Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2583-2592.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240803
• Food Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of a quality evaluation system for fresh-eating tomatoes based on Delphi method and analytic hierarchy process
WANG Tonglin1( ), SHAO Zhiyong1, NIE Zhixing1, GUO Saisai1, LIU Lihong2, WANG Qiaomei2, ZHENG Jirong1,*(
), SHAO Zhiyong1, NIE Zhixing1, GUO Saisai1, LIU Lihong2, WANG Qiaomei2, ZHENG Jirong1,*( )
)
- 1. Hangzhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
2. Department of Horticulture, Zhejiang University/Key Laboratory of Horticultural Plant Growth and Quality Control, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Hangzhou 310058, China
-
Received:2024-09-12Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Tonglin, SHAO Zhiyong, NIE Zhixing, GUO Saisai, LIU Lihong, WANG Qiaomei, ZHENG Jirong. Construction of a quality evaluation system for fresh-eating tomatoes based on Delphi method and analytic hierarchy process[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2583-2592.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240803
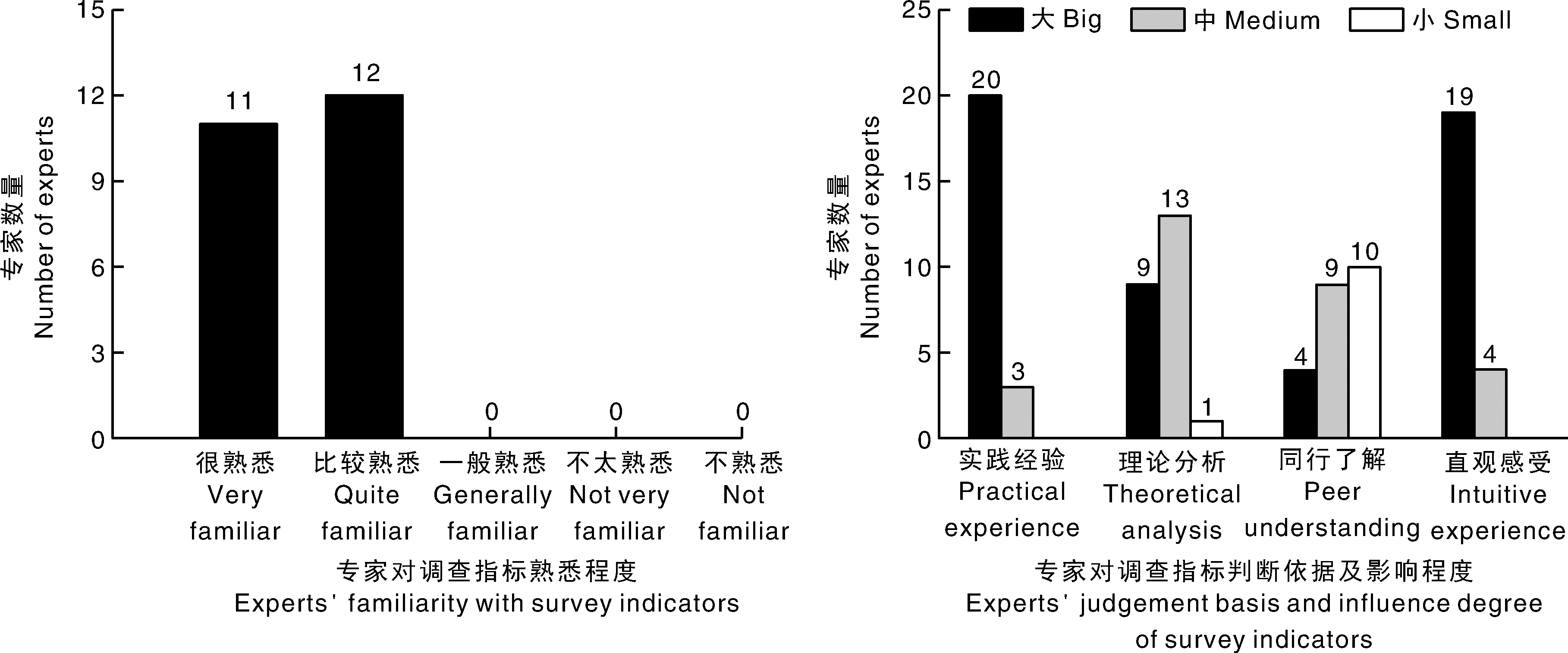
| 判断依据 Judgment basis | 大 Large | 中 Medium | 小 Small |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实践经验Practical experience | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 理论分析Theoretical analysis | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 同行了解Peer understanding | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 直观感受Intuitive feeling | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Table 1 Scoring table of experts’ judgment basis and influence degree of survey indicators
| 判断依据 Judgment basis | 大 Large | 中 Medium | 小 Small |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实践经验Practical experience | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| 理论分析Theoretical analysis | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 同行了解Peer understanding | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 直观感受Intuitive feeling | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 维度层 Dimension | 要素层 Element | 指标层 Indicator | 指标内容解释 Explanation of indicator content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风味品质 Flavor | 味道 Taste | 酸甜味 Sweet and sour taste | 果肉入口后的主要味觉体验 The main taste experience after the fruit pulp enters the mouth |
| quality | 香味 Aroma | 果肉咀嚼过程中鼻腔感受到特异果香 During the process of chewing fruit pulp, the nasal cavity feels a unique fruity aroma | |
| 鲜味 Umami | 果肉入口后有甜而不腻、清爽增香的感觉 After the fruit pulp pulp enters the mouth, it gives a sweet but not greasy, refreshing and fragrant feeling | ||
| 负面味道 Negative taste | 果肉入口后产生苦、涩及其他令人厌恶的感受 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it produces bitterness, astringency, and other unpleasant feelings | ||
| 口感 Mouthfeel | 汁水量 Juice content | 果肉经轻度咀嚼,汁水从中涌出的量 The amount of juice that emerges from lightly chewed fruit pulp | |
| 化渣度 The degree of fruit digest residue | 果肉经咀嚼之后,不会在口腔中留下明显的果渣的程度 The degree of the fruit pulp, after being chewed, with not obvious fruit residue left in the mouth | ||
| 质地 Texture | 在咀嚼过程中,口腔对果肉的触觉感受 The tactile sensation of the flesh in the mouth during chewing | ||
| 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 营养 Nutrition | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solid content | 果肉中所有溶解于水的化合物的总称,包括糖、酸、维生素、矿物质等(其中糖酸占绝大部分) The general term for all compounds dissolved in water in fruit pulp, including sugars, acids, vitamins, minerals, etc. (with sugars and acids accounting for the vast majority) |
| 功能 Function | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content | 单位质量果肉的类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content per unit mass of fruit pulp | |
| VC含量VC content | 单位质量果肉的VC含量VC content per unit mass of fruit pulp | ||
| 其他功能物质含量 Content of other functional substances | 单位质量果肉中GABA、花青素、黄酮、氨基酸等物质含量 Content of GABA, anthocyanins, flavonoids, amino acids and other substances in the unit mass of fruit pulp | ||
| 商品品质 Commercial quality | 耐贮运性 Storage and transportation resistance | 硬度 Firmness | 果实赤道位置硬度,硬度指标直接影响贮运性和货架期 The firmness of fruits at the equatorial position directly affects their storage and shelf life |
| 外观 Appearance | 果形 Fruit shape | 果实外形表现,包含圆润程度、充盈程度、楞沟深浅等 Fruit appearance, including roundness, fullness, depth of grooves, etc | |
| 果面光泽度 Fruit glossiness | 果实表面光滑、整洁的程度 The smoothness and neatness of the fruit surface | ||
| 果实大小Fruit size | 单个番茄果实质量Individual tomato fruit quality | ||
| 果实着色均匀程度 Fruit color uniformity | 果实通体颜色均匀程度 The uniformity of the overall color of the fruit | ||
| 果梗洼疤痕大小 Scar size of fruit stem depression | 果实果梗端形成的木质化疤痕的面积及程度等 The area and degree of lignified scars formed at the end of the fruit stalk, etc | ||
| 萼片有无及大小状态 Sepals presence and size status | 果实萼片的有无、大小、卷曲状态、新鲜程度 The presence, size, curled state, and freshness of fruit sepals |
Table 2 First draft of quality evaluation model for fresh-eating tomato
| 维度层 Dimension | 要素层 Element | 指标层 Indicator | 指标内容解释 Explanation of indicator content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风味品质 Flavor | 味道 Taste | 酸甜味 Sweet and sour taste | 果肉入口后的主要味觉体验 The main taste experience after the fruit pulp enters the mouth |
| quality | 香味 Aroma | 果肉咀嚼过程中鼻腔感受到特异果香 During the process of chewing fruit pulp, the nasal cavity feels a unique fruity aroma | |
| 鲜味 Umami | 果肉入口后有甜而不腻、清爽增香的感觉 After the fruit pulp pulp enters the mouth, it gives a sweet but not greasy, refreshing and fragrant feeling | ||
| 负面味道 Negative taste | 果肉入口后产生苦、涩及其他令人厌恶的感受 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it produces bitterness, astringency, and other unpleasant feelings | ||
| 口感 Mouthfeel | 汁水量 Juice content | 果肉经轻度咀嚼,汁水从中涌出的量 The amount of juice that emerges from lightly chewed fruit pulp | |
| 化渣度 The degree of fruit digest residue | 果肉经咀嚼之后,不会在口腔中留下明显的果渣的程度 The degree of the fruit pulp, after being chewed, with not obvious fruit residue left in the mouth | ||
| 质地 Texture | 在咀嚼过程中,口腔对果肉的触觉感受 The tactile sensation of the flesh in the mouth during chewing | ||
| 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 营养 Nutrition | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solid content | 果肉中所有溶解于水的化合物的总称,包括糖、酸、维生素、矿物质等(其中糖酸占绝大部分) The general term for all compounds dissolved in water in fruit pulp, including sugars, acids, vitamins, minerals, etc. (with sugars and acids accounting for the vast majority) |
| 功能 Function | 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content | 单位质量果肉的类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content per unit mass of fruit pulp | |
| VC含量VC content | 单位质量果肉的VC含量VC content per unit mass of fruit pulp | ||
| 其他功能物质含量 Content of other functional substances | 单位质量果肉中GABA、花青素、黄酮、氨基酸等物质含量 Content of GABA, anthocyanins, flavonoids, amino acids and other substances in the unit mass of fruit pulp | ||
| 商品品质 Commercial quality | 耐贮运性 Storage and transportation resistance | 硬度 Firmness | 果实赤道位置硬度,硬度指标直接影响贮运性和货架期 The firmness of fruits at the equatorial position directly affects their storage and shelf life |
| 外观 Appearance | 果形 Fruit shape | 果实外形表现,包含圆润程度、充盈程度、楞沟深浅等 Fruit appearance, including roundness, fullness, depth of grooves, etc | |
| 果面光泽度 Fruit glossiness | 果实表面光滑、整洁的程度 The smoothness and neatness of the fruit surface | ||
| 果实大小Fruit size | 单个番茄果实质量Individual tomato fruit quality | ||
| 果实着色均匀程度 Fruit color uniformity | 果实通体颜色均匀程度 The uniformity of the overall color of the fruit | ||
| 果梗洼疤痕大小 Scar size of fruit stem depression | 果实果梗端形成的木质化疤痕的面积及程度等 The area and degree of lignified scars formed at the end of the fruit stalk, etc | ||
| 萼片有无及大小状态 Sepals presence and size status | 果实萼片的有无、大小、卷曲状态、新鲜程度 The presence, size, curled state, and freshness of fruit sepals |
| 维度层 Dimension | 指标层 Indicator | 第一次问卷结果 First questionnaire results | 第二次问卷结果 Second questionnaire results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | CV | SD | CV | ||||
| (A1)风味品质 | (B1)酸甜味Sweet and sour taste | 4.91 | 0.29 | 0.059 | 4.89 | 0.31 | 0.063 |
| Flavor quality | (B2)香味Aroma | 3.57 | 1.12 | 0.314 | 3.54 | 0.66 | 0.187 |
| (B3)鲜味Umami | 3.78 | 1.04 | 0.276 | 3.88 | 0.97 | 0.249 | |
| (B4)负面味道Negative taste | 4.30 | 1.06 | 0.247 | 4.49 | 0.99 | 0.220 | |
| (B5)汁水量Juice content | 4.04 | 0.88 | 0.217 | 3.85 | 0.75 | 0.194 | |
| (B6)化渣度The degree of fruit digest residue | 4.04 | 0.88 | 0.217 | 3.88 | 0.79 | 0.205 | |
| (B7)质地Texture | 3.78 | 0.74 | 0.195 | 3.84 | 0.56 | 0.147 | |
| (A2)营养品质 | (B8)可溶性固形物含量Total soluble solid content | 4.30 | 0.88 | 0.203 | 4.12 | 0.62 | 0.151 |
| Nutritional quality | (B9)类胡萝卜素含量Carotenoid content | 3.96 | 0.82 | 0.208 | 4.09 | 0.84 | 0.206 |
| (B10)VC含量VC content | 3.83 | 0.72 | 0.187 | 3.94 | 0.76 | 0.193 | |
| (B11)其他功能物质含量 | 3.04 | 1.02 | 0.336 | 3.20 | 1.06 | 0.330 | |
| Content of other functional substances | |||||||
| (A3)商品品质 | (B12)硬度Firmness | 3.65 | 0.93 | 0.256 | 3.68 | 0.65 | 0.177 |
| Commercial quality | (B13)果形Fruit shape | 4.30 | 0.97 | 0.226 | 4.34 | 0.73 | 0.167 |
| (B14)果面光泽度Fruit glossiness | 3.96 | 0.93 | 0.235 | 4.15 | 0.59 | 0.142 | |
| (B15)果实大小Fruit size | 2.83 | 1.03 | 0.364 | 2.92 | 0.69 | 0.238 | |
| (B16)果实着色均匀程度Fruit color uniformity | 3.96 | 0.93 | 0.235 | 3.95 | 0.69 | 0.174 | |
| (B17)果梗洼疤痕大小Scar size of fruit stem depression | 2.91 | 0.90 | 0.309 | 2.97 | 0.73 | 0.247 | |
| (B18)萼片有无及大小状态 | 3.26 | 1.05 | 0.323 | 3.29 | 0.78 | 0.238 | |
| Sepals presence and size status | |||||||
Table 3 Scoring results of expert importance
| 维度层 Dimension | 指标层 Indicator | 第一次问卷结果 First questionnaire results | 第二次问卷结果 Second questionnaire results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD | CV | SD | CV | ||||
| (A1)风味品质 | (B1)酸甜味Sweet and sour taste | 4.91 | 0.29 | 0.059 | 4.89 | 0.31 | 0.063 |
| Flavor quality | (B2)香味Aroma | 3.57 | 1.12 | 0.314 | 3.54 | 0.66 | 0.187 |
| (B3)鲜味Umami | 3.78 | 1.04 | 0.276 | 3.88 | 0.97 | 0.249 | |
| (B4)负面味道Negative taste | 4.30 | 1.06 | 0.247 | 4.49 | 0.99 | 0.220 | |
| (B5)汁水量Juice content | 4.04 | 0.88 | 0.217 | 3.85 | 0.75 | 0.194 | |
| (B6)化渣度The degree of fruit digest residue | 4.04 | 0.88 | 0.217 | 3.88 | 0.79 | 0.205 | |
| (B7)质地Texture | 3.78 | 0.74 | 0.195 | 3.84 | 0.56 | 0.147 | |
| (A2)营养品质 | (B8)可溶性固形物含量Total soluble solid content | 4.30 | 0.88 | 0.203 | 4.12 | 0.62 | 0.151 |
| Nutritional quality | (B9)类胡萝卜素含量Carotenoid content | 3.96 | 0.82 | 0.208 | 4.09 | 0.84 | 0.206 |
| (B10)VC含量VC content | 3.83 | 0.72 | 0.187 | 3.94 | 0.76 | 0.193 | |
| (B11)其他功能物质含量 | 3.04 | 1.02 | 0.336 | 3.20 | 1.06 | 0.330 | |
| Content of other functional substances | |||||||
| (A3)商品品质 | (B12)硬度Firmness | 3.65 | 0.93 | 0.256 | 3.68 | 0.65 | 0.177 |
| Commercial quality | (B13)果形Fruit shape | 4.30 | 0.97 | 0.226 | 4.34 | 0.73 | 0.167 |
| (B14)果面光泽度Fruit glossiness | 3.96 | 0.93 | 0.235 | 4.15 | 0.59 | 0.142 | |
| (B15)果实大小Fruit size | 2.83 | 1.03 | 0.364 | 2.92 | 0.69 | 0.238 | |
| (B16)果实着色均匀程度Fruit color uniformity | 3.96 | 0.93 | 0.235 | 3.95 | 0.69 | 0.174 | |
| (B17)果梗洼疤痕大小Scar size of fruit stem depression | 2.91 | 0.90 | 0.309 | 2.97 | 0.73 | 0.247 | |
| (B18)萼片有无及大小状态 | 3.26 | 1.05 | 0.323 | 3.29 | 0.78 | 0.238 | |
| Sepals presence and size status | |||||||
| 品质指标 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | B10 | B12 | B13 | B14 | B16 | B18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators | |||||||||||||||
| B1 | 1 | 1.380 | 1.261 | 1.089 | 1.270 | 1.261 | 1.274 | 1.188 | 1.196 | 1.241 | 1.328 | 1.127 | 1.179 | 1.239 | 1.487 |
| B2 | 0.725 | 1 | 0.914 | 0.789 | 0.92 | 0.914 | 0.923 | 0.861 | 0.867 | 0.899 | 0.962 | 0.816 | 0.854 | 0.898 | 1.078 |
| B3 | 0.793 | 1.095 | 1 | 0.864 | 1.007 | 1.001 | 1.010 | 0.943 | 0.949 | 0.984 | 1.053 | 0.894 | 0.935 | 0.983 | 1.180 |
| B4 | 0.918 | 1.267 | 1.158 | 1 | 1.166 | 1.158 | 1.170 | 1.091 | 1.098 | 1.139 | 1.219 | 1.035 | 1.082 | 1.137 | 1.366 |
| B5 | 0.788 | 1.087 | 0.993 | 0.858 | 1 | 0.994 | 1.003 | 0.936 | 0.942 | 0.977 | 1.046 | 0.888 | 0.929 | 0.976 | 1.172 |
| B6 | 0.793 | 1.094 | 0.999 | 0.863 | 1.006 | 1 | 1.010 | 0.942 | 0.948 | 0.984 | 1.053 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.982 | 1.179 |
| B7 | 0.785 | 1.083 | 0.990 | 0.855 | 0.997 | 0.990 | 1 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.974 | 1.042 | 0.885 | 0.926 | 0.972 | 1.168 |
| B8 | 0.841 | 1.161 | 1.061 | 0.916 | 1.068 | 1.061 | 1.072 | 1 | 1.007 | 1.044 | 1.117 | 0.948 | 0.992 | 1.042 | 1.252 |
| B9 | 0.836 | 1.154 | 1.054 | 0.91 | 1.061 | 1.054 | 1.065 | 0.993 | 1 | 1.037 | 1.110 | 0.942 | 0.986 | 1.035 | 1.243 |
| B10 | 0.806 | 1.112 | 1.016 | 0.878 | 1.023 | 1.017 | 1.027 | 0.958 | 0.964 | 1 | 1.070 | 0.908 | 0.950 | 0.998 | 1.199 |
| B12 | 0.753 | 1.039 | 0.949 | 0.82 | 0.956 | 0.950 | 0.959 | 0.895 | 0.901 | 0.934 | 1 | 0.849 | 0.888 | 0.933 | 1.120 |
| B13 | 0.887 | 1.225 | 1.119 | 0.967 | 1.127 | 1.119 | 1.131 | 1.055 | 1.062 | 1.101 | 1.179 | 1 | 1.046 | 1.099 | 1.320 |
| B14 | 0.848 | 1.171 | 1.069 | 0.924 | 1.077 | 1.070 | 1.080 | 1.008 | 1.015 | 1.052 | 1.126 | 0.956 | 1 | 1.051 | 1.262 |
| B16 | 0.807 | 1.114 | 1.018 | 0.879 | 1.025 | 1.018 | 1.028 | 0.959 | 0.966 | 1.002 | 1.072 | 0.910 | 0.952 | 1 | 1.201 |
| B18 | 0.672 | 0.928 | 0.848 | 0.732 | 0.854 | 0.848 | 0.856 | 0.799 | 0.804 | 0.834 | 0.893 | 0.758 | 0.793 | 0.833 | 1 |
Table 4 AHP judgment matrix
| 品质指标 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | B10 | B12 | B13 | B14 | B16 | B18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators | |||||||||||||||
| B1 | 1 | 1.380 | 1.261 | 1.089 | 1.270 | 1.261 | 1.274 | 1.188 | 1.196 | 1.241 | 1.328 | 1.127 | 1.179 | 1.239 | 1.487 |
| B2 | 0.725 | 1 | 0.914 | 0.789 | 0.92 | 0.914 | 0.923 | 0.861 | 0.867 | 0.899 | 0.962 | 0.816 | 0.854 | 0.898 | 1.078 |
| B3 | 0.793 | 1.095 | 1 | 0.864 | 1.007 | 1.001 | 1.010 | 0.943 | 0.949 | 0.984 | 1.053 | 0.894 | 0.935 | 0.983 | 1.180 |
| B4 | 0.918 | 1.267 | 1.158 | 1 | 1.166 | 1.158 | 1.170 | 1.091 | 1.098 | 1.139 | 1.219 | 1.035 | 1.082 | 1.137 | 1.366 |
| B5 | 0.788 | 1.087 | 0.993 | 0.858 | 1 | 0.994 | 1.003 | 0.936 | 0.942 | 0.977 | 1.046 | 0.888 | 0.929 | 0.976 | 1.172 |
| B6 | 0.793 | 1.094 | 0.999 | 0.863 | 1.006 | 1 | 1.010 | 0.942 | 0.948 | 0.984 | 1.053 | 0.893 | 0.935 | 0.982 | 1.179 |
| B7 | 0.785 | 1.083 | 0.990 | 0.855 | 0.997 | 0.990 | 1 | 0.933 | 0.939 | 0.974 | 1.042 | 0.885 | 0.926 | 0.972 | 1.168 |
| B8 | 0.841 | 1.161 | 1.061 | 0.916 | 1.068 | 1.061 | 1.072 | 1 | 1.007 | 1.044 | 1.117 | 0.948 | 0.992 | 1.042 | 1.252 |
| B9 | 0.836 | 1.154 | 1.054 | 0.91 | 1.061 | 1.054 | 1.065 | 0.993 | 1 | 1.037 | 1.110 | 0.942 | 0.986 | 1.035 | 1.243 |
| B10 | 0.806 | 1.112 | 1.016 | 0.878 | 1.023 | 1.017 | 1.027 | 0.958 | 0.964 | 1 | 1.070 | 0.908 | 0.950 | 0.998 | 1.199 |
| B12 | 0.753 | 1.039 | 0.949 | 0.82 | 0.956 | 0.950 | 0.959 | 0.895 | 0.901 | 0.934 | 1 | 0.849 | 0.888 | 0.933 | 1.120 |
| B13 | 0.887 | 1.225 | 1.119 | 0.967 | 1.127 | 1.119 | 1.131 | 1.055 | 1.062 | 1.101 | 1.179 | 1 | 1.046 | 1.099 | 1.320 |
| B14 | 0.848 | 1.171 | 1.069 | 0.924 | 1.077 | 1.070 | 1.080 | 1.008 | 1.015 | 1.052 | 1.126 | 0.956 | 1 | 1.051 | 1.262 |
| B16 | 0.807 | 1.114 | 1.018 | 0.879 | 1.025 | 1.018 | 1.028 | 0.959 | 0.966 | 1.002 | 1.072 | 0.910 | 0.952 | 1 | 1.201 |
| B18 | 0.672 | 0.928 | 0.848 | 0.732 | 0.854 | 0.848 | 0.856 | 0.799 | 0.804 | 0.834 | 0.893 | 0.758 | 0.793 | 0.833 | 1 |
| 维度层 Dimension | 指标层 Indicator | 指标内容解释 Explanation of indicator content | 权重 Weight/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风味品质 Flavor quality | 酸甜味 Sweet and sour taste | 果肉入口后的主要味觉体验 The main taste experience after the fruit pulp enters the mouth | 8.16 |
| 香味 Aroma | 果肉咀嚼过程中鼻腔感受到特异果香 During the process of chewing fruit pulp, the nasal cavity feels a unique fruity aroma | 5.91 | |
| 鲜味 Umami | 果肉入口后有甜而不腻、清爽增香的感觉 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it gives a sweet but not greasy, refreshing and fragrant feeling | 6.47 | |
| 负面味道 Negative taste | 果肉入口后产生苦、涩及其他令人厌恶的感受 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it produces bitterness, astringency, and other unpleasant feelings | 7.49 | |
| 汁水量 Juice content | 果肉经轻度咀嚼,汁水从中涌出的量 The amount of juice that emerges from lightly chewed fruit pulp | 6.43 | |
| 化渣度 The degree of fruit digest residue | 果肉经咀嚼之后,不会在口腔中留下明显的果渣的程度 The degree of the fruit pulp, after being chewed, with not obvious fruit residue left in the mouth | 6.47 | |
| 质地 Texture | 在咀嚼过程中,口腔对果肉的触觉感受 The tactile sensation of the flesh in the mouth during chewing | 6.41 | |
| 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solid content | 果肉中所有溶解于水的化合物的总称,包括糖、酸、维生素、矿物质等 (其中糖酸占绝大部分) The general term for all compounds dissolved in water in fruit pulp, including sugars, acids, vitamins, minerals, etc. (with sugars and acids accounting for the vast majority) | 6.87 |
| 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content | 单位质量果肉的类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content per unit mass of fruit pulp | 6.82 | |
| VC含量 VC content | 单位质量果肉的VC含量 VC content per unit mass of fruit pulp | 6.58 | |
| 商品品质 Commercial quality | 硬度 Firmness | 果实赤道位置硬度,硬度指标直接影响贮运性和货架期 The firmness of fruits at the equatorial position directly affects their storage and shelf life | 6.15 |
| 果形 Fruit shape | 果实外形表现,包含圆润程度、充盈程度、楞沟深浅等 Fruit appearance, including roundness, fullness, depth of grooves, etc | 7.24 | |
| 果面光泽度 Fruit glossiness | 果实表面光滑、整洁的程度 The smoothness and neatness of the fruit surface | 6.92 | |
| 果实着色均匀程度 Fruit color uniformity | 果实通体颜色均匀程度 The uniformity of the overall color of the fruit | 6.59 | |
| 萼片有无及大小状态 Sepals presence and size status | 果实萼片的有无、大小、卷曲状态、新鲜程度 The presence, size, curled state, and freshness of fruit sepals | 5.49 |
Table 5 Tomato quality evaluation system
| 维度层 Dimension | 指标层 Indicator | 指标内容解释 Explanation of indicator content | 权重 Weight/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风味品质 Flavor quality | 酸甜味 Sweet and sour taste | 果肉入口后的主要味觉体验 The main taste experience after the fruit pulp enters the mouth | 8.16 |
| 香味 Aroma | 果肉咀嚼过程中鼻腔感受到特异果香 During the process of chewing fruit pulp, the nasal cavity feels a unique fruity aroma | 5.91 | |
| 鲜味 Umami | 果肉入口后有甜而不腻、清爽增香的感觉 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it gives a sweet but not greasy, refreshing and fragrant feeling | 6.47 | |
| 负面味道 Negative taste | 果肉入口后产生苦、涩及其他令人厌恶的感受 After the fruit pulp enters the mouth, it produces bitterness, astringency, and other unpleasant feelings | 7.49 | |
| 汁水量 Juice content | 果肉经轻度咀嚼,汁水从中涌出的量 The amount of juice that emerges from lightly chewed fruit pulp | 6.43 | |
| 化渣度 The degree of fruit digest residue | 果肉经咀嚼之后,不会在口腔中留下明显的果渣的程度 The degree of the fruit pulp, after being chewed, with not obvious fruit residue left in the mouth | 6.47 | |
| 质地 Texture | 在咀嚼过程中,口腔对果肉的触觉感受 The tactile sensation of the flesh in the mouth during chewing | 6.41 | |
| 营养品质 Nutritional quality | 可溶性固形物含量 Total soluble solid content | 果肉中所有溶解于水的化合物的总称,包括糖、酸、维生素、矿物质等 (其中糖酸占绝大部分) The general term for all compounds dissolved in water in fruit pulp, including sugars, acids, vitamins, minerals, etc. (with sugars and acids accounting for the vast majority) | 6.87 |
| 类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content | 单位质量果肉的类胡萝卜素含量 Carotenoid content per unit mass of fruit pulp | 6.82 | |
| VC含量 VC content | 单位质量果肉的VC含量 VC content per unit mass of fruit pulp | 6.58 | |
| 商品品质 Commercial quality | 硬度 Firmness | 果实赤道位置硬度,硬度指标直接影响贮运性和货架期 The firmness of fruits at the equatorial position directly affects their storage and shelf life | 6.15 |
| 果形 Fruit shape | 果实外形表现,包含圆润程度、充盈程度、楞沟深浅等 Fruit appearance, including roundness, fullness, depth of grooves, etc | 7.24 | |
| 果面光泽度 Fruit glossiness | 果实表面光滑、整洁的程度 The smoothness and neatness of the fruit surface | 6.92 | |
| 果实着色均匀程度 Fruit color uniformity | 果实通体颜色均匀程度 The uniformity of the overall color of the fruit | 6.59 | |
| 萼片有无及大小状态 Sepals presence and size status | 果实萼片的有无、大小、卷曲状态、新鲜程度 The presence, size, curled state, and freshness of fruit sepals | 5.49 |
| [1] | 程远, 万红建, 刘超超, 等. 十六个樱桃番茄品种果实风味品质相关指标比较分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(11): 1859-1869. |
| CHENG Y, WAN H J, LIU C C, et al. Comparative analysis of flavor/nutrient determination parameters in 16 different cherry tomato varieties[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(11): 1859-1869. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 叶志彪. 园艺产品品质分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2011. |
| [3] | 周艳超, 薛坤, 葛海燕, 等. 基于主成分与聚类分析的樱桃番茄品质综合评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(12): 2320-2329. |
| ZHOU Y C, XUE K, GE H Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of cherry tomato quality based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(12): 2320-2329. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 张璐瑶, 沈晖, 田军仓. 基于模糊综合评价法的压砂地欧李品种筛选[J]. 北方园艺, 2019(3): 189-196. |
| ZHANG L Y, SHEN H, TIAN J C. Screening of Cerasus humilis in gravel-mulched field based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2019(3): 189-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 李波, 邢经伟, 姚名泽, 等. 深埋秸秆量和滴灌量对温室番茄品质、产量及IWUE的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2019, 50(1): 51-59. |
| LI B, XING J W, YAO M Z, et al. Effects of the amounts of deep-buried straw and drip irrigation on quality, yield and IWUE of tomato in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019, 50(1): 51-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 陈维强, 吴璠, 蒋月超, 等. 德尔菲法及层次分析法构建手术室护士急救能力评价指标体系研究[J]. 罕少疾病杂志, 2024, 31(8): 153-155. |
| CHEN W Q, WU F, JIANG Y C, et al. Construct the evaluation index system of the operation RoomNurse’s first-aid capability based on Delphi method and analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Rare and Uncommon Diseases, 2024, 31(8): 153-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 郁琴芳, 陈嘉媛, 宋萑. 教师家校合作素养指标建设的德尔菲法调查研究[J]. 教师教育研究, 2022, 34(6): 44-52. |
| YU Q F, CHEN J Y, SONG H. A Delphi study on the evaluation index system establishment of home-school cooperation competency of teachers[J]. Teacher Education Research, 2022, 34(6): 44-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 营星星. 人工智能辅助医院财务管理的实效及其优化: 基于层次分析法的实证研究[J]. 会计之友, 2023(1): 118-125. |
| YING X X. Effectiveness and optimization of artificial intelligence-assisted hospital financial management:An empirical study based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Friends of Accounting, 2023(1): 118-125. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 郭秀花. 实用医学调查分析技术[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2005. |
| [10] | 姚转香. 基于层次分析法的城市轨道交通运营安全评价研究[J]. 黑龙江科学, 2024, 15(16): 106-108. |
| YAO Z X. Research on operation safety evaluation of urban rail transit based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Heilongjiang Science, 2024, 15(16): 106-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 贺珍. 问卷设计五原则[J]. 秘书之友, 2018(9): 16-18. |
| HE Z. Five principles of questionnaire design[J]. Secretary’s Companion, 2018(9): 16-18. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 谭跃进. 定量分析方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2012. |
| [13] | 赵博, 崔萌萌, 缪佩, 等. 萼片对番茄果实发育及品质形成的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2015, 20(2): 93-100. |
| ZHAO B, CUI M M, MIAO P, et al. Effects of Calyx on tomato fruit development and quality formation[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20(2): 93-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 孙崇德. 园艺产品品质与营养健康[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2021. |
| [15] | 尚乐乐, 宋建文, 王嘉颖, 等. 番茄果实品质形成及其分子机理研究进展[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2019(4): 21-28. |
| SHANG L L, SONG J W, WANG J Y, et al. Research progress on quality formation and molecular mechanism of tomato fruit[J]. China Vegetables, 2019(4): 21-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 张晓鸣. 食品风味化学[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2018. |
| [17] | KLEE H J, TIEMAN D M. Genetic challenges of flavor improvement in tomato[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2013, 29(4): 257-262. |
| [18] | 汪俏梅, 苗慧莹. 蔬菜营养与功能[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2022. |
| [19] | 汪俏梅. 园艺产品营养与功能[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2021. |
| [20] | LU Y, ZHU H L. The regulation of nutrient and flavor metabolism in tomato fruit[J]. Vegetable Research, 2022, 2(1): 1-14. |
| [21] | 胡珂, 李娜. 倍受青睐的抗氧化家族: 类胡萝卜素[J]. 大学化学, 2010, 25(S1): 94-98. |
| HU K, LI N. Carotenoids: a favored antioxidant family[J]. University Chemistry, 2010, 25(S1): 94-98. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 周相助, 刘明月, 严逸男, 等. 番茄花萼形态多样性、相关性分析及因子模型构建[J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(2): 280-286. |
| ZHOU X Z, LIU M Y, YAN Y N, et al. Morphological diversity, correlation analysis and mathematic model construction of tomato sepals[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(2): 280-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘继斐. 评价指标相关性的处理方法研究[J]. 管理科学文摘, 2006(12): 50-51. |
| LIU J F. Research on the processing method of correlation of evaluation indexes[J]. Digest of Management Science, 2006(12): 50-51. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | XU Weimeng, XU Yan, CHEN Guoli. Comprehensive evaluation of waxy corn quality based on various analytical methods [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(9): 1840-1848. |
| [2] | ZHU Weijing, WU Jia, HONG Chunlai, ZHU Fengxiang, HONG Leidong, ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Shuo, ZHU Huifen. Effects of straw mulching on water, heat, fertility status of soil and yield and quality of flat peach [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(9): 1924-1932. |
| [3] | HE Shixiong, YANG Lei, QI Anmin, CHENG Ji, WANG Min, LI Yingkui, HONG Lin. Effects of interstock on leaf photosynthetic characteristics, physicochemical properties and fruit quality of three mandarin hybrids [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1680-1693. |
| [4] | ZHANG Shunchang, XU Jigen, FU Chengyue, PU Zhanxu, HU Lipeng, WU Hao, LI Junbing, XIN Liang, LEI Yuanjun. Effect of amino acid calcium spraying on peel cracking and quality of citrus hybrid Hongmeiren [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1706-1715. |
| [5] | YAN Fulin, LANG Yunhu, JIAN Yingquan, CHEN Xiongfei, WEI Wei, WANG Zhiwei, AN Jiangyong, REN Deqiang, DING Ning, WEI Shenghua. Response of yield and quality of Radix Ardisia to soil physiochemical properties [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1766-1775. |
| [6] | FENG Yiyu, REN Hongjie. Quantitative assessment of new quality productive forces in China’s livestock industry: based on panel data in 2007-2021 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1805-1816. |
| [7] | HUANG Xianke, HUANG Xiaolin, ZHANG Xiang, LI Min, CAI Yilong, CHEN Ran. Effects of oyster shells on the growth performance of Penaeus vannamei and water quality, and microbial community characteristics on shell surfaces [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(7): 1441-1450. |
| [8] | WANG Chengyang, LIU Jieya, WU Minyi, XIE Boyi, HONG Decheng, LENG Feng, WU Guoquan. Effect of calcium treatment on the fruit quality of Reliance grape under waterlogging [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(7): 1451-1458. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Meng. The estimation of new quality productive forces level, developmental retardation and cultivation path of feed enterprises [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(7): 1580-1594. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ruonan, MEN Xiaoming, QIN Kaipeng, WANG Binbin, WU Jie, DING Xiangbin, XU Ziwei, QI Keke. Comparative study on growth performance, carcass quality, meat performance and profitability of different crossbreed combinations of Lvjiahei pigs [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1203-1211. |
| [11] | XIANG Ying, CONG Jianmin, PAN Danhong, TAO Yonggang. Comprehensive evaluation of the growth process of different tomato varieties under spring organic greenhouse planting [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1252-1261. |
| [12] | LIU Wenqi, HU Qizan, YUE Zhichen, TAO Peng, LEI Juanli, LI Biyuan, ZHAO Yanting, WANG Huasen. Effects of high temperature in summer on the appearance and nutritional quality of Brassica juncea [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1262-1271. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chengcheng, FAN Tao, ZHANG Jianming, ZHAO Fengliang, XIN Xiaoting, NIU Haiyue, LIU Daqun. Changes of bacterial community and quality during pickling process of Jinyun pickled and dried mustard [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1336-1343. |
| [14] | YUE Li, ZHUANG Hongmei, ZULIPIYA· Maimaiti, WANG Jiamin, MAO Hongyan, ZHANG Yingxian, NIGARY· Yadikar, YU Ming. Comprehensive evaluation of the texture quality of turnip succulent root based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(5): 1057-1071. |
| [15] | SU Yang, SHANG Xiaolan, QIAN Zhongming, WU Lingen, HUANG Jiaqi, ZHUANG Haifeng, ZHAO Yufei, DANG Hongyang, XU Lijun. Effects of synergistic enhancement of straw returning to the field with decomposition agent and biochar on soil quality and rice growth [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(5): 1139-1148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||