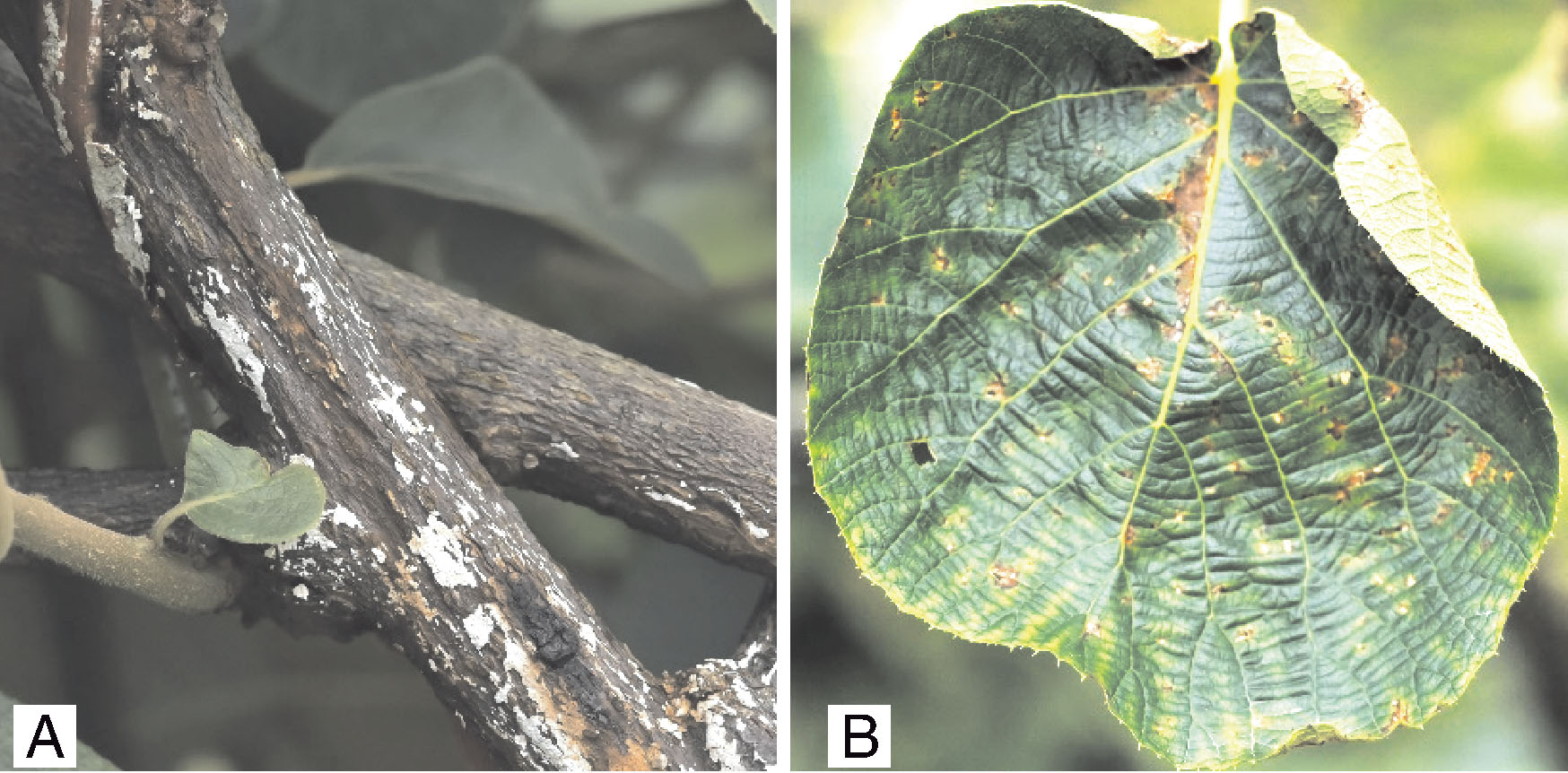
Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2116-2128.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240651
• Plant Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification of pathogenic bacteria of kiwifruit canker in mountainous area and screening of different types of efficient control fungicides
LI Qiang1( ), LIU Sitong1, HUANG Xianbin1,2, JIANG Junlong1, DENG Jianyu1, WANG Jiaoyu2, LI Ling1,*
), LIU Sitong1, HUANG Xianbin1,2, JIANG Junlong1, DENG Jianyu1, WANG Jiaoyu2, LI Ling1,*
- 1. College of Advanced Agricultural Sciences, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Institute of Plant Protection and Microbiology, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
-
Received:2024-07-18Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Qiang, LIU Sitong, HUANG Xianbin, JIANG Junlong, DENG Jianyu, WANG Jiaoyu, LI Ling. Identification of pathogenic bacteria of kiwifruit canker in mountainous area and screening of different types of efficient control fungicides[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2116-2128.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240651
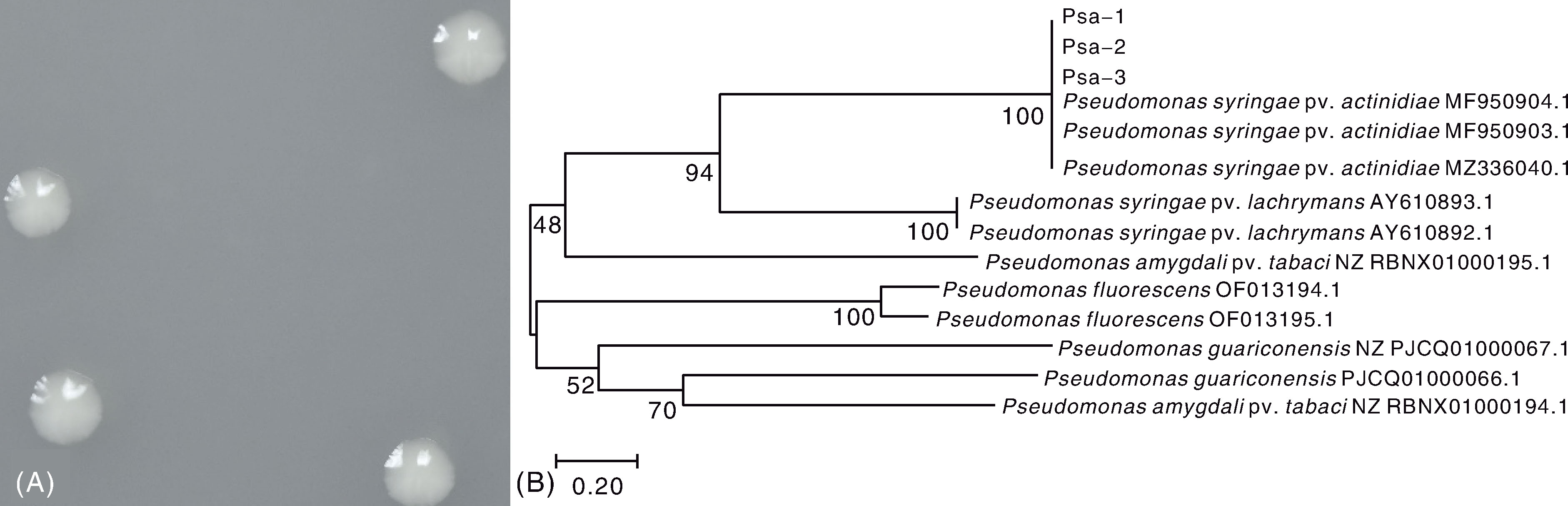
Fig.2 Identification of pathogen of kiwifruit canker disease A, Colony characteristics of the pathogen(28 ℃,4 d); B, Phylogenetic tree of Psa-1-Psa-3 strains constructed based on 16S rDNA sequence.
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 类型 Type | Psa-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抑菌圈直径 Diameter of inhibition zone/mm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | ||
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 16.03±2.18 | 72.76 |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 6.11±0.75 | 50.46 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 7.42±1.25 | 55.28 |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌SC Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% copper hydroxide WG | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 6.56±0.44 | 52.21 |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 14.67±2.00 | 70.97 |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 生物化学杀菌剂 Biochemical fungicide | 8.50±1.47 | 58.62 |
| 30%噻唑锌SC 30% zinc thiazole SC | 无机杀菌剂 Inorganic fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 20%乙酸铜WG 20% acetic acid WG | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP +20% kasugamycin WG | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicide | 33.22±0.80 | 84.70 |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicides | 13.50±0.25 | 69.23 |
| 27%春雷霉素·溴菌腈WP 27% kasugamycin·bromothalonil WP | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicides | 12.58±0.95 | 67.71 |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 生物体+有机合成+生物化学杀菌剂 Biological+organic synthesis+ biochemical fungicides | 6.31±0.42 | 51.24 |
| 40%春雷霉素·噻唑锌SC 40% kasugamycin·zinc thiazole SC | 生物化学+生物体杀菌剂 Biochemical+biological fungicides | 2.58±0.45 | 30.10 |
| 45%春雷霉素·喹啉铜SC 45% kasugamycin·oxine-copper SC | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 3.06±0.98 | 33.74 |
| 33%春雷霉素·喹啉铜SC 33% kasugamycin·oxine-copper SC | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 1.22±1.61 | 16.92 |
| 25%氨基寡糖素·乙蒜素ME 25% oligosaccharins·ethylicin ME | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 1.03±0.08 | 14.62 |
| 6%氨基寡糖素·极细链格孢激活蛋白WP 6% oligosaccharins·activator protein WP | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 0±0 | 0 |
| CK | 0±0 | 0 | |
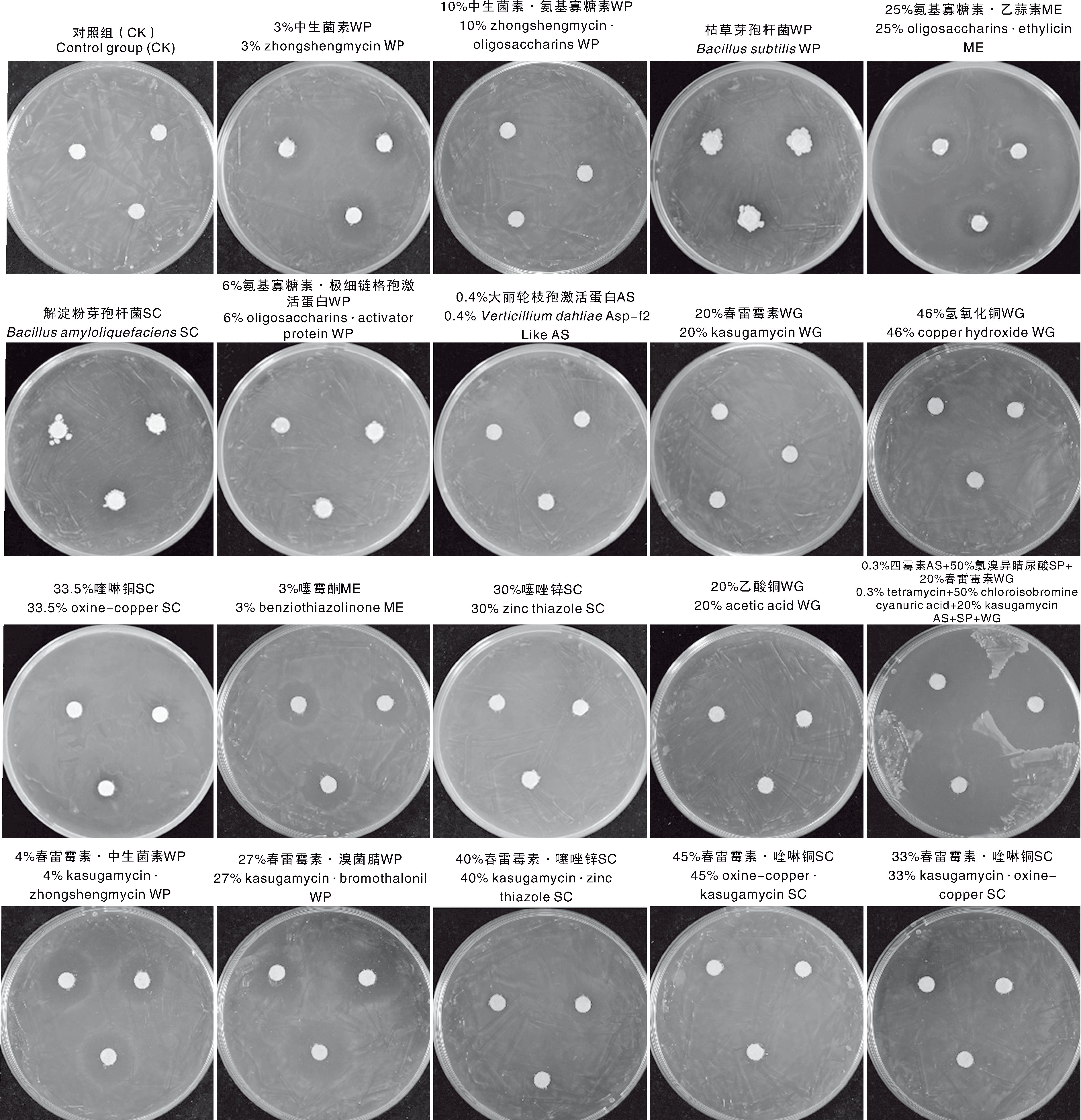
Table 1 Preliminary results of indoor toxicity screening of 19 fungicides
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 类型 Type | Psa-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抑菌圈直径 Diameter of inhibition zone/mm | 抑菌率 Inhibition rate/% | ||
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 16.03±2.18 | 72.76 |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 6.11±0.75 | 50.46 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 7.42±1.25 | 55.28 |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌SC Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% copper hydroxide WG | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 6.56±0.44 | 52.21 |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | 生物体杀菌剂 Biological fungicide | 14.67±2.00 | 70.97 |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 生物化学杀菌剂 Biochemical fungicide | 8.50±1.47 | 58.62 |
| 30%噻唑锌SC 30% zinc thiazole SC | 无机杀菌剂 Inorganic fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 20%乙酸铜WG 20% acetic acid WG | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicide | 0±0 | 0 |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP +20% kasugamycin WG | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicide | 33.22±0.80 | 84.70 |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicides | 13.50±0.25 | 69.23 |
| 27%春雷霉素·溴菌腈WP 27% kasugamycin·bromothalonil WP | 有机合成杀菌剂 Organic synthetic fungicides | 12.58±0.95 | 67.71 |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 生物体+有机合成+生物化学杀菌剂 Biological+organic synthesis+ biochemical fungicides | 6.31±0.42 | 51.24 |
| 40%春雷霉素·噻唑锌SC 40% kasugamycin·zinc thiazole SC | 生物化学+生物体杀菌剂 Biochemical+biological fungicides | 2.58±0.45 | 30.10 |
| 45%春雷霉素·喹啉铜SC 45% kasugamycin·oxine-copper SC | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 3.06±0.98 | 33.74 |
| 33%春雷霉素·喹啉铜SC 33% kasugamycin·oxine-copper SC | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 1.22±1.61 | 16.92 |
| 25%氨基寡糖素·乙蒜素ME 25% oligosaccharins·ethylicin ME | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 1.03±0.08 | 14.62 |
| 6%氨基寡糖素·极细链格孢激活蛋白WP 6% oligosaccharins·activator protein WP | 生物化学+有机合成杀菌剂 Biochemical+organic synthetic fungicides | 0±0 | 0 |
| CK | 0±0 | 0 | |
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 线性方程 Linear equation | 有效中浓度 Median effective concentration (EC50)/(mg· L-1) | 决定系数 Coefficient of determination (R2) | 95%置信限 95% confidence limit/(mg· L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | y=0.107 4x+0.481 | 1.502 8 | 0.966 3 | 0~18.43 |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | y=0.139 6x+0.247 5 | 64.378 3 | 0.934 6 | 7.44~148.83 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | y=0.437 3x-0.782 3 | 855.681 0 | 0.977 0 | 631.57~1 304.87 |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | y=0.303 7x-0.354 8 | 652.558 9 | 0.986 0 | 416.86~972.95 |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% Copper hydroxide WG | y=0.552 3x-1.172 5 | 1 067.199 0 | 0.957 0 | 785.58~1 511.34 |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | y=0.578 1x-0.640 8 | 94.050 5 | 0.977 4 | 60.95~138.73 |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | y=0.477 6x-0.675 5 | 289.244 2 | 0.977 2 | 250.64~453.42 |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP +20% kasugamycin WG | y=0.109 8x+0.536 9 | 0.435 9 | 0.944 6 | 0.00~6.27 |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | y=0.210 6x+0.143 7 | 49.185 0 | 0.924 0 | 17.23~81.85 |
| 27%春雷霉素·溴菌腈WP 27% kasugamycin·bromothalonil WP | y=0.506 4x-0.871 9 | 511.827 0 | 0.973 2 | 403.84~720.95 |
Table 2 Toxicity measurement results of 10 fungicides against kiwifruit canker pathogens
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 线性方程 Linear equation | 有效中浓度 Median effective concentration (EC50)/(mg· L-1) | 决定系数 Coefficient of determination (R2) | 95%置信限 95% confidence limit/(mg· L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | y=0.107 4x+0.481 | 1.502 8 | 0.966 3 | 0~18.43 |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | y=0.139 6x+0.247 5 | 64.378 3 | 0.934 6 | 7.44~148.83 |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | y=0.437 3x-0.782 3 | 855.681 0 | 0.977 0 | 631.57~1 304.87 |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | y=0.303 7x-0.354 8 | 652.558 9 | 0.986 0 | 416.86~972.95 |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% Copper hydroxide WG | y=0.552 3x-1.172 5 | 1 067.199 0 | 0.957 0 | 785.58~1 511.34 |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | y=0.578 1x-0.640 8 | 94.050 5 | 0.977 4 | 60.95~138.73 |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | y=0.477 6x-0.675 5 | 289.244 2 | 0.977 2 | 250.64~453.42 |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP +20% kasugamycin WG | y=0.109 8x+0.536 9 | 0.435 9 | 0.944 6 | 0.00~6.27 |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | y=0.210 6x+0.143 7 | 49.185 0 | 0.924 0 | 17.23~81.85 |
| 27%春雷霉素·溴菌腈WP 27% kasugamycin·bromothalonil WP | y=0.506 4x-0.871 9 | 511.827 0 | 0.973 2 | 403.84~720.95 |
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 叶片发病率 Leaf incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 4.67±2.18 eE | 0.69±0.38 fF | 93.14±3.72 aA |
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | 6.81±0.23 deDE | 0.83±0.10 efEF | 91.72±1.03 abAB |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 10.60±1.29 deDE | 2.02±0.87 efEF | 79.92±8.59 abAB |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 11.27±5.39 deDE | 2.21±0.57 efEF | 78.12±5.67 abAB |
| 6%氨基寡糖素·极细链格孢激活蛋白WP 6% oligosaccharins·activator protein WP | 15.84±0.63 cdCD | 4.20±0.18 cdCD | 58.32±1.75 cdCD |
| 25%氨基寡糖素·乙蒜素ME 25% oligosaccharins·ethylicin ME | 28.80±6.72 abAB | 8.06±0.75 bB | 20.10±7.40 eE |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | 22.81±8.10 bcBC | 5.52±0.94 cC | 45.25±9.37 dD |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% copper hydroxide WG | 16.87±1.24 cdCD | 1.97±0.12 efEF | 80.44±1.20 abAB |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 9.82±1.76 deDE | 1.36±0.28 efEF | 86.55±2.79 abAB |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | 16.75±1.20 cdCD | 2.00±0.28 efEF | 80.13±2.73 abAB |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | 16.40±2.12 cdCD | 2.66±0.19 deDE | 73.59±1.92 bcBC |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP+ 20% kasugamycin WG | 12.90±3.17 cdeCDE | 4.48±1.08 cdCD | 55.61±10.71 cdCD |
| CK | 36.96±1.29 aA | 10.08±0.76 aA |
Table 3 Results of field control effect of 12 different fungicides on kiwifruit canker
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 叶片发病率 Leaf incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 4.67±2.18 eE | 0.69±0.38 fF | 93.14±3.72 aA |
| 3%中生菌素WP 3% zhongshengmycin WP | 6.81±0.23 deDE | 0.83±0.10 efEF | 91.72±1.03 abAB |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 10.60±1.29 deDE | 2.02±0.87 efEF | 79.92±8.59 abAB |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 11.27±5.39 deDE | 2.21±0.57 efEF | 78.12±5.67 abAB |
| 6%氨基寡糖素·极细链格孢激活蛋白WP 6% oligosaccharins·activator protein WP | 15.84±0.63 cdCD | 4.20±0.18 cdCD | 58.32±1.75 cdCD |
| 25%氨基寡糖素·乙蒜素ME 25% oligosaccharins·ethylicin ME | 28.80±6.72 abAB | 8.06±0.75 bB | 20.10±7.40 eE |
| 20%春雷霉素WG 20% kasugamycin WG | 22.81±8.10 bcBC | 5.52±0.94 cC | 45.25±9.37 dD |
| 46%氢氧化铜WG 46% copper hydroxide WG | 16.87±1.24 cdCD | 1.97±0.12 efEF | 80.44±1.20 abAB |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 9.82±1.76 deDE | 1.36±0.28 efEF | 86.55±2.79 abAB |
| 3%噻霉酮ME 3% benziothiazolinone ME | 16.75±1.20 cdCD | 2.00±0.28 efEF | 80.13±2.73 abAB |
| 4%春雷霉素·中生菌素WP 4% kasugamycin·zhongshengmycin WP | 16.40±2.12 cdCD | 2.66±0.19 deDE | 73.59±1.92 bcBC |
| 0.3%四霉素AS+50%氯溴异睛尿酸SP+20%春雷霉素WG 0.3% tetramycin AS+50% chloroisobromine cyanuric acid SP+ 20% kasugamycin WG | 12.90±3.17 cdeCDE | 4.48±1.08 cdCD | 55.61±10.71 cdCD |
| CK | 36.96±1.29 aA | 10.08±0.76 aA |
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 稀释倍数 Dilution | 叶片发病率 Leaf incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 800 | 8.27±3.27 ef | 0.92±0.36 d | 90.22±3.87 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 500 | 4.29±3.36 f | 0.93±0.75 d | 90.10±7.94 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 1 000 | 10.54±1.77 cdef | 1.17±0.20 d | 87.53±2.10 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 1 600 | 10.67±1.66 cdef | 2.27±0.39 cd | 75.86±4.21 ab |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 3 000 | 3.53±1.23 f | 0.78±0.27 d | 91.65±2.91 a |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 1 500 | 9.22±4.34 def | 1.35±0.54 d | 85.64±5.70 a |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 800 | 9.56±0.26 def | 2.73±0.25 cd | 70.97±2.62 ab |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 5 000 | 19.70±0.11 bc | 4.32±1.07 bc | 54.03±11.36 bc |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 800 | 8.39±0.73 ef | 1.40±0.29 d | 85.12±3.05 a |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 1 000 | 11.49±3.43 cdef | 1.62±0.54 d | 82.79±5.75 a |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 500 | 11.39±1.14 cdef | 3.06±1.35 cd | 67.39±14.41 ab |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 300 | 28.09±7.83 ab | 5.73±1.90 b | 38.94±20.27 c |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 200 | 11.37±0.26 cdef | 1.39±0.09 d | 85.23±1.01 a |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 300 | 15.39±0.19 cde | 1.71±0.02 d | 81.79±0.23 a |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 500 | 18.59±1.92 cd | 2.53±0.25 cd | 73.07±2.65 ab |
| CK | 32.54±4.17 a | 9.39±0.67 a |
Table 4 Results of field test of 4 different concentrations of fungicides against kiwifruit canker disease
| 杀菌剂名称和剂型 Name and formulation of fungicide | 稀释倍数 Dilution | 叶片发病率 Leaf incidence/% | 病情指数 Disease index | 防治效果 Control effect/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 800 | 8.27±3.27 ef | 0.92±0.36 d | 90.22±3.87 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 500 | 4.29±3.36 f | 0.93±0.75 d | 90.10±7.94 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 1 000 | 10.54±1.77 cdef | 1.17±0.20 d | 87.53±2.10 a |
| 10%中生菌素·氨基寡糖素WP 10% zhongshengmycin·oligosaccharins WP | 1 600 | 10.67±1.66 cdef | 2.27±0.39 cd | 75.86±4.21 ab |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 3 000 | 3.53±1.23 f | 0.78±0.27 d | 91.65±2.91 a |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 1 500 | 9.22±4.34 def | 1.35±0.54 d | 85.64±5.70 a |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 800 | 9.56±0.26 def | 2.73±0.25 cd | 70.97±2.62 ab |
| 枯草芽孢杆菌WP Bacillus subtilis WP | 5 000 | 19.70±0.11 bc | 4.32±1.07 bc | 54.03±11.36 bc |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 800 | 8.39±0.73 ef | 1.40±0.29 d | 85.12±3.05 a |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 1 000 | 11.49±3.43 cdef | 1.62±0.54 d | 82.79±5.75 a |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 500 | 11.39±1.14 cdef | 3.06±1.35 cd | 67.39±14.41 ab |
| 33.5%喹啉铜SC 33.5% oxine-copper SC | 300 | 28.09±7.83 ab | 5.73±1.90 b | 38.94±20.27 c |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 200 | 11.37±0.26 cdef | 1.39±0.09 d | 85.23±1.01 a |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 300 | 15.39±0.19 cde | 1.71±0.02 d | 81.79±0.23 a |
| 0.4%大丽轮枝孢激活蛋白AS 0.4% Verticillium dahliae Asp-f2 Like AS | 500 | 18.59±1.92 cd | 2.53±0.25 cd | 73.07±2.65 ab |
| CK | 32.54±4.17 a | 9.39±0.67 a |
| [1] | PEREIRA C, COSTA P, PINHEIRO L, et al. Kiwifruit bacterial canker: an integrative view focused on biocontrol strategies[J]. Planta, 2021, 253(2): 49. |
| [2] | BAI J, LIU Y X, LIU M J, et al. Application of phage therapy against red-fleshed kiwifruit canker[J]. Biological Control, 2022, 169: 104893. |
| [3] | KOH Y J, JUNG J S, HUR J S. Current status of occurrence of major diseases on kiwifruits and their control in Korea[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 2003(610): 437-443 |
| [4] | EVERETT K R, HENSHALL W R. Epidemiology and population ecology of kiwifruit blossom blight[J]. Plant Pathology, 1994, 43(5): 824-830. |
| [5] | MICHAILIDES T J, ELMER P A G. Botrytis gray mold of kiwifruit caused by Botrytis cinerea in the United States and New Zealand[J]. Plant Disease, 2000, 84(3): 208-223. |
| [6] | LI L, PAN H, DENG L, et al. First report of Alternaria tenuissima causing brown spot disease of kiwifruit foliage in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2019, 103(3): 582. |
| [7] | BASHIRI S, JAMALI S, GOLMOHAMMADI M. Antagonistic activities of Streptomyces against root knot nematode of kiwifruit[J]. Journal of Iranian Plant Protection Research, 2015, 29(3): 310-317. |
| [8] | 杨清平, 王立华, 谢志斌, 等. 湖北猕猴桃主要病害及其有机病害治理技术[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(10): 2307-2311. |
| YANG Q P, WANG L H, XIE Z B, et al. The occurring regularity and ODM technology of organic kiwifruit diseases in Hubei Province[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(10): 2307-2311. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | DONATI I, BURIANI G, CELLINI A, et al. New insights on the bacterial canker of kiwifruit (Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae)[J]. Journal of Berry Research, 2020, 4(2): 53-67. |
| [10] | DONATI I, CELLINI A, SANGIORGIO D, et al. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae: ecology, infection dynamics and disease epidemiology[J]. Microbial Ecology, 2020, 80(1): 81-102. |
| [11] | 石志军, 张慧琴, 肖金平, 等. 不同猕猴桃品种对溃疡病抗性的评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2014, 26(3): 752-759. |
| SHI Z J, ZHANG H Q, XIAO J P, et al. The resistance evaluation of different kiwifruit varieties to canker[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2014, 26(3): 752-759. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 钟彩虹, 李黎, 潘慧, 等. 猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病的发生规律及综合防治技术[J]. 中国果树, 2020(1): 9-13. |
| ZHONG C H, LI L, PAN H, et al. Occurrence rule and comprehensive control of kiwifruit bacterial canker disease[J]. China Fruits, 2020(1): 9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 游雨欣, 戴德江, 罗金燕, 等. 猕猴桃溃疡病防治策略的研究现状与展望[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(6): 1322-1328. |
| YOU Y X, DAI D J, LUO J Y, et al. Research status and prospect of control strategies for kiwifruit canker[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(6): 1322-1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | ZHANG M Y, WANG L F, TANG W, et al. Antibacterial mechanism of the novel antimicrobial peptide Jelleine-Ic and its efficacy in controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae in kiwifruit[J]. Pest Management Science, 2023, 79(10): 3681-3692. |
| [15] | BUTLER M I, STOCKWELL P A, BLACK M A, et al. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae from recent outbreaks of kiwifruit bacterial canker belong to different clones that originated in China[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57464. |
| [16] | 胡和香. 猕猴桃溃疡病的发生及防治[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2021(8): 183-184. |
| HU H X. Occurrence and control of kiwifruit canker[J]. Agricultural Development & Equipments, 2021(8): 183-184. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | SERIZAWA S, ICHIKAWA T, TAKIKAWA Y, et al. Occurrence of bacterial canker of kiwifruit in Japan: description of symptoms, isolation of the pathogen and screening of bactericides[J]. Japanese Journal of Phytopathology, 1989, 55(4): 427-436. |
| [18] | 余京华, 朱德平, 邓红军, 等. 猕猴桃溃疡病高效综合防控策略与方法[J]. 中国农技推广, 2020, 36(12): 76-77. |
| YU J H, ZHU D P, DENG H J, et al. Strategies and methods for efficient and comprehensive prevention and control of kiwifruit canker[J]. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 2020, 36(12): 76-77. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 黄露, 何芬, 秦智慧, 等. 杀菌剂对猕猴桃溃疡病菌的室内毒力测定及田间防效[J]. 中国南方果树, 2017, 46(2): 137-140. |
| HUANG L, HE F, QIN Z H, et al. Laboratory toxicity test and field control effect of fungicides against Actinidia ulcer[J]. South China Fruits, 2017, 46(2): 137-140. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 李泉厂, 陈金焕, 王西红. 不同药剂防治猕猴桃溃疡病效果研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2013(11): 130-131. |
| LI Q C, CHEN J H, WANG X H. Study on the control effect of different chemicals on kiwifruit canker[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(11): 130-131. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | MONCHIERO M, GULLINO M L, PUGLIESE M, et al. Efficacy of different chemical and biological products in the control of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae on kiwifruit[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2015, 44(1): 13-23. |
| [22] | 秦虎强, 赵志博, 高小宁, 等. 猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病菌对17种杀菌剂的敏感性及不同药剂田间防效[J]. 西北农业学报, 2015, 24(9): 145-151. |
| QIN H Q, ZHAO Z B, GAO X N, et al. Bactericidal activities of seventeen bactericides and their field applications against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2015, 24(9): 145-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 杜贞娜, 晏子英, 候忠余, 等. 猕猴桃溃疡病病原菌的鉴定及生防菌的筛选[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(4): 755-761. |
| DU Z N, YAN Z Y, HOU Z Y, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogen causing canker and screening of biocontrol bacteria in kiwifruit[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(4): 755-761. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | PRIMO E D, SANTORO M V, GIORDANO W F, et al. Identification and genetic diversity analysis of strain Pseudomonas syringae S5: a pathogen responsible for bacteriosis in Avena sativa plants[J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 2019, 167(3): 146-155. |
| [25] | REES-GEORGE J, VANNESTE J L, CORNISH D A, et al. Detection of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers based on the 16S-23S rDNA intertranscribed spacer region and comparison with PCR primers based on other gene regions[J]. Plant Pathology, 2010, 59(3): 453-464. |
| [26] | 龙安琪, 朱泽, 李强, 等. 浙贝母芽枝霉斑病病原菌鉴定、生物学特性及生物药剂防治效果研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 2023, 53(6): 1047-1055. |
| LONG A Q, ZHU Z, LI Q, et al. Identification biological characteristics, and inhibition efficacy of plant-derived antifungal agents of pathogen Cladosporium spp. causing mildew spot of Fritillaria thunbergii[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2023, 53(6): 1047-1055. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 高蓬明, 王瑞, 马立志. 猕猴桃溃疡病防治药剂的室内毒力及田间防治效果[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2013, 41(4): 85-88. |
| GAO P M, WANG R, MA L Z. Indoor toxicity and field efficacy of fungicides on bacterial canker for kiwifruit[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(4): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 江景勇, 潘仙鹏, 刘守平, 等. 台州猕猴桃溃疡病防治药剂筛选及应用[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2022(12): 59-62. |
| JIANG J Y, PAN X P, LIU S P, et al. Screening and field application of bactericides for controlling kiwifruit bacterial canker in Taizhou[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2022(12): 59-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 陈佳, 王垚, 陈学堂, 等. 防治猕猴桃溃疡病涂抹剂的研制及其应用[J]. 农药学学报, 2023, 25(3): 678-688. |
| CHEN J, WANG Y, CHEN X T, et al. Development and application of paints for controlling kiwifruit canker[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2023, 25(3): 678-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 秦虎强, 刘巍, 刘宁娟, 等. 陕西猕猴桃溃疡病绿色综合防控技术[J]. 陕西林业科技, 2021, 49(2): 72-75. |
| QIN H Q, LIU W, LIU N J, et al. Integrated control of kiwi psa by environment-friendly methods in Shaanxi[J]. Shaanxi Forest Science and Technology, 2021, 49(2): 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 王明召, 阳廷密, 唐明丽, 等. 猕猴桃溃疡病田间发生情况调查[J]. 南方园艺, 2020, 31(6): 46-49. |
| WANG M Z, YANG T M, TANG M L, et al. Investigation of the occurrence of kiwifruit canker in kiwifruit orchards[J]. Southern Horticulture, 2020, 31(6): 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | OPGENORTH D C. Pseudomonas canker of kiwifruit[J]. Plant Disease, 1983, 67(11): 1283. |
| [33] | TAKIKAWA Y, SERIZAWA S, ICHIKAWA T, et al. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae pv. nov.: the causal bacterium of canker of kiwifruit in Japan[J]. Japanese Journal of Phytopathology, 1989, 55(4): 437-444. |
| [34] | EVERETT K R, TAYLOR R K, ROMBERG M K, et al. First report of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae causing kiwifruit bacterial canker in New Zealand[J]. Australasian Plant Disease Notes, 2011, 6(1): 67-71. |
| [35] | HAN H S, KOH Y J, HUR J S, et al. Identification and characterization of coronatine-producing Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2003, 13(1): 110-118. |
| [36] | 王瑞, 雷霁卿, 查仕连, 等. 二十种生物源杀菌剂对三株猕猴桃溃疡病病原菌的毒力测定[J]. 北方园艺, 2018(21): 54-59. |
| WANG R, LEI J Q, ZHA S L, et al. Toxicity test of twenty kinds of bio-fungicides to three kiwifruit canker pathogens[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2018(21): 54-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 龙友华, 夏锦书. 猕猴桃溃疡病防治药剂室内筛选及田间药效试验[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2010 (10): 84-86. |
| LONG Y H, XIA J S. Indoor screening and field trial of bactericides against kiwifruit canker[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2010 (10): 84-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 阳廷密, 王明召, 张素英, 等. 猕猴桃溃疡病防治药剂药效评价[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(7): 1231-1236. |
| YANG T M, WANG M Z, ZHANG S Y, et al. Efficacy evaluation of bactericides for kiwifruit canker[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2017, 48(7): 1231-1236. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | QIN H Q, ZHAO Z B, GAO X N, et al. Bactericidal activities of four bactericides and their field application against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae[J]. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2016, 43(2): 321-328. |
| [40] | 杨贵琴, 莫飞旭, 陈听听, 等. 防治猕猴桃溃疡病药剂组合的筛选与应用[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2020, 40(11): 73-76. |
| YANG G Q, MO F X, CHEN T T, et al. Screening and application of highly effective mixture for kiwifruit canker disease control[J]. China Plant Protection, 2020, 40(11): 73-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 张毅, 徐进. 猕猴桃溃疡病防治田间药效试验[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2012, 58(1): 32-34. |
| ZHANG Y, XU J. Field efficacy test of kiwifruit canker control[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 58(1): 32-34. (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 赵菊琴. 猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病防治药剂筛选与施药方法研究[J]. 西北园艺(果树), 2020(10): 36-39. |
| ZHAO J Q. Screening of control agents for bacterial canker of kiwifruit and study on application method[J]. Northwest Horticulture, 2020(10): 36-39. (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 卢海博, 谢世兴, 张佳琪, 等. 维大力浸种对低温胁迫下玉米种子萌发及幼苗生理生化指标的影响[J]. 种子, 2023, 42(5): 86-90. |
| LU H B, XIE S X, ZHANG J Q, et al. Effects of VDAL seed-soaking on seed germination and physiological and biochemical parameters of maize under low temperature stress[J]. Seed, 2023, 42(5): 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 姚廷山, 周彦, 周常勇. 应用铜制剂防治柑橘溃疡病的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(9): 1711-1718. |
| YAO T S, ZHOU Y, ZHOU C Y. Advances in copper resistant mechanisms and control methods of citrus canker[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2016, 43(9): 1711-1718. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | BORKOW G, GABBAY J. Putting copper into action: copper-impregnated products with potent biocidal activities[J]. FASEB Journal, 2004, 18(14): 1728-1730. |
| [46] | 黄云. 植物病害生物防治学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010. |
| [47] | 李双双, 潘忠成, 张心心, 等. 中生菌素对水稻稻瘟病菌的室内生物活性研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2023(23): 97-100. |
| LI S S, PAN Z C, ZHANG X X, et al. Indoor biological activity of zhongshengmycin against rice blast fungi[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023(23): 97-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [48] | 王燕, 王春伟, 高洁, 等. 不同杀菌剂及其配比对人参菌核病菌的毒力测定[J]. 北方园艺, 2014(7): 115-119. |
| WANG Y, WANG C W, GAO J, et al. Toxicity test of different fungicides and its mixed preparations against Sclerotinia schinseng[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2014(7): 115-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | GAO Qiang, WANG Lili, ZHANG Jianlong, YANG Bo, LI Feng, ZHU Xianzhi, LIU Aixin, HAN Chao, TIAN Lei. Screening and identification of Bacillus altitudinis strain CY1 and its control effects against tobacco black shank [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 405-416. |
| [2] | YAN Zhongli, LI Yonghui, LI Yucheng, LI Wei, ZHANG Xuesheng, HONG Yong, GE Li’ao. Control effect of aerobic composting with avermectin loaded by cyanobacteria on strawberry red spiders [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(10): 2264-2272. |
| [3] | ZHAO Saisai, ZHANG Haojie, CAI Xiulei, WANG Lirong, SHEN Xiaoran, CAO Zhi, SHAN Hu. Study on antibacterial and quorum quenching activity of a Pseudoalteromonas sp. DL3 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(1): 50-57. |
| [4] | TANG Xiao, MA Ming. Antibacterial activity and stability of Extracts of four common rice dumplings leaves [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(6): 1287-1397. |
| [5] | WANG Lifang, YE Liang, XIE Zhongwen, DANG Xiangli. Antibacterial activity of tea antimicrobial peptide extraction and its effect on preservation of chilled meat [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(10): 2268-2276. |
| [6] | JIANG Yuhang, XIN Weigang, ZHANG Qili, DENG Xianyu, WANG Feng, LIN Lianbing. Isolation and identification of fungi from mildewed feed corn and study on anti-mildew and antifungal effects of lactobacillin [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(7): 1283-1291. |
| [7] | LI Yu, LIU Cuijun, AI Lunqiang, FANG Xinyue, LIU Yu, YUAN Mingyuan, RAN Yalan, HE Meijun. Study on volatile components and antibacterial activity of ethyl acetate component of Fritillaria hupehensis Hsiao et K. C. Hsia [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 1088-1094. |
| [8] | YUE Denggao, CHENG Liang, GUO Qingyun. Antibacterial activities and optimization of fermentation conditions of lipopeptides produced by Aureobasidium pullulans PA-2 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(3): 479-489. |
| [9] | GUO Xuesong, TIAN Libo, SHANG Sang, ZOU Kaixi, CHEN Hongrong, LI Wanyu, YUE Xiaoqi. Isolation, identification and characterization of antagonistic actinomycetes A10 and A17 against Botryodiplodia theobromae [J]. , 2020, 32(3): 460-468. |
| [10] | LIU Zhihui, HAO Rongrong, XU Yongfeng, YANG Chengde, ZHANG Junlian. Screening, identification and biocontrol effect of microbial antagonist against Fusarium solani causing potato dry rot [J]. , 2019, 31(7): 1105-1111. |
| [11] | WEN Huiping, XIAO Jianzhong, LEI Weimin, JI Jiana. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from Chimonanthus salicifolius S.Y.H by HPLC combined with response surface methodology and its antibacterial activity [J]. , 2018, 30(2): 298-306. |
| [12] | JIANG Han, LIU Jiao, LI Ping, GU Qing. Heterologous expression and purification of plantaricin JK and analysis of its antibacterial activity [J]. , 2017, 29(2): 332-337. |
| [13] | QIAN Zhuoquan;YIN Haozhen;HUANG Xiaolin;LIN Shaozhen;NAN Haihan;*. Antibacterial and antioxidant bioassay of three kinds of algae [J]. , 2014, 26(2): 0-384387. |
| [14] | WU Jing;LIANG Yong\|li;SHI Yyu\|ying;LI Yyu\|feng;MA Xiu\|li;JIANG Yi\|fei;SONG Min\|xun;* . Fusion expression of Silkie Cathelicidins genes in Escherichia coli and detection of their antibacterial activity [J]. , 2013, 25(6): 0-1214. |
| [15] | LIU Hui-hui;LI Shu-ping;ZHAO Qian;ZHAO Shu-jiang;*. Identification of marine fungal strain NJ0104 with the anti-microbial activities of their metabolites to bacterial pathogen of Pseudosciaena [J]. , 2012, 24(5): 0-807. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||