Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2057-2065.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250139
• Animal Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA method for detecting antibodies against fowlpox virus ORF127 protein
HUA Jionggang1( ), ZHU Yinchu1, YE Jialin2, ZHANG Cun1, CHEN Liu1, NI Zheng1, FU Yuan1, HUO Suxin1, YUN Tao1,*(
), ZHU Yinchu1, YE Jialin2, ZHANG Cun1, CHEN Liu1, NI Zheng1, FU Yuan1, HUO Suxin1, YUN Tao1,*( )
)
- 1. Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Livestock and Poultry Biotech Breeding, Key Laboratory of Livestock and Poultry Resources (Poultry) Evaluation and Utilization, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Poultry Breeding Industry and Green Farming Technology, Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Sciences, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
2. International Division, Hangzhou High School, Hangzhou 310020, China
-
Received:2025-02-24Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HUA Jionggang, ZHU Yinchu, YE Jialin, ZHANG Cun, CHEN Liu, NI Zheng, FU Yuan, HUO Suxin, YUN Tao. Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA method for detecting antibodies against fowlpox virus ORF127 protein[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2057-2065.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250139
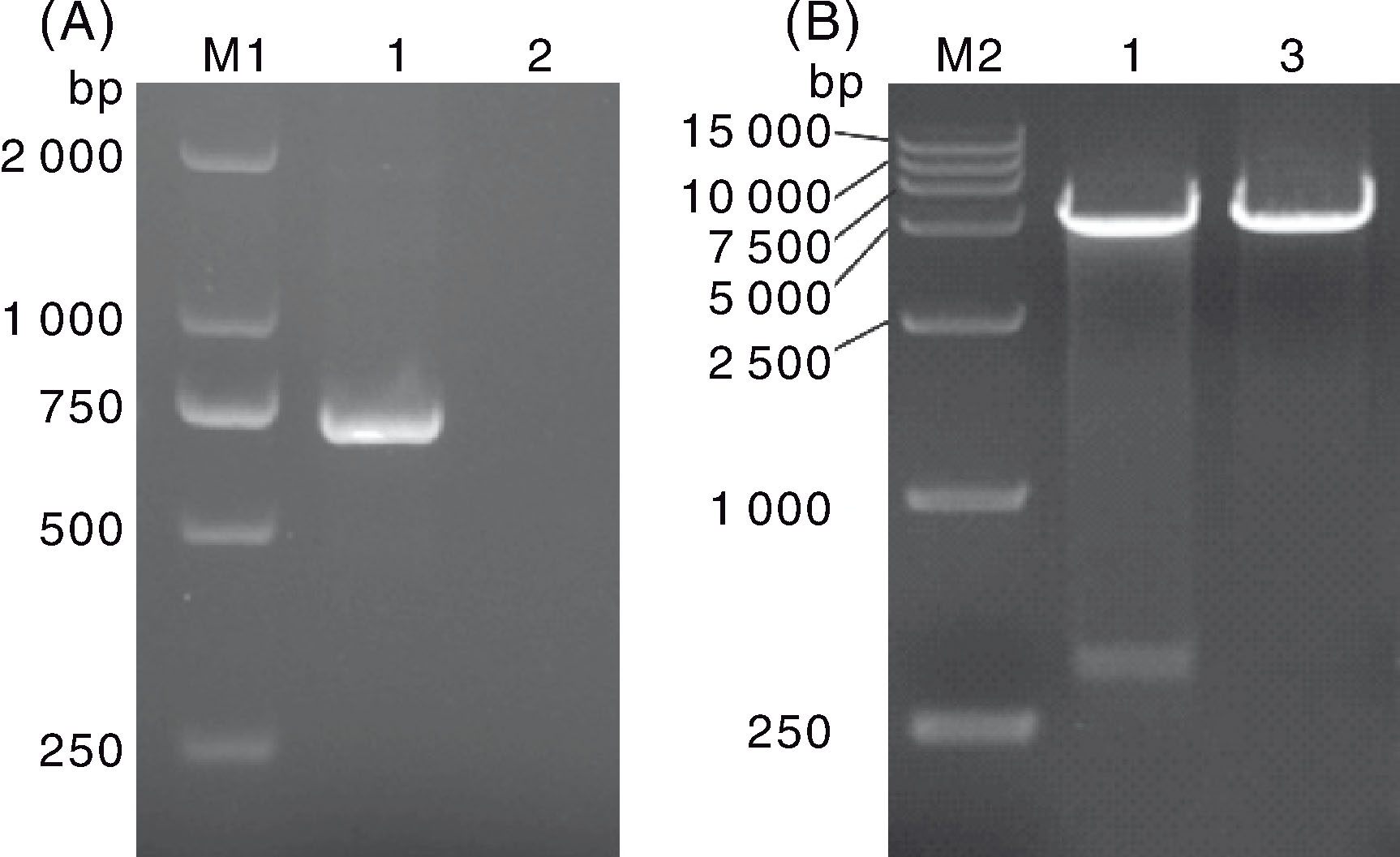
Fig.2 PCR (A) and restriction enzyme digestion (B) identification results of the recombinant plasmid M1, DL 2 000 DNA marker; M2, DL 15 000 DNA marker; 1, PCR products of pET-28-FPV-127; 2, Negative control; 3, pET-28.
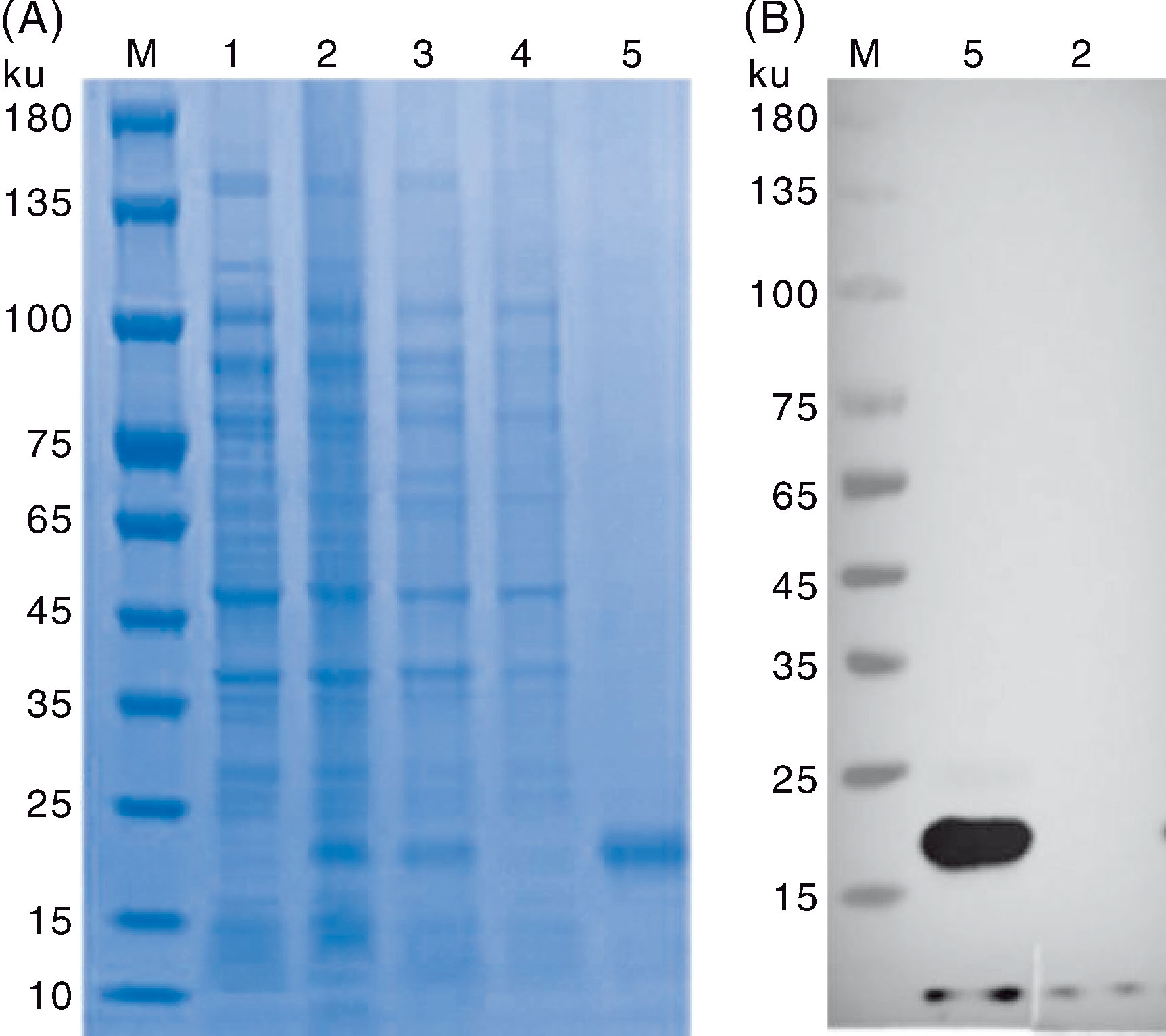
Fig.3 SDS-PAGE electrophoresis (A) and Western blot identification (B) of FPV-127 truncated protein M, Color prestained protein marker(10-180 ku); 1, Uninduced pET-28a-127/BL21; 2, Induced pET-28a-127/BL21; 3, Supernatant after cell lysis; 4, Precipitation after cell lysis; 5, FPV-127 truncated protein purified by nickel affinity chromatography.
| 血清稀释度 Serum dilution | 项目 Item | 不同FPV-127抗原质量浓度的吸光度Absorbance of FPV-127 antigens with different mass concentration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 μg·mL-1 | 10 μg·mL-1 | 5 μg·mL-1 | 2.5 μg·mL-1 | 1.25 μg·mL-1 | 0.625 μg·mL-1 | ||
| 1∶25 | P | 2.220 | 2.003 | 1.590 | 1.138 | 0.793 | 0.671 |
| N | 0.673 | 0.403 | 0.243 | 0.167 | 0.129 | 0.210 | |
| P/N | 3.299 | 4.970 | 6.543 | 6.814 | 6.117 | 3.195 | |
| 1∶50 | P | 2.146 | 1.799 | 1.130 | 0.753 | 0.486 | 0.404 |
| N | 0.389 | 0.243 | 0.145 | 0.101 | 0.088 | 0.086 | |
| P/N | 5.517 | 7.403 | 7.793 | 7.485 | 5.523 | 4.698 | |
| 1∶100 | P | 2.117 | 1.474 | 0.896 | 0.497 | 0.291 | 0.252 |
| N | 0.257 | 0.148 | 0.096 | 0.074 | 0.062 | 0.066 | |
| P/N | 8.237 | 9.959 | 9.333 | 6.716 | 4.694 | 3.818 | |
| 1∶200 | P | 1.896 | 1.145 | 0.562 | 0.311 | 0.189 | 0.149 |
| N | 0.215 | 0.123 | 0.099 | 0.065 | 0.067 | 0.054 | |
| P/N | 8.817 | 9.309 | 5.677 | 4.785 | 2.821 | 2.759 | |
Table 1 Absorbance at 450 nm of antigens with different mass concentrations and serum with different dilutions
| 血清稀释度 Serum dilution | 项目 Item | 不同FPV-127抗原质量浓度的吸光度Absorbance of FPV-127 antigens with different mass concentration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 μg·mL-1 | 10 μg·mL-1 | 5 μg·mL-1 | 2.5 μg·mL-1 | 1.25 μg·mL-1 | 0.625 μg·mL-1 | ||
| 1∶25 | P | 2.220 | 2.003 | 1.590 | 1.138 | 0.793 | 0.671 |
| N | 0.673 | 0.403 | 0.243 | 0.167 | 0.129 | 0.210 | |
| P/N | 3.299 | 4.970 | 6.543 | 6.814 | 6.117 | 3.195 | |
| 1∶50 | P | 2.146 | 1.799 | 1.130 | 0.753 | 0.486 | 0.404 |
| N | 0.389 | 0.243 | 0.145 | 0.101 | 0.088 | 0.086 | |
| P/N | 5.517 | 7.403 | 7.793 | 7.485 | 5.523 | 4.698 | |
| 1∶100 | P | 2.117 | 1.474 | 0.896 | 0.497 | 0.291 | 0.252 |
| N | 0.257 | 0.148 | 0.096 | 0.074 | 0.062 | 0.066 | |
| P/N | 8.237 | 9.959 | 9.333 | 6.716 | 4.694 | 3.818 | |
| 1∶200 | P | 1.896 | 1.145 | 0.562 | 0.311 | 0.189 | 0.149 |
| N | 0.215 | 0.123 | 0.099 | 0.065 | 0.067 | 0.054 | |
| P/N | 8.817 | 9.309 | 5.677 | 4.785 | 2.821 | 2.759 | |
| 项目 Item | 不同酶标二抗稀释度的吸光度Absorbance with different dilutions of enzyme-labeled second antibody | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1∶10 000 | 1∶15 000 | 1∶20 000 | 1∶25 000 | 1∶30 000 | 1∶35 000 | |
| P | 2.227 | 2.073 | 1.833 | 1.693 | 1.540 | 1.352 |
| N | 0.207 | 0.133 | 0.110 | 0.108 | 0.103 | 0.101 |
| P/N | 10.758 | 15.586 | 16.664 | 15.676 | 14.951 | 13.386 |
Table 2 Absorbance at 450 nm of enzyme-labeled secondary antibody with different dilutions when serum was diluted 100-fold
| 项目 Item | 不同酶标二抗稀释度的吸光度Absorbance with different dilutions of enzyme-labeled second antibody | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1∶10 000 | 1∶15 000 | 1∶20 000 | 1∶25 000 | 1∶30 000 | 1∶35 000 | |
| P | 2.227 | 2.073 | 1.833 | 1.693 | 1.540 | 1.352 |
| N | 0.207 | 0.133 | 0.110 | 0.108 | 0.103 | 0.101 |
| P/N | 10.758 | 15.586 | 16.664 | 15.676 | 14.951 | 13.386 |
| 血清 Serum | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | D450 D450 |
|---|---|---|
| 阳性血清Positive serum | 100 | 1.394 |
| 200 | 0.988 | |
| 400 | 0.652 | |
| 800 | 0.403 | |
| 1 600 | 0.259 | |
| 3 200 | 0.165 | |
| 6 400 | 0.117 | |
| 阴性血清Negative serum | 100 | 0.123 |
Table 3 Sensitivity test results of indirect ELISA method
| 血清 Serum | 稀释倍数 Dilution ratio | D450 D450 |
|---|---|---|
| 阳性血清Positive serum | 100 | 1.394 |
| 200 | 0.988 | |
| 400 | 0.652 | |
| 800 | 0.403 | |
| 1 600 | 0.259 | |
| 3 200 | 0.165 | |
| 6 400 | 0.117 | |
| 阴性血清Negative serum | 100 | 0.123 |
| 血清编号 Serum number | 批内重复试验Intra batch repeated experiment | 批间重复试验Inter batch repeated experiment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D450平均值 Average of D450 value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% | D450平均值 Average of D450 value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% | |
| 1 | 1.448 | 0.029 | 2.00 | 1.410 | 0.041 | 2.91 |
| 2 | 1.161 | 0.021 | 1.81 | 1.132 | 0.024 | 2.12 |
| 3 | 0.779 | 0.015 | 1.93 | 0.768 | 0.022 | 2.86 |
| 4 | 0.615 | 0.019 | 3.08 | 0.628 | 0.045 | 7.16 |
| 5 | 0.388 | 0.012 | 3.09 | 0.376 | 0.015 | 3.99 |
| 6 | 0.341 | 0.014 | 4.09 | 0.352 | 0.012 | 3.41 |
| 7 | 0.163 | 0.009 | 5.52 | 0.162 | 0.010 | 6.17 |
| 8 | 0.113 | 0.008 | 7.07 | 0.110 | 0.004 | 3.63 |
Table 4 Repeatability test results of indirect ELISA method
| 血清编号 Serum number | 批内重复试验Intra batch repeated experiment | 批间重复试验Inter batch repeated experiment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D450平均值 Average of D450 value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% | D450平均值 Average of D450 value | 标准差 Standard deviation | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation/% | |
| 1 | 1.448 | 0.029 | 2.00 | 1.410 | 0.041 | 2.91 |
| 2 | 1.161 | 0.021 | 1.81 | 1.132 | 0.024 | 2.12 |
| 3 | 0.779 | 0.015 | 1.93 | 0.768 | 0.022 | 2.86 |
| 4 | 0.615 | 0.019 | 3.08 | 0.628 | 0.045 | 7.16 |
| 5 | 0.388 | 0.012 | 3.09 | 0.376 | 0.015 | 3.99 |
| 6 | 0.341 | 0.014 | 4.09 | 0.352 | 0.012 | 3.41 |
| 7 | 0.163 | 0.009 | 5.52 | 0.162 | 0.010 | 6.17 |
| 8 | 0.113 | 0.008 | 7.07 | 0.110 | 0.004 | 3.63 |
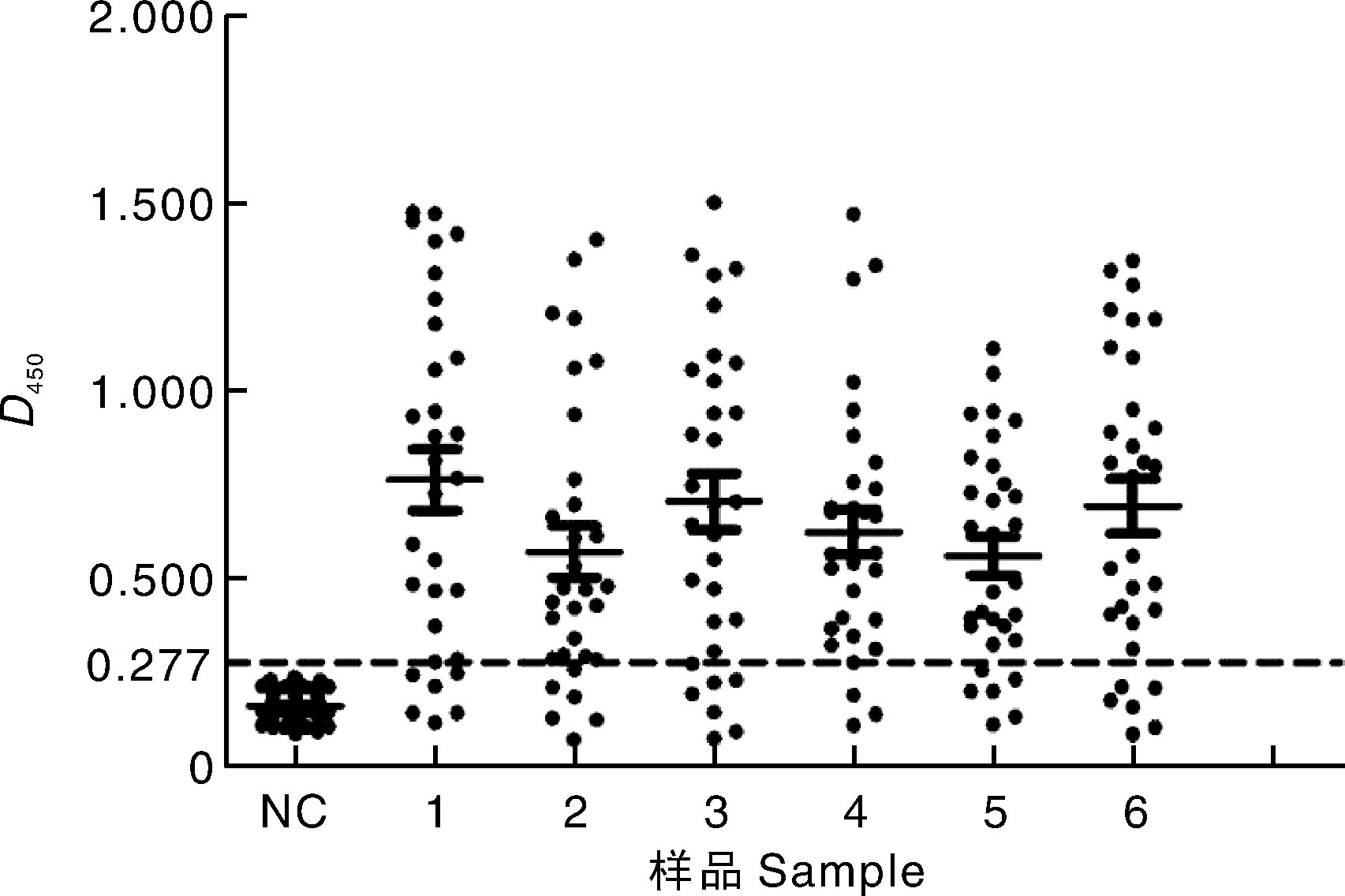
Fig.4 Indirect ELISA detection results of clinical samples NC, FPV negative serum samples; 1-6, Serum samples collected from each chicken farm after FPV vaccine immunization.
| [1] | BERTELLONI F, CECCHERELLI R, MARZONI M, et al. Molecular detection of Avipox virus in wild birds in central Italy[J]. Animals, 2022, 12(3): 338. |
| [2] | MATOS M, BILIC I, PALMIERI N, et al. Epidemic of cutaneous fowlpox in a naïve population of chickens and turkeys in Austria: detailed phylogenetic analysis indicates co-evolution of fowlpox virus with reticuloendotheliosis virus[J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2022, 69(5): 2913-2923. |
| [3] | 姜绍全, 王金亮, 秦燕. 海兰褐蛋鸡痘病毒的分离与鉴定[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2015, 36(1): 36-37. |
| JIANG S Q, WANG J L, QIN Y. Isolation and identification of poxvirus from hailan brown laying hens[J]. Shandong Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 36(1): 36-37. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | KIM T J, SCHNITZLEIN W M, MCALOOSE D, et al. Characterization of an avianpox virus isolated from an Andean condor (Vultur gryphus)[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2003, 96(3): 237-246. |
| [5] | YEHIA N, ELSAYED S, AL-SAEED F A, et al. Current situation and genomic characterization of fowlpox virus in lower Egypt during 2022[J]. Poultry Science, 2023, 102(8): 102769. |
| [6] | AFONSO C L, TULMAN E R, LU Z, et al. The genome of fowlpox virus[J]. Journal of Virology, 2000, 74(8): 3815-3831. |
| [7] | WELI S C, TRYLAND M. Avipoxviruses: infection biology and their use as vaccine vectors[J]. Virology Journal, 2011, 8: 49. |
| [8] | 赵宏吉, 张金花, 司朵朵, 等. 山羊痘病毒G9蛋白的原核表达及间接ELISA方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2021, 43(3): 280-284. |
| ZHAO H J, ZHANG J H, SI D D, et al. Prokaryotic expression of G9 protein of GTPV and establishment of an indirect ELISA[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 43(3): 280-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 叶伟成, 云涛, 朱寅初, 等. 基于番鸭细小病毒VP3蛋白的间接ELISA方法建立[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(11): 2740-2745, 2750. |
| YE W C, YUN T, ZHU Y C, et al. Establishment of indirect ELISA assay based on VP3 protein of Muscovy duck parvovirus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(11): 2740-2745, 2750. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | OJEDA S, DOMI A, MOSS B. Vaccinia virus G9 protein is an essential component of the poxvirus entry-fusion complex[J]. Journal of Virology, 2006, 80(19): 9822-9830. |
| [11] | GRAY R D M, ALBRECHT D, BEERLI C, et al. Nanoscale polarization of the entry fusion complex of vaccinia virus drives efficient fusion[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(10): 1636-1644. |
| [12] | FOO C H, WHITBECK J C, PONCE-DE-LEÓN M, et al. The myristate moiety and amino terminus of vaccinia virus l1 constitute a bipartite functional region needed for entry[J]. Journal of Virology, 2012, 86(10): 5437-5451. |
| [13] | SHINODA K, WYATT L S, MOSS B. The neutralizing antibody response to the vaccinia virus A28 protein is specifically enhanced by its association with the H2 protein[J]. Virology, 2010, 405(1): 41-49. |
| [14] | ADEBAJO M C, ADEMOLA S I, OLUWASEUN A. Seroprevalence of fowl pox antibody in indigenous chickens in jos north and south council areas of Plateau state, Nigeria: implication for vector vaccine[J]. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012, 2012(1): 154971. |
| [15] | MOCKETT A P A, SOUTHEE D J, TOMLEY F M, et al. Fowlpox virus: its structural proteins and immunogens and the detection of viral-specific antibodies by ELISA[J]. Avian Pathology, 1987, 16(3): 493-504. |
| [16] | 雪鹏, 刘悦竹, 姜世金, 等. 用间接ELISA检测鸡痘病毒抗体的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2005, 41(6): 15-16. |
| WANG X P, LIU Y Z, JIANG S J, et al. Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA to detect antibodies against poultry pox[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2005, 41(6): 15-16. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 张体银, 孙蕾, 孙学辉, 等. 应用间接ELISA检测鸡痘病毒抗体方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2005, 27(6): 540-543. |
| ZHANG T Y, SUN L, SUN X H, et al. Development of indirect ELISA for detection of antibodies against fowlpox virus[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2005, 27(6): 540-543. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 纪朋艳, 卢广林. 检测鸡痘病毒抗体间接ELISA方法的建立[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2012(23): 94-95. |
| JI P Y, LU G L. Establishment of indirect ELISA for detection of fowlpox virus antibody[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2012(23): 94-95. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张琪, 庞文静, 付明哲, 等. 山羊痘病毒ORF103蛋白的原核表达及间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2017, 47(5): 537-543. |
| ZHANG Q, PANG W J, FU M Z, et al. Prokaryotic expression of ORF103 protein of capripox virus and establishment of indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against the virus[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2017, 47(5): 537-543. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | VENKATESAN G, KUMAR TELI M, SANKAR M, et al. Expression and evaluation of recombinant P32 protein based ELISA for sero-diagnostic potential of capripox in sheep and goats[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2018, 37: 48-54. |
| [21] | DASHPRAKASH M, VENKATESAN G, KUMAR A, et al. Prokaryotic expression, purification and evaluation of goatpox virus ORF117 protein as a diagnostic antigen in indirect ELISA to detect goatpox[J]. Archives of Virology, 2019, 164(4): 1049-1058. |
| [22] | 邓舜洲, 蒋新华, 冷闯, 等. 猪痘病毒P35基因的原核表达及间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2013, 33(10): 1488-1492. |
| DENG S Z, JIANG X H, LENG C, et al. Establishment of an indirect ELISA for detection of antibodies against swinepox virus with the recombinant P35 as the coating antigen[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2013, 33(10): 1488-1492. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 朱俊达, 王爽, 任书凝, 等. 基于猴痘病毒A27L蛋白的间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2022, 58(10): 1-7. |
| ZHU J D, WANG S, REN S N, et al. Establishment of indirect ELISA method for detection of monkeypox virus antibody based on A27L protein[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 58(10): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | SHEN Zhengrong, DAI Yuanxing, GUO Liuming, WANG Zhiyao, ZHANG Hengmu. Preparation and application of specific antibody against coat protein (CP) of Chinese wheat mosaic virus (CWMV) [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(9): 2042-2050. |
| [2] | LI Ju, BI Donglin, YANG Xiaoli, YANG Dongliang, ZHANG Xiaowen, LIU Fangcheng, LI Qiongyi, BAI Jialin. Preparation and identification of monoclonal antibodies against non-structural protein C of Peste des petits ruminants virus [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(5): 1047-1054. |
| [3] | LI Tian’en, ZHOU Sihan, SUN Hongchao, FU Yuan, SHI Tuanyuan, YAN Wenchao. Cloning and expression analysis of two hypothetical dense granule protein genes of Eimeria tenella in chickens [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(3): 503-514. |
| [4] | XUE Jiaoxiong, ZHAO Tingfang, ZHANG Qian, TANG Qinghai, GAO Cuicui, ZHAO Cheng, ZHANG Yan, QUAN Feiyang, LIU Ting, YANG Can, YANG Hai, WANG Wenxiu. Preparation of small molecule antibody Fab specific to S1 protein of canine coronavirus [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(11): 2568-2583. |
| [5] | TANG Guoliang, ZHANG Yubao, WANG Ruoyu, WANG Yajun, ZHAO Xia, SU Xuesi, JIN Weijie. Prokaryotic expression of Konjac mosaic virus capsid protein and preparation of polyclonal antibody [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(11): 2471-2481. |
| [6] | ZHU Yinchu, WANG Hongyu, YUN Tao, HUA Jionggang, YE Weicheng, NI Zheng, CHEN Liu, ZHANG Cun. Isolation and identification of goose astrovirus in Zhejiang Province, China, and preparation of polyclone antibodies against capside protein [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(10): 2149-2159. |
| [7] | SHEN Weifeng, GUO Qi, LIU Li, NIU Baolong, WENG Hongbiao, LOU Bao. Cloning, expression and application in detection of SWP2 gene in Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 993-1000. |
| [8] | LIU Junwen, WANG Di, ZHU Yanyan, XING Gang, ZHAN Songhe, LIU Xiaolu, WEI Jianzhong, SUN Pei, LIU Xuelan, LI Yu. Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA based on protein by expression and cloning of CbpB gene of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(5): 816-824. |
| [9] | SU Xuesi, ZHANG Yubao, WANG Ruoyu, WANG Yajun, TANG Guoliang, JIN Weijie. Prokaryotic expression of Plantago asiatica mosaic virus capsid protein and preparation of its polyclonal antibody [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(1): 104-111. |
| [10] | LIU Jinyu, HUANG Ying. Prokaryotic expression and antibody preparation of full-length and N-terminal half of SpTrz2 protein in Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(1): 34-42. |
| [11] | PAN Chuanyan, LIN Yong, FENG Pengfei, ZHANG Yongde, LUO Honglin. Prokaryotic expression and polyclonal antibody preparation of Hsc70 in Nile tilapia [J]. , 2019, 31(8): 1272-1279. |
| [12] | YAN Han, YANG Ruixiu, GAI Xiaotong, LI Gang, ZHAO Zhiguo, GAO Zenggui. Establishment of ELISA for Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis [J]. , 2018, 30(12): 2081-2086. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lin, YU Bin, NI Zheng, CHEN Liu, YUN Tao, YE Weicheng, HUA Jionggang, CUI Yanshun, ZHANG Cun. Identification of linear B cell epitope for E protein of duck Tembusu virus [J]. , 2017, 29(12): 2009-2014. |
| [14] | YAN Huili, XI Jun*, GAO Xuemei, HE Mengxue, CHEN Zhe, LU Qiyu. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies against Gly m Bd 28K and identification of their immunological properties [J]. , 2016, 28(5): 748-. |
| [15] | LI Jianqiu1, ZHOU Caiqin2,YU Bin3,WU Xuejun2, ZHAO Lingyan 2, ZHOU Lei2, ZHANG Cun3, XU Hui2,*. Seroepidemiological investigation and analysis on duck Tembusu virus antibody level in Zhejiang Province [J]. , 2016, 28(4): 563-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||