Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2468-2478.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240730
• Animal Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of a double quantitative PCR method for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 and Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei
TAN Rongxiang1( ), SI Guangjie2, SUN Haitao2, XU Ting1,*(
), SI Guangjie2, SUN Haitao2, XU Ting1,*( )
)
- 1. School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Shaoxing University, Shaoxing 312000, Zhejiang, China
2. Zhejiang Huazhen Sci & Tech Co., Ltd., Zhuji 311804, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2024-08-13Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TAN Rongxiang, SI Guangjie, SUN Haitao, XU Ting. Establishment of a double quantitative PCR method for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1 and Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2468-2478.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240730
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequence(5'→3') | 扩增片段长度 Product length/bp | 目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIV1-QF | GCCATTCCCGAACTCACC | 154 | 双重qPCR方法检测DIV1 |
| DIV1-QR | CTTCACCCTTTGCCGCTT | Detection of DIV1 by double qPCR method | |
| SWP-stdF | TTAAGTAATTACGAGTTTGGC | 318 | 构建pMD-SWP标准质粒 |
| SWP-stdR | GTTATTTACAGTTTTGCGTTG | Construction of pMD-SWP standard plasmid | |
| EHP-QF | TGGCGGCACAATTCTCAAACAT | 102 | 双重qPCR方法检测EHP |
| EHP-QR | GCTGTGTCTGTGTAAATATCGTC | Detection of EHP by double qPCR method |
Table 1 Sequences of primers used in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequence(5'→3') | 扩增片段长度 Product length/bp | 目的 Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIV1-QF | GCCATTCCCGAACTCACC | 154 | 双重qPCR方法检测DIV1 |
| DIV1-QR | CTTCACCCTTTGCCGCTT | Detection of DIV1 by double qPCR method | |
| SWP-stdF | TTAAGTAATTACGAGTTTGGC | 318 | 构建pMD-SWP标准质粒 |
| SWP-stdR | GTTATTTACAGTTTTGCGTTG | Construction of pMD-SWP standard plasmid | |
| EHP-QF | TGGCGGCACAATTCTCAAACAT | 102 | 双重qPCR方法检测EHP |
| EHP-QR | GCTGTGTCTGTGTAAATATCGTC | Detection of EHP by double qPCR method |
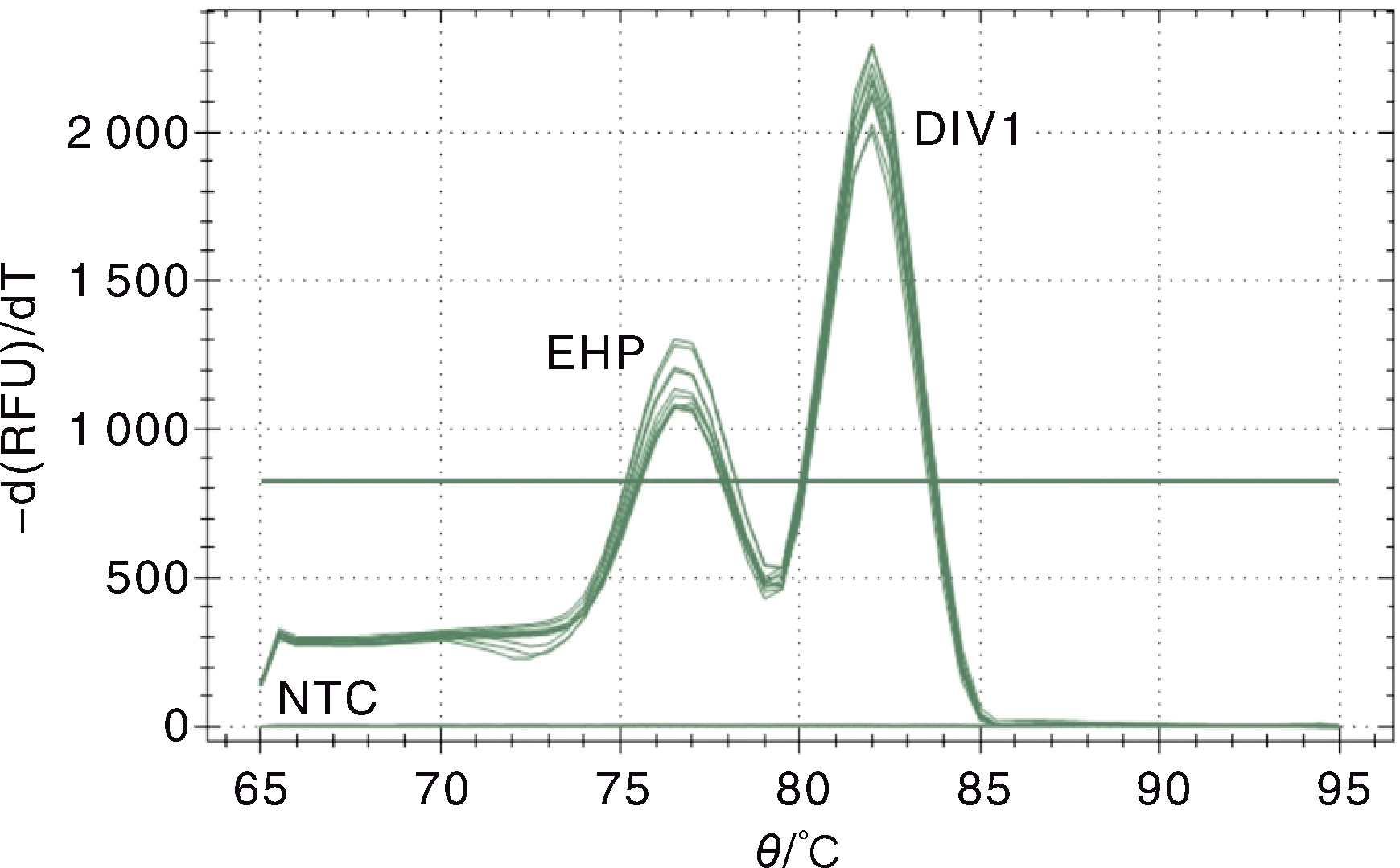
Fig.2 Melting curve of the double SYBR Green I qPCR for Decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) and Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) EHP, The melting curve of EHP standard plasmid pMD-SWP; DIV1,The melting curve of DIV1 standard plasmid pMD-MCP; NTC,Negative control.
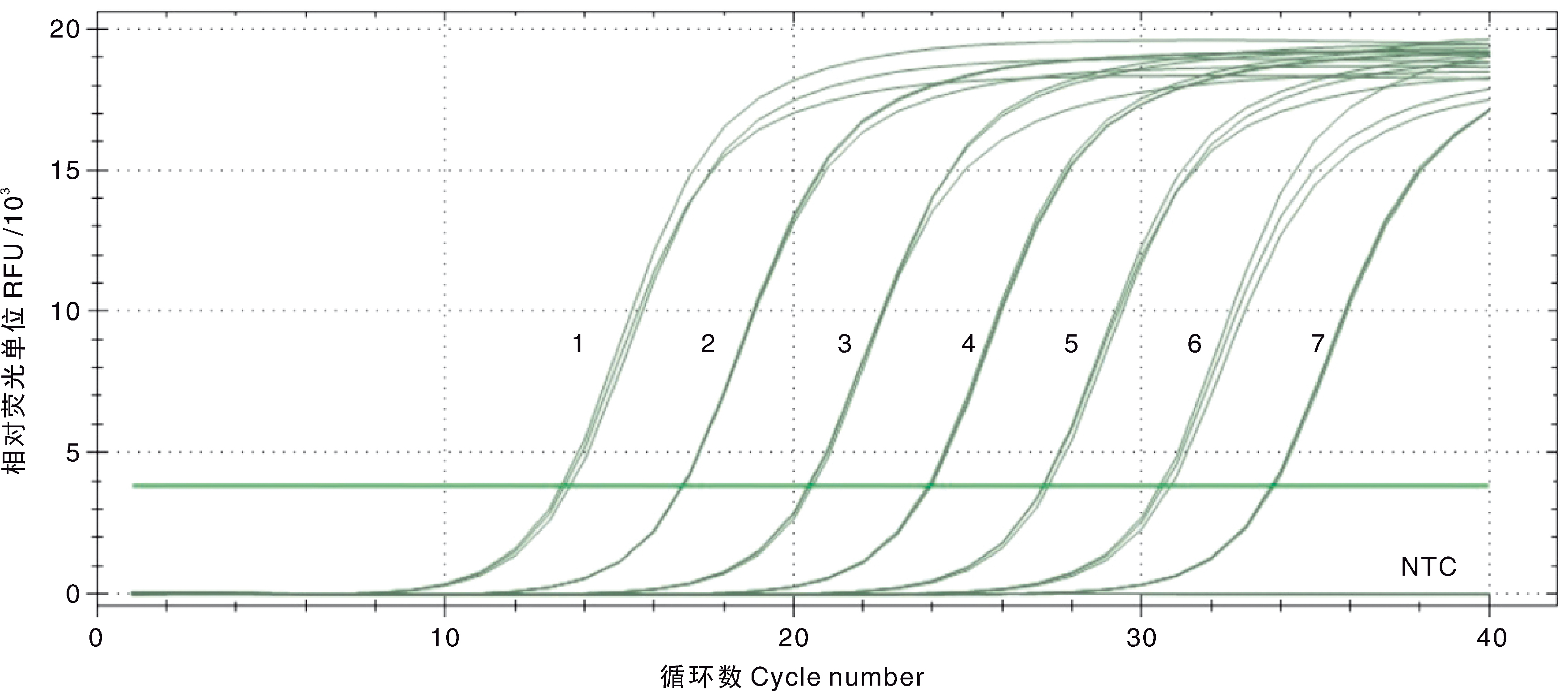
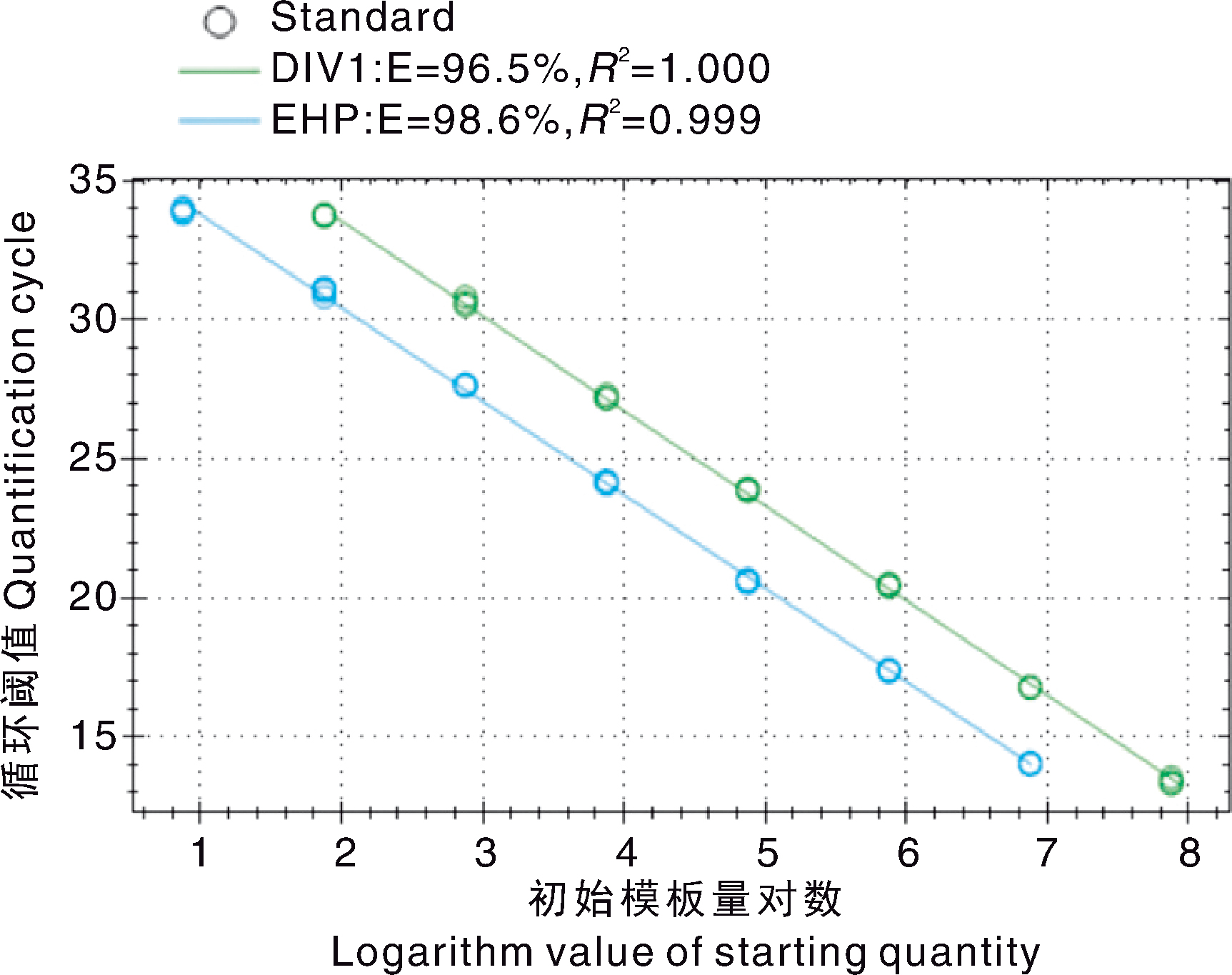
Fig.3 Amplification curve and sensitivity of the double SYBR Green I qPCR for DIV1 1-7, 7.5×107-7.5×101 copies·μL-1 of the standard plasmids pMD-MCP; NTC, Negative control.
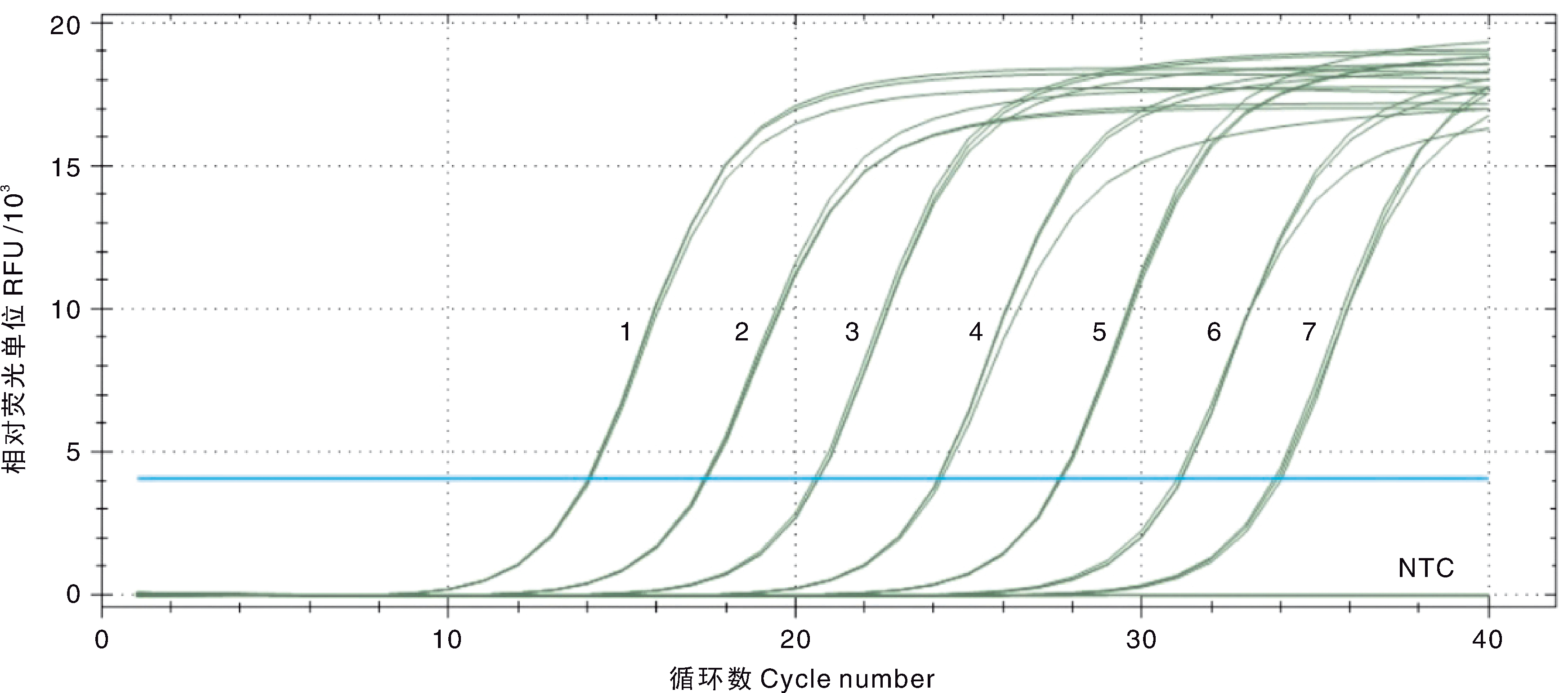
Fig.4 Amplification curve and sensitivity of the double SYBR Green I qPCR for EHP 1-7, 1.5×107-1.5×101 copies·μL-1 of the standard plasmids pMD-SWP; NTC, Negative control.
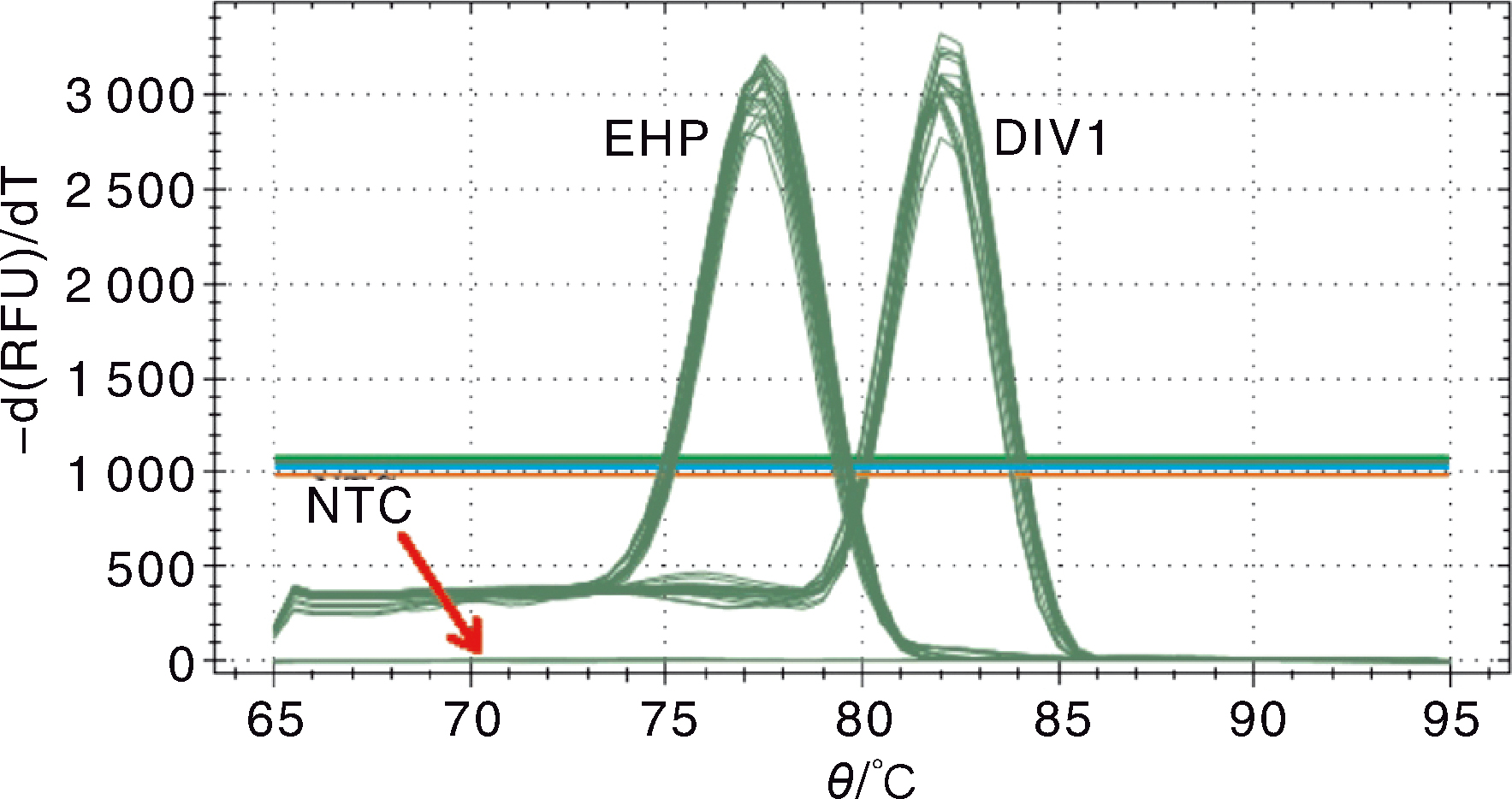
Fig.6 Melting curve for the double SYBR Green I qPCR for DIV1 and EHP EHP, Serial dilution of standard plasmid pMD-SWP; DIV1, Serial dilution of standard plasmid pMD-MCP; NTC, Negative control.
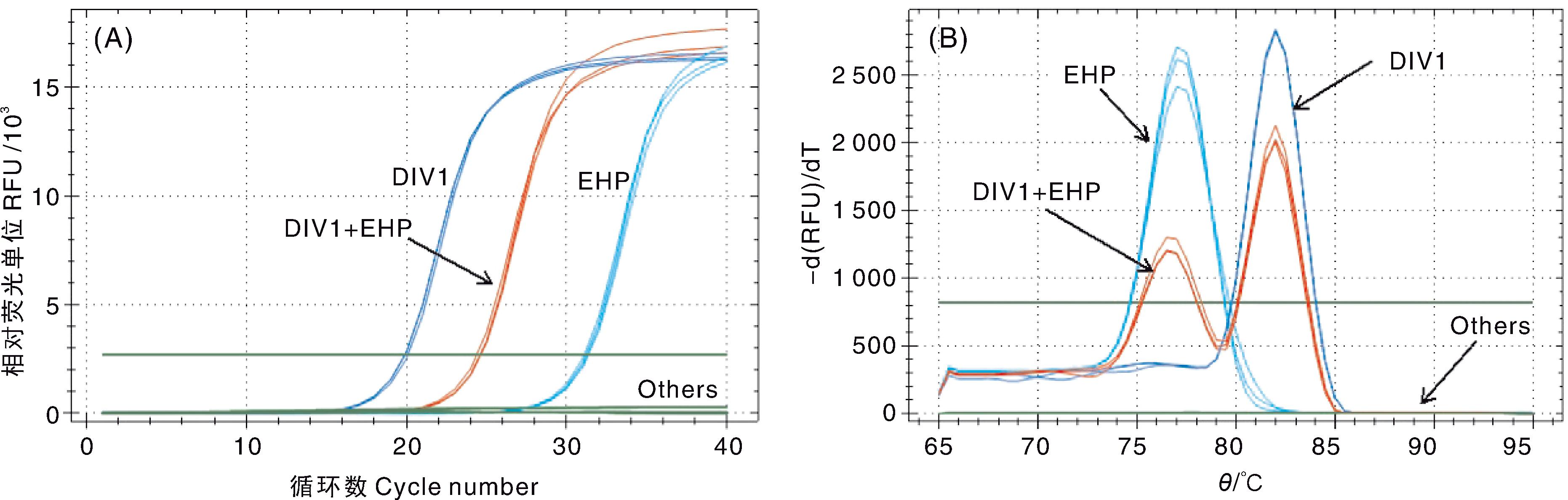
Fig.7 Analysis of the specificity of the double SYBR Green I qPCR A, Amplification curve; B, Melting curve. DIV1, DIV1 positive sample; EHP, EHP positive sample; DIV1+EHP, DIV1 and EHP co-infection sample; Others, Samples infected with other shrimp pathogens, healthy L. vannamei juveniles and negative control.
| pMD-MCP标准品拷贝数 Copies of the standard plasmid | 组内重复Intra-assay variability | 组间重复 Inter-assay variability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1天Day 1 | 第5天Day 5 | 第10天Day 10 | ||||||
| pMD-MCP/(copies·μL-1) | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% |
| 7.5×107 | 13.43±0.12 | 0.92 | 13.77±0.06 | 0.46 | 13.35±0.03 | 0.19 | 13.52±0.21 | 1.52 |
| 7.5×106 | 16.80±0.02 | 0.10 | 17.04±0.12 | 0.68 | 17.00±0.06 | 0.35 | 16.94±0.13 | 0.76 |
| 7.5×105 | 20.46±0.06 | 0.31 | 20.52±0.02 | 0.09 | 20.40±0.02 | 0.10 | 20.46±0.06 | 0.30 |
| 7.5×104 | 23.90±0.05 | 0.21 | 24.35±0.08 | 0.33 | 24.04±0.07 | 0.30 | 24.09±0.21 | 0.86 |
| 7.5×103 | 27.21±0.08 | 0.31 | 27.55±0.06 | 0.21 | 27.54±0.08 | 0.27 | 27.43±0.18 | 0.64 |
| 7.5×102 | 30.65±0.15 | 0.50 | 31.12±0.02 | 0.06 | 30.94±0.02 | 0.05 | 30.90±0.22 | 0.71 |
| 7.5×101 | 33.75±0.04 | 0.12 | 34.12±0.02 | 0.05 | 33.62±0.08 | 0.25 | 33.83±0.23 | 0.68 |
Table 2 Intra-assay and inter-assay variability of the double SYBR Green I qPCR detection assay for DIV1
| pMD-MCP标准品拷贝数 Copies of the standard plasmid | 组内重复Intra-assay variability | 组间重复 Inter-assay variability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1天Day 1 | 第5天Day 5 | 第10天Day 10 | ||||||
| pMD-MCP/(copies·μL-1) | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% |
| 7.5×107 | 13.43±0.12 | 0.92 | 13.77±0.06 | 0.46 | 13.35±0.03 | 0.19 | 13.52±0.21 | 1.52 |
| 7.5×106 | 16.80±0.02 | 0.10 | 17.04±0.12 | 0.68 | 17.00±0.06 | 0.35 | 16.94±0.13 | 0.76 |
| 7.5×105 | 20.46±0.06 | 0.31 | 20.52±0.02 | 0.09 | 20.40±0.02 | 0.10 | 20.46±0.06 | 0.30 |
| 7.5×104 | 23.90±0.05 | 0.21 | 24.35±0.08 | 0.33 | 24.04±0.07 | 0.30 | 24.09±0.21 | 0.86 |
| 7.5×103 | 27.21±0.08 | 0.31 | 27.55±0.06 | 0.21 | 27.54±0.08 | 0.27 | 27.43±0.18 | 0.64 |
| 7.5×102 | 30.65±0.15 | 0.50 | 31.12±0.02 | 0.06 | 30.94±0.02 | 0.05 | 30.90±0.22 | 0.71 |
| 7.5×101 | 33.75±0.04 | 0.12 | 34.12±0.02 | 0.05 | 33.62±0.08 | 0.25 | 33.83±0.23 | 0.68 |
| pMD-SWP标准品拷贝数 Copies of the standard plasmid | 组内重复Intra-assay variability | 组间重复 Inter-assay variability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1天Day 1 | 第5天Day 5 | 第10天Day 10 | ||||||
| pMD-SWP/(copies·μL-1) | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% |
| 1.5×107 | 14.05±0.03 | 0.23 | 14.13±0.04 | 0.30 | 14.17±0.02 | 0.13 | 14.11±0.06 | 0.41 |
| 1.5×106 | 17.40±0.04 | 0.23 | 17.48±0.05 | 0.26 | 17.45±0.05 | 0.29 | 17.45±0.05 | 0.31 |
| 1.5×105 | 20.62±0.07 | 0.32 | 20.75±0.10 | 0.46 | 20.80±0.11 | 0.53 | 20.72±0.12 | 0.55 |
| 1.5×104 | 24.15±0.06 | 0.24 | 24.33±0.13 | 0.55 | 24.47±0.04 | 0.18 | 24.32±0.16 | 0.65 |
| 1.5×103 | 27.64±0.03 | 0.12 | 27.83±0.03 | 0.10 | 27.83±0.02 | 0.05 | 27.77±0.10 | 0.35 |
| 1.5×102 | 31.09±0.07 | 0.21 | 31.31±0.14 | 0.45 | 31.16±0.14 | 0.45 | 31.19±0.14 | 0.45 |
| 1.5×101 | 33.91±0.11 | 0.32 | 33.89±0.20 | 0.58 | 34.60±0.15 | 0.43 | 34.13±0.37 | 1.09 |
Table 3 Intra-assay and inter-assay variability of the double SYBR Green I qPCR detection assay for EHP
| pMD-SWP标准品拷贝数 Copies of the standard plasmid | 组内重复Intra-assay variability | 组间重复 Inter-assay variability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1天Day 1 | 第5天Day 5 | 第10天Day 10 | ||||||
| pMD-SWP/(copies·μL-1) | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% | Cq | CV/% |
| 1.5×107 | 14.05±0.03 | 0.23 | 14.13±0.04 | 0.30 | 14.17±0.02 | 0.13 | 14.11±0.06 | 0.41 |
| 1.5×106 | 17.40±0.04 | 0.23 | 17.48±0.05 | 0.26 | 17.45±0.05 | 0.29 | 17.45±0.05 | 0.31 |
| 1.5×105 | 20.62±0.07 | 0.32 | 20.75±0.10 | 0.46 | 20.80±0.11 | 0.53 | 20.72±0.12 | 0.55 |
| 1.5×104 | 24.15±0.06 | 0.24 | 24.33±0.13 | 0.55 | 24.47±0.04 | 0.18 | 24.32±0.16 | 0.65 |
| 1.5×103 | 27.64±0.03 | 0.12 | 27.83±0.03 | 0.10 | 27.83±0.02 | 0.05 | 27.77±0.10 | 0.35 |
| 1.5×102 | 31.09±0.07 | 0.21 | 31.31±0.14 | 0.45 | 31.16±0.14 | 0.45 | 31.19±0.14 | 0.45 |
| 1.5×101 | 33.91±0.11 | 0.32 | 33.89±0.20 | 0.58 | 34.60±0.15 | 0.43 | 34.13±0.37 | 1.09 |
| 巢式PCR检测 Detection by nested-PCR | 双重SYBR Green I qPCR检测Detection by double SYBR Green I qPCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性Positive | 阴性Negative | 总计Total | ||
| DIV1 | 阳性Positive | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| 阴性Negative | 2 | 49 | 51 | |
| 总计Total | 6 | 49 | 55 | |
| EHP | 阳性Positive | 9 | 0 | 9 |
| 阴性Negative | 0 | 46 | 46 | |
| 总计Total | 9 | 46 | 55 | |
Table 4 Detection results of clinical samples by nested-PCR and double SYBR Green I qPCR
| 巢式PCR检测 Detection by nested-PCR | 双重SYBR Green I qPCR检测Detection by double SYBR Green I qPCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性Positive | 阴性Negative | 总计Total | ||
| DIV1 | 阳性Positive | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| 阴性Negative | 2 | 49 | 51 | |
| 总计Total | 6 | 49 | 55 | |
| EHP | 阳性Positive | 9 | 0 | 9 |
| 阴性Negative | 0 | 46 | 46 | |
| 总计Total | 9 | 46 | 55 | |
| [1] | QIU L, CHEN M M, WAN X Y, et al. Characterization of a new member of Iridoviridae, Shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV), found in white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 11834. |
| [2] | XU L, WANG T, LI F, et al. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a new pathogenic iridovirus from redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2016, 120(1): 17-26. |
| [3] | LI F, XU L M, YANG F. Genomic characterization of a novel iridovirus from redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus: evidence for a new genus within the family Iridoviridae[J]. Journal of General Virology, 2017, 98(10): 2589-2595. |
| [4] | QIU L, CHEN M M, WANG R Y, et al. Complete genome sequence of shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV) isolated from white leg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Archives of Virology, 2018, 163(3): 781-785. |
| [5] | CHEN X, QIU L, WANG H L, et al. Susceptibility of Exopalaemon carinicauda to the infection with shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus (SHIV 20141215), a strain of decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(4): 387. |
| [6] | QIU L, CHEN X, ZHAO R H, et al. Description of a natural infection with decapod iridescent virus 1 in farmed giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(4): 354. |
| [7] | 潘长坤, 袁会芳, 王甜甜, 等. 红螯螯虾虹彩病毒在两种螃蟹内的研究[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2017, 36(1): 82-86. |
| PAN C K, YUAN H F, WANG T T, et al. Study of Cherax quadricarinatus iridescent virus in two crabs[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | SRISALA J, SANGUANRUT P, THAIUE D, et al. Infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV) and decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) detected in captured, wild Penaeus monodon[J]. Aquaculture, 2021, 545: 737262. |
| [9] | CHAYABURAKUL K, NASH G, PRATANPIPAT P, et al. Multiple pathogens found in growth-retarded black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon cultivated in Thailand[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2004, 60: 89-96. |
| [10] | TOURTIP S, WONGTRIPOP S, STENTIFORD G D, et al. Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei sp. nov. (Microsporida: Enterocytozoonidae), a parasite of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon(Decapoda: Penaeidae): fine structure and phylogenetic relationships[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2009, 102(1): 21-29. |
| [11] | ARANGUREN L F, HAN J E, TANG K F J. Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) is a risk factor for acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) and septic hepatopancreatic necrosis (SHPN) in the Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei[J]. Aquaculture, 2017, 471: 37-42. |
| [12] | CHAIJARASPHONG T, MUNKONGWONGSIRI N, STENTIFORD G D, et al. The shrimp microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP): biology, pathology, diagnostics and control[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2021, 186: 107458. |
| [13] | TANG K F J, HAN J E, ARANGUREN L F, et al. Dense populations of the microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) in feces of Penaeus vannamei exhibiting white feces syndrome and pathways of their transmission to healthy shrimp[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2016, 140: 1-7. |
| [14] | SALACHAN P V, JAROENLAK P, THITAMADEE S, et al. Laboratory cohabitation challenge model for shrimp hepatopancreatic microsporidiosis (HPM) caused by Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP)[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2017, 13(1): 9. |
| [15] | CARO L F A, MAI H N, SCHOFIELD P, et al. A laboratory challenge model for evaluating Enyterocytozoon hepatopenaei susceptibility in selected lines of Pacific whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2023, 196: 107853. |
| [16] | 刘珍, 张庆利, 万晓媛, 等. 虾肝肠胞虫(Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei)实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及对虾样品的检测[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(2): 119-126. |
| LIU Z, ZHANG Q L, WAN X Y, et al. Development of real-time PCR assay for detecting microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei and the application in shrimp samples with different growth rates[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(2): 119-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | RAJENDRAN K V, SHIVAM S, EZHIL PRAVEENA P, et al. Emergence of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) in farmed Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei in India[J]. Aquaculture, 2016, 454: 272-280. |
| [18] | BIJU N, SATHIYARAJ G, RAJ M, et al. High prevalence of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in shrimps Penaeus monodon and Litopenaeus vannamei sampled from slow growth ponds in India[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2016, 120(3): 225-230. |
| [19] | WAN SAJIRI W M H, KUA B C, BORKHANUDDIN M H. Detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) (microsporidia) in several species of potential macrofauna-carriers from shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) ponds in Malaysia[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2023,198: 107910. |
| [20] | TANG K F J, PANTOJA C R, REDMAN R M, et al. Development of in situ hybridization and PCR assays for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP), a microsporidian parasite infecting penaeid shrimp[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2015, 130: 37-41. |
| [21] | 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站. 2020我国重要水生动物疫病状况分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. |
| [22] | JAROENLAK P, SANGUANRUT P, WILLIAMS B A P, et al. A nested PCR assay to avoid false positive detection of the microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) in environmental samples in shrimp farms[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0166320. |
| [23] | CHEN Z W, HUANG J, ZHANG F, et al. Detection of shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus by recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2020, 49: 101475. |
| [24] | LI G, CONG F, CAI W Y, et al. Development of a recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) fluorescence assay for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP)[J]. Aquaculture Reports, 2021, 19: 100584. |
| [25] | TONG G X, YIN W L, WU X Q, et al. Rapid detection of decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1) by recombinase polymerase amplification[J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2022, 300: 114362. |
| [26] | T S K, A N K, J J S R, et al. Visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for the rapid diagnosis of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei(EHP) infection[J]. Parasitology Research, 2018, 117(5): 1485-1493. |
| [27] | GONG H Y, LI Q Y, ZHANG H, et al. Development and comparison of qPCR and qLAMP for rapid detection of the decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1)[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2021, 182: 107567. |
| [28] | LIU Y M, QIU L, SHENG A Z, et al. Quantitative detection method of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei using TaqMan probe real-time PCR[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2018, 151: 191-196. |
| [29] | QIU L, CHEN M M, WAN X Y, et al. Detection and quantification of shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus by TaqMan probe based real-time PCR[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2018, 154: 95-101. |
| [30] | XU T, TAN R X, ZHU Y T, et al. Establishment of a SYBR Green I-based real-time PCR for the detection of decapod iridescent virus 1[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2023, 201: 107998. |
| [31] | QIU L, CHEN X, GUO X M, et al. A TaqMan probe based real-time PCR for the detection of Decapod iridescent virus 1[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2020, 173: 107367. |
| [32] | 侯月娥, 曾俊霞, 蓝间媛, 等. EHP、SHIV双重TaqMan实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的构建及应用[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2022, 30(1): 112-119. |
| HOU Y E, ZENG J X, LAN J Y, et al. Development of a duplex TaqMan real-time PCR assay for detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei and shrimp hemocyte iridovirus[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 2022, 30(1): 112-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 汪浩, 汪玮, 施慧, 等. 基于孢子壁蛋白基因靶点的虾肝肠胞虫实时荧光定量PCR体系的构建及应用[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020(6): 477-483. |
| WANG H, WANG W, SHI H, et al. Establishment and application of a real-time PCR assay targeted on the spore wall protein gene for detecting microsporidian Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University(Natural Science), 2020(6): 477-483. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | SHEN Weifeng, GUO Qi, LIU Li, NIU Baolong, WENG Hongbiao, LOU Bao. Cloning, expression and application in detection of SWP2 gene in Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 993-1000. |
| [2] | ZHANG Hongyu, WANG Haibo, YANG Yibin, ZHAO Mingjun, XIA Lei. Ecological safety assessment of Bcillus cereus D7 isolated from shrimp [J]. , 2018, 30(9): 1585-1591. |
| [3] | HUANG Zhanrui, WANG Yaling, WANG Xiaobo, MO Bing, QIU Mei, SUN Lijun, CHEN Kangjian, LIU Jian. Effect of masked T-2 toxin residues in Litopenaeus vannamei on routine blood and serum biochemical indexes of mice [J]. , 2017, 29(7): 1110-1118. |
| [4] | ZHU Ning\|yu, KONG Lei, ZHENG Tian\|lun. Analysis on presence of virus in Penaeus vannamei shrimp larvae in Zhejiang Province in 2013 [J]. , 2015, 27(5): 756-. |
| [5] | WANG Xin;WU Yi\|fei;YAO Xiao\|hong;LIU Yong;SUN Hong;TANG Jiang\|wu*. Effect of probiotics on water quality and bacterial community in shrimp pools at later stage of cultivation [J]. , 2014, 26(1): 0-47. |
| [6] | XIANG Xiu-ping;HAN Jian-zhong*. Comparative studies on 2-DE protein patterns of shrimp meats [J]. , 2011, 23(1): 74-78. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||