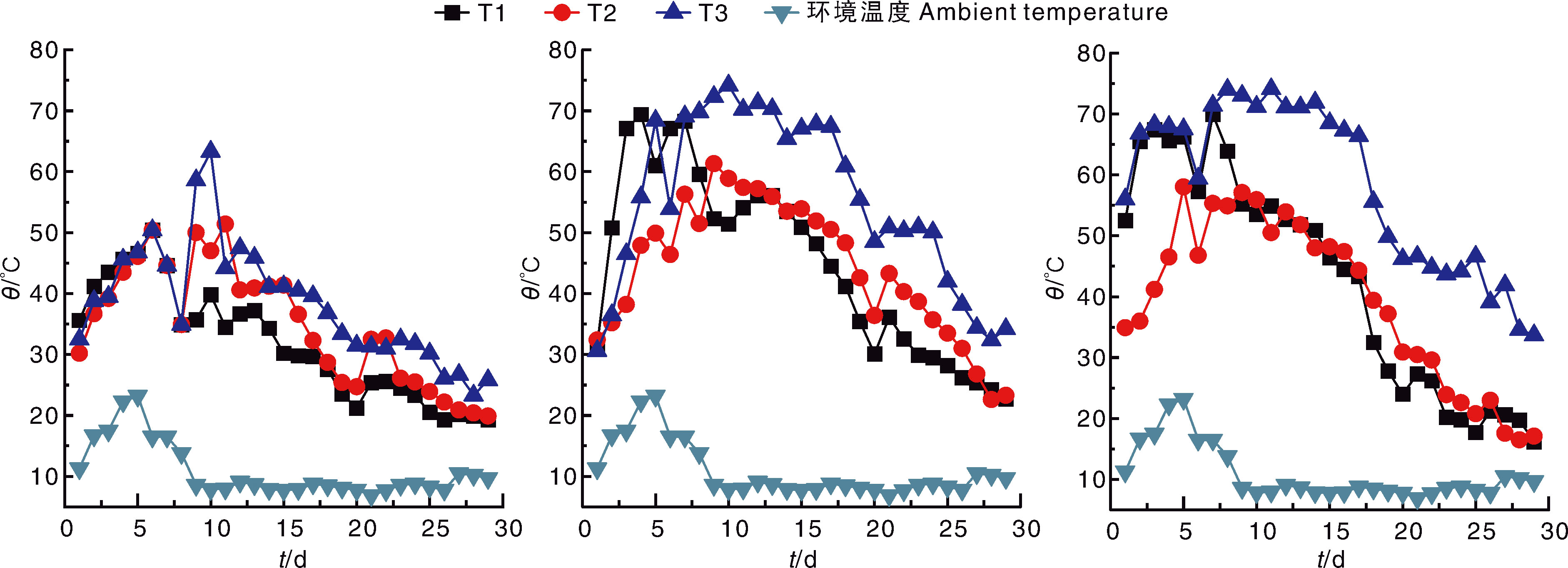
Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2165-2178.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240942
• Environmental Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of initial substrate pH value on physicochemical properties and microbial community during composting
WAN Hefeng1( ), LIU Guohua1, WU Yuxiang1,*(
), LIU Guohua1, WU Yuxiang1,*( ), JIANG Juan1,2, ZHANG Zhenming2, LIU Yong3
), JIANG Juan1,2, ZHANG Zhenming2, LIU Yong3
- 1. Guizhou Institute of Biology, Guizhou Academy of Sciences, Guiyang 550009, China
2. College of Resource and Environmental Engineering, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China
3. School of Biological and Environmental Engineering, Guiyang University, Guiyang 550005, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WAN Hefeng, LIU Guohua, WU Yuxiang, JIANG Juan, ZHANG Zhenming, LIU Yong. Influence of initial substrate pH value on physicochemical properties and microbial community during composting[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2165-2178.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240942
| 原料 Raw material | 含水率 Moisture content/% | 容重 Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量 Organic matter content/% | 总氮含量 Total nitrogen content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酒糟Vinasse | 76.92±1.16 | 0.27±0.01 | 3.12±0.07 | 29.47±0.79 | 4.39±0.16 |
| 锯末Sawdust | 30.57±1.77 | 0.24±0.08 | 7.18±0.05 | 66.91±0.12 | 2.13±0.81 |
| 味精下脚料By-product of monosodium glutamate | 32.80±1.13 | 0.41±0.03 | 4.87±0.02 | 16.15±0.09 | 5.50±0.27 |
| 牛粪Cow dung | 70.31±0.70 | 0.51±0.05 | 8.53±0.31 | 53.19±0.23 | 3.01±0.12 |
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of raw materials
| 原料 Raw material | 含水率 Moisture content/% | 容重 Bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量 Organic matter content/% | 总氮含量 Total nitrogen content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酒糟Vinasse | 76.92±1.16 | 0.27±0.01 | 3.12±0.07 | 29.47±0.79 | 4.39±0.16 |
| 锯末Sawdust | 30.57±1.77 | 0.24±0.08 | 7.18±0.05 | 66.91±0.12 | 2.13±0.81 |
| 味精下脚料By-product of monosodium glutamate | 32.80±1.13 | 0.41±0.03 | 4.87±0.02 | 16.15±0.09 | 5.50±0.27 |
| 牛粪Cow dung | 70.31±0.70 | 0.51±0.05 | 8.53±0.31 | 53.19±0.23 | 3.01±0.12 |
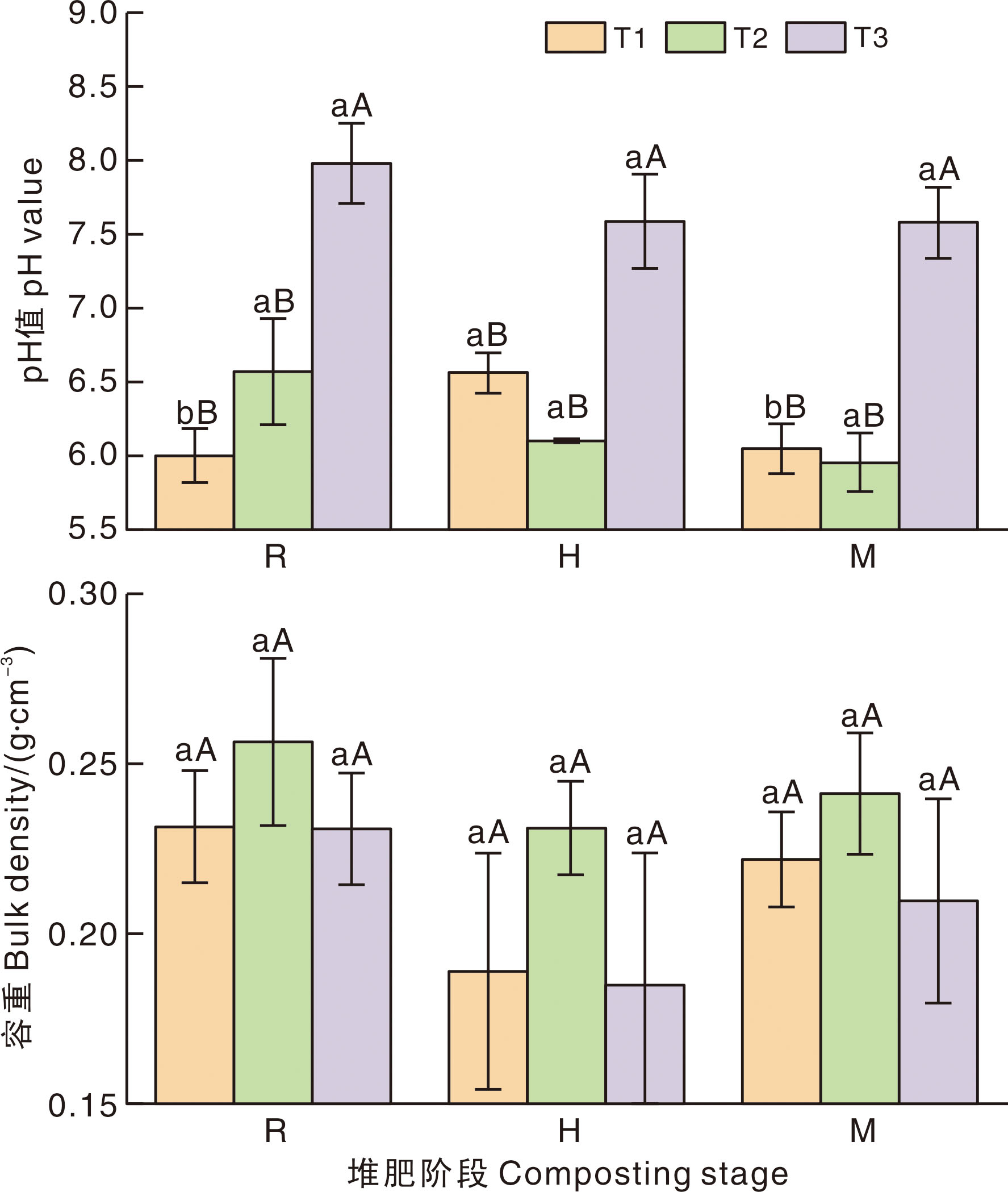
Fig.2 Changes of pH value and bulk density under treatments during composting Bars marked without the same lowercase letters indicate singificant (p<0.05) difference within compsoting stages for the same treatment, and bars marked without the same uppercase letters indicate significant difference within treatments at the same composting stage. R, Tempertaure-rising stage; H, High temperature stage; M, Maturiy stage.
| 处理 Treatment | 堆肥阶段 Composting stage | ωTN | ωTP | ωTK | ωTOC | ωAP | ωAK | ωAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | R | 41.87± 3.15 bA | 4.62± 0.72 aA | 11.95± 1.43 aB | 228.90± 23.56 aB | 1.89± 0.08 aA | 11.49± 2.31 aA | 12.42± 1.33 aA |
| H | 39.68± 2.82 bB | 4.35± 0.36 aA | 11.59± 1.02 aA | 244.70± 25.33 aB | 1.69± 0.09 aAB | 11.12± 0.88 aA | 11.42± 2.83 aA | |
| M | 51.46± 3.36 aA | 4.56± 0.41 aB | 12.18± 1.29 aA | 295.90± 28.56 aAB | 1.89± 0.08 aAB | 11.24± 0.66 aB | 13.79± 1.54 aA | |
| T2 | R | 33.14± 1.77 bB | 4.98± 0.49 aA | 17.07± 1.52 aA | 306.50± 10.16 aA | 2.03± 0.14 aA | 16.51± 1.56 aA | 10.98± 1.40 aA |
| H | 48.37± 1.33 aA | 4.23± 0.61 aA | 14.10± 0.68 bA | 299.20± 29.94 aAB | 1.42± 0.09 bB | 13.45± 0.89 abA | 13.03± 1.62 aA | |
| M | 45.52± 1.46 aA | 4.53± 0.46 aB | 13.21± 0.42 bA | 252.90± 27.74 aB | 1.67± 0.10 bB | 12.65± 0.94 bB | 12.49± 1.79 aA | |
| T3 | R | 17.60± 2.95 aC | 5.54± 0.86 abA | 13.16± 1.07 bB | 158.50± 10.52 bC | 2.30± 0.19 aA | 12.47± 2.32 aA | 2.26± 0.31 aB |
| H | 12.12± 2.63 aC | 4.54± 0.46 bA | 12.02± 1.06 bA | 349.30± 17.47 aA | 1.86± 0.14 aA | 11.37± 1.25 aA | 1.88± 0.61 aB | |
| M | 16.21± 3.60 aB | 6.95± 0.52 aA | 16.51± 0.95 aA | 334.10± 13.44 aA | 2.13± 0.16 aA | 15.53± 1.26 aA | 2.27± 0.25 aB |
Table 2 Changes of nutrients content under treatments during composting g·kg-1
| 处理 Treatment | 堆肥阶段 Composting stage | ωTN | ωTP | ωTK | ωTOC | ωAP | ωAK | ωAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | R | 41.87± 3.15 bA | 4.62± 0.72 aA | 11.95± 1.43 aB | 228.90± 23.56 aB | 1.89± 0.08 aA | 11.49± 2.31 aA | 12.42± 1.33 aA |
| H | 39.68± 2.82 bB | 4.35± 0.36 aA | 11.59± 1.02 aA | 244.70± 25.33 aB | 1.69± 0.09 aAB | 11.12± 0.88 aA | 11.42± 2.83 aA | |
| M | 51.46± 3.36 aA | 4.56± 0.41 aB | 12.18± 1.29 aA | 295.90± 28.56 aAB | 1.89± 0.08 aAB | 11.24± 0.66 aB | 13.79± 1.54 aA | |
| T2 | R | 33.14± 1.77 bB | 4.98± 0.49 aA | 17.07± 1.52 aA | 306.50± 10.16 aA | 2.03± 0.14 aA | 16.51± 1.56 aA | 10.98± 1.40 aA |
| H | 48.37± 1.33 aA | 4.23± 0.61 aA | 14.10± 0.68 bA | 299.20± 29.94 aAB | 1.42± 0.09 bB | 13.45± 0.89 abA | 13.03± 1.62 aA | |
| M | 45.52± 1.46 aA | 4.53± 0.46 aB | 13.21± 0.42 bA | 252.90± 27.74 aB | 1.67± 0.10 bB | 12.65± 0.94 bB | 12.49± 1.79 aA | |
| T3 | R | 17.60± 2.95 aC | 5.54± 0.86 abA | 13.16± 1.07 bB | 158.50± 10.52 bC | 2.30± 0.19 aA | 12.47± 2.32 aA | 2.26± 0.31 aB |
| H | 12.12± 2.63 aC | 4.54± 0.46 bA | 12.02± 1.06 bA | 349.30± 17.47 aA | 1.86± 0.14 aA | 11.37± 1.25 aA | 1.88± 0.61 aB | |
| M | 16.21± 3.60 aB | 6.95± 0.52 aA | 16.51± 0.95 aA | 334.10± 13.44 aA | 2.13± 0.16 aA | 15.53± 1.26 aA | 2.27± 0.25 aB |
| 处理 Treatment | Cd含量 Cd content | As含量 As content | Cr含量 Cr content | Pb含量 Pb content | Hg含量 Hg content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.17±0.05 c | 4.17±0.42 a | 11.45±2.53 b | 4.27±0.69 b | 0.06±0.01 a |
| T2 | 0.26±0.02 b | 3.81±0.37 b | 10.81±1.54 b | 4.63±0.53 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| T3 | 0.34±0.04 a | 4.38±0.33 a | 15.65±3.59 a | 2.99±0.28 c | 0.06±0.01 a |
Table 3 Heavy metals content under treatments mg·kg-1
| 处理 Treatment | Cd含量 Cd content | As含量 As content | Cr含量 Cr content | Pb含量 Pb content | Hg含量 Hg content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.17±0.05 c | 4.17±0.42 a | 11.45±2.53 b | 4.27±0.69 b | 0.06±0.01 a |
| T2 | 0.26±0.02 b | 3.81±0.37 b | 10.81±1.54 b | 4.63±0.53 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| T3 | 0.34±0.04 a | 4.38±0.33 a | 15.65±3.59 a | 2.99±0.28 c | 0.06±0.01 a |
| 类别 Category | 处理 Treatment | 堆肥阶段 Composting stage | Chao指数 Chao index | 覆盖度 Coverage | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌Bacteria | T1 | R | 1 097.7 | 0.999 27 | 7.988 | 0.987 |
| T1 | H | 721.4 | 0.999 89 | 6.625 | 0.926 | |
| T2 | R | 1 310.9 | 0.999 20 | 8.740 | 0.994 | |
| T2 | H | 975.9 | 0.999 68 | 7.927 | 0.983 | |
| T3 | R | 1 053.7 | 0.998 85 | 7.395 | 0.977 | |
| T3 | H | 1 166.7 | 0.998 47 | 8.191 | 0.991 | |
| 真菌Fungi | T1 | R | 120.4 | 0.999 92 | 3.921 | 0.891 |
| T1 | H | 155.1 | 0.999 95 | 4.240 | 0.892 | |
| T2 | R | 337.5 | 0.999 80 | 5.139 | 0.943 | |
| T2 | H | 326.2 | 0.999 96 | 5.160 | 0.918 | |
| T3 | R | 299.8 | 0.999 80 | 2.317 | 0.411 | |
| T3 | H | 282.4 | 0.999 88 | 6.047 | 0.940 |
Table 4 Microbial community α-diversity under treatments
| 类别 Category | 处理 Treatment | 堆肥阶段 Composting stage | Chao指数 Chao index | 覆盖度 Coverage | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌Bacteria | T1 | R | 1 097.7 | 0.999 27 | 7.988 | 0.987 |
| T1 | H | 721.4 | 0.999 89 | 6.625 | 0.926 | |
| T2 | R | 1 310.9 | 0.999 20 | 8.740 | 0.994 | |
| T2 | H | 975.9 | 0.999 68 | 7.927 | 0.983 | |
| T3 | R | 1 053.7 | 0.998 85 | 7.395 | 0.977 | |
| T3 | H | 1 166.7 | 0.998 47 | 8.191 | 0.991 | |
| 真菌Fungi | T1 | R | 120.4 | 0.999 92 | 3.921 | 0.891 |
| T1 | H | 155.1 | 0.999 95 | 4.240 | 0.892 | |
| T2 | R | 337.5 | 0.999 80 | 5.139 | 0.943 | |
| T2 | H | 326.2 | 0.999 96 | 5.160 | 0.918 | |
| T3 | R | 299.8 | 0.999 80 | 2.317 | 0.411 | |
| T3 | H | 282.4 | 0.999 88 | 6.047 | 0.940 |
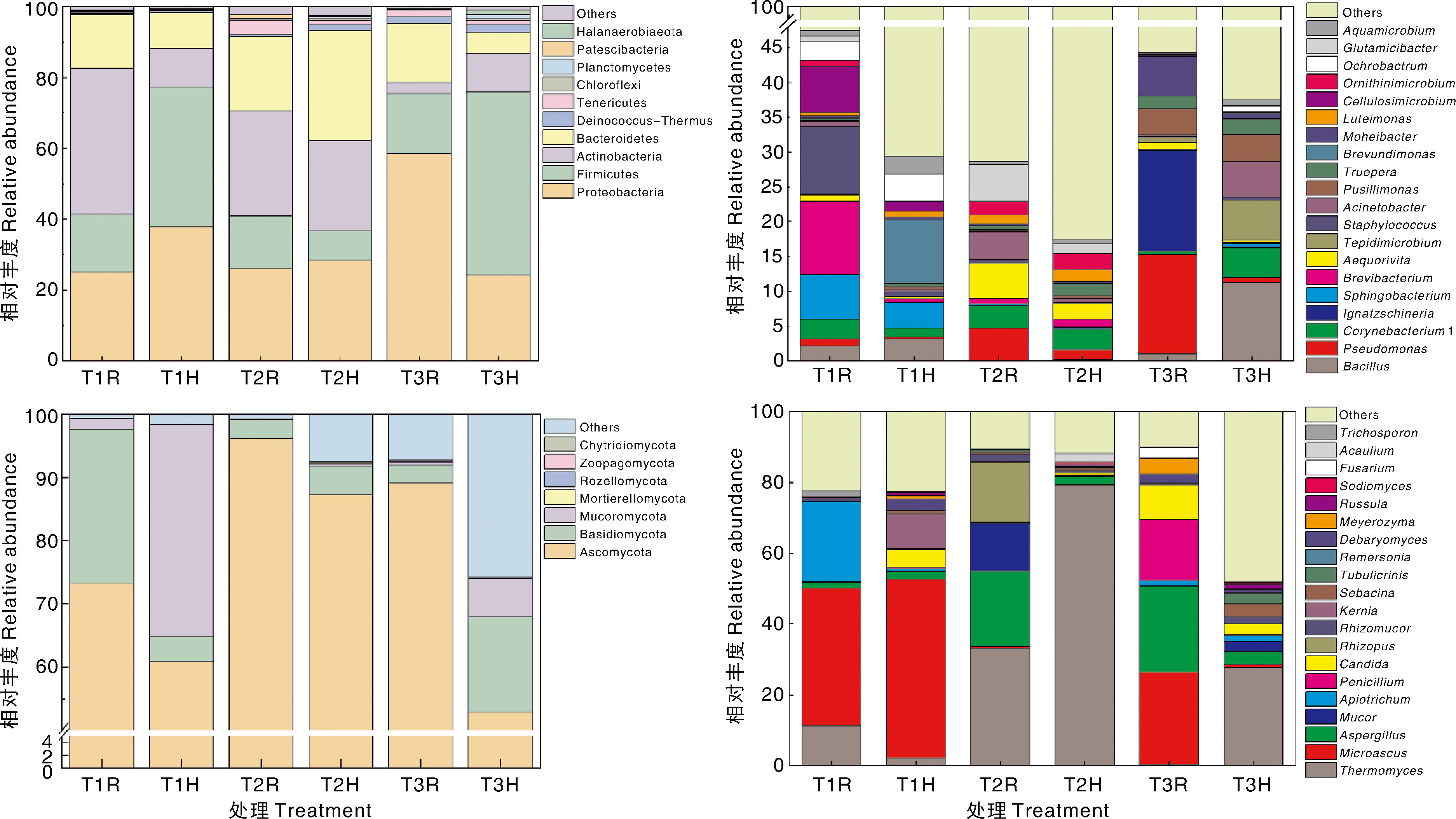
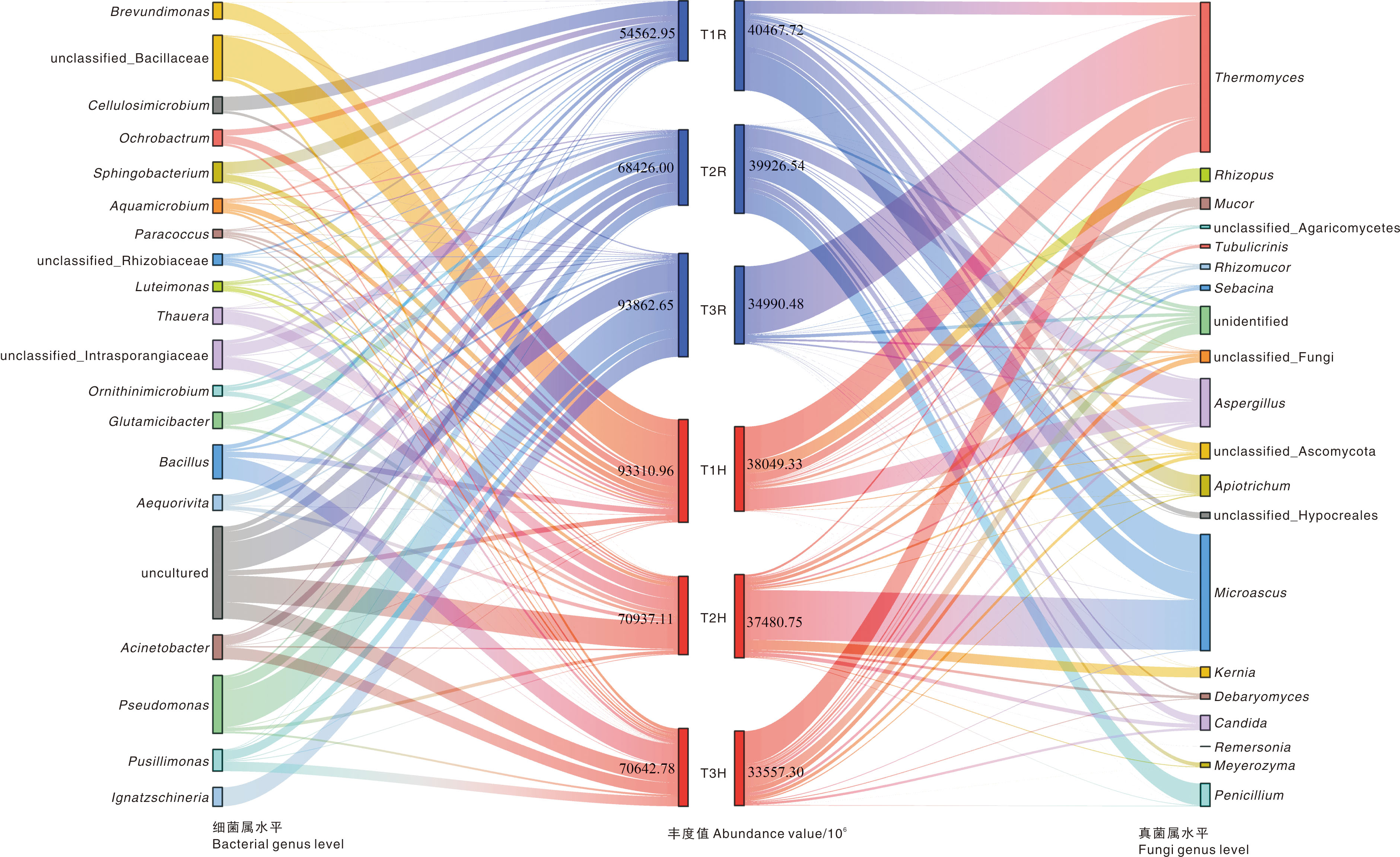
Fig.3 Changes of bacterial (up) and fungal (down) community at phylum (left) and genus (right) levels during composting T1R, T1 treatment, temperature-rising stage; T1H, T1 treatment,high temperature stage; T2R, T2 treatment, temperature-rising stage; T2H, T2 treatment, high temperature stage; T3R, T3 treatment, temperature-rising stage; T3H, T3 treatment, high temperature stage.The same as below.
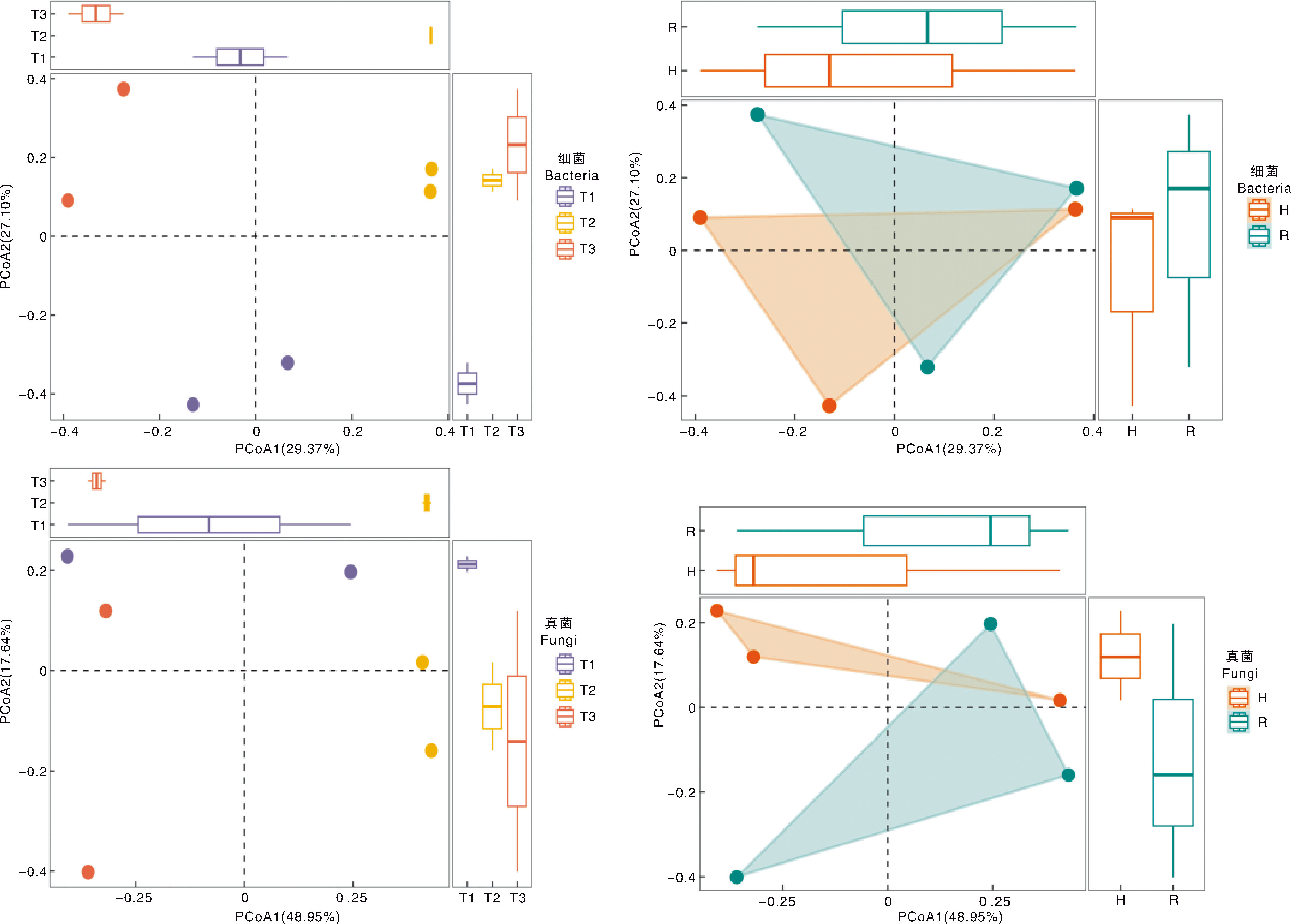
Fig.4 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of microorganisms ASV (amplicon sequence variant) at different composting stages under treatments PCoA1, Principle coordinate 1; PCoA2, Principle coordinate 2. R, Temperature-rising stage; H, High temperature stage. The blue circle represents the temperature-rising stage, and the red circle represents the high temperature stage.
| [1] | XU D H, ROS G H, ZHU Q C, et al. Major drivers of soil acidification over 30 years differ in paddy and upland soils in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 916: 170189. |
| [2] | RAMOS T B, GONÇALVES M C, VAN GENUCHTEN M T. Soil salinization in Portugal: an in-depth exploration of impact, advancements, and future considerations[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2024, 23(4): e20314. |
| [3] | KANG F, MENG Y S, GE Y N, et al. Calcium-based polymers for suppression of soil acidification by improving acid-buffering capacity and inhibiting nitrification[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2024, 139: 138-149. |
| [4] | 胡天睿, 蔡泽江, 王伯仁, 等. 有机肥替代化学氮肥提升红壤抗酸化能力[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(11): 2052-2059. |
| HU T R, CAI Z J, WANG B R, et al. Swine manure as part of the total N source improves red soil resistance to acidification[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(11): 2052-2059. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | WANG L Y, ZHANG L L. A review on the improvement of saline-alkali soil by organic fertilizer[J]. Academic Journal of Science and Technology, 2024, 10(3): 10-11. |
| [6] | 盘礼东, 李瑞. 有机覆盖措施对土壤肥力的影响研究现状及展望[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 39(6): 91-101. |
| PAN L D, LI R. Research status and prospect of effects of organic mulching on soil fertility[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 39(6): 91-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | KONG Y L, ZHANG J, ZHANG X S, et al. Applicability and limitation of compost maturity evaluation indicators: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 489: 151386. |
| [8] | LIU X Y, ZUBAIR M, KONG L Y, et al. Shifts in bacterial diversity characteristics during the primary and secondary fermentation stages of bio-compost inoculated with effective microorganisms agent[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 382: 129163. |
| [9] | HUANG L T, HOU J Y, LIU H T. Machine-learning intervention progress in the field of organic waste composting: simulation, prediction, optimization, and challenges[J]. Waste Management, 2024, 178: 155-167. |
| [10] | CHEN A Q, HAN Z Y, XIE X Y, et al. Co-composting sugar-containing waste with chicken manure: a new approach to carbon sequestration[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 356: 120609. |
| [11] | CHIA W Y, CHEW K W, LE C F, et al. Sustainable utilization of biowaste compost for renewable energy and soil amendments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 267: 115662. |
| [12] | 王友玲, 邱慧珍, 李孟婵, 等. 不同通风方式下牛粪堆肥过程中微生物群落演替及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(8): 189-201. |
| WANG Y L, QIU H Z, LI M C, et al. Microbial community succession and response to environmental factors during composting under different ventilation conditions[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2023, 43(8): 189-201. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 黄周轲, 王莉, 叶小梅. 黑水虻生物堆肥处理鸡粪养分转化及气体排放规律研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2024, 47(2): 292-297. |
| HUANG Z K, WANG L, YE X M. A study of nutrient transformation and gas emission during chicken manure biocomposting with black soldier fly[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2024, 47(2): 292-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 葛勉慎, 周海宾, 沈玉君, 等. 添加剂对牛粪堆肥不同阶段真菌群落演替的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(12): 5173-5181. |
| GE M S, ZHOU H B, SHEN Y J, et al. Effect of additives on the succession of fungal community in different phases of cattle manure composting[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(12): 5173-5181. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 王霞, 敖灵, 曾珊, 等. 白酒酒糟营养解析及其动物饲料化应用研究进展[J]. 中国饲料, 2023(22): 280-288. |
| WANG X, AO L, ZENG S, et al. Research progress on nutrition analysis and animal feed application of Baijiu distiller’s grains[J]. China Feed, 2023(22): 280-288. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 陈煜, 韦艳群, 李顺豪, 等. 不同比例花生秧、玉米粉对浓香型白酒糟厌氧发酵营养价值的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(4): 2690-2701. |
| CHEN Y, WEI Y Q, LI S H, et al. Effects of different proportions of peanut seedlings and corn flour on nutritional value in anaerobic fermentation of highly flavored type Baijiu distiller’s grains[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(4): 2690-2701. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | APRILLIZA M N, KRISHNA N H, MARIYONO, et al. Feed durability and feed quality of concentrate feed with addition of monosodium glutamate manufacturing by-products[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2023, 1177(1): 012053. |
| [18] | LIU L, KONG H M, LU B B, et al. The use of concentrated monosodium glutamate wastewater as a conditioning agent for adjusting acidity and minimizing ammonia volatilization in livestock manure composting[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 161: 131-136. |
| [19] | 刘英杰, 李琬婷, 王海候, 等. 锯末添加量对餐厨废弃物生物干化效率和细菌群落的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(15): 208-216. |
| LIU Y J, LI W T, WANG H H, et al. Effects of sawdust addition on bio-drying efficiency and bacterial community of food waste[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(15): 208-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | HAN L P, LI L, XU Y, et al. Short-term high-temperature pretreated compost increases its application value by altering key bacteria phenotypes[J]. Waste Management, 2024, 180: 135-148. |
| [21] | HU J L, CYLE K T, YUAN W Q, et al. Soil dependence of biochar composts in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions: an overlooked biophysical mechanism[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2024, 198: 105374. |
| [22] | XIONG S G, LIU Y D, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of chemical additives and mature compost on reducing nitrogen loss during food waste composting[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2023, 30(13): 39000-39011. |
| [23] | XIE T, ZHANG Z H, ZHANG D W, et al. Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment and compound microbial agents on compost maturity and gaseous emissions during aerobic composting of kitchen waste[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 854: 158712. |
| [24] | LU M L, HAO Y H, LIN B F, et al. The bioaugmentation effect of microbial inoculants on humic acid formation during co-composting of bagasse and cow manure[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 252(Pt 1): 118604. |
| [25] | WANG Z, XU Y L, YANG T, et al. Effects of biochar carried microbial agent on compost quality, greenhouse gas emission and bacterial community during sheep manure composting[J]. Biochar, 2023, 5(1): 3. |
| [26] | WEI Y H, LIANG Z W, ZHANG Y. Evolution of physicochemical properties and bacterial community in aerobic composting of swine manure based on a patent compost tray[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 343: 126136. |
| [27] | WANG Q Q, LI N, JIANG S N, et al. Composting of post-consumption food waste enhanced by bioaugmentation with microbial consortium[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 907: 168107. |
| [28] | LIU S, ZHANG X Y, QU C, et al. Ore improver additions alter livestock manure compost ecosystem C: N: P stoichiometry[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 244: 117904. |
| [29] | RAZA S, AHMAD J. Composting process: a review[J]. International Journal of Biological Research, 2016, 4(2): 102-104. |
| [30] | WANG R, ZHANG J Y, SUI Q W, et al. Effect of red mud addition on tetracycline and copper resistance genes and microbial community during the full scale swine manure composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 216: 1049-1057. |
| [31] | REN S T, LU A Q, GUO X Y, et al. Effects of co-composting of lincomycin mycelia dregs with furfural slag on lincomycin degradation, degradation products, antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 272: 83-91. |
| [32] | 姜新有, 王晓东, 周江明, 等. 初始pH值对畜禽粪便和菌渣混合高温堆肥的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(9): 1595-1602. |
| JIANG X Y, WANG X D, ZHOU J M, et al. Effects of initial pH values on maturity and nitrogen loss during co-composting of pig manure and edible fungus residue[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(9): 1595-1602. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 陈霞, 罗友进, 程玥晴, 等. 不同微生物菌剂对中药渣堆肥过程及理化性质的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(12): 2756-2763. |
| CHEN X, LUO Y J, CHENG Y Q, et al. Effect of different microbial agents on Chinese herbal residue composting process and its physical-chemical properties[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(12): 2756-2763. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | SUN Z Y, ZHANG J, ZHONG X Z, et al. Production of nitrate-rich compost from the solid fraction of dairy manure by a lab-scale composting system[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 51: 55-64. |
| [35] | 路一鸣, 李军, 代雨, 等. 翻堆对好氧堆肥腐殖质电子转移能力的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(12): 5748-5757. |
| LU Y M, LI J, DAI Y, et al. Effects of turning on the electron transfer capacity of humic substances in aerobic composting[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(12): 5748-5757. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 常远, 李若琪, 李珺, 等. 好氧堆肥腐殖酸形成机制及促腐调控技术概述[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(10): 5291-5302. |
| CHANG Y, LI R Q, LI J, et al. Mechanism and regulation method of humic acid formation in composting: a review[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(10): 5291-5302. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 蔡涵冰, 冯雯雯, 董永华, 等. 畜禽粪便和桃树枝工业化堆肥过程中微生物群演替及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(2): 997-1004. |
| CAI H B, FENG W W, DONG Y H, et al. Microbial community succession in industrial composting with livestock manure and peach branches and relations with environmental factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(2): 997-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 邹嘉成, 杜闫彬, 苏凯文, 等. 粉煤灰添加对城市多源有机废弃物联合堆肥效能及堆体细菌群落的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(6): 3638-3648. |
| ZOU J C, DU Y B, SU K W, et al. Effects of fly ash on the efficiency and bacterial community structure of urban multi-source organic solid waste[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45(6): 3638-3648. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | LIU X, RONG X M, JIANG P, et al. Biodiversity and core microbiota of key-stone ecological clusters regulate compost maturity during cow-dung-driven composting[J]. Environmental Research, 2024, 245: 118034. |
| [40] | 蒲俊华, 卢建, 赵华轩, 等. 发酵饲料对蛋鸡粪便堆肥氨气排放与微生物群落的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(8): 1876-1887. |
| PU J H, LU J, ZHAO H X, et al. Effects of fermented feed on the ammonia emission and microbial community of layer manure compost[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(8): 1876-1887. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 周亚文, 张宇航, 沈玉君, 等. 初始含水率对人粪污好氧堆肥腐熟及微生物群落结构变化的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(12): 4108-4120. |
| ZHOU Y W, ZHANG Y H, SHEN Y J, et al. Effect of the initial moisture content on the maturity extent and the microbial community structure of the aerobic compost with human excrement[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2022, 16(12): 4108-4120. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 王萌萌, 范博文, 赵立琴, 等. 牛粪对双孢菇菌渣堆肥过程中碳氮转化及真菌群落的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(1): 162-173. |
| WANG M M, FAN B W, ZHAO L Q, et al. Effects of cattle manure on carbon and nitrogen transformation and fungal communities during composting of Agaricus bisporus fungus residues[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(1): 162-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 曹丽娜, 王岩, 王跃, 等. 添加麦秸对鸡粪堆肥过程中氮素减排及细菌群落的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42(11): 2560-2569. |
| CAO L N, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Effects of wheat straw addition on nitrogen emission reduction and bacterial community during chicken manure composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2023, 42(11): 2560-2569. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | HERNÁNDEZ-LARA A, ROS M, CUARTERO J, et al. Bacterial and fungal community dynamics during different stages of agro-industrial waste composting and its relationship with compost suppressiveness[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 805: 150330. |
| [45] | 刘尚斌, 郑祥洲, 王煌平, 等. 蝇蛆预处理及辅料添加对鸡粪堆肥氨挥发和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(5): 1151-1162. |
| LIU S B, ZHENG X Z, WANG H P, et al. Effects of excipient incorporation and fly maggot pretreatment on ammonia emissions and green-house gases emissions during chicken manure composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(5): 1151-1162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 杨森, 佟敏, 崔亚茹, 等. 牛粪与玉米秸秆沼渣混合堆肥及其对环境影响研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2023, 44(12): 168-173. |
| YANG S, TONG M, CUI Y R, et al. Study on mixed compost of cow dung and corn stalk biogas residue and its impact on environment[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2023, 44(12): 168-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [47] | 王兴明, 章珍, 储昭霞, 等. 秸秆炭协助蚯蚓堆肥条件下污泥中重金属时间性变化特征[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2024, 14(2): 528-537. |
| WANG X M, ZHANG Z, CHU Z X, et al. Temporal changes of heavy metals in sludge under the condition of straw charcoal assisted earthworm composting[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2024, 14(2): 528-537. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | WANG G Y, YANG Y, KONG Y L, et al. Key factors affecting seed germination in phytotoxicity tests during sheep manure composting with carbon additives[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 421: 126809. |
| [49] | WANG J, GU J, WANG X J, et al. Enhanced removal of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during swine manure composting inoculated with mature compost[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 411: 125135. |
| [50] | 赵芹, 程东会, 王燕, 等. 不同物料堆肥过程中溶解性有机质和腐殖酸的物质结构演化时序差异分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2023, 13(4): 1514-1524. |
| ZHAO Q, CHENG D H, WANG Y, et al. Analysis of the time series difference of the material structure evolution of DOM and humic acid during composting of different materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2023, 13(4): 1514-1524. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [51] | MILI C, TAYUNG K. Application of compatible lignocellulolytic fungal consortia for quality composting of leaf litter and assessment of the end products[J]. Bioresource Technology Reports, 2024, 25: 101800. |
| [52] | LI M H, LI S Y, MENG Q Y, et al. Feedstock optimization with rice husk chicken manure and mature compost during chicken manure composting: quality and gaseous emissions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 387: 129694. |
| [53] | HUANG B, JIA H J, HAN X B, et al. Effects of biocontrol Bacillus and fermentation bacteria additions on the microbial community, functions and antibiotic resistance genes of prickly ash seed oil meal-biochar compost[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 340: 125668. |
| [54] | CHUNG W J, CHANG S W, CHAUDHARY D K, et al. Effect of biochar amendment on compost quality, gaseous emissions and pathogen reduction during in-vessel composting of chicken manure[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 283: 131129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||