Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2602-2614.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241114
• Food Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization of the color protection process for pear-Dendrobium compound puree and the influence of sterilization methods on its storage quality
GAN Yuping1( ), GONG Weiqi2, ZHOU Chenyang1, LI Chuntian3, WANG Junwen1, LIU Chenxing1, XIA Qile1, LU Shengmin1,*(
), GONG Weiqi2, ZHOU Chenyang1, LI Chuntian3, WANG Junwen1, LIU Chenxing1, XIA Qile1, LU Shengmin1,*( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory for Quality and Safety of Agro-Products, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Logistics and Processing of Fresh Food, Key Laboratory of Postharvest Handling of Fruits, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Institute of Food Science, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
2. Zhejiang Tiefengtang Health Technology Co., Ltd., Yueqing 325615, Zhejiang, China
3. Wuyi Tianyu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd., Wuyi 321205,Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2024-12-22Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GAN Yuping, GONG Weiqi, ZHOU Chenyang, LI Chuntian, WANG Junwen, LIU Chenxing, XIA Qile, LU Shengmin. Optimization of the color protection process for pear-Dendrobium compound puree and the influence of sterilization methods on its storage quality[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2602-2614.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241114
| 水平 Level | 因素Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A)柠檬酸 质量分数 Citric acid mass fraction | (B)抗坏血酸 质量分数 Ascorbic acid mass fraction | (C)氯化钠 质量分数 Sodium chloride mass fraction | |
| 1 | 0.6 | 0.02 | 0.6 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.04 | 0.9 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 0.06 | 1.2 |
Table 1 Orthogonal experimental design %
| 水平 Level | 因素Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A)柠檬酸 质量分数 Citric acid mass fraction | (B)抗坏血酸 质量分数 Ascorbic acid mass fraction | (C)氯化钠 质量分数 Sodium chloride mass fraction | |
| 1 | 0.6 | 0.02 | 0.6 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.04 | 0.9 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 0.06 | 1.2 |
| 项目 Item | 评价标准 Evaluation criteria | 分值 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 色泽(25分) | 颜色暗淡,呈淡粉红色,无光泽The color is dull, pale pink, and matte | 1~7 |
| Color (25 points) | 有光泽,呈粉红色Glossy and pink | 8~15 |
| 颜色呈光亮的粉红色The color is a bright pink | 16~25 | |
| 酸甜度(25分) | 过酸或者过甜Too sour or too sweet | 1~7 |
| Sweetness and sourness (25 points) | 酸味或者甜味清淡The taste is light and sour or sweet | 8~15 |
| 酸味中带甜,口感适宜The sour taste is sweet and sour, and the taste is suitable | 16~25 | |
| 组织状态(25分) | 果泥有可见颗粒,组织不均匀The puree has visible particles and uneven tissue | 1~7 |
| Tissue status (25 points) | 果泥细腻,组织稍不均匀The puree is delicate and the tissue is slightly uneven | 8~15 |
| 果泥细腻,组织均匀The puree is delicate and evenly organized | 16~25 | |
| 香气(25分) | 没有梨果香味No pear fruit scent | 1~7 |
| Aroma (25 points) | 有淡淡梨果香味,无其他香味It has a faint pear fruit fragrance and no other fragrance | 8~15 |
| 有清新的混合水果香气There is a fresh aroma of mixed fruits | 16~25 |
Table 2 Sensory evaluation criteria
| 项目 Item | 评价标准 Evaluation criteria | 分值 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 色泽(25分) | 颜色暗淡,呈淡粉红色,无光泽The color is dull, pale pink, and matte | 1~7 |
| Color (25 points) | 有光泽,呈粉红色Glossy and pink | 8~15 |
| 颜色呈光亮的粉红色The color is a bright pink | 16~25 | |
| 酸甜度(25分) | 过酸或者过甜Too sour or too sweet | 1~7 |
| Sweetness and sourness (25 points) | 酸味或者甜味清淡The taste is light and sour or sweet | 8~15 |
| 酸味中带甜,口感适宜The sour taste is sweet and sour, and the taste is suitable | 16~25 | |
| 组织状态(25分) | 果泥有可见颗粒,组织不均匀The puree has visible particles and uneven tissue | 1~7 |
| Tissue status (25 points) | 果泥细腻,组织稍不均匀The puree is delicate and the tissue is slightly uneven | 8~15 |
| 果泥细腻,组织均匀The puree is delicate and evenly organized | 16~25 | |
| 香气(25分) | 没有梨果香味No pear fruit scent | 1~7 |
| Aroma (25 points) | 有淡淡梨果香味,无其他香味It has a faint pear fruit fragrance and no other fragrance | 8~15 |
| 有清新的混合水果香气There is a fresh aroma of mixed fruits | 16~25 |
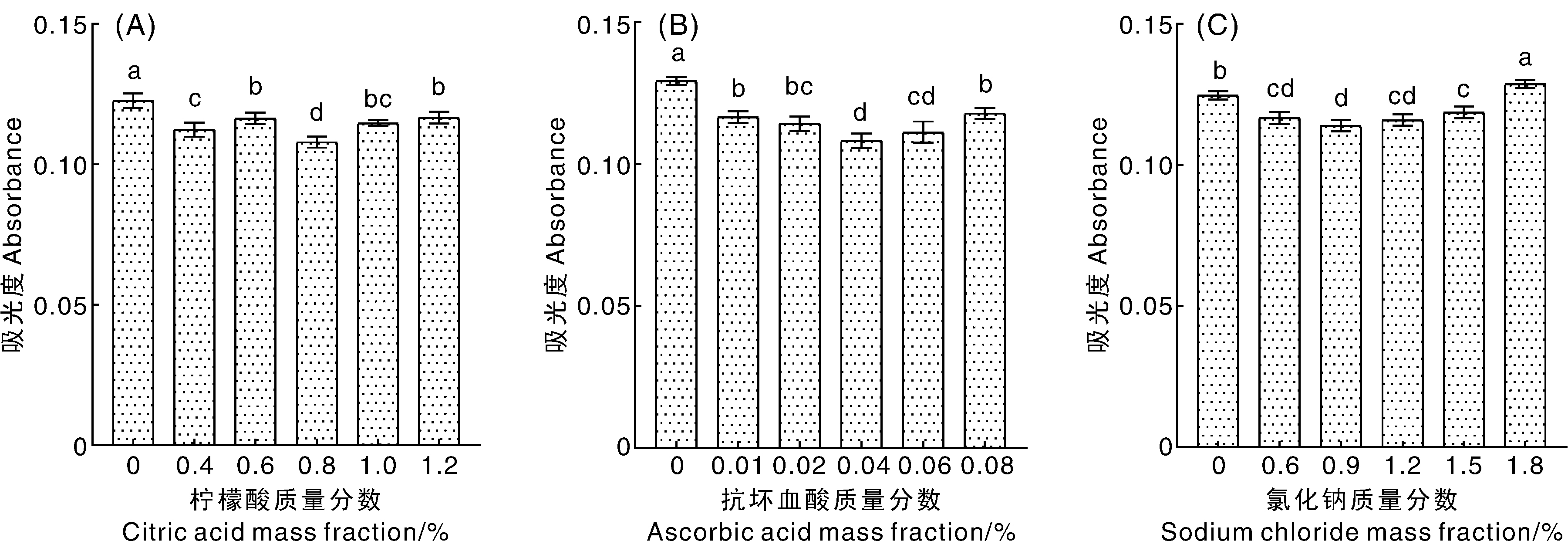
Fig.1 Results of single factor test of inhibitor on browning of pear puree Bars marked without the same lowercase letter indicated significant differences at p<0.05.The same as below.
| 实验号 Experiment number | A/% | B/% | C/% | 吸光度 Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.079 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.084 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.095 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.105 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.099 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.112 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.110 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.106 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.125 |
Table 3 Result of orthogonal experiment
| 实验号 Experiment number | A/% | B/% | C/% | 吸光度 Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.079 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.084 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0.095 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.105 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.099 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.112 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0.110 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.106 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.125 |
| 因素 Factor | k1 | k2 | k3 | R | 最优水平 Optimal level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.086 | 0.105 | 0.114 | 0.028 | 1 |
| B | 0.098 | 0.096 | 0.111 | 0.014 | 2 |
| C | 0.099 | 0.105 | 0.101 | 0.006 | 1 |
Table 4 Result of range analysis
| 因素 Factor | k1 | k2 | k3 | R | 最优水平 Optimal level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.086 | 0.105 | 0.114 | 0.028 | 1 |
| B | 0.098 | 0.096 | 0.111 | 0.014 | 2 |
| C | 0.099 | 0.105 | 0.101 | 0.006 | 1 |
| 处理条件 Processing conditions | 时间 Time/d | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 0 | 30.21±0.01 Cl | 15.98±0.01 Bn | 29.37±0.01 Bk | 0 |
| 巴氏杀菌Pasteurization | 0 | 30.02±0.01 Dn | 15.89±0.01 Co | 29.39±0.04 Bk | 0.21 |
| 2 | 30.31±0.01 k | 16.00±0.03 n | 29.40±0.06 k | 0.11 | |
| 4 | 31.52±0.01 e | 16.49±0.01 h | 30.30±0.03 h | 1.69 | |
| 6 | 31.83±0.05 b | 16.48±0.08 hi | 30.41±0.11 fg | 1.99 | |
| 8 | 31.96±0.02 a | 16.35±0.00 l | 30.05±0.03 j | 1.91 | |
| 10 | 31.04±0.02 h | 16.54±0.02 g | 30.19±0.03 i | 1.29 | |
| 微波杀菌 | 0 | 30.68±0.01 Bj | 15.91±0.01 Co | 29.39±0.01 Bk | 0.48 |
| Microwave sterilization | 2 | 30.12±0.01 m | 16.11±0.01 m | 29.36±0.02 k | 0.16 |
| 4 | 31.59±0.01 d | 16.39±0.01 k | 30.33±0.06 gh | 1.73 | |
| 6 | 31.45±0.01 f | 16.56±0.01 g | 30.52±0.04 e | 1.79 | |
| 8 | 31.63±0.01 c | 16.43±0.01 j | 30.13±0.02 ij | 1.67 | |
| 10 | 31.36±0.03 g | 16.45±0.01 ij | 30.20±0.11 i | 1.49 | |
| 高温蒸汽杀菌 | 0 | 31.97±0.01 Aa | 20.50±0.02 Af | 32.07±0.07 Ab | 5.55 |
| High-temperature | 2 | 29.12±0.01 q | 21.94±0.01 a | 30.47±0.03 ef | 6.16 |
| steam sterilization | 4 | 31.37±0.01 g | 21.22±0.01 d | 32.18±0.02 a | 6.06 |
| 6 | 30.94±0.01 i | 21.25±0.00 c | 31.86±0.09 c | 6.05 | |
| 8 | 29.88±0.01 o | 21.33±0.01 b | 30.76±0.03 d | 5.54 | |
| 10 | 29.84±0.02 p | 20.95±0.01 e | 30.42±0.05 fg | 5.09 |
Table 5 Color difference changes of pear-Dendrobium compound puree under different sterilization treatments during storage
| 处理条件 Processing conditions | 时间 Time/d | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 0 | 30.21±0.01 Cl | 15.98±0.01 Bn | 29.37±0.01 Bk | 0 |
| 巴氏杀菌Pasteurization | 0 | 30.02±0.01 Dn | 15.89±0.01 Co | 29.39±0.04 Bk | 0.21 |
| 2 | 30.31±0.01 k | 16.00±0.03 n | 29.40±0.06 k | 0.11 | |
| 4 | 31.52±0.01 e | 16.49±0.01 h | 30.30±0.03 h | 1.69 | |
| 6 | 31.83±0.05 b | 16.48±0.08 hi | 30.41±0.11 fg | 1.99 | |
| 8 | 31.96±0.02 a | 16.35±0.00 l | 30.05±0.03 j | 1.91 | |
| 10 | 31.04±0.02 h | 16.54±0.02 g | 30.19±0.03 i | 1.29 | |
| 微波杀菌 | 0 | 30.68±0.01 Bj | 15.91±0.01 Co | 29.39±0.01 Bk | 0.48 |
| Microwave sterilization | 2 | 30.12±0.01 m | 16.11±0.01 m | 29.36±0.02 k | 0.16 |
| 4 | 31.59±0.01 d | 16.39±0.01 k | 30.33±0.06 gh | 1.73 | |
| 6 | 31.45±0.01 f | 16.56±0.01 g | 30.52±0.04 e | 1.79 | |
| 8 | 31.63±0.01 c | 16.43±0.01 j | 30.13±0.02 ij | 1.67 | |
| 10 | 31.36±0.03 g | 16.45±0.01 ij | 30.20±0.11 i | 1.49 | |
| 高温蒸汽杀菌 | 0 | 31.97±0.01 Aa | 20.50±0.02 Af | 32.07±0.07 Ab | 5.55 |
| High-temperature | 2 | 29.12±0.01 q | 21.94±0.01 a | 30.47±0.03 ef | 6.16 |
| steam sterilization | 4 | 31.37±0.01 g | 21.22±0.01 d | 32.18±0.02 a | 6.06 |
| 6 | 30.94±0.01 i | 21.25±0.00 c | 31.86±0.09 c | 6.05 | |
| 8 | 29.88±0.01 o | 21.33±0.01 b | 30.76±0.03 d | 5.54 | |
| 10 | 29.84±0.02 p | 20.95±0.01 e | 30.42±0.05 fg | 5.09 |
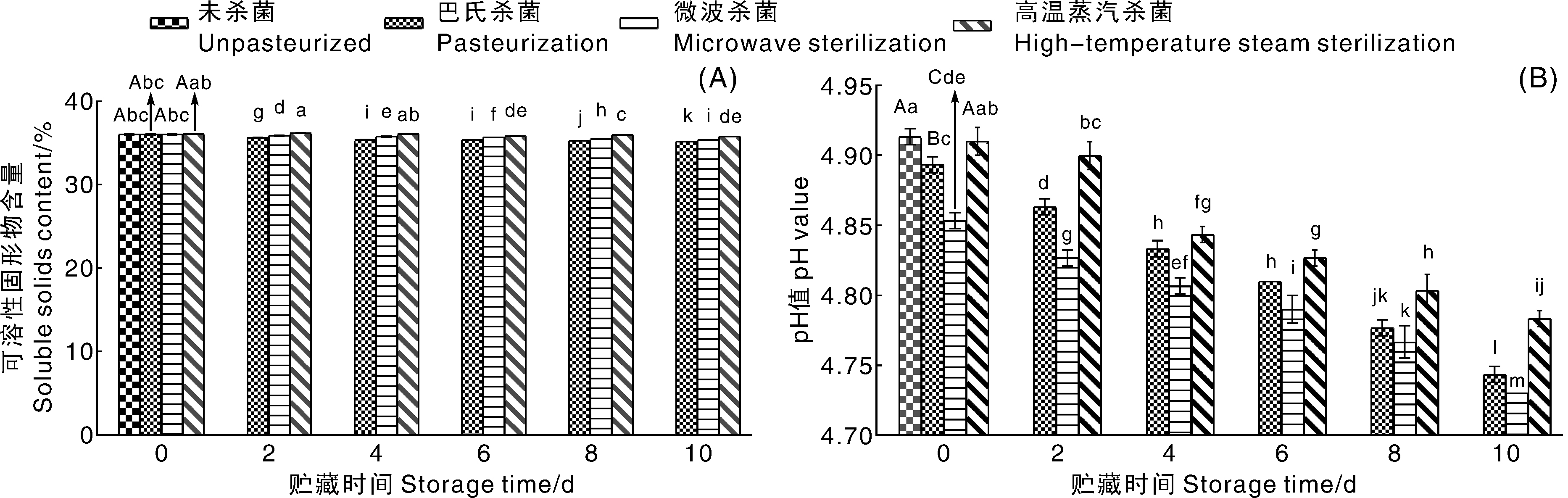
Fig.2 Total soluble solid content (A) and pH value (B) of pear-Dendrobium compound puree treated with different sterilization treatments during storage Bars marked without the same uppercase letters of each column indicated significant (p<0.05) difference between the unsterilized and the three sterilized samples at the initial storage time (0 d), and bars marked without the same lowercase letters of each column indicated significant difference among the three sterilized samples at different storage times. The same as below.
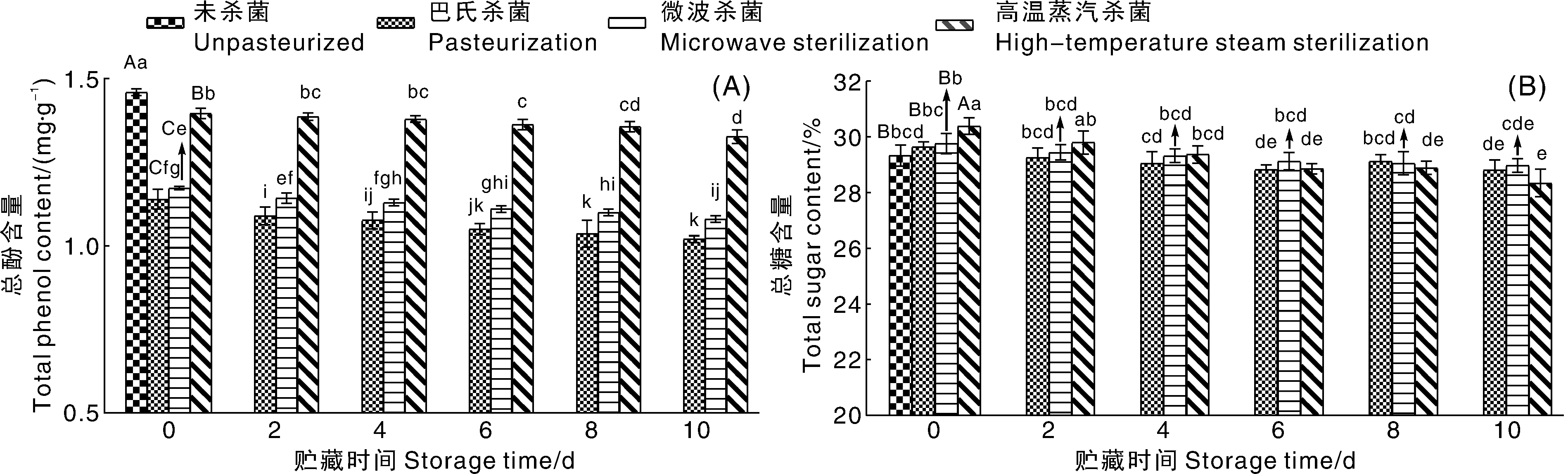
Fig.3 Total phenol content (A) and total sugar content (B) of pear-Dendrobium compound puree treated with different sterilization treatments during storage
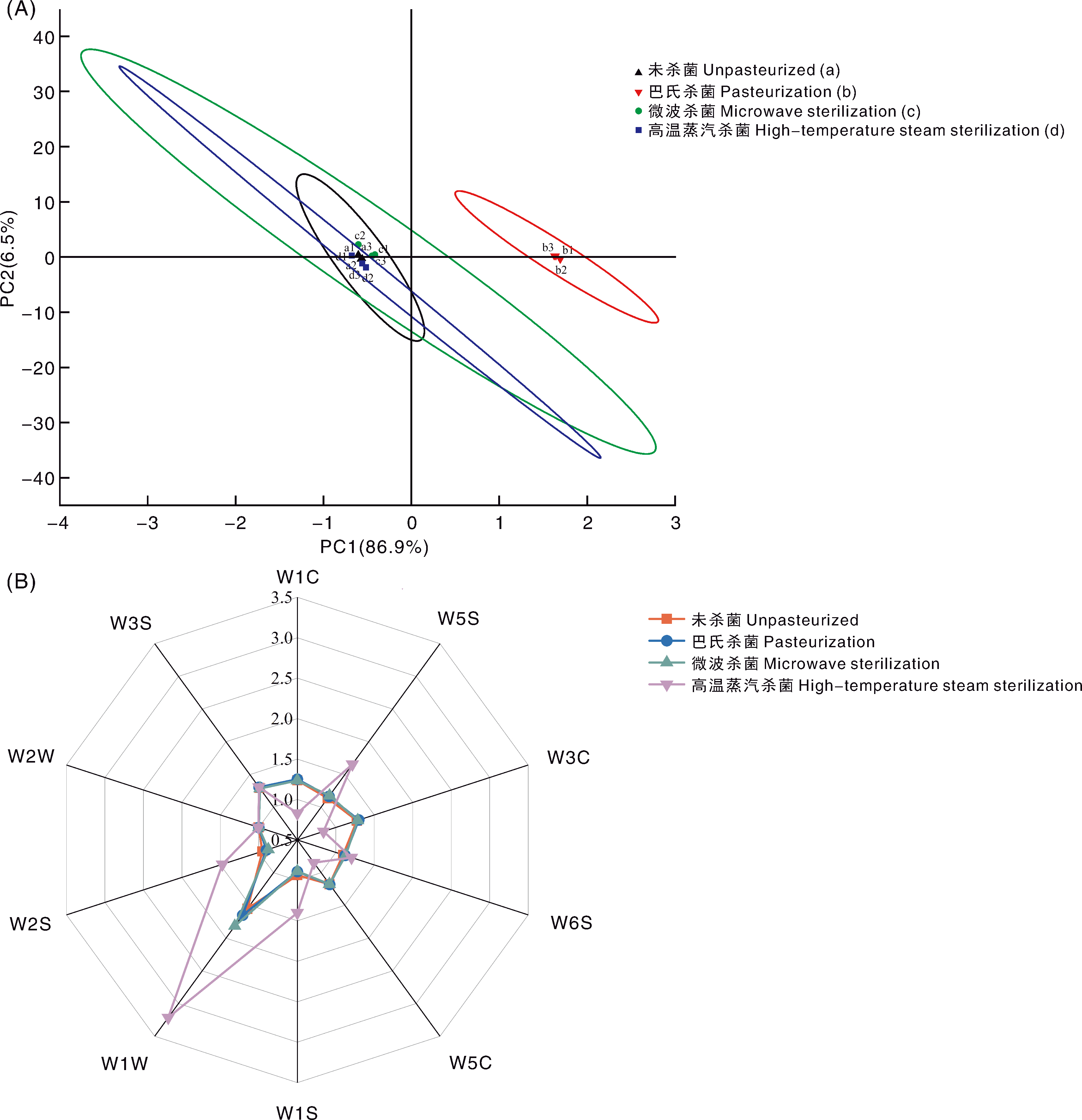
Fig.4 Flavor of pear-Dendrobium compound puree under different sterilization treatments (A) Principal component analysis; (B) Sensor radar map. W1C, Aromatic compounds; W5S, Nitrogen oxides; W3C, Ammonia and aromatic molecules; W6S, Hydrides; W5C, Alkenes, aromatic and polar molecules; W1S, Alkanes; W1W, Sulfur compounds; W2S, Alcohols and some aromatic compounds; W2W, Aromatic compounds and sulfur-containing organic compounds; W3S, Alkanes and aliphatic compounds.
| 处理条件 Processing condition | 时间 Time/d | 菌落总数 Total number of colonies/(CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 未处理Not processed | 0 | 13.33±5.78 bc |
| 巴氏杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| Pasteurization | 2 | ND |
| 4 | ND | |
| 6 | 6.67±11.55 cd | |
| 8 | 16.67±5.78 b | |
| 10 | 26.67±5.78 a | |
| 微波杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| Microwave sterilization | 2 | ND |
| 4 | 3.33±5.78 d | |
| 6 | 6.67±5.78 cd | |
| 8 | 13.33±11.55 bc | |
| 10 | 16.67±5.78 b | |
| 高温蒸汽杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| High-temperature | 2 | ND |
| steam sterilization | 4 | ND |
| 6 | ND | |
| 8 | ND | |
| 10 | ND |
Table 6 Total number of bacterial colonies of pear-Dendrobium compound puree after different sterilization treatments during storage
| 处理条件 Processing condition | 时间 Time/d | 菌落总数 Total number of colonies/(CFU·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 未处理Not processed | 0 | 13.33±5.78 bc |
| 巴氏杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| Pasteurization | 2 | ND |
| 4 | ND | |
| 6 | 6.67±11.55 cd | |
| 8 | 16.67±5.78 b | |
| 10 | 26.67±5.78 a | |
| 微波杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| Microwave sterilization | 2 | ND |
| 4 | 3.33±5.78 d | |
| 6 | 6.67±5.78 cd | |
| 8 | 13.33±11.55 bc | |
| 10 | 16.67±5.78 b | |
| 高温蒸汽杀菌 | 0 | ND |
| High-temperature | 2 | ND |
| steam sterilization | 4 | ND |
| 6 | ND | |
| 8 | ND | |
| 10 | ND |
| [1] | 墨菲. 致力深耕中国婴幼儿辅食市场嘉宝有机果泥正式国产上市[J]. 中国食品, 2021(10): 156. |
| MO F. Committed to deepening the baby food supplement market in China, Jiabao organic puree was officially listed in China[J]. China Food, 2021(10): 156. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 李慧芸, 张宝善. 果汁非酶褐变的机制及控制措施[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2005, 26(6): 145-147. |
| LI H Y, ZHANG B S. Nonenzymatic browning mechanism and controlling measurements of fruit juice[J]. Food Research and Development, 2005, 26(6): 145-147. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 王娟, 王然, 王佳, 等. 七种日韩梨果泥贮藏稳定性研究[J]. 食品科学, 2011, 32(16): 357-360. |
| WANG J, WANG R, WANG J, et al. Stability of seven kinds of Japanese and Korean pear purees during storage[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(16): 357-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 刘红锦, 徐为民, 王静, 等. 果蔬的褐变及其控制方法[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2008, 29(4): 159-162. |
| LIU H J, XU W M, WANG J, et al. Browning mechanism and inhibition of fruits and vegetables[J]. Food Research and Development, 2008, 29(4): 159-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 葛可佑. 中国营养科学全书[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004: 255-257. |
| [6] | 潘叙恩, 周秀清, 蒋志红, 等. 雪梨枇杷低糖果酱的研制[J]. 现代食品科技, 2011, 27(6): 695-697. |
| PAN X E, ZHOU X Q, JIANG Z H, et al. Preparation of low sugar jam using loquat fruit and pear[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2011, 27(6): 695-697. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 王文辉, 贾晓辉, 杜艳民, 等. 我国梨果生产与贮藏现状、存在的问题与发展趋势[J]. 保鲜与加工, 2013, 13(5): 1-8. |
| WANG W H, JIA X H, DU Y M, et al. Current situation, problems and development trend of production and storage of pear in China[J]. Storage and Process, 2013, 13(5): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 何近刚, 冯云霄, 李丽梅, 等. ‘黄冠’梨果实采收和贮藏品质评价体系的建立[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2019, 42(4): 35-43. |
| HE J G, FENG Y X, LI L M, et al. Establishment of evaluation system for fruit quality and storage quality of ‘Huangguan’ pear[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2019, 42(4): 35-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 李玲, 邓晓兰, 赵兴兵, 等. 铁皮石斛化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 肿瘤药学, 2011, 1(2): 90-94. |
| LI L, DENG X L, ZHAO X B, et al. Advances in studies on chemical constituents in Dendrobium candidum and their pharmacological effects[J]. Anti-tumor Pharmacy, 2011, 1(2): 90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 蓝希明, 赵益, 王高玉, 等. 铁皮石斛抗肿瘤作用机制的研究进展与思考[J]. 江西中医药, 2017, 48(4): 68-70. |
| LAN X M, ZHAO Y, WANG G Y, et al. Research progress and thinking on anti-tumor mechanism of Dendrobium candidum[J]. Jiangxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 48(4): 68-70. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | KIM S, JO K, BYUN B S, et al. Chemical and biological properties of puffed Dendrobium officinale extracts: evaluation of antioxidant and anti-fatigue activities[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2020, 73: 104144. |
| [12] | WEI W, LI Z P, ZHU T, et al. Anti-fatigue effects of the unique polysaccharide marker of Dendrobium officinale on BALB/c mice[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(1): 155. |
| [13] | 王再花, 叶广英, 曾灿彪, 等. 铁皮石斛饮料杀菌工艺研制及品质分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(16): 124-130. |
| WANG Z H, YE G Y, ZENG C B, et al. Dendrobium officinale beverage: sterilization process and quality analysis[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(16): 124-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | DO NASCIMENTO R F, CANTERI M H G, RODRIGUES S Á, et al. Use of sodium metabisulphite and ascorbic acid to control browning in ready-to-eat processed potatoes during prolonged storage[J]. Potato Research, 2020, 63(4): 615-625. |
| [15] | ZHOU L, LIU W, STOCKMANN R, et al. Effect of citric acid and high pressure thermal processing on enzyme activity and related quality attributes of pear puree[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2018, 45: 196-207. |
| [16] | 王颖, 杜易潼, 薛婉玉, 等. 植物源性天然抗氧化剂的机理及其在食品保鲜中的应用[J]. 中国调味品, 2023, 48(1): 204-209. |
| WANG Y, DU Y T, XUE W Y, et al. Mechanism of natural plant-derived antioxidants and their application in food preservation[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(1): 204-209. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 赵鹏广, 刘伟, 尚俊杰, 等. 护色与浓缩工艺对梨膏品质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2019, 40(13): 138-144. |
| ZHAO P G, LIU W, SHANG J J, et al. Effect of color protection and concentration process on the quality of pear paste[J]. Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(13): 138-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 吴胤霆, 王洋, 张楠, 等. 火龙果南酸枣复合果泥配方优化及香气分析[J]. 中国调味品, 2023, 48(12): 159-165. |
| WU Y T, WANG Y, ZHANG N, et al. Formula optimization and aroma analysis of compound puree of pitaya and Choerospondias axillaris[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(12): 159-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 胡晓云, 甘蓓, 徐昕洁, 等. 有机婴幼儿果蔬泥护色工艺的研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016, 28(4): 39-42. |
| HU X Y, GAN B, XU X J, et al. Study on color protection process of organic fruit and vegetable paste for infants[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2016, 28(4): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 邓汶欣, 王洋, 刘秋辰, 等. 温度和抑制剂改善雪梨南酸枣复合果泥储藏期褐变[J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2022, 33(10): 8-17. |
| DENG W X, WANG Y, LIU Q C, et al. Temperature and inhibitor improve browning of snow pear Choerospondias axillaris blend fruit puree during storage[J]. China Food Additives, 2022, 33(10): 8-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 杨瑾越, 赵静, 秦梦薇, 等. 养胃养颜石斛西梅果冻的加工工艺研究[J]. 安徽化工, 2024, 50(3): 60-63. |
| YANG J Y, ZHAO J, QIN M W, et al. Study on the processing technology of Dendrobium sagojelly for nourishing stomach and nourishing beauty[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 2024, 50(3): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 肖川泉, 张楠, 罗小丹, 等. 南酸枣复合果泥配方与护色工艺的优化研究[J]. 中国调味品, 2024, 49(1): 25-32. |
| XIAO C Q, ZHANG N, LUO X D, et al. Study on optimization of formula and color protection process of Choerospondias axillaris compound puree[J]. China Condiment, 2024, 49(1): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 宋菲红, 蒋玉梅, 盛文军, 等. 苹果沙棘复合果泥配方优化及品质分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(6): 184-194. |
| SONG F H, JIANG Y M, SHENG W J, et al. Formula optimization and aroma composition analysis of apple sea-buckthorn complex puree[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(6): 184-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 唐征, 肖逸, 杜长江, 等. 不同杀菌方式对百香果汁有机物含量、色泽和褐变系数的影响分析[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2024(18): 60-62. |
| TANG Z, XIAO Y, DU C J, et al. Effect of different sterilization methods on organic content, color and browning coefficient of passion fruit juice[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2024(18): 60-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 何翊辰, 林欣瑜, 齐高博, 等. 南瓜香蕉果糕制备工艺及不同杀菌方式影响[J]. 农产品加工, 2019(19): 22-24. |
| HE Y C, LIN X Y, QI G B, et al. Effects of preparation and sterilization of pumpkin banana cake[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2019(19): 22-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | YOU Y L, LI N, HAN X, et al. Influence of different sterilization treatments on the color and anthocyanin contents of mulberry juice during refrigerated storage[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2018, 48: 1-10. |
| [27] | 肖阳, 曹雁平, 薛卫星, 等. 低糖香蕉酱的研制[J]. 食品工业科技, 2000, 21(2): 56-57. |
| XIAO Y, CAO Y P, XUE W X, et al. Development of the low sugar banana jam[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2000, 21(2): 56-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | CHEN R H, YU M, JIANG B, et al. Effect of different sterilization methods on the appearance, composition, and flavor of sugarcane juice[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2024, 89(3): 1755-1772. |
| [29] | 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2007. |
| [30] | 冯若怡, 王晓钰, 杨云舒, 等. 超高压处理对复合苹果泥微生物和品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(17): 37-44. |
| FENG R Y, WANG X Y, YANG Y S, et al. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on microbe and quality of mixed apple puree[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(17): 37-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 柳青, 赵晓燕, 张超, 等. 超高压处理对草莓汁贮藏期微生物及品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报, 2014, 14(11): 111-117. |
| LIU Q, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG C, et al. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure processing on microorganism and qualities of strawberry juice during storage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2014, 14(11): 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 郭雷, 吕明生, 王淑军, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定樱桃酒中总糖[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2010, 31(6): 130-132. |
| GUO L, LU M S, WANG S J, et al. Determination of total sugar from cherry wine by phenol-sulfuric acid method[J]. Food Research and Development, 2010, 31(6): 130-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 陈其钢, 王向未. 山药、山楂、蓝莓复合蔬菜泥的开发研究[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2014, 35(22): 17-20. |
| CHEN Q G, WANG X W. The research of compound in yam, hawthorn, blueberry vegetable puree[J]. Food Research and Development, 2014, 35(22): 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | FRANCIS F J, CLYDESDALE F M. Food colorimetry: theory and applications[M]. Connecticut: The Avi Publishing Company, Inc., 1975. |
| [35] | 梁凤玲. 矮箕青菜贮期品质变化规律及保鲜技术研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2012. |
| LIANG F L. Study on change rules of quality and preservation techniques of Bok choy during storage[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 冀晓龙, 王敏, 田汉英, 等. 不同杀菌方式对梨枣汁贮藏过程中品质变化的影响[J]. 现代食品科技, 2013, 29(9): 2211-2217. |
| JI X L, WANG M, TIAN H Y, et al. Effect of different sterilization methods on quality of pear jujube juice during storage[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2013, 29(9): 2211-2217. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 余秀丽, 施瑞城. 微波处理对芒果原浆杀菌效果和品质的影响研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(3): 572-579. |
| YU X L, SHI R C. Effect of microwave treatment on the sterilization effect and quality of mango puree[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(3): 572-579. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 冯伦元. 食品微生物在食品保鲜中的应用及其作用机制研究[J]. 中国食品, 2024(22): 135-137. |
| FENG L Y. Application of food microorganism in food preservation and its mechanism[J]. China Food, 2024(22): 135-137. (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 熊海燕, 李莹. 不同果汁发酵液中酵母菌生长曲线的测定及pH值的变化[J]. 农产品加工(学刊), 2009(4): 26-27. |
| XIONG H Y, LI Y. Measurement of yeast growth curve and pH values in different fermented fruit juices[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing, 2009(4): 26-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 林鑫勰, 余岳芳, 朱玉燕, 等. 不同热杀菌处理的NFC橙汁品质变化分析[J]. 保鲜与加工, 2022, 22(8): 51-58. |
| LIN X X, YU Y F, ZHU Y Y, et al. Quality changes in NFC orange juice treated with different thermal sterilization[J]. Storage and Process, 2022, 22(8): 51-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | 卫萍, 游向荣, 张雅媛, 等. 不同杀菌方式对低糖香蕉果酱品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2015, 36(7): 97-100. |
| WEI P, YOU X R, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Effect of different sterilization ways on quality of low-sugar banana jam[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(7): 97-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 杨晓娜, 徐玲, 赵昶灵, 等. 龙陵紫皮石斛花色苷色素抑菌作用初探[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(14): 139-143. |
| YANG X N, XU L, ZHAO C L, et al. Study on inhibitory effect of anthocyanin from Dendrobium devonianum in Longling[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(14): 139-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | 刘春兰, 杨逸, 何林, 等. 植物多糖抑菌作用研究方法进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2013, 24(7): 1725-1727. |
| LIU C L, YANG Y, HE L, et al. Advance of research methods of polysaccharide in bacteriostatic effect[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2013, 24(7): 1725-1727. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [44] | 牛慧慧, 张慧云, 邹文惠, 等. 不同杀菌方式对百香果汁感官和营养品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(20): 145-151. |
| NIU H H, ZHANG H Y, ZOU W H, et al. Effects of sterilization methods on the sensory related characteristics and nutritional quality of passion fruit juice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(20): 145-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | YANG Guiren, MU Honglei, WU Weijie, FANG Xiangjun, CHEN Huizhi, NIU Ben, CHEN Hangjun, GAO Haiyan. Research on the process optimization and maintenance of anthocyanins in Chinese bayberry juice by casein [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(1): 178-188. |
| [2] | ZONG Zihao, HE Dingsheng, NIU Ben, HUANG Jun, FANG Xiangjun, WU Weijie, CHEN Hangjun, GAO Haiyan. Effect of different hollow packaging on storage and transportation quality of bayberry harvested in rainy days [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(1): 196-204. |
| [3] | CHEN Dailiang, HAN Yanchao, WU Weijie, DENG Shanggui, CHEN Hangjun, GAO Haiyan. Effect of special cushioning packaging on storage quality of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(4): 801-807. |
| [4] | ZHANG Na, ZHOU Muchuan, WANG Qinggang, DING Yuxian, CHEN Aiqiang. Effect of hot water treatment on storage quality of Nanfengtangerine and heat transfer analysis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(2): 370-377. |
| [5] | FENG Luoluo, GAO Haiyan, ZHANG Runguang, YAN Xinpeng, ZHANG Yani, HAN Qiqi, ZHANG Youlin. Effects of different gas composition storage on physiological changes and quality of Dog-head jujube fruit [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(4): 704-713. |
| [6] | ZHU Weicheng, GAO Haiyan, HAN Yanchao, LI Daxiang, CHEN Hangjun. Effects of different pre-cooling methods on cooling speed and storage quality of postharvest water bamboo shoot [J]. , 2020, 32(10): 1873-1879. |
| [7] | WANG Jian, SONG Ya, FANG Jia\|ning, YANG Jing*. Effect of phytic acid on the quality of fresh\|cut red cabbage [J]. , 2015, 27(11): 2017-. |
| [8] | ZHU Li\|ya1,2, GAO Hai\|yan2, CHEN Hang\|jun2,*, FANG Xiang\|jun2. Effect of different storage temperatures on quality of vacuum freeze\|dried strawberry powder [J]. , 2014, 26(6): 1622-. |
| [9] | WANG Rong-qing;ZHOU Guo-zhi;RUAN Mei-ying;YE Qing-jing;YAO Zhu-0ping;LI Zhi-miao;YANG Yue-jian* . Breeding of tomato hybrid F1 Zheza 205 with good quality, high yield and long shelf-life [J]. , 2013, 25(4): 0-746. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

