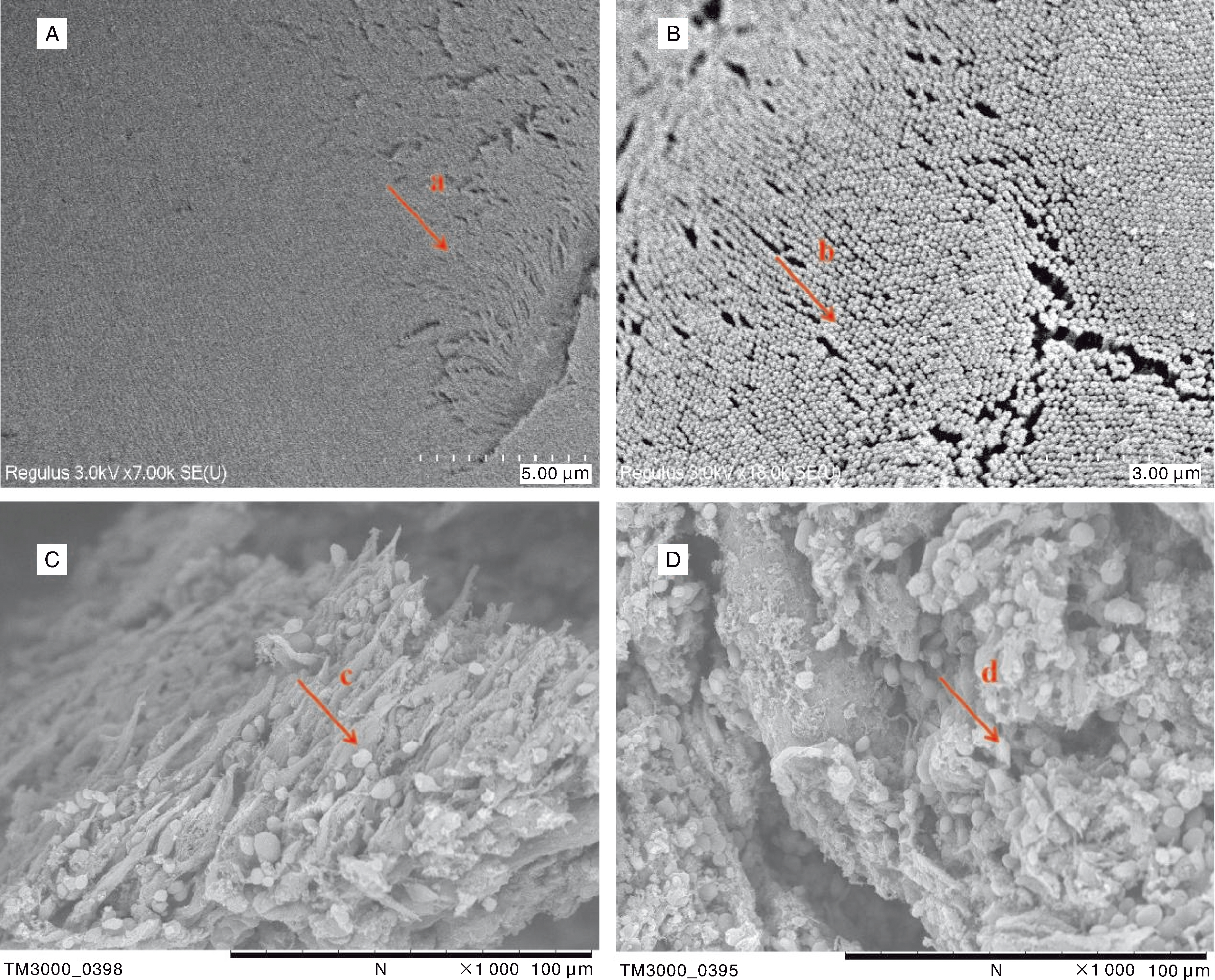
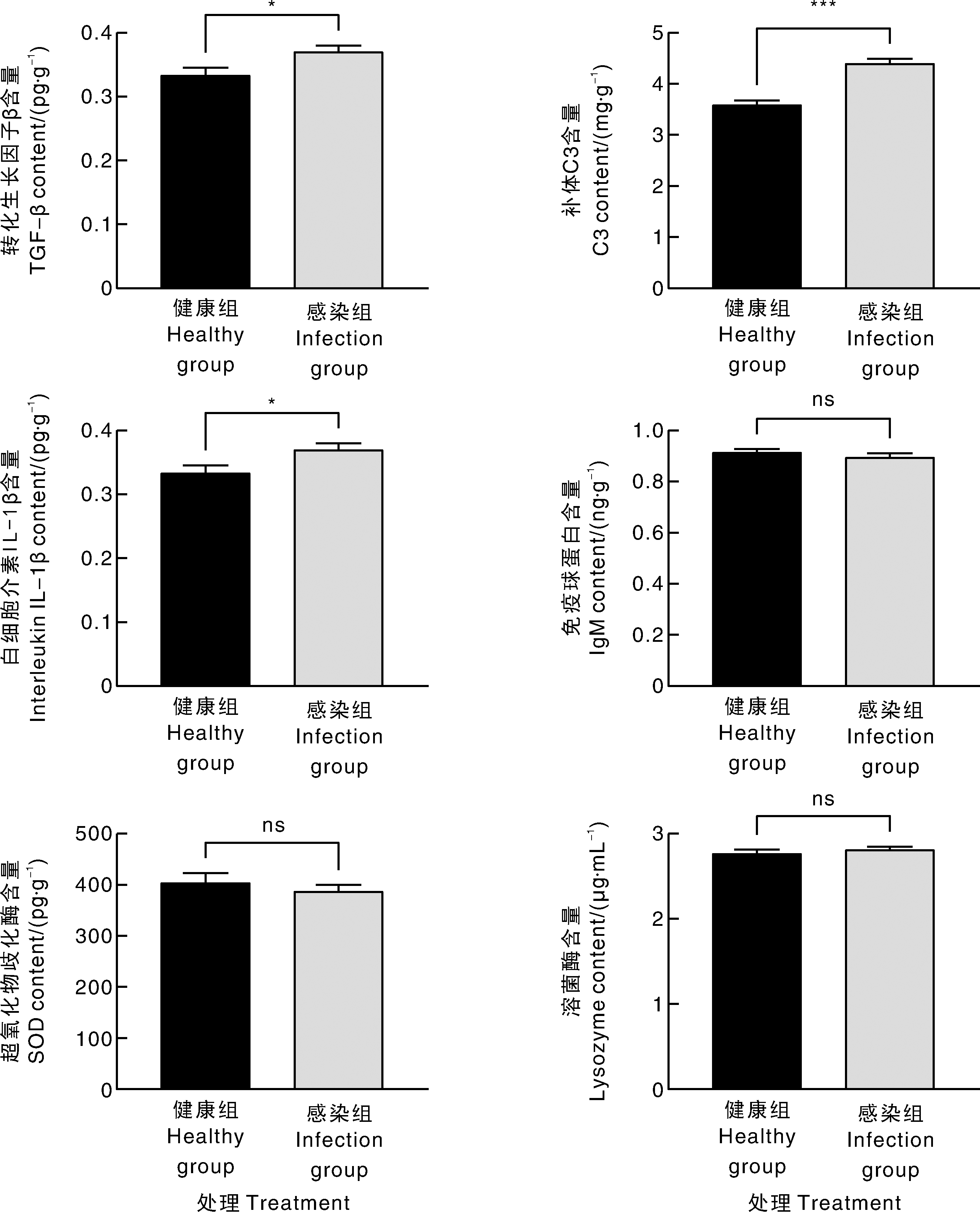
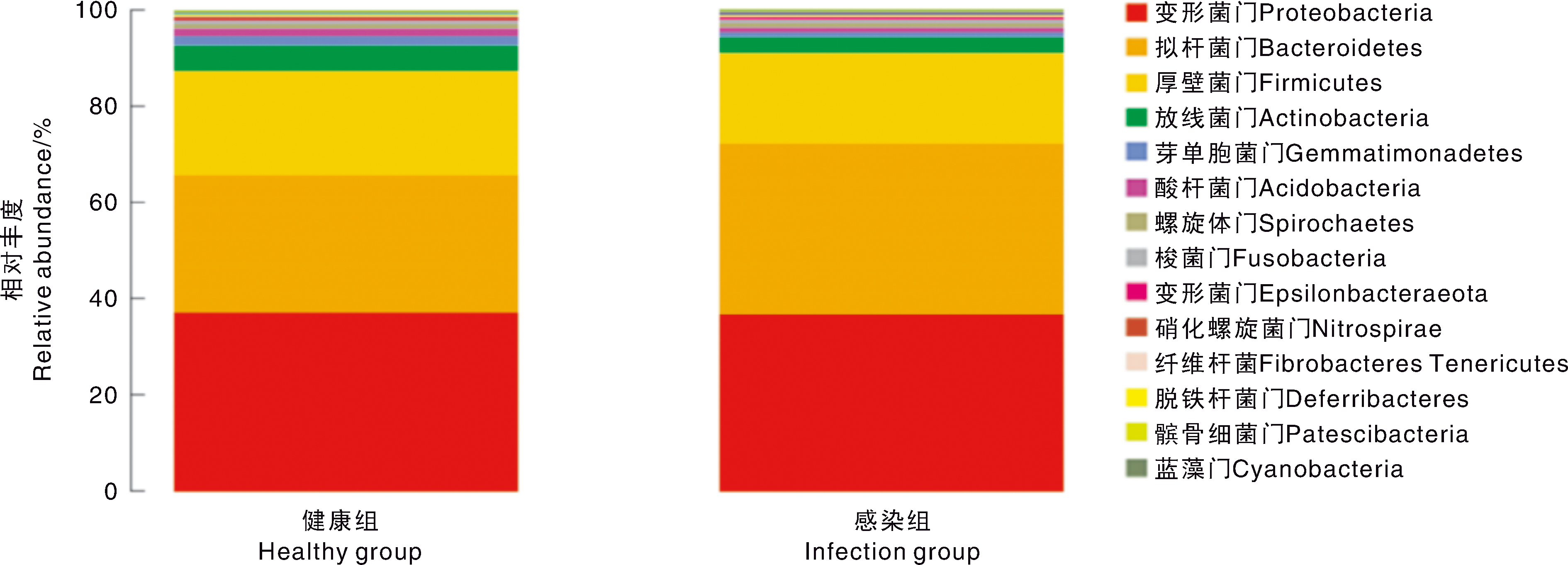
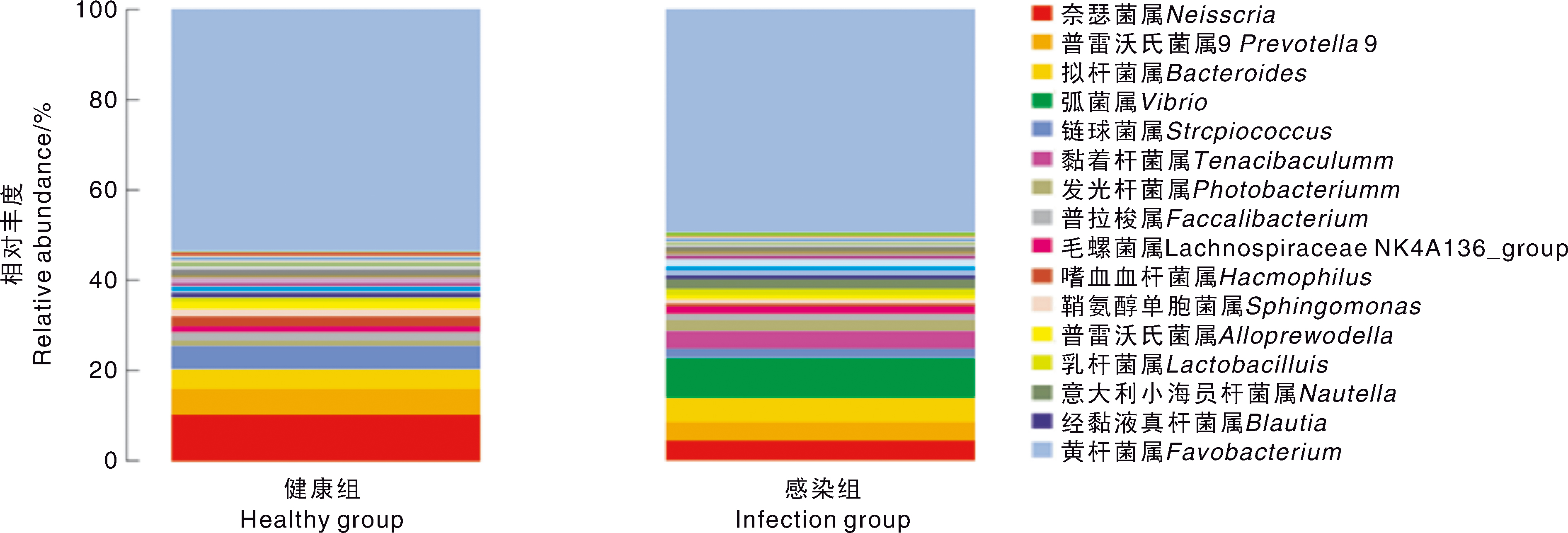
| [1] |
成奇, 潘连德. 刺激隐核虫生物学和刺激隐核虫病临床诊治的研究进展[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准, 2014, 4(5): 16-23.
|
|
CHENG Q, PAN L D. Review on the biological characteristics of Cryptocaryon irritans and the diagnosis and treatment of cryptocaryoniosis[J]. Chinese Fishery Quality and Standards, 2014, 4(5): 16-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
LI Y W, JIANG B, MO Z Q, et al. Cryptocaryon irritans(Brown, 1951) is a serious threat to aquaculture of marine fish[J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2022, 14(1): 218-236.
|
| [3] |
ZHENG L B, QIU J Y, CHEN J, et al. Histopathological changes and piscidin 5-like location in infected Larimichthys crocea with parasite Cryptocaryon irritans[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2020, 99: 52-58.
|
| [4] |
陈爱平, 江育林, 钱冬, 等. 刺激隐核虫病[J]. 中国水产, 2011(8): 39-40.
|
|
CHEN A P, JIANG Y L, QIAN D, et al. Cryptocaryoniasis[J]. China Fisheries, 2011(8): 39-40. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
但学明, 李安兴, 林小涛, 等. 卵形鲳鯵对刺激隐核虫的免疫应答和免疫保护研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2008, 32(1): 13-18.
|
|
DAN X M, LI A X, LIN X T, et al. Immune response and immunoprotection of pompanos (Trachinotus ovatus) against Cryptocaryon irritans[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2008, 32(1): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
JEE B Y, KIM K H, PARK S I, et al. A new strain of Cryptocaryon irritans from the cultured olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2000, 43(3): 211-215.
|
| [7] |
YIN F, GONG H, KE Q Z, et al. Stress, antioxidant defence and mucosal immune responses of the large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea challenged with Cryptocaryon irritans[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 47(1): 344-351.
|
| [8] |
INGRAM G A. Substances involved in the natural resistance of fish to infection-a review[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 1980, 16(1): 23-60.
|
| [9] |
MURRAY C K, FLECHER T C. The immunohistochemical localization of lysozyme in plaice (Pleuronectessa L) tissues[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 1976, 9(4): 329-334.
|
| [10] |
LIE Ø, EVENSEN Ø, SØRENSEN A, et al. Study on lysozyme activity in some fish species[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 1989, 6: 1-5.
|
| [11] |
BILLER J D, TAKAHASHI L S. Oxidative stress and fish immune system: phagocytosis and leukocyte respiratory burst activity[J]. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, 2018, 90(4): 3403-3414.
|
| [12] |
NAYAK S K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2010, 41(11): 1553-1573.
|
| [13] |
POND M J, STONE D M, ALDERMAN D J. Comparison of conventional and molecular techniques to investigate the intestinal microflora of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 261(1): 194-203.
|
| [14] |
WU S G, WANG G T, ANGERT E R, et al. Composition, diversity, and origin of the bacterial community in grass carp intestine[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): e30440.
|
| [15] |
YANG Y K, LIN H Z, XING Y F, et al. Response signatures of intestinal microbiota and gene transcription of the tiger grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus to nervous necrosis virus infection[J]. Aquaculture, 2022, 550: 737848.
|
| [16] |
DENG Y Q, ZHANG Y Q, CHEN H X, et al. Gut-liver immune response and gut microbiota profiling reveal the pathogenic mechanisms of Vibrio harveyi in pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂×E. fuscoguttatus♀)[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2020, 11: 607754.
|
| [17] |
FU P P, XIONG F, FENG W W, et al. Effect of intestinal tapeworms on the gut microbiota of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio[J]. Parasites & Vectors, 2019, 12(1): 252.
|
| [18] |
JIANG B, LI Y W, ABDULLAHI A Y, et al. Placemat and rotational culturing: a novel method to control Cryptocaryon irritans infection by removing tomonts[J]. Aquaculture, 2016, 459: 84-88.
|
| [19] |
YIN F, BAO P B, LIU X, et al. Antiparasitic effect of copper alloy surface on Cryptocaryon irritans in aquaculture of Larimichthys crocea[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2019, 85(3): e01982-18.
|
| [20] |
KAWANO F, HIRAZAWA N. Antiparasitic effect of in-feed inhibitors of folic acid synthesis and dihydrofolate reductase against ciliate Cryptocaryon irritans infection in the red sea bream Pagrus major and against ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection in black pop-eyed goldfish Carassius auratus[J]. Aquaculture, 2012, 330: 1-7.
|
| [21] |
HUANG X H, SUN Z Y, GUO G W, et al. Cloning and characterization of a surface antigen CiSA-32.6 from Cryptocaryon irritans[J]. Experimental Parasitology, 2012, 130(3): 189-194.
|
| [22] |
陈睿毅, 楼宝, 詹炜, 等. 小黄鱼亲鱼培育和催产技术的初步试验[J]. 水产科学, 2016, 35(3): 250-254.
|
|
CHEN R Y, LOU B, ZHAN W, et al. Broodstock cultivation and spawning induction techniques in small yellow croaker pseudosciaena Polyactis[J]. Fisheries Science, 2016, 35(3): 250-254. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [23] |
沈宁远. 小黄鱼主要病原荧光定量PCR快速检测方法及病害预警模型建立[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2023.
|
|
SHEN N Y. Rapid detection of main pathogens in Larimichthys polyactis by fluorescence quantitative PCR and the establishment of a disease warning model[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [24] |
EDGAR R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 996-998.
|
| [25] |
DEITCH E A. Bacterial translocation or lymphatic drainage of toxic products from the gut: what is important in human beings?[J]. Surgery, 2002, 131(3): 241-244.
|
| [26] |
MO Z Q, WU H C, HU Y T, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals innate immune mechanisms of an underlying parasite-resistant grouper hybrid (Epinephelus fuscogutatus×Epinephelus lanceolatus)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2021, 119: 67-75.
|
| [27] |
周丽颖, 钟立强, 张世勇, 等. 芽孢杆菌和乳酸菌对斑点叉尾鮰肠道菌群及代谢组学的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2023, 42(10): 1100-1114.
|
|
ZHOU L Y, ZHONG L Q, ZHANG S Y, et al. Effects of Bacillus and Lactobacillus on the intestinal microbiota and metabolomics of channel catfish(Ictalurus punctatus)[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2023, 42(10): 1100-1114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [28] |
郝爽, 张振国, 尤宏争, 等. 复合益生菌对凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群结构的影响[J]. 水产科学, 2022, 41(4): 597-604.
|
|
HAO S, ZHANG Z G, YOU H Z, et al. Effects of compound probiotics on intestinal microflora of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Fisheries Science, 2022, 41(4): 597-604. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [29] |
黄雪敏, 温崇庆, 梁华芳, 等. 健康和发病凡纳滨对虾糠虾期育苗池水体的菌群结构比较[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2018, 38(4): 27-34.
|
|
HUANG X M, WEN C Q, LIANG H F, et al. Comparison of bacterial community structure in larval rearing water between healthy and diseased Litopenaeus vannamei Mysis[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2018, 38(4): 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
 ), 黄慧灵2, 韩明明3,*(
), 黄慧灵2, 韩明明3,*( ), 沈宁远2, 赵旭东2, 楼宝3
), 沈宁远2, 赵旭东2, 楼宝3
 ), HUANG Huiling2, HAN Mingming3,*(
), HUANG Huiling2, HAN Mingming3,*( ), SHEN Ningyuan2, ZHAO Xudong2, LOU Bao3
), SHEN Ningyuan2, ZHAO Xudong2, LOU Bao3