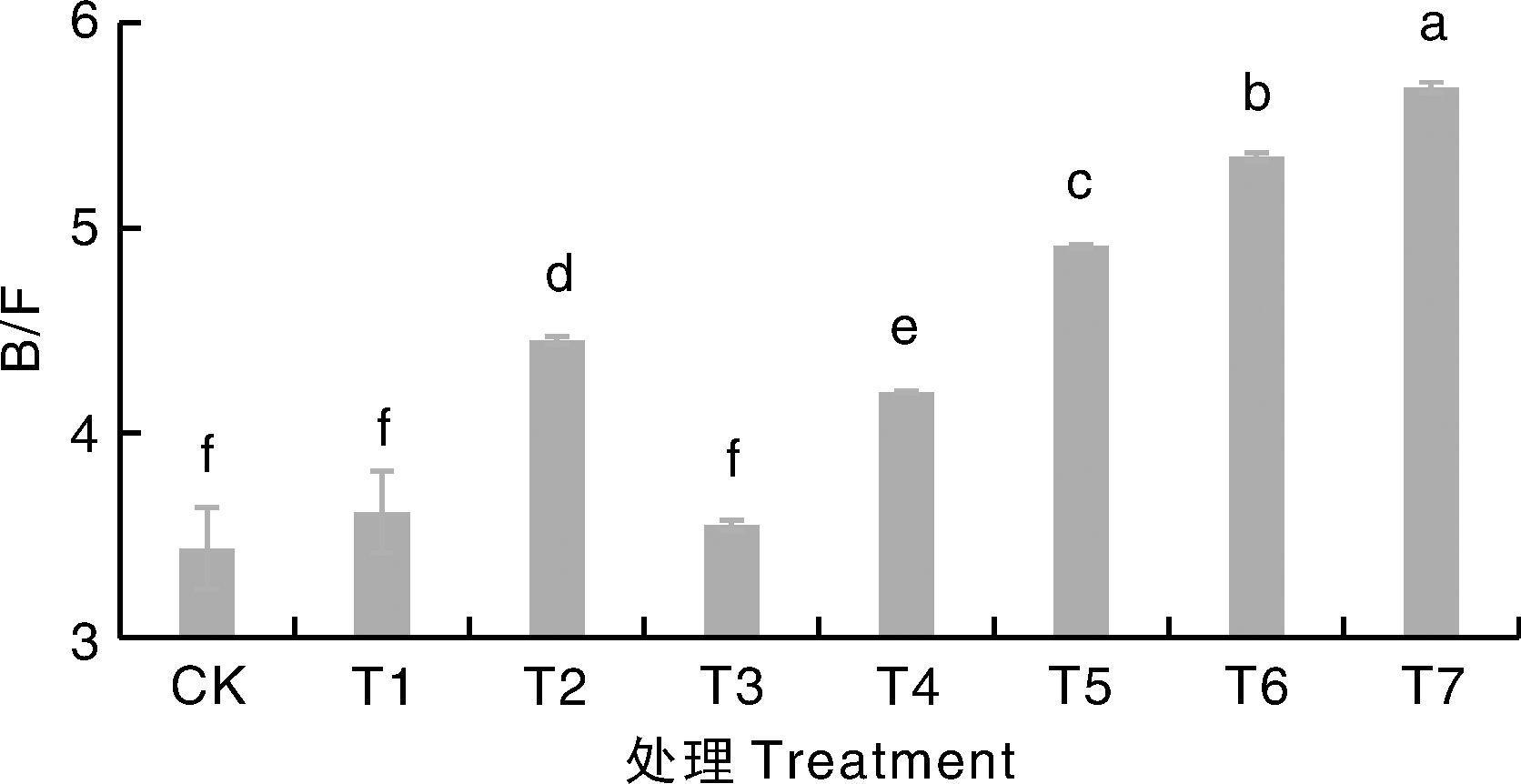
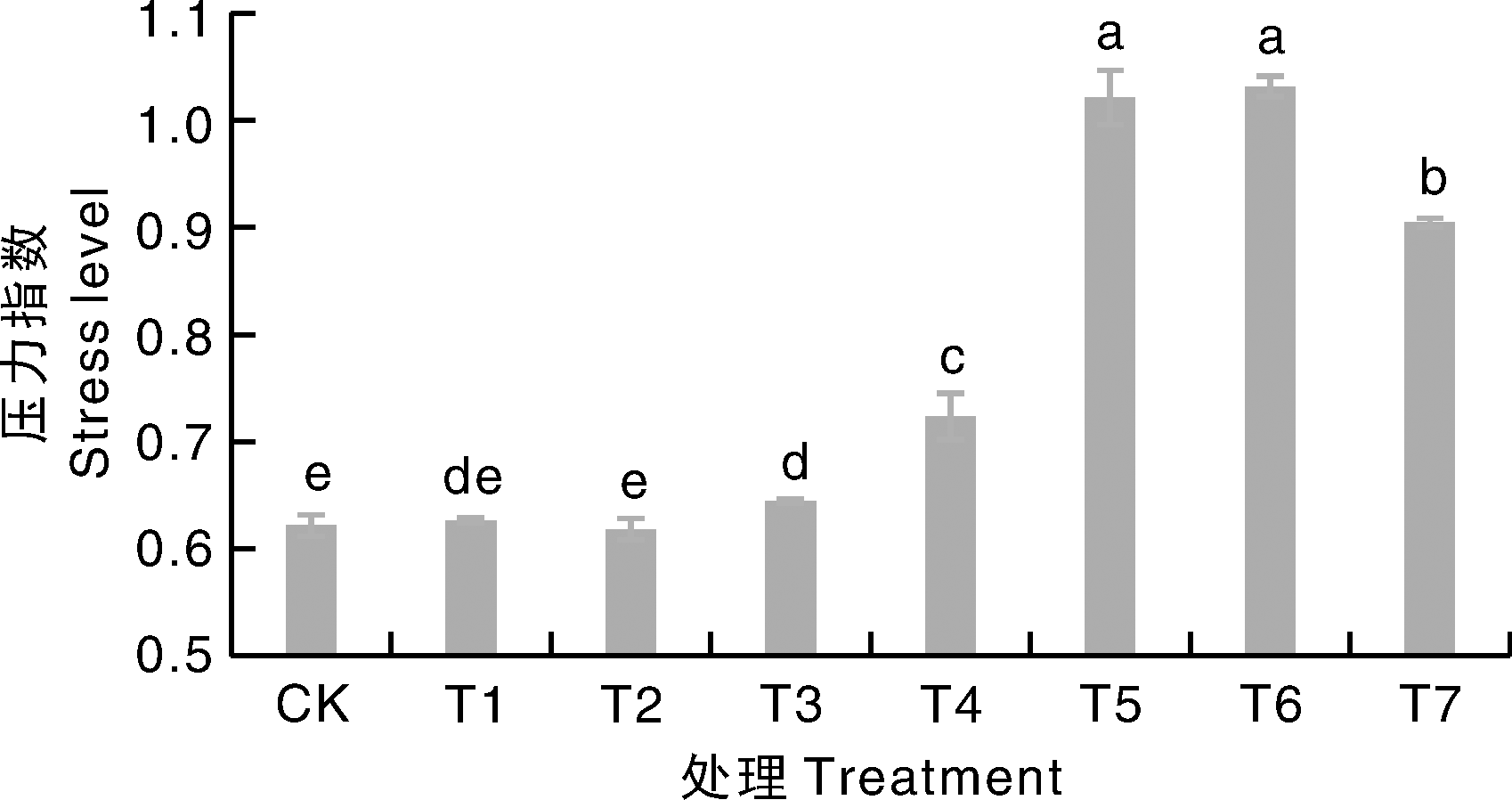
图1 不同处理下细菌与真菌的丰度之比(B/F) 柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。柱子所对应的数值为该处理下各重复的几何平均值。
Fig.1 The ratio of abundance of bacteria to fungi (B/F) under different treatments Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference at p<0.05. The same as below. The value corresponding to the bar is the geometric mean of the repetitions under this treatment.
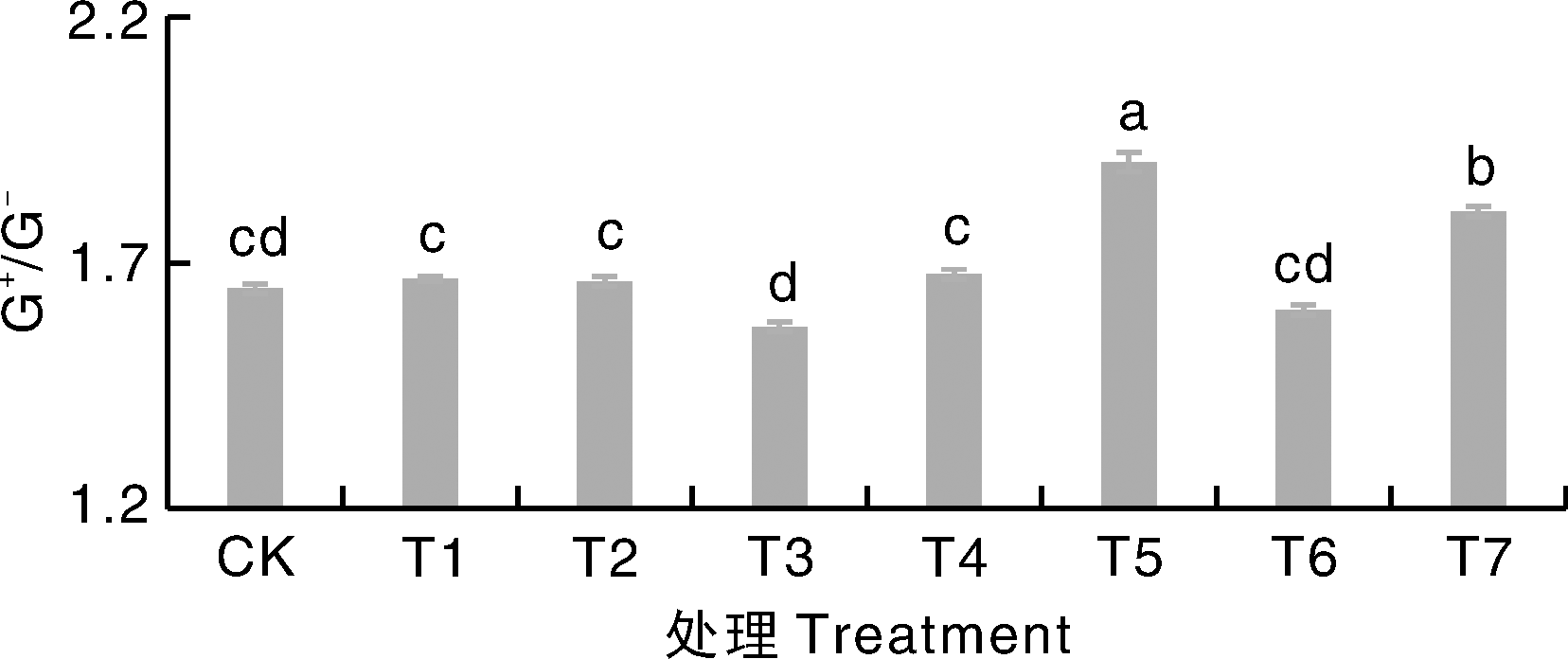
图2 不同处理下革兰氏阳性菌与革兰氏阴性菌的丰度之比(G+/G-) 柱子所对应的数值为该处理下各重复的几何平均值。
Fig.2 The ratio of abundance of Gram-positive bacteria to Gram-negative bacteria (G+/G-) under different treatments The value corresponding to the bar is the geometric mean of the repetitions under this treatment.
| [1] | 焦红军. 党参的药理作用及其临床应用[J]. 临床医学, 2005, 25(4): 89-92. |
| JIAO H J. Pharmacological action and clinical application of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Clinical Medicine, 2005, 25(4): 89-92. | |
| [2] | 尹荣秀, 张邦喜, 周瑞荣, 等. 配方肥对党参产量及品质的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2017, 37(2): 7-8. |
| YIN R X, ZHANG B X, ZHOU R R, et al. Effect of special fertilizer on yield and quality of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2017, 37(2): 7-8. | |
| [3] | 周武先, 刘翠君, 何银生, 等. 3种改良剂对连作川党参生长及土壤生化性质的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(1): 43-52. |
| ZHOU W X, LIU C J, HE Y S, et al. Effects of three amendments on the growth of Codonopsis tangshen and soil biochemical properties in a continuous cropping system[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(1): 43-52. | |
| [4] | 杨阳, 李海亮, 马凯丽, 等. 连作对党参根际土壤理化性质、微生物活性及群落特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(11): 6387-6398. |
| YANG Y, LI H L, MA K L, et al. Effect of continuous cropping on the physicochemical properties, microbial activity, and community characteristics of the rhizosphere soil of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(11): 6387-6398. | |
| [5] | SU Y, ZI H Y, WEI X M, et al. Application of manure rather than plant-origin organic fertilizers alters the fungal community in continuous cropping tobacco soil[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 818956. |
| [6] | ASHIUCHI M, MISONO H. Biochemistry and molecular genetics of poly-γ-glutamate synthesis[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2002, 59(1): 9-14. |
| [7] | YAO J, XU H, SHI N N, et al. Analysis of carbon metabolism and improvement of γ-polyglutamic acid production from Bacillus subtilis NX-2[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2010, 160(8): 2332-2341. |
| [8] | SANDA F, FUJIYAMA T, ENDO T. Chemical synthesis of poly-γ-glutamic acid by polycondensation of γ-glutamic acid dimer: synthesis and reaction of poly-γ-glutamic acid methyl ester[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2001, 39(5): 732-741. |
| [9] | KUMAR R, PAL P. Fermentative production of poly (γ-glutamic acid) from renewable carbon source and downstream purification through a continuous membrane-integrated hybrid process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 177: 141-148. |
| [10] | 彭英云, 张涛, 缪铭, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸的合成、性质和应用[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2012, 38(6): 133-138. |
| PENG Y Y, ZHANG T, MIAO M, et al. The synthesis, properties and application of γ-polyglutamic acid[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2012, 38(6): 133-138. | |
| [11] | 谢丽霞, 李强栋, 刘昀雯. 不同浓度γ-聚谷氨酸的新型微生物菌肥对小白菜的应用效果[J]. 现代园艺, 2025(20): 5-6. |
| XIE L W, LI Q D, LIU Y W. Application effect of new microbial fertilizer with different concentrations of γ-polyglutamic acid on pakchoi[J]. Modern Horticulture, 2025(20): 5-6. | |
| [12] | 穆文强, 尚庆茂, 武瑞赟, 等. 含复合贝莱斯芽孢杆菌和γ-聚谷氨酸的功能性育苗基质混配工艺优化[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2023, 28(6): 183-193. |
| MU W Q, SHANG Q M, WU R Y, et al. Blending technology optimization of compound Bacillus velezensis and γ-polyglutamic acid for functional seedling medium[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28(6): 183-193. | |
| [13] | 何宇, 吕卫光, 李双喜, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸发酵液对小白菜生长及氮磷肥料利用率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 329-337. |
| HE Y, LYU W G, LI S X, et al. Effects of γ-polyglutamic acid fermentation broth on growth of pakchoi and utilization rate of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(2): 329-337. | |
| [14] | 王竟夷, 王玉, 廖晓晓, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸基复合保水剂对白灵菇生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(8): 102-107. |
| WANG J Y, WANG Y, LIAO X X, et al. Effects of adding γ-polyglutamic acid-based composite water-retaining agent on the growth of Pleurotus nebrodensis[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(8): 102-107. | |
| [15] | 付文杰, 万亚珍, 张文辉, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸磷肥增效剂对石灰性土壤有效磷的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(2): 17-22. |
| FU W J, WAN Y Z, ZHANG W H, et al. Effect of polyglutamic acid phosphate fertilizer synergist on available phosphorus in calcareous soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(2): 17-22. | |
| [16] | 陶龙锦, 张经博, 董正武, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸配施化肥对新疆棉田土壤微生物群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 微生物学报, 2024, 64(10): 3702-3722. |
| TAO L J, ZHANG J B, DONG Z W, et al. Effects of γ-polyglutamic acid combined with chemical fertilizer on soil microbial community structure and function in Xinjiang cotton fields[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2024, 64(10): 3702-3722. | |
| [17] | 肖天昊, 曹辉, 周昕. 不同施肥梯度下γ-聚谷氨酸肥料增效剂对草坪的影响[J]. 草学, 2024(2): 58-62. |
| XIAO T H, CAO H, ZHOU X. Effects of different fertilization gradients and different γ-polyglutamic acid chemical fertilizer synergist levels on turf[J]. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2024(2): 58-62. | |
| [18] | 李东亚, 樊志磊, 韩伟豪, 等. 无机复合肥料中添加聚谷氨酸对油麦菜生长及产量的影响[J]. 肥料与健康, 2023, 50(5): 40-43. |
| LI D Y, FAN Z L, HAN W H, et al. Effects of polyglutamic acid addition to inorganic compound fertilizer on growth and yield of Lactuca sativa var. longifoliaf Lam[J]. Fertilizer & Health, 2023, 50(5): 40-43. | |
| [19] | 王倩倩. 氨基酸类增效剂对蔬菜生长及土壤微生物的影响[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. |
| WANG Q Q. Effects of amino acid synergists on vegetable growth and soil microorganisms[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. | |
| [20] | 周正虎, 王传宽. 微生物对分解底物碳氮磷化学计量的响应和调节机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(6): 620-630. |
| ZHOU Z H, WANG C K. Responses and regulation mechanisms of microbial decomposers to substrate carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(6): 620-630. | |
| [21] | JEFFRIES P, GIANINAZZI S, PEROTTO S, et al. The contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sustainable maintenance of plant health and soil fertility[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2003, 37(1): 1-16. |
| [22] | LUO X S, FU X Q, YANG Y, et al. Microbial communities play important roles in modulating paddy soil fertility[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 20326. |
| [23] | 李杰, 卢宗云, 石元亮, 等. 新型聚氨酸增效肥料对小白菜根系活性与产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(1): 134-139. |
| LI J, LU Z Y, SHI Y L, et al. Effect of new type synergist of poly amino acid fertilizer on pakchoi root activity and yield[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(1): 134-139. | |
| [24] | 褚群. γ-聚谷氨酸和解磷菌M20对番茄和西瓜穴盘苗基质养分供应和根际细菌群落结构的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2016. |
| CHU Q. Effect of γ-PGA and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria M20 on nutrient availabilty and rhizosphere bacterial community structure of tomato and watermelon plug seedlings[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016. | |
| [25] | YIN A M, JIA Y P, QIU T L, et al. Poly-γ-glutamic acid improves the drought resistance of maize seedlings by adjusting the soil moisture and microbial community structure[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 129: 128-135. |
| [26] | 薛建辉, 周之栋, 吴永波. 喀斯特石漠化山地退化土壤生态修复研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6): 135-145. |
| XUE J H, ZHOU Z D, WU Y B. Research progresses on ecological remediation of the degraded soil in Karst rocky desertification mountainous areas[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 46(6): 135-145. | |
| [27] | WANG L J, WANG P, SHENG M Y, et al. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2018, 16: e00449. |
| [28] | 张绪瑛, 杨燕, 黄静, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸钙的制备及其性质研究[J]. 食品科学, 2009, 30(8): 76-79. |
| ZHANG X Y, YANG Y, HUANG J, et al. Study on preparation and properties of γ-polyglutamic acid calcium salt[J]. Food Science, 2009, 30(8): 76-79. | |
| [29] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| [30] | 林先贵. 土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010. |
| [31] | 许光辉. 土壤微生物分析方法手册[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. |
| [32] | BOSSIO D, SCOW K. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1998, 35(3): 265-278. |
| [33] | BOSSIO D A, SCOW K M, GUNAPALA N, et al. Determinants of soil microbial communities: effects of agricultural management, season, and soil type on phospholipid fatty acid profiles[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1998, 36(1): 1-12. |
| [34] | KONG C H, WANG P, GU Y, et al. Fate and impact on microorganisms of rice allelochemicals in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56(13): 5043-5049. |
| [35] | WANG M C, LIU Y H, WANG Q, et al. Impacts of methamidophos on the biochemical, catabolic, and genetic characteristics of soil microbial communities[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(3): 778-788. |
| [36] | ZHANG C P, XU J, LIU X G, et al. Impact of imazethapyr on the microbial community structure in agricultural soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 81(6): 800-806. |
| [37] | HAMMESFAHR U, HEUER H, MANZKE B, et al. Impact of the antibiotic sulfadiazine and pig manure on the microbial community structure in agricultural soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(7): 1583-1591. |
| [38] | 王卫国, 王卫, 赵永亮, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸的研究及应用进展[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(2): 117-122. |
| WANG W G, WANG W, ZHAO Y L, et al. Progress in research and application of poly-γ-glutamic acid[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(2): 117-122. | |
| [39] | 何宇, 吕卫光, 张娟琴, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(18): 18-22. |
| HE Y, LÜ W G, ZHANG J Q, et al. Research progress of γ-polyglutamic acid[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(18): 18-22. | |
| [40] | 庞琳娜. γ-聚谷氨酸对土壤水氮运移及油麦菜生理生长的影响[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019. |
| PANG L N. Effects of γ-PGA on soil water and nitrogen move and physiological growth index of lettuce[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019. | |
| [41] | 石肖肖, 史文娟, 庞琳娜, 等. γ-聚谷氨酸对土壤水氮运移特性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(3): 190-197. |
| SHI X X, SHI W J, PANG L N, et al. Effects of γ-polyglutamic acid on soil water and nitrogen transport characteristics[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(3): 190-197. | |
| [42] | HO G H, HO T I, HSIEH K H, et al. γ-Polyglutamic acid produced by Bacillus subtilis(natto): structural characteristics, chemical properties and biological functionalities[J]. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2006, 53(6): 1363-1384. |
| [43] | XU Z Q, LEI P, FENG X H, et al. Effect of poly(γ-glutamic acid) on microbial community and nitrogen pools of soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B: Soil & Plant Science, 2013, 63(8): 657-668. |
| [44] | 夏芳, 蔡皓, 陈守文. 聚γ-谷氨酸延缓磷酸钙沉淀及螯合钙离子的研究[J]. 食品科学, 2008, 29(3): 56-59. |
| XIA F, CAI H, CHEN S W. Effects of poly-γ-glutamic acid on retarding calcium phosphate depositing and it’s chelation with calcium ion[J]. Food Science, 2008, 29(3): 56-59. | |
| [45] | 张宸. 聚谷氨酸生物的合成及其在修复和改良土壤中的应用[J]. 水土保持通报, 2018, 38(2): 323-328. |
| ZHANG C. Biosynthesis of poly-γ-glutamic acid and its application to soil remediation and improvement[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 38(2): 323-328. | |
| [46] | PERROTT K W, SARATHCHANDRA S U, WALLER J E. Seasonal storage and release of phosphorus and potassium by organic matter and the microbial biomass in a high producing pastoral soil[J]. Soil Research, 1990, 28(4): 593. |
| [47] | 李俊艳, 胡红青, 李荣纪, 等. 改性磷矿粉对油菜幼苗生长和土壤性质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 441-446. |
| LI J Y, HU H Q, LI R J, et al. Modified phosphate rock by γ-poly glutamic acid and its effects on the growth of rapeseed seedlings and soil properties[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(2): 441-446. | |
| [48] | 周雅心, 王晓彤, 王广磊, 等. 炉渣与生物炭施加对稻田土壤细菌多样性及群落组成的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(3): 1213-1223. |
| ZHOU Y X, WANG X T, WANG G L, et al. Effect of the slag and biochar application on bacterial diversity and community composition of paddy field[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(3): 1213-1223. | |
| [49] | 彭宇, 闫会转, 肖中林, 等. 不同施肥处理对盆栽辣椒土壤酶活性及土壤微生物含量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2200-2208. |
| PENG Y, YAN H Z, XIAO Z L, et al. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil enzyme activity and soil microbial content of potted pepper[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(9): 2200-2208. | |
| [50] | 李忠奎, 凌爱芬, 李红丽, 等. 基于多样性测序对健康与易感病烟田根际土壤微生物群落分析[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2019, 53(6): 918-925. |
| LI Z K, LING A F, LI H L, et al. Analysis of rhizosphere soil microbial communities in healthy and susceptible tobacco fields based on diversity sequencing[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2019, 53(6): 918-925. | |
| [51] | PREEM J K, TRUU J, TRUU M, et al. Bacterial community structure and its relationship to soil physico-chemical characteristics in alder stands with different management histories[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 49: 10-17. |
| [52] | YANG L, TAN L L, ZHANG F H, et al. Duration of continuous cropping with straw return affects the composition and structure of soil bacterial communities in cotton fields[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2018, 64(3): 167-181. |
| [1] | 李传哲, 董青君, 纪力, 汪吉东, 陈川, 章安康, 张永春, 邵文奇. 新型肥料对典型黄河故道区土壤养分、微生物群落及稻麦产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 136-147. |
| [2] | 朱高烁, 高爱民, 李百成, 刘康康. 党参种子丸粒化包衣性能仿真与试验[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2615-2624. |
| [3] | 万合锋, 刘国华, 武玉祥, 蒋娟, 张珍明, 刘勇. 物料初始pH值对堆肥理化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(10): 2165-2178. |
| [4] | 何宇, 吕卫光, 李双喜, 郑宪清, 张翰林, 张娟琴, 张海韵, 白娜玲, 刘善良. γ-聚谷氨酸发酵液对小白菜生长及氮磷肥料利用率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 329-337. |
| [5] | 袁文雅, 康益晨, 杨昕宇, 张茹艳, 周春涛, 王勇, 陈喜鹏, 余慧芳, 秦舒浩. 清水苜蓿土壤浸提液对连作马铃薯根际土壤环境酶活性和微生物群落的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(2): 240-247. |
| [6] | 高志远, 杨淑娜, 王朝丽, 王智豪, 奚昕琰, 何娟, 贾惠娟. 不同熏蒸方式对连作桃园土壤的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(10): 2251-2258. |
| [7] | 徐雪芬, 倪春辉, 李惠霞, 李焕宇, 李文豪, 陈垣, 胡芳弟. 党参根腐病病原菌鉴定及其室内毒力测定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(1): 96-103. |
| [8] | 史传奇, 胡宝忠, 于少鹏, 孟博, 杨春雪, 刘嘉, 丁俊男. 不同处理条件下金鱼藻净水效果与微生物群落变化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(6): 1070-1081. |
| [9] | 李美霖, 陈宇眺, 洪晓富, 乔宇颖, 王青霞, 陈喜靖, 沈阿林, 喻曼. 不同氮肥管理方式对稻田土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(2): 308-316. |
| [10] | 胡心意, 傅庆林, 刘琛, 丁能飞, 林义成. 秸秆还田和耕作深度对稻田耕层土壤的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(7): 1202-1210. |
| [11] | 戚甫友, 范伟军, 胡秀, 梁韩枝, 吴永清, 许炳强. 土党参茎段的愈伤组织诱导与植株再生[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(8): 1313-1320. |
| [12] | 韩丽娜, 丁哲利, 曾会才, 郑伟, 何应对, 葛宇. 功能性有机肥对大白菜生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(10): 1718-1723. |
| [13] | 毛伟华1,吴三玲1,张旭2. 土壤微生物16S rDNA 的Ion Torrent PGM高通量检测方法构建与应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(12): 2165-. |
| [14] | 徐幼平;蔡新忠;祝小祥;*. 水旱作物轮作田块土壤中微生物群落结构的PLFA法比较分析[J]. , 2013, 25(5): 0-1061. |
| [15] | 官雪芳;林碧芬;徐庆贤;钱蕾;林斌;* . 种植年限对土壤性状、微生物群落及脐橙果实品质的影响[J]. , 2012, 24(1): 0-113. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||