Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2293-2307.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240790
• Horticultural Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of optimizing fertilizer management on yield, quality and greenhouse gas emissions of Citrus×aurantium L. Changshanhuyou
SHEN Jiayu1,2( ), DENG Yan3, LI Bei3, WANG Jiayu3, ZHANG Jiwen4, PENG Guofang5, WU Qun6, ZHU Qichao3, ZHANG Weifeng1,2,3, DUAN Zhiping3,*(
), DENG Yan3, LI Bei3, WANG Jiayu3, ZHANG Jiwen4, PENG Guofang5, WU Qun6, ZHU Qichao3, ZHANG Weifeng1,2,3, DUAN Zhiping3,*( )
)
- 1. College of Resources and Environment, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei 230036, China
2. Anhui Key Laboratory of Farmland Ecological Conservation and Efficient Utilization of Nutrient Resources, Hefei 230036, China
3. College of Resources and Environment, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China
4. Quzhou Agricultural Characteristic Industry Development Center, Quzhou 324000, Zhejiang, China
5. Dabaoshan Citrus Professional Cooperative of Changshan County, Changshan 324204, Zhejiang, China
6. Quzhou Agricultural Forestry Science Research Institute, Quzhou 324003, China
-
Received:2024-09-07Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08 -
Contact:*段志平,E-mail: d_zhiping12@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHEN Jiayu, DENG Yan, LI Bei, WANG Jiayu, ZHANG Jiwen, PENG Guofang, WU Qun, ZHU Qichao, ZHANG Weifeng, DUAN Zhiping. Effects of optimizing fertilizer management on yield, quality and greenhouse gas emissions of Citrus×aurantium L. Changshanhuyou[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2293-2307.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240790
| 处理 Treatment | 单株挂果数量 Fruit quantity per plant | 单果重 Single fruit weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 320.92±4.19 c | 272.05±6.26 b | 69.46±0.77 c |
| FP | 441.25±8.17 a | 275.86±4.98 ab | 88.92±1.05 a |
| OPT | 426.73±2.80 ab | 285.69±1.55 a | 88.72±1.02 a |
| OPT50%N | 418.07±10.79 b | 281.93±5.97 ab | 84.90±0.20 b |
Table 1 Fruit yield under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 单株挂果数量 Fruit quantity per plant | 单果重 Single fruit weight/g | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 320.92±4.19 c | 272.05±6.26 b | 69.46±0.77 c |
| FP | 441.25±8.17 a | 275.86±4.98 ab | 88.92±1.05 a |
| OPT | 426.73±2.80 ab | 285.69±1.55 a | 88.72±1.02 a |
| OPT50%N | 418.07±10.79 b | 281.93±5.97 ab | 84.90±0.20 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 横径 Transverse diameter/mm | 纵径 Vertical diameter/mm | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solids content/% | 可滴定酸度 Titratable acidity/% | 固酸比 Ratio of total soluble solids content to titratable acidity | 维生素C含量 Vitamin C content/(mg·g-1) | 可食率 Edible rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 86.41±2.23 ab | 72.00±1.67 a | 11.13±0.15 b | 1.08±0.08 ab | 10.37±0.72 ab | 0.293 7±0.004 5 b | 65.48±0.29 b |
| FP | 87.74±1.06 ab | 75.39±1.22 a | 11.57±0.15 a | 1.25±0.07 a | 9.29±0.60 b | 0.304 6±0.005 1 ab | 65.22±0.34 b |
| OPT | 89.80±1.52 a | 75.55±2.06 a | 11.63±0.21 a | 0.98±0.04 b | 11.86±0.68 a | 0.309 7±0.008 8 a | 67.59±0.22 a |
| OPT50%N | 85.78±0.98 b | 73.60±2.27 a | 11.50±0.10 ab | 0.98±0.10 b | 11.80±1.12 a | 0.303 1±0.003 6 ab | 67.55±0.25 a |
Table 2 Fruit quality under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 横径 Transverse diameter/mm | 纵径 Vertical diameter/mm | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solids content/% | 可滴定酸度 Titratable acidity/% | 固酸比 Ratio of total soluble solids content to titratable acidity | 维生素C含量 Vitamin C content/(mg·g-1) | 可食率 Edible rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 86.41±2.23 ab | 72.00±1.67 a | 11.13±0.15 b | 1.08±0.08 ab | 10.37±0.72 ab | 0.293 7±0.004 5 b | 65.48±0.29 b |
| FP | 87.74±1.06 ab | 75.39±1.22 a | 11.57±0.15 a | 1.25±0.07 a | 9.29±0.60 b | 0.304 6±0.005 1 ab | 65.22±0.34 b |
| OPT | 89.80±1.52 a | 75.55±2.06 a | 11.63±0.21 a | 0.98±0.04 b | 11.86±0.68 a | 0.309 7±0.008 8 a | 67.59±0.22 a |
| OPT50%N | 85.78±0.98 b | 73.60±2.27 a | 11.50±0.10 ab | 0.98±0.10 b | 11.80±1.12 a | 0.303 1±0.003 6 ab | 67.55±0.25 a |
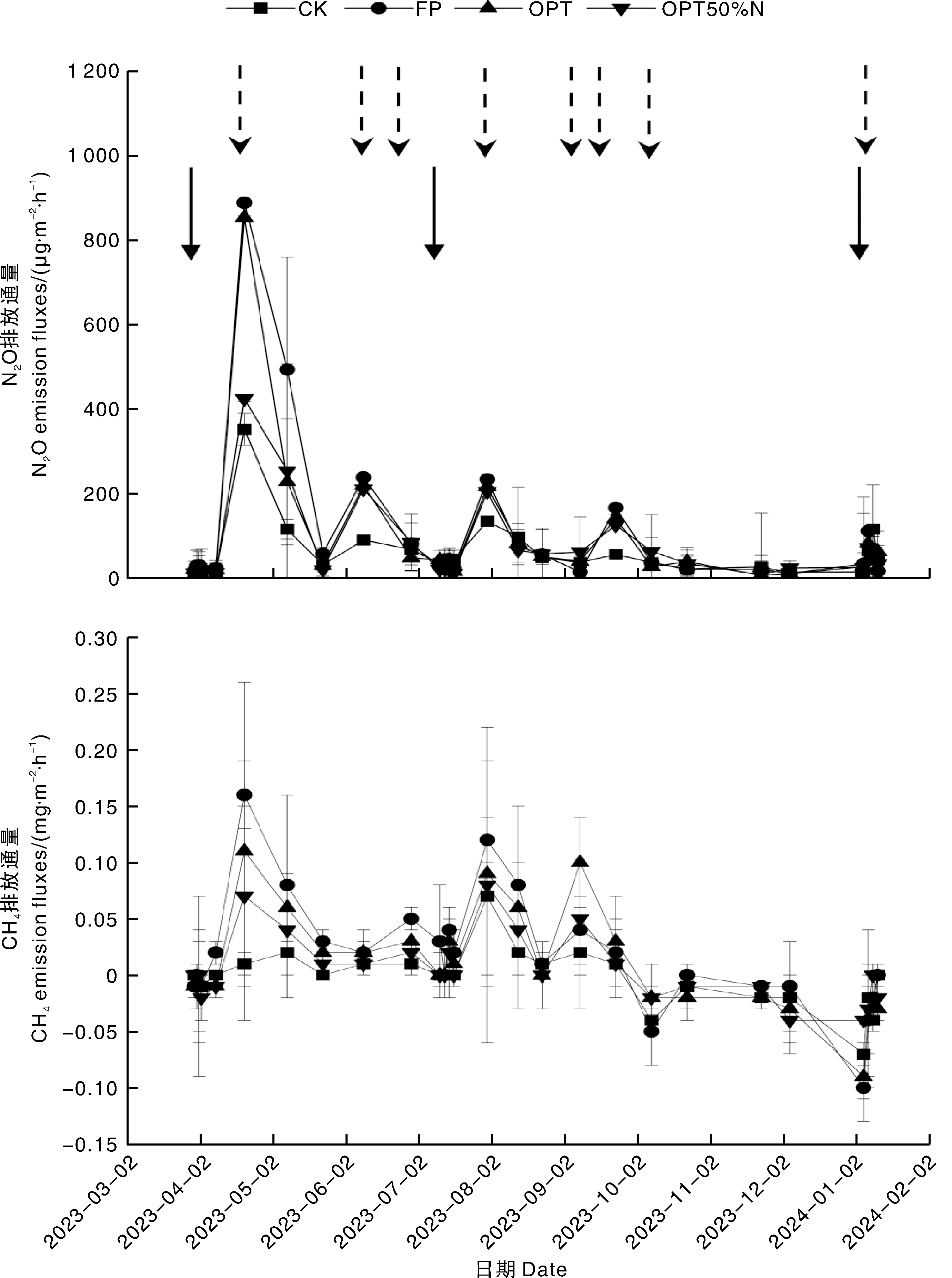
Fig.2 N2O and CH4 emission fluxes under different treatments Solid line arrows indicate fertilization, and the corresponding dates are 2023-03-28, 2023-07-09, 2024-01-03, respectively. Dashed arrows indicate precipatation above 10 mm within 24 h, and the corresponding dates are 2023-04-18, 2023-06-07, 2023-06-24, 2023-07-29, 2023-09-04, 2023-09-15, 2023-10-06, 2024-01-05, respectively.
| 处理 Treatment | N2O累积排放量 Cumulative N2O emission/(kg·hm-2) | CH4累积排放量 Cumulative CH4 emission/(kg·hm-2) | GWP/(kg·hm-2) | GHGI/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.28±0.23 c | -0.03±0.01 d | 1 275.18±68.82 c | 0.02±0.01 b |
| FP | 8.77±0.54 a | 0.13±0.01 a | 2 618.15±160.45 a | 0.03±0.01 a |
| OPT | 7.06±0.32 ab | 0.09±0.02 b | 2 107.23±96.33 b | 0.02±0.01 b |
| OPT50%N | 6.06±0.48 bc | 0.05±0.01 c | 1 807.56±141.82 b | 0.02±0.01 b |
Table 3 Global warming potential (GWP) and greenhouse gas intensity (GHGI) under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | N2O累积排放量 Cumulative N2O emission/(kg·hm-2) | CH4累积排放量 Cumulative CH4 emission/(kg·hm-2) | GWP/(kg·hm-2) | GHGI/(kg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.28±0.23 c | -0.03±0.01 d | 1 275.18±68.82 c | 0.02±0.01 b |
| FP | 8.77±0.54 a | 0.13±0.01 a | 2 618.15±160.45 a | 0.03±0.01 a |
| OPT | 7.06±0.32 ab | 0.09±0.02 b | 2 107.23±96.33 b | 0.02±0.01 b |
| OPT50%N | 6.06±0.48 bc | 0.05±0.01 c | 1 807.56±141.82 b | 0.02±0.01 b |
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis: working group I: contribution to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[R]. Switzerland: IPCC, 2022. |
| [2] | ZHANG M, GUO S L, LI B. Impact of different nitrogen-horizontal placements on greenhouse gas exchange in an apple orchard[J]. CLEAN: Soil, Air, Water, 2019, 47(4): 1800417. |
| [3] | 张嫒, 郑朝霞, 赵志远, 等. 有机无机肥长期配施对果园土壤碳库及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(10): 5823-5831. |
| ZHANG A, ZHENG Z X, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Effects of long-term combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil carbon pool and greenhouse gas emissions in orchards[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(10): 5823-5831. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | SOMPOUVISET T, MA Y T, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers effects on the global warming potential and greenhouse gas emission in apple orchard in Loess Plateau region of China[J]. Forests, 2023, 14(2): 337. |
| [5] | AGUILERA E, GUZMÁN G, ALONSO A. Greenhouse gas emissions from conventional and organic cropping systems in Spain I: herbaceous crops[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 35(2): 713-724. |
| [6] | 马艳婷, 赵志远, 冯天宇, 等. 有机无机肥配施对苹果园温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(9): 2039-2048. |
| MA Y T, ZHAO Z Y, FENG T Y, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions from an apple orchard with the mixed application of organic and chemical fertilizers[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(9): 2039-2048. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 闫湘, 金继运, 何萍, 等. 提高肥料利用率技术研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(2): 450-459. |
| YAN X, JIN J Y, HE P, et al. Recent advances in technology of increasing fertilizer use efficiency[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(2): 450-459. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 刘振岩, 李震三. 山东果树[M]. 上海: 上海科技出版社, 2000: 59-60. |
| [9] | 武松伟, 梁珊珊, 胡承孝, 等. 我国柑橘园“因土补肥” 与化肥减施增效生态分区[J]. 华中农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(2): 9-19. |
| WU S W, LIANG S S, HU C X, et al. Ecological region division of soil based supplementary fertilization and decrement fertilization in China citrus orchards[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 41(2): 9-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 杨波, 毕旭灿, 汪丽霞, 等. 常山胡柚种质资源收集开发利用研究进展[J]. 果树资源学报, 2024, 5(1): 88-92. |
| YANG B, BI X C, WANG L X, et al. Colletion, preserving, utilization and research prospect of Changshan pomelo germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Fruit Resources, 2024, 5(1): 88-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 李志坚, 李燕青, 李壮. 柑橘园养分管理技术[J]. 果树实用技术与信息, 2023(10): 19-22. |
| LI Z J, LI Y Q, LI Z. Nutrient management techniques in citrus orchards[J]. Applied Technology and Information for Fruit Tree, 2023(10): 19-22. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 李荣会, 王中秋, 汪东东, 等. 叶面喷施中微肥对胡柚果实产量及品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(2): 308-309. |
| LI R H, WANG Z Q, WANG D D, et al. Effect of spraying medium and trace elements fertilizer on yield and quality of citrus paradise[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(2): 308-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 何龙生, 姜新育, 周率, 等. 胡柚专用肥对常山胡柚果实品质和土壤养分的影响研究[J]. 浙江柑橘, 2023, 40(4): 17-23. |
| HE L S, JIANG X Y, ZHOU L, et al. Effect of special fertilizer on the fruit quality and soil nutrients of Citrus×aurantium Changshanhuyou[J]. Zhejiang Citrus, 2023, 40(4): 17-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 郑君, 吴文明, 毕旭灿, 等. 常山胡柚专用肥试验初报[J]. 浙江柑桔, 2004, 21(4): 16-17. |
| ZHENG J, WU W M, BI X C, et al. Preliminary report on the special fertilizer for Citrus×aurantium Changshanhuyou[J]. Zhejiang Citrus, 2004, 21(4): 16-17. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 刘小曼, 刘晓东, 刘伟栋, 等. 我国不同种类柑橘养分状况及氮磷钾推荐用量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(4): 565-574. |
| LIU X M, LIU X D, LIU W D, et al. Nutritional status of different citrus trees and the recommended dosages of N, P and K for citrus production in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(4): 565-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 黄鸿. 湖北省秭归地区三个品种脐橙矫正施肥及其效应研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2012. |
| HUANG H. Research on the nutrient diagnosis and fertilization of three navel orange cultivars in Zigui, Hubei Province[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 巨晓棠. 氮肥有效率的概念及意义: 兼论对传统氮肥利用率的理解误区[J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 51(5): 921-933. |
| JU X T. The concept and meanings of nitrogen fertilizer availability ratio: discussing misunderstanding of traditional nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, 51(5): 921-933. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 邓秀新, 彭抒昂. 柑橘学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013. |
| [19] | 井浩然. 湖北猕猴桃、椪柑专用肥施用效果研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2023. |
| JING H R. Research on the effect of special fertilizer application for kiwifruit and ponkan in Hubei Province[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 彭柱青. 打孔施肥对柑橘果实产量、品质及养分利用的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| PENG Z Q. Effects of drilling fertilization on fruit yield, quality and nutrient utilization in citrus[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 路永莉, 周建斌, 海龙, 等. 基于猕猴桃树体养分携出量确定果园合理施肥量: 以周至县俞家河流域为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(8): 1765-1772. |
| LU Y L, ZHOU J B, HAI L, et al. Determination of optimal fertilizer quantities based on nutrient removal in kiwi vines: a case study of Yujiahe catchment, in Zhouzhi County[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(8): 1765-1772. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 康福蓉. 氮肥运筹对柑橘园氨挥发与氮素淋洗的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022. |
| KANG F R. Study on the effects of nitrogen management on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen leaching in citrus orchard[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 葛顺峰, 姜远茂, 魏绍冲, 等. 不同供氮水平下幼龄苹果园氮素去向初探[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 949-955. |
| GE S F, JIANG Y M, WEI S C, et al. Nitrogen balance under different nitrogen application rates in young apple orchards[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(4): 949-955. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 李卓瑞, 韦高玲. 不同生物炭添加量对土壤中氮磷淋溶损失的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2): 333-338. |
| LI Z R, WEI G L. Effects of biochar with different additive amounts on the leaching loss of nitrogen and phosphorus in soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(2): 333-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | ZHANG B G, LI Q, CAO J, et al. Reducing nitrogen leaching in a subtropical vegetable system[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 241: 133-141. |
| [26] | 张杰. 河北主产区葡萄园不同水肥管理净温室效应研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG J. Analysis of net greenhouse warming potential in grape yard under different water and fertilizer managements in the main growing regions in Hebei[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 25-114. |
| [28] | 王琛. 矮砧密植苹果园不同水肥管理氮素去向及净温室效应研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2021. |
| WANG C. Nitrogen distribution and net greenhouse effect under different water and fertilizer management in low-stock and densely planted apple orchards[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王贺, 邓明江, 王旋, 等. 减施化肥对京津地区苹果生长发育的影响[J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(2): 196-203. |
| WANG H, DENG M J, WANG X, et al. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer use on apple tree growth and development in Beijing and Tianjin orchards[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(2): 196-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 刘文, 江涛, 卢盛杰, 等. 柑橘专用有机无机复混肥在纽荷尔脐橙上的应用效果[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2020(1): 49-50. |
| LIU W, JIANG T, LU S J, et al. Application effect of citrus special organic-inorganic compound fertilizer on Newhall navel orange[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2020(1): 49-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 王鹏, 崔恒, 陈敏, 等. 专用肥配合种植光叶苕子提高柑橘品质和养分效率[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(3): 178-186. |
| WANG P, CUI H, CHEN M, et al. Special formula fertilizer combined with planting smooth vetch improved fruit quality, and nutrient efficiency of citrus[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(3): 178-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 裴宇, 伍玉鹏, 张威, 等. 化肥减量配合有机替代对柑橘果实、叶片及橘园土壤的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(4): 88-95. |
| PEI Y, WU Y P, ZHANG W, et al. The impacts of substituting organic fertilizers for chemical fertilizer on fruit, leaf and soil in citrus orchard[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(4): 88-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | FIKRY A M, RADHI K S, ABOUREHAB M A S, et al. Effect of inorganic and organic nitrogen sources and biofertilizer on murcott mandarin fruit quality[J]. Life, 2022, 12(12): 2120. |
| [34] | MARATHE R, BHARAMBE P, SHARMA R, et al. Soil properties of Vertisol and yield of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) as influenced by integrated use of organic manures, inorganic and bio-fertilizers[J]. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 79: 3-7. |
| [35] | 李志国, 曾华, 聂新星, 等. 施用不同氮、磷、钾肥和有机肥对‘红阳’猕猴桃生长及产量的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2015, 33(1): 98-108. |
| LI Z G, ZENG H, NIE X X, et al. Effect of different N, P, K and organic fertilization rates on growth and yield of Actinidia chinensis ‘Hongyang’[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2015, 33(1): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 鲁剑巍, 陈防, 张竹青, 等. 磷肥用量对油菜产量、养分吸收及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2005, 27(1):73-76. |
| LU J W, CHEN F, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Effect of phosphor application rate on rapeseed yield, nutrient absorption and profit[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2005, 27(1):73-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 王帅, 杨劲峰, 韩晓日, 等. 不同施肥处理对旱作春玉米光合特性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2008(6): 23-27. |
| WANG S, YANG J F, HAN X R, et al. Effect of fertilizer application on photosynthetic traits of spring maize[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2008(6): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 储成才, 王毅, 王二涛. 植物氮磷钾养分高效利用研究现状与展望[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2021, 51(10): 1415-1423. |
| CHU C C, WANG Y, WANG E T. Improving the utilization efficiency of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium: current situation and future perspectives[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2021, 51(10): 1415-1423. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | 袁洁, 区善汉, 刘冰浩, 等. 赤霉素和尿素处理对无核沃柑幼树成花及树体生长的影响[J]. 中国南方果树, 2023, 52(2): 5-8. |
| YUAN J, OU S H, LIU B H, et al. Effect of GA3 and urea on flower formation and growth of yong seedless orah tree[J]. South China Fruits, 2023, 52(2): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 朱金籴, 朱学刚, 杜文青, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥对设施番茄光合特性、品质和产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2025 (3): 185-189. |
| ZHU J D, ZHU X G, DU W Q, et al. Effects of fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer on growth, phytosynthetic characteristics, quality and yield of tomatoes cultivated in facilities[J]. Crops, 2025 (3): 185-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 王继廉, 朱继兵, 杨洪菊. 中肥力地块葡萄化肥减量增效试验总结[J]. 云南农业, 2024(10): 74-77. |
| WANG J L, ZHU J B, YANG H J. Summary of the experiments on reducing fertilizer use and increasing use efficiency in middle fertility vineyard[J]. Yunnan Agriculture, 2024(10): 74-77. (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 杨艳芝. 农药化肥减量增效技术在农业病虫害防治中的应用[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2024, 14(8): 7-9. |
| YANG Y Z. Application of pesticide and fertilizer reduction and efficiency enhancement technology in agricultural pest and disease control[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2024, 14(8): 7-9. (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | PERTUSATTI J, PRADO A G S. Buffer capacity of humic acid: thermodynamic approach[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 314(2): 484-489. |
| [44] | 田蕊, 汪亮, 杨威, 等. 外源施加腐殖酸液态膜对苹果光合特性和果实品质的影响[J]. 植物科学学报, 2023, 41(5): 668-676. |
| TIAN R, WANG L, YANG W, et al. Effects of exogenous application of humic acid liquid film on photosynthetic characteristics and fruit quality of Malus domestica Borkh[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2023, 41(5): 668-676. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 何流, 徐新翔, 贾志航, 等. 黄腐酸类肥料在苹果上的减肥增效效果[J]. 北方园艺, 2018(18): 16-21. |
| HE L, XU X X, JIA Z H, et al. Research of humic acid fertilizer on apple in fertilizer reducing and efficiency increasing[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2018(18): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 朱家昌. “双碳” 背景下的中国碳排放分析与预测[D]. 大连: 东北财经大学, 2023. |
| ZHU J C. Analysis and prediction of carbon emission in China under the background of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[D]. Dalian: Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 李劼, 徐晋涛. 我国农业低碳技术的减排潜力分析[J]. 农业经济问题, 2022, 43(3): 117-135. |
| LI J, XU J T. Analyses of carbon reduction potential of low carbon technologies in China[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2022, 43(3): 117-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 王文赞. 苹果园有机肥替代部分化肥的农学和环境效应研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2022. |
| WANG W Z. Agronomic and environmental effects of organic fertilizer replaced part of chemical fertilizer in apple orchard[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | 陈梦蝶, 崔晓阳. 土壤有机碳矿物固持机制及其影响因素[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(2): 175-183. |
| CHEN M D, CUI X Y. Mechanisms and influencing factors of soil organic carbon sequestration by minerals[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(2): 175-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [50] | ZHU J, PENG H, JI X H, et al. Effects of reduced inorganic fertilization and rice straw recovery on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community in double-rice paddy soils[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2019, 94: 103116. |
| [51] | 黄志鹏, 吴海宁, 唐秀梅, 等. 化肥减施对花生根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 花生学报, 2020, 49(3): 8-13. |
| HUANG Z P, WU H N, TANG X M, et al. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer application on bacterial community structure and diversity in peanut rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2020, 49(3): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | 谭海燕, 马芳, 杨从林, 等. 长期减量施肥对设施耕地土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2021, 11(2): 39-44. |
| TAN H Y, MA F, YANG C L, et al. Effects of long-term reducing fertilization on soil nutrient content in protected cultivated land[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11(2): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [53] | 刘蕊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 等. 农田氧化亚氮减排技术及其与绿肥协同应用分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 196-210. |
| LIU R, CHANG D N, ZHOU G P, et al. Techniques of N2O emission reduction in farmland and their synergistic application with green manure[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 196-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | 李文娟, 蔡延江, 朱同彬, 等. 土壤团聚体氧化亚氮排放及其微生物学机制研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(5): 1132-1144. |
| LI W J, CAI Y J, ZHU T B, et al. Release of nitrous oxide from soil aggregates and its microbial mechanism[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(5): 1132-1144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [55] | 尹丹, 朱忆雯, 胡敏, 等. 水稻根际微生物及其驱动的土壤碳氮磷循环[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2024, 30(11): 2207-2220. |
| YIN D, ZHU Y W, HU M, et al. Rice rhizosphere microbiomes and their driving cycling of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2024, 30(11): 2207-2220. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [56] | 徐云连, 马友华, 吴蔚君, 等. 长期减量化施肥对水稻产量和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(6): 254-258. |
| XU Y L, MA Y H, WU W J, et al. Effects of long-term reducing fertilization on yield and soil fertility of rice[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(6): 254-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [57] | 王慧颖, 徐明岗, 周宝库, 等. 黑土细菌及真菌群落对长期施肥响应的差异及其驱动因素[J]. 中国农业科学, 2018, 51(5): 914-925. |
| WANG H Y, XU M G, ZHOU B K, et al. Response and driving factors of bacterial and fungal community to long-term fertilization in black soil[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(5): 914-925. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [58] | 张瑞, 范志伟, 徐胜光, 等. 化肥减施与外源MeJA对连作草莓根际土壤微生物的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2024, 42(5): 1068-1076. |
| ZHANG R, FAN Z W, XU S G, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction and exogenous MeJA addition on rhizosphere microorganisms in continuous cropping strawberry[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2024, 42(5): 1068-1076. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [59] | 张思远. 不同管理措施下农田土壤温室气体排放对降水的响应[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2017. |
| ZHANG S Y. Response of greenhouse gas emissions to precipitation under different management measures in dry farming system[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [60] | 韩慧, 乔林明, 王晓璐, 等. 极端降水条件下土壤中O2浓度对CO2和N2O浓度变化的调控作用[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(10): 1555-1564. |
| HAN H, QIAO L M, WANG X L, et al. Effects of soil O2 on CO2 and N2O concentration change under extreme precipitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(10): 1555-1564. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [61] | 程功, 刘廷玺, 王冠丽, 等. 降雨和凋落物对人工杨树林土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(6): 1398-1407. |
| CHENG G, LIU T X, WANG G L, et al. Effects of rainfall and litter on soil greenhouse gas fluxes in artificial poplar forest[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(6): 1398-1407. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [62] | WANG J S, LUO Y Q, QUAN Q, et al. Effects of warming and clipping on CH4 and N2O fluxes in an alpine meadow[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2021, 297: 108278. |
| [63] | 王远铭, 葛梅红, 程宁宁, 等. 不同施肥模式下芒果园氮素养分平衡及氮气排放[J]. 西南农业学报, 2025, 38(1): 160-170. |
| WANG Y M, GE M H, CHENG N N, et al. Nitrogen nutrient balance and nitrogen emission in mango orchard under different fertilization modes[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 38(1): 160-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [64] | 祖若川, 王静波. 化肥减量对太湖流域土壤肥力、水稻产量及氮磷养分吸收的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(2): 293-297. |
| ZU R C, WANG J B. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction on soil fertility, rice yield and nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient uptake in Tai Lake region[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 66(2): 293-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [65] | 王晓丽, 安梦洁, 张春媛, 等. 改良剂调控盐碱胁迫对棉田土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(2): 180-187. |
| WANG X L, AN M J, ZHANG C Y, et al. Effects of modifier on soil microbial diversity in cotton field under saline-alkali stress[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 2022, 40(2): 180-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [66] | YANG F, TANG C Y, ANTONIETTI M. Natural and artificial humic substances to manage minerals, ions, water, and soil microorganisms[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(10): 6221-6239. |
| [67] | 靖吉越, 郭新送, 朱福军, 等. 腐殖酸类肥料在园艺作物中应用的研究进展[J]. 肥料与健康, 2024, 51(4): 1-6. |
| JING J Y, GUO X S, ZHU F J, et al. Research progress on the application of humic acid fertilizers in horticultural crops[J]. Fertilizer & Health, 2024, 51(4): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [68] | 李鹏, 徐荣茂, 张洪江, 等. 黄腐酸复合肥对猕猴桃生长及果实的影响[J]. 腐植酸, 2023(1): 38-43. |
| LI P, XU R M, ZHANG H J, et al. Effects of fulvic acid compound fertilizers on growth and fruit of kiwifruit[J]. Humic Acid, 2023(1): 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [69] | 李德金, 周海生, 向冬妹, 等. “纽翠绿” 腐殖酸有机液肥在泸溪椪柑上的应用效果研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(6): 149-153. |
| LI D J, ZHOU H S, XIANG D M, et al. Study on the application effect of “New Green” humic acid organic liquid fertilizer on Luxi mandarin western Hunan, China[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(6): 149-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [70] | 张筠筠, 王竞, 孙权, 等. 化肥减施对贺兰山东麓土壤肥力及酿酒葡萄品质的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(7): 1601-1606. |
| ZHANG J J, WANG J, SUN Q, et al. Effect of chemical fertilizer reduction on soil fertility and wine grape quality in east piedmont area of Helan Mountain, Ningxia[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(7): 1601-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [71] | 马悦欣. 有机肥与化肥配施在盛果期苹果园应用效果研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023. |
| MA Y X. Study on the application effect of organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer in apple orchards at peak fruit stage[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [72] | FENG H D, CHEN H Y, DANG Z G, et al. Soil properties, leaf nutrients and fruit quality response to substituting chemical fertilizer with organic manure in a mango orchard[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2020, 18(3): 4025-4033. |
| [73] | 安祥瑞, 江尚焘, 谢昶琰, 等. 减施化肥配施有机肥对荔枝园土壤微生物区系的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(4): 1099-1108. |
| AN X R, JIANG S T, XIE C Y, et al. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizers combined with organic fertilizers on soil microbial community in litchi orchards[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(4): 1099-1108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [74] | WAN L J, TIAN Y, HE M, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer application on soil properties, citrus growth physiology, and yield[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(12): 1207. |
| [75] | 黄春辉, 曲雪艳, 刘科鹏, 等. ‘金魁’猕猴桃园土壤理化性状、叶片营养与果实品质状况分析[J]. 果树学报, 2014, 31(6): 1091-1099. |
| HUANG C H, QU X Y, LIU K P, et al. Analysis of soil physicochemical properties, leaf nutrients and fruit qualities in the orchards of ‘Jinkui’ kiwifruit(Actinidia deliciosa)[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2014, 31(6): 1091-1099. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [76] | 田伟龙, 黄文江, 陶书田, 等. 种养结合梨园土壤有机质、酶活性及果实品质差异研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(13): 165-168. |
| TIAN W L, HUANG W J, TAO S T, et al. Difference of soil organic matter and soil enzyme activity and fruit quality in crop-animal mixed pear orchard[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(13): 165-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [77] | 洪华阳, 魏天齐, 周红梅, 等. 修复连作大蒜土壤生产力衰退的有机质补偿方案与初步机理[J]. 土壤学报, 2024, 61(5): 1386-1397. |
| HONG H Y, WEI T Q, ZHOU H M, et al. Organic matter compensation scheme and preliminary mechanism for remediation of soil productivity decline in continuous cropping garlic[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2024, 61(5): 1386-1397. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [78] | 丛山. 温度和水分对有机质及活性炭组分的影响[J]. 中国农业信息, 2016, 28(12): 116-119. |
| CONG S. Effects of temperature and moisture on organic matter and activate carbon fractions[J]. China Agricultural Information, 2016, 28(12): 116-119. (in Chinese) | |
| [79] | RAZA T, QADIR M F, KHAN K S, et al. Unraveling the potential of microbes in decomposition of organic matter and release of carbon in the ecosystem[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 344: 118529. |
| [1] | SHEN Jiayu, DENG Yan, ZHANG Jiwen, PENG Guofang, WU Qun, ZHU Qichao, ZHANG Weifeng, LI Bei. Evaluation of carbon emissions and storage status of citrus orchard in Quzhou City, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2340-2353. |
| [2] | YANG Le, LI Wenyang, LUO Jianli, ZHENG Wei, ZHANG Biyang, WANG Zhen, YAN Tengfei. Effects of plastic film mulching and natural grass growing on soil nutrients, pH, water content and temperature in peach orchard [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(12): 2719-2726. |
| [3] | XU Kai, ZHANG Shaoyu, YUAN Jicun, YAN Shuai, HOU Guixue, ZHAO Deying. Effects of plastic film and straw mulching on soil nutrients of pear orchard [J]. , 2017, 29(3): 421-427. |
| [4] | ZHAO Wei\|ming;WANG Yan\|yan;MA Jia\|wei;HU Yang\|yong;TONG Gen\|ping;ZHAO Ke\|li;YE Zheng\|qian;*. Phosphorus status and its leaching loss risks in the soils of Chinese hickory orchards in Linan City, Zhejiang Province [J]. , 2014, 26(1): 0-158. |
| [5] | MA Jiawei;HUANG Qiying;CHENG Lize;YE Zhengqian*;WANG Xyudong. Effect of edible fungus residue on dynamic changes of red soil nutrients and rice yield [J]. , 2013, 25(1): 0-151. |
| [6] | MA Wan-zhu;ZHANG Ming-kui;*;LU Xiao-nan;ZHANG Tian-yu. Effects of canopy position on spatial variations of nutrients in sandy soils in citrus garden [J]. , 2010, 22(3): 0-348. |
| [7] | WU Quan-cong;ZHENG Shi-hua. Investigation on the species of natural enemy insects in peach orchard in Lishui [J]. , 2010, 22(1): 0-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||