浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2479-2493.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250031
感染哈维氏弧菌小黄鱼的组织病理学和转录组学分析
黄慧灵1( ), 韩明明2,*(
), 韩明明2,*( ), 潘鑫煜3, 赵旭东1, 颉志刚2, 徐剑斌3, 楼宝2
), 潘鑫煜3, 赵旭东1, 颉志刚2, 徐剑斌3, 楼宝2
- 1.浙江海洋大学 水产学院,浙江 舟山 316022
2.浙江省农业科学院 水生生物研究所,浙江 杭州 310021
3.浙江万里学院 生物与环境学院,浙江 宁波 315100
-
收稿日期:2025-01-13出版日期:2025-12-25发布日期:2026-01-09 -
作者简介:黄慧灵(1999—),女,广西南宁人,硕士研究生,研究方向为水产养殖病害防控。E-mail:3477782440@qq.com -
通讯作者:*韩明明,E-mail:sealion1984@126.com -
基金资助:宁波市公益性科技计划项目(2021S053);浙江省科技计划项目(2023C02029)
Histopathological and transcriptomic analyses of Larimichthys polyactis infected with Vibrio harveyi
HUANG Huiling1( ), HAN Mingming2,*(
), HAN Mingming2,*( ), PAN Xinyu3, ZHAO Xudong1, XIE Zhigang2, XU Jianbin3, LOU Bao2
), PAN Xinyu3, ZHAO Xudong1, XIE Zhigang2, XU Jianbin3, LOU Bao2
- 1. School of Fishery, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan 316022, Zhejiang, China
2. Institute of Hydrobiology, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
3. College of Biological and Environmental Sciences, Zhejiang Wanli University, Ningbo 315100, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2025-01-13Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
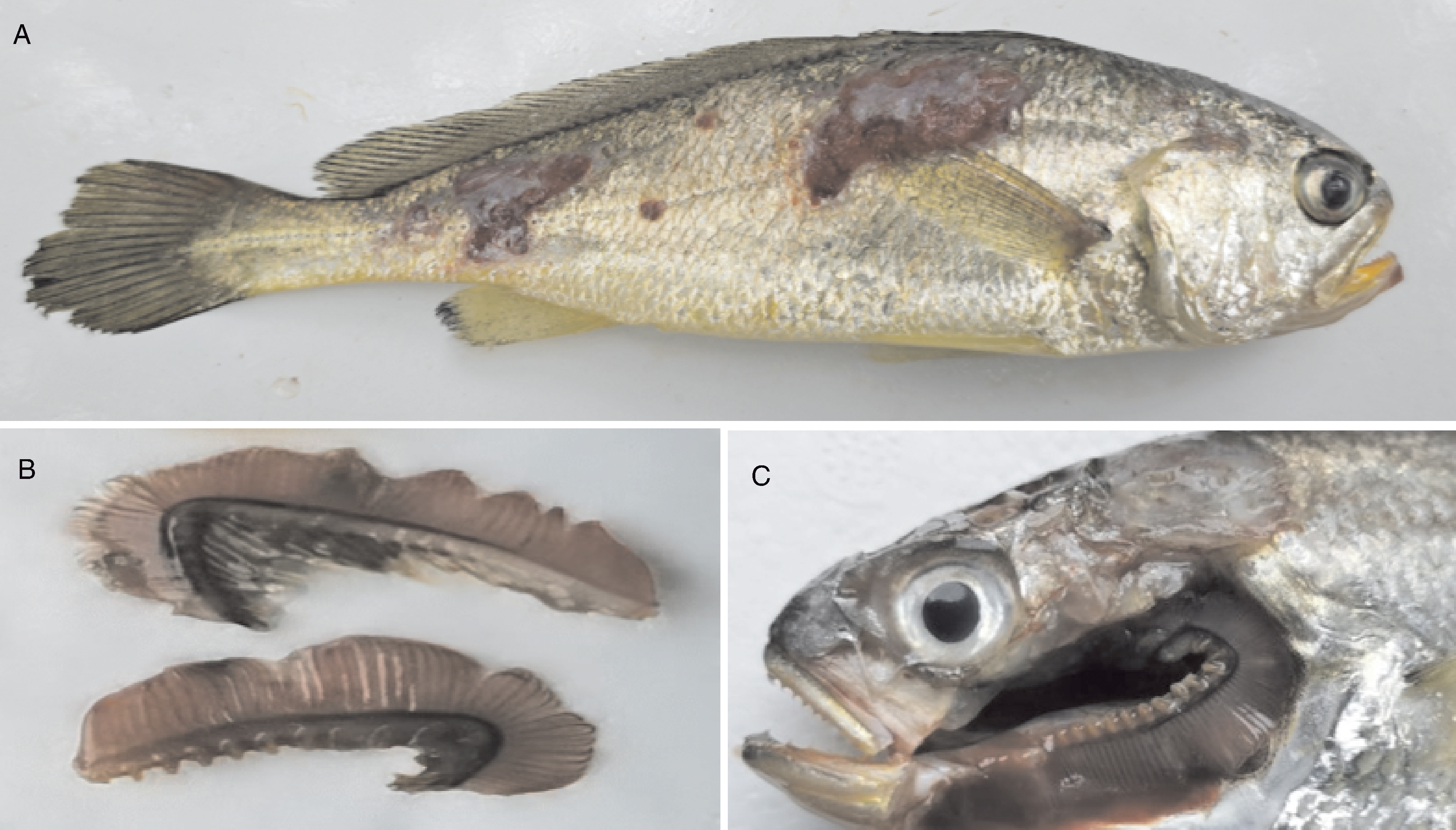
摘要: 为探究鱼类对哈维氏弧菌(Vibrio harveyi)的免疫响应机制,本研究以小黄鱼(Larimichthys polyactis)为对象,对哈维氏弧菌感染后的肝、鳃丝和皮肤进行转录组测序与组织病理学观察。结果显示,感染小黄鱼体表出现鳞片脱落和皮肤溃烂,鳃丝呈现严重充血。镜检下发现,皮肤表层组织坏死,鳃小片上皮细胞坏死且结构破坏,肝实质萎缩并伴随肝细胞空泡变性。转录组分析表明,感染小黄鱼的肝、鳃丝和皮肤中的多个免疫相关信号通路被激活,包括细胞外基质(ECM)受体相互作用、JAK-STAT信号通路、细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用、核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain,NOD)样受体信号通路、RIG-I样受体信号通路、Toll样受体信号通路和胞质DNA感知通路等。本研究从基因和信号通路层面揭示了哈维氏弧菌感染引起小黄鱼多组织病理损伤的分子机制,为后续研究相关病害防控策略提供了参考依据。
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄慧灵, 韩明明, 潘鑫煜, 赵旭东, 颉志刚, 徐剑斌, 楼宝. 感染哈维氏弧菌小黄鱼的组织病理学和转录组学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2479-2493.
HUANG Huiling, HAN Mingming, PAN Xinyu, ZHAO Xudong, XIE Zhigang, XU Jianbin, LOU Bao. Histopathological and transcriptomic analyses of Larimichthys polyactis infected with Vibrio harveyi[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2479-2493.
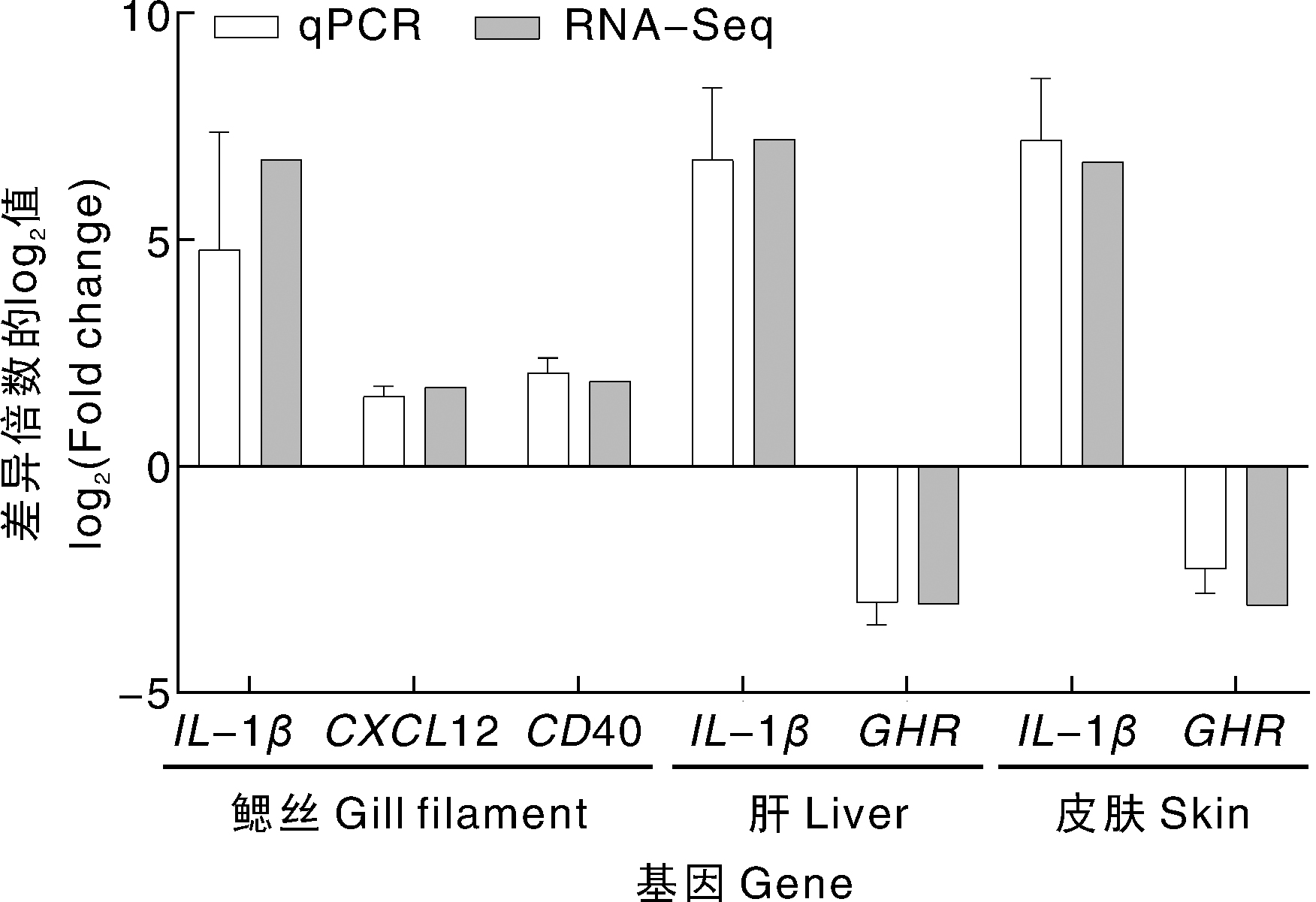
| 基因名称Gene name | 正向引物序列Forward primer sequence(5'→3') | 反向引物序列Reverse primer sequence(5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | CGCTGAGAACCGCAAAGTTC | TCCCCATCCCTATGGCAAGA |
| CXCL12 | TGGCTGCGTTCATGGTGATA | TGGCAATCACTTGGAAGGGG |
| CD40 | ATCTGCACTTTCAGGCTCCC | GGTTCACAGGTTTTGTGCGG |
| GHR | TACCTGGCGAGGGGTATCAA | ACTGTGTAGTCTGCAACGGG |
| β-actin | GACCTGACAGACTACCTCATG | AGTTGAAGGTGGTCTCGTGGA |
表1 荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qPCR
| 基因名称Gene name | 正向引物序列Forward primer sequence(5'→3') | 反向引物序列Reverse primer sequence(5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | CGCTGAGAACCGCAAAGTTC | TCCCCATCCCTATGGCAAGA |
| CXCL12 | TGGCTGCGTTCATGGTGATA | TGGCAATCACTTGGAAGGGG |
| CD40 | ATCTGCACTTTCAGGCTCCC | GGTTCACAGGTTTTGTGCGG |
| GHR | TACCTGGCGAGGGGTATCAA | ACTGTGTAGTCTGCAACGGG |
| β-actin | GACCTGACAGACTACCTCATG | AGTTGAAGGTGGTCTCGTGGA |

图3 小黄鱼感染哈维氏弧菌后皮肤、鳃丝和肝组织病理学变化 A,健康组小黄鱼体侧皮肤;B,感染组小黄鱼皮肤;外层为表皮(e),内层为真皮(d),皮下为肌肉层(m);C,健康组小黄鱼的鳃丝;D,感染组小黄鱼的鳃丝,鳃丝末端和鳃小片肿胀、肥大(红色箭头),鳃小片上皮细胞坏死瓦解(黑色箭头);E,健康组小黄鱼肝;F,感染组小黄鱼肝,细胞质内可见大小不等的空泡(红色*号)。
Fig.3 Histopathological changes of skin, gill filament and liver of small yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harveyi A, Skin on the side of the body of healthy small yellow croaker; B, Skin of infected small yellow croaker; e, Outer epidermis; d, Inner dermis; m, Subcutaneous muscular layer; C, Gill filament of healthy small yellow croaker; D, Gill filament of infected small yellow croaker, the gill filament ends and gill vesicles were swollen and hypertrophied (red arrow), and the epithelium of the gill vesicles disintegrated (black arrow); E, Liver from the healthy control group of small yellow croaker; F, Liver of infected small yellow croaker, with varying sizes of vacuoles (red asterisk) in the cytoplasm.
| 样本 Sample | 原始数据 Raw read | 清洁数据 Clean read | 清洁碱基 Clean base/106 | 错误率 Error rate | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量 GC content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLT1 | 25 811 984 | 25 382 197 | 3.81 | 0.040 | 97.56 | 93.42 | 47.60 |
| CLT2 | 22 604 472 | 22 261 471 | 3.34 | 0.040 | 97.51 | 93.04 | 45.23 |
| CLT3 | 22 846 568 | 22 321 730 | 3.35 | 0.045 | 96.07 | 89.46 | 45.07 |
| CLT4 | 21 956 789 | 21 105 640 | 3.17 | 0.045 | 96.23 | 89.82 | 45.94 |
| CGT1 | 22 563 965 | 21 938 469 | 3.29 | 0.045 | 96.01 | 89.48 | 45.89 |
| CGT2 | 20 877 706 | 20 481 017 | 3.07 | 0.040 | 97.76 | 93.44 | 49.52 |
| CGT3 | 21 898 399 | 21 367 459 | 3.21 | 0.045 | 95.82 | 89.32 | 46.48 |
| CGT4 | 22 199 876 | 21 659 664 | 3.25 | 0.045 | 96.19 | 89.62 | 46.88 |
| CST1 | 20 117 968 | 19 684 762 | 2.95 | 0.045 | 96.37 | 90.12 | 48.65 |
| CST2 | 21 091 055 | 20 753 025 | 3.11 | 0.045 | 96.20 | 89.82 | 48.54 |
| CST3 | 20 946 972 | 20 508 232 | 3.08 | 0.045 | 96.72 | 90.66 | 49.66 |
| CST4 | 22 411 714 | 21 951 426 | 3.29 | 0.045 | 96.50 | 90.16 | 49.14 |
| TLT1 | 24 475 009 | 24 120 187 | 3.62 | 0.040 | 98.18 | 94.52 | 47.55 |
| TLT2 | 22 261 232 | 21 643 146 | 3.25 | 0.045 | 96.71 | 90.64 | 46.44 |
| TLT3 | 22 053 389 | 21 382 638 | 3.21 | 0.045 | 96.78 | 90.70 | 49.92 |
| TLT4 | 22 326 636 | 21 874 132 | 3.28 | 0.045 | 96.75 | 90.70 | 48.40 |
| TGT1 | 21 772 087 | 21 171 477 | 3.18 | 0.045 | 96.44 | 90.47 | 48.39 |
| TGT2 | 21 576 158 | 20 786 124 | 3.12 | 0.045 | 96.73 | 90.78 | 48.41 |
| TGT3 | 22 763 423 | 22 085 161 | 3.31 | 0.045 | 96.60 | 90.43 | 48.12 |
| TGT4 | 22 229 333 | 21 595 373 | 3.24 | 0.045 | 96.50 | 90.17 | 47.91 |
| TST1 | 21 890 142 | 21 093 258 | 3.16 | 0.045 | 96.53 | 90.33 | 49.22 |
| TST2 | 22 084 348 | 21 560 450 | 3.23 | 0.045 | 96.85 | 90.74 | 49.21 |
| TST3 | 21 902 085 | 21 508 753 | 3.23 | 0.045 | 96.51 | 90.14 | 48.20 |
| TST4 | 22 222 789 | 21 703 208 | 3.26 | 0.045 | 96.59 | 90.27 | 49.08 |
表2 测序数据统计
Table 2 Sequencing data statistics
| 样本 Sample | 原始数据 Raw read | 清洁数据 Clean read | 清洁碱基 Clean base/106 | 错误率 Error rate | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量 GC content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLT1 | 25 811 984 | 25 382 197 | 3.81 | 0.040 | 97.56 | 93.42 | 47.60 |
| CLT2 | 22 604 472 | 22 261 471 | 3.34 | 0.040 | 97.51 | 93.04 | 45.23 |
| CLT3 | 22 846 568 | 22 321 730 | 3.35 | 0.045 | 96.07 | 89.46 | 45.07 |
| CLT4 | 21 956 789 | 21 105 640 | 3.17 | 0.045 | 96.23 | 89.82 | 45.94 |
| CGT1 | 22 563 965 | 21 938 469 | 3.29 | 0.045 | 96.01 | 89.48 | 45.89 |
| CGT2 | 20 877 706 | 20 481 017 | 3.07 | 0.040 | 97.76 | 93.44 | 49.52 |
| CGT3 | 21 898 399 | 21 367 459 | 3.21 | 0.045 | 95.82 | 89.32 | 46.48 |
| CGT4 | 22 199 876 | 21 659 664 | 3.25 | 0.045 | 96.19 | 89.62 | 46.88 |
| CST1 | 20 117 968 | 19 684 762 | 2.95 | 0.045 | 96.37 | 90.12 | 48.65 |
| CST2 | 21 091 055 | 20 753 025 | 3.11 | 0.045 | 96.20 | 89.82 | 48.54 |
| CST3 | 20 946 972 | 20 508 232 | 3.08 | 0.045 | 96.72 | 90.66 | 49.66 |
| CST4 | 22 411 714 | 21 951 426 | 3.29 | 0.045 | 96.50 | 90.16 | 49.14 |
| TLT1 | 24 475 009 | 24 120 187 | 3.62 | 0.040 | 98.18 | 94.52 | 47.55 |
| TLT2 | 22 261 232 | 21 643 146 | 3.25 | 0.045 | 96.71 | 90.64 | 46.44 |
| TLT3 | 22 053 389 | 21 382 638 | 3.21 | 0.045 | 96.78 | 90.70 | 49.92 |
| TLT4 | 22 326 636 | 21 874 132 | 3.28 | 0.045 | 96.75 | 90.70 | 48.40 |
| TGT1 | 21 772 087 | 21 171 477 | 3.18 | 0.045 | 96.44 | 90.47 | 48.39 |
| TGT2 | 21 576 158 | 20 786 124 | 3.12 | 0.045 | 96.73 | 90.78 | 48.41 |
| TGT3 | 22 763 423 | 22 085 161 | 3.31 | 0.045 | 96.60 | 90.43 | 48.12 |
| TGT4 | 22 229 333 | 21 595 373 | 3.24 | 0.045 | 96.50 | 90.17 | 47.91 |
| TST1 | 21 890 142 | 21 093 258 | 3.16 | 0.045 | 96.53 | 90.33 | 49.22 |
| TST2 | 22 084 348 | 21 560 450 | 3.23 | 0.045 | 96.85 | 90.74 | 49.21 |
| TST3 | 21 902 085 | 21 508 753 | 3.23 | 0.045 | 96.51 | 90.14 | 48.20 |
| TST4 | 22 222 789 | 21 703 208 | 3.26 | 0.045 | 96.59 | 90.27 | 49.08 |
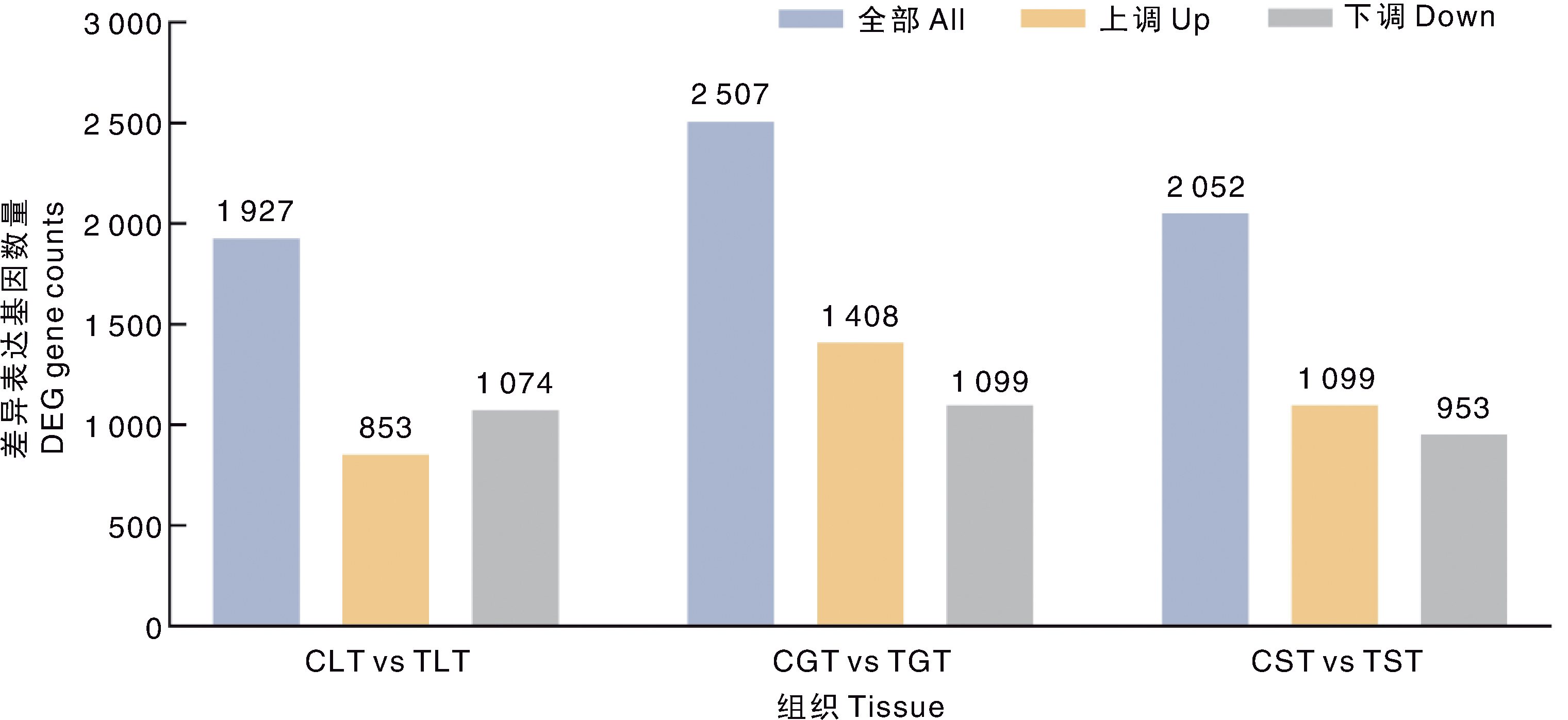
图4 感染哈维氏弧菌小黄鱼肝、鳃丝和皮肤中的差异表达基因数量 TLT,感染组肝;TGT,感染组鳃丝;TST,感染组皮肤;CLT,健康组肝;CGT,健康组鳃丝;CST,健康组皮肤。
Fig.4 Numbers of differentially expressed genes in the liver, gill filament, and skin of small yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harveyi TLT, Liver of infected group; TGT, Gill filament of infected group; TST, Skin of infected group; CLT, Liver of healthy group; CGT, Gill filament of healthy group; CST, Skin of healthy group.
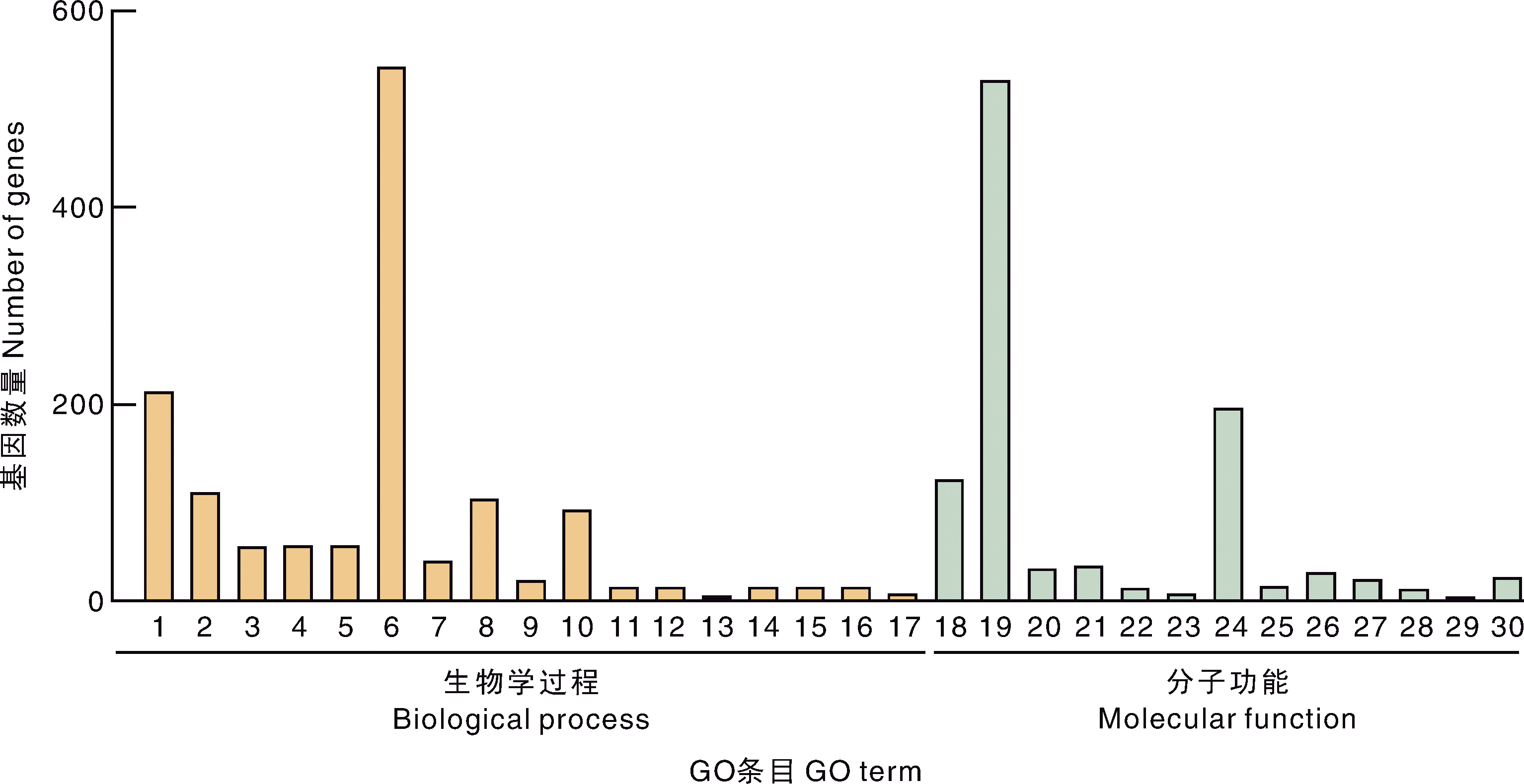
图5 感染哈维氏弧菌后小黄鱼肝中差异表达基因的GO功能富集 1,单组织体代谢过程;2,氧化还原反应过程;3,羧酸代谢过程;4,有机酸代谢过程;5,含氧酸代谢过程;6,代谢过程;7,细胞氨基酸代谢过程;8,小分子代谢过程;9,α-氨基酸代谢过程;10,有机氮化合物代谢过程;11,单生物碳水化合物分解代谢过程;12,蛋白质翻译中的tRNA氨酰化;13,L-丝氨酸代谢过程;14,碳水化合物分解代谢过程;15,氨基酸激活;16,tRNA氨酰化;17,丝氨酸家族氨基酸代谢过程;18,氧化还原酶活性;19,催化活性;20,铁离子结合;21,辅因子结合;22,NAD结合;23,羟甲基和甲酰基及相关转移酶活性;24,小分子结合;25,氧化还原酶活性,作用于CH—OH基团的供体,NAD或NADP作为受体;26,氧化还原酶活性,作用于配对供体,伴随分子氧的引入或还原;27,四吡咯结合;28,维生素结合;29,甘氨酸羟甲基转移酶活性;30,辅酶结合。
Fig.5 GO functional enrichment of differentially expressed genes in the liver of small yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harveyi 1, Single-organism metabolic process; 2, Oxidation-reduction process; 3, Carboxylic acid metabolic process; 4, Organic acid metabolic process; 5, Oxoacid metabolic process;6, Metabolic process; 7, Cellular amino acid metabolic process; 8, Small molecule metabolic process; 9, Alpha-amino acid metabolic process; 10, Organonitrogen compound metabolic process; 11, Single-organism carbohydrate catabolic process; 12, tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation; 13, L-serine metabolic process; 14, Carbohydrate catabolic process; 15, Amino acid activation; 16, tRNA aminoacylation; 17, Serine family amino acid metabolic process; 18, Oxidoreductase activity; 19, Catalytic activity; 20, Iron ion binding; 21, Cofactor binding; 22, NAD binding; 23, Hydroxymethyl-, formyl-and related transferase activity; 24, Small molecule binding; 25, Oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH—OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor; 26, Oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen; 27, Tetrapyrrole binding; 28, Vitamin binding; 29, Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase activity; 30, Coenzyme binding.
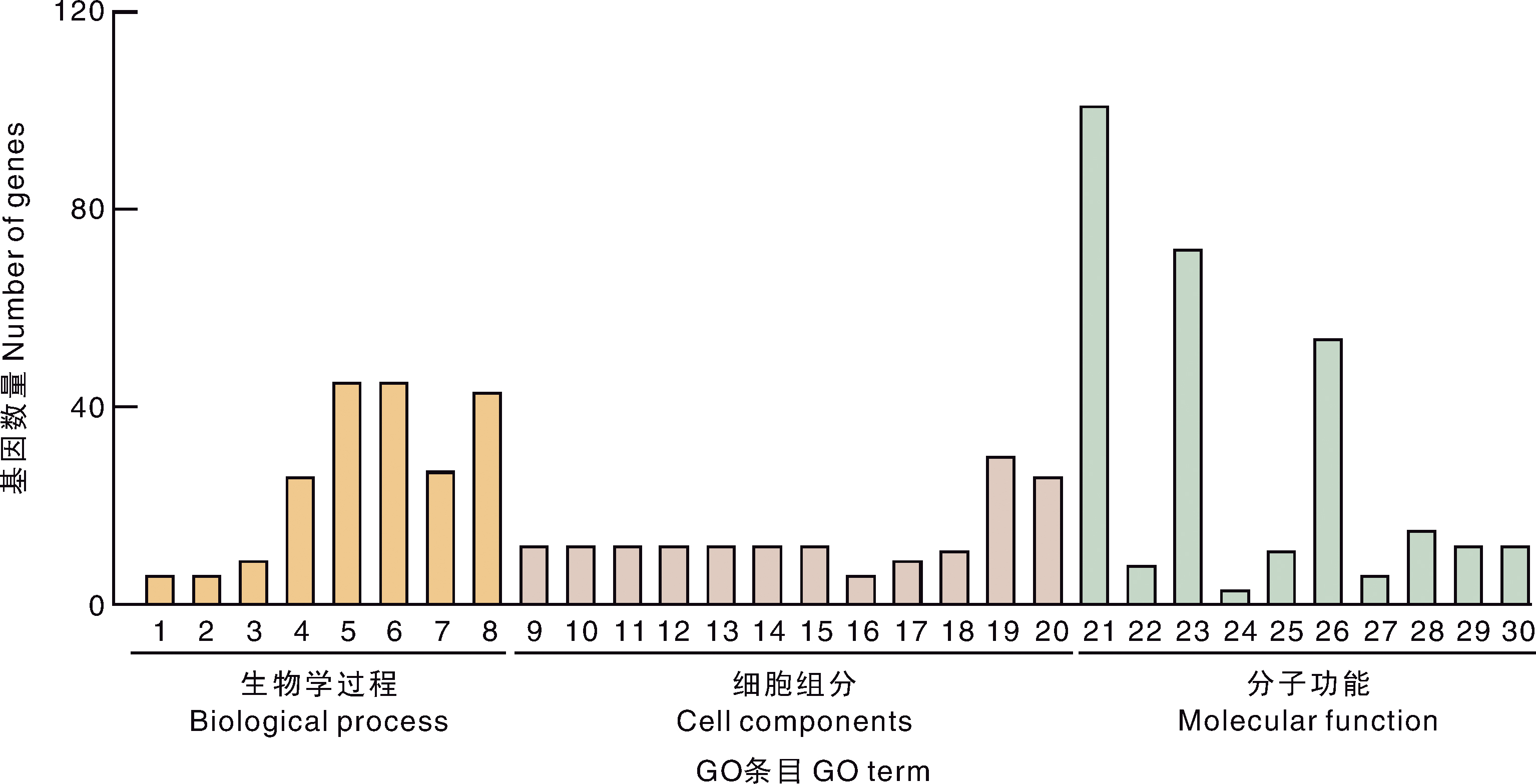
图6 感染哈维氏弧菌后小黄鱼鳃丝中差异表达基因的GO功能富集 1,气体运输;2,氧气输送;3,谷氨酰胺家族氨基酸代谢过程;4,免疫反应;5,有机酸代谢过程;6,含氧酸代谢过程;7,免疫系统过程;8,羧酸代谢过程;9,肌钙蛋白复合体;10,横纹肌细丝;11,肌原纤维;12,肌节;13,肌丝;14,收缩纤维;15,收缩纤维部分;16,血红蛋白复合体;17,胶原蛋白;18,细胞外基质部分;19,肌动蛋白细胞骨架;20,细胞外基质;21,钙离子结合;22,水解酶活性,作用于碳氮键(但不是肽键);23,脂质结合;24,羧基或氨基甲酰转移酶活性;25,细胞外基质结构成分;26,磷脂结合;27,氧气结合;28,水解酶活性,作用于酸酐,催化物质的跨膜运动;29,细胞因子活性;30,磷酸吡哆醛结合。
Fig.6 GO functional enrichment of differentially expressed genes in the gill filament of small yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harveyi 1, Gas transport; 2, Oxygen transport; 3, Glutamine family amino acid metabolic process; 4, Immune response; 5, Organic acid metabolic process; 6, Oxoacid metabolic process; 7, Immune system process; 8, Carboxylic acid metabolic process; 9, Troponin complex; 10, Striated muscle thin filament; 11, Myofibril; 12, Sarcomere; 13, Myofilament; 14, Contractile fiber; 15, Contractile fiber part; 16, Hemoglobin complex; 17, Collagen; 18, Extracellular matrix part; 19, Actin cytoskeleton; 20, Extracellular matrix; 21, Calcium ion binding; 22, Hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds; 23, Lipid binding; 24, Carboxyltransferase or carbamoyltransferase activity; 25, Extracellular matrix structural constituent; 26, Phospholipid binding; 27, Oxygen binding; 28, Hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances; 29, Cytokine activity; 30, Pyridoxal phosphate binding.
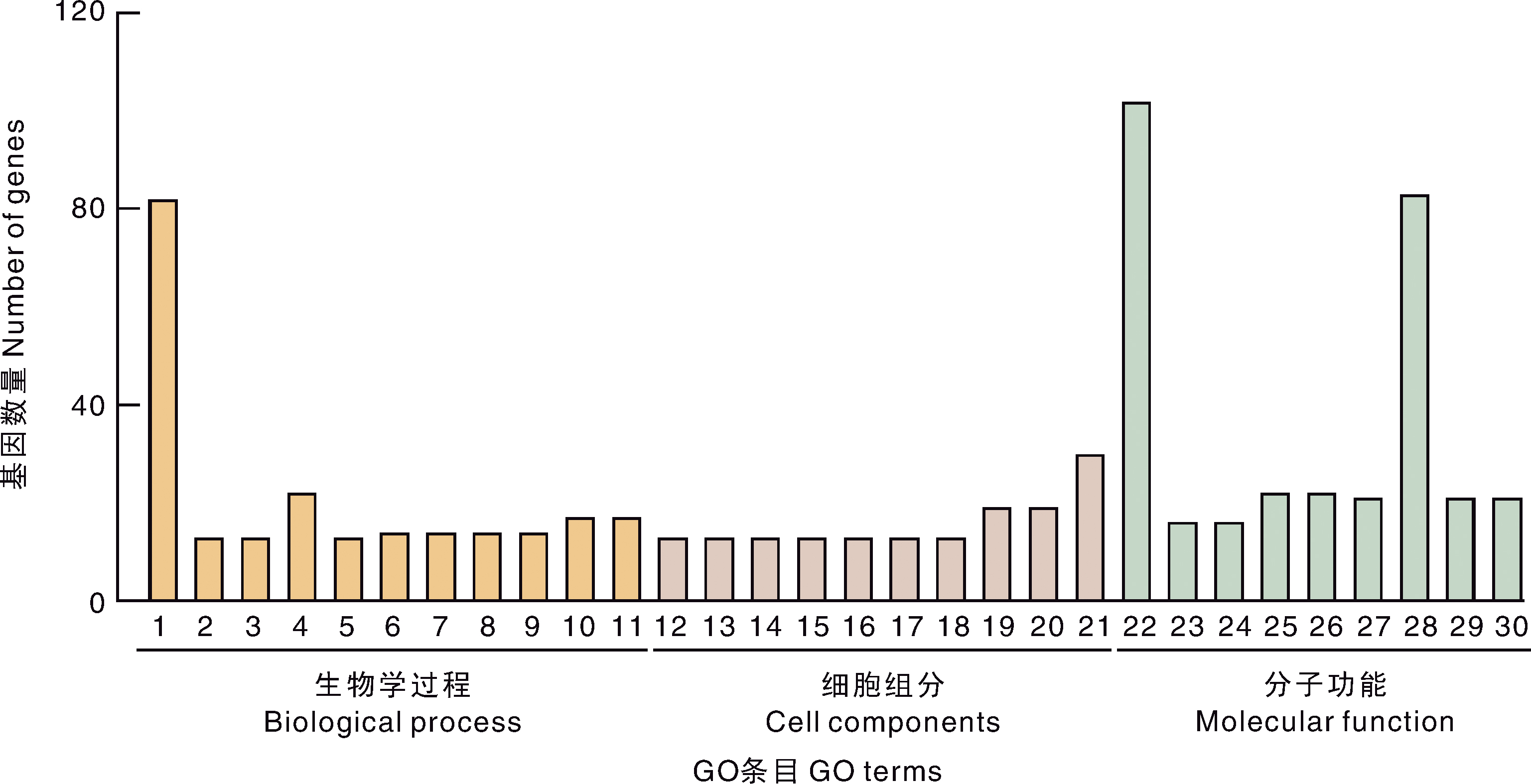
图7 感染哈维氏弧菌后小黄鱼皮肤中差异表达基因的GO功能富集 1,氧化还原过程;2,能量耦合质子输运,电化学梯度下降;3,ATP合成耦合电子传递;4,含嘌呤化合物补救;5,ATP生物合成过程;6,三磷酸核苷生物合成过程;7,嘌呤核苷三磷酸生物合成过程;8,核糖核苷三磷酸生物合成过程;9,嘌呤核糖核苷三磷酸生物合成过程;10,嘌呤核苷生物合成过程;11,嘌呤核糖核苷生物合成过程;12,肌钙蛋白复合体;13,横纹肌肌丝;14,肌原纤维;15,肌节;16,肌丝;17,收缩纤维;18,收缩纤维部分;19,线粒体内膜;20,细胞器内膜;21,线粒体;22,氧化还原酶活性;23,阳离子转运ATP酶活性;24,离子跨膜转运偶联的ATP酶活性;25,初级活性跨膜转运蛋白活性;26,P-P键水解驱动的跨膜转运蛋白活性;27,物质跨膜转运偶联的ATP酶活性;28,阳离子跨膜转运蛋白活性;29,物质转运偶联的ATP酶活性;30,水解酶活性,作用于酸酐,催化物质的跨膜运动。
Fig.7 GO functional enrichment of differentially expressed genes in the skin of small yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harveyi 1, Oxidation-reduction process; 2, Energy coupled proton transport, decreased electrochemical gradient; 3, ATP synthesis coupled electron transport; 4, Purine-containing compound salvage; 5, ATP biosynthetic process; 6, Nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process; 7, Purine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process; 8, Ribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process; 9, Purine ribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process; 10, Purine nucleoside biosynthetic process; 11, Purine ribonucleoside biosynthetic process; 12, Troponin complex; 13, Striated muscle thin filament; 14, Myofibril; 15, Sarcomere; 16, Myofilament; 17, Contractile fiber; 18, Contractile fiber part; 19, Mitochondrial inner membrane; 20, Organelle inner membrane; 21, Mitochondrion; 22, Oxidoreductase activity; 23, Cation-transporting ATPase activity; 24, ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of ions; 25, Primary active transmembrane transporter activity; 26, P-P-bond-hydrolysis-driven transmembrane transporter activity; 27, ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of substances; 28, Cation transmembrane transporter activity; 29, ATPase activity, coupled to movement of substances; 30, Hydrolase activity, acting on acid anhydrides, catalyzing transmembrane movement of substances.
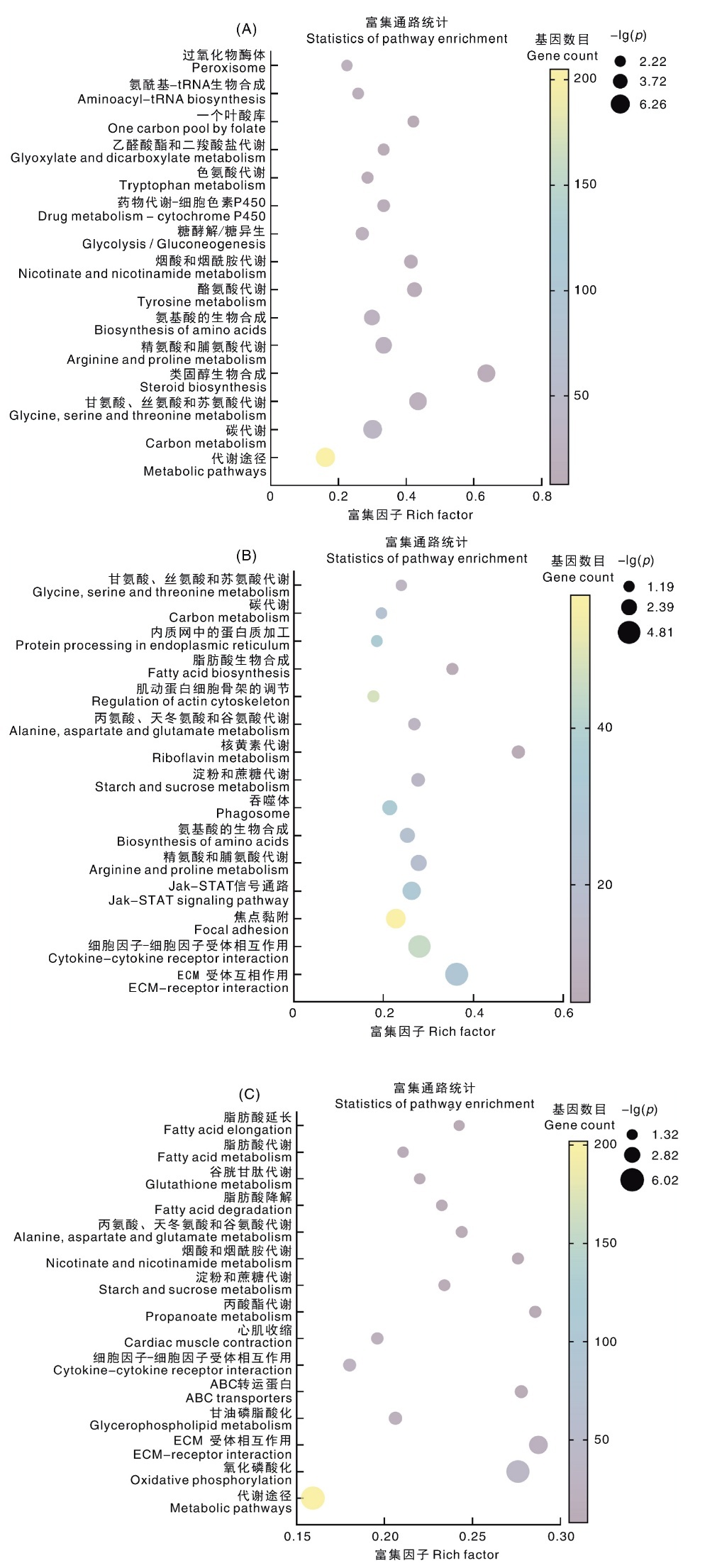
图8 感染哈维氏弧菌后小黄鱼肝、鳃丝和皮肤中差异表达基因的KEGG通路富集(富集排名前15) A,肝;B,鳃丝;C,皮肤。
Fig.8 KEGG pathway enrichment of differentially expressed genes in liver, gill filament and skin of little yellow croaker infected with Vibrio harvevi(Top 15 of enriched pathways) A, Liver ; B, Gill filament ; C, Skin.
| 信号通路 Signaling pathway | p值p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TLT vs CLT | TGT vs CGT | TST vs CST | |
| ECM受体相互作用ECM-receptor interaction | 0.053 83 | 1.55×10-5 | 1.80×10-4 |
| 类固醇生物合成Steroid biosynthesis | 4.68×10-5 | 0.204 51 | 0.709 55 |
| 药物代谢-细胞色素P450 Drug metabolism-cytochrome P450 | 0.001 61 | 0.760 06 | 0.093 75 |
| 过氧化物酶体Peroxisome | 0.006 07 | 0.638 46 | 0.540 21 |
| JAK-STAT信号通路JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 0.513 82 | 8.80×10-4 | 0.074 86 |
| 细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 0.719 27 | 2.50×10-5 | 0.014 39 |
| 黏着斑Focal adhesion | 0.749 86 | 3.10×10-4 | 0.125 39 |
| 吞噬体Phagosome | 0.950 17 | 0.009 32 | 0.804 68 |
| 肌动蛋白细胞骨架的调节Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 0.987 48 | 0.042 31 | 0.944 52 |
| NOD样受体信号通路NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.632 37 | 0.137 23 | 0.460 77 |
| RIG-I样受体信号通路RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.788 59 | 0.405 46 | 0.955 60 |
| Toll样受体信号通路Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.937 22 | 0.513 55 | 0.968 32 |
| MAPK信号通路MAPK signaling pathway | 0.999 00 | 0.854 76 | 0.800 23 |
| 内吞作用Endocytosis | 0.998 29 | 0.849 45 | 0.998 04 |
| 钙信号通路Calcium signaling pathway | 0.996 86 | 0.464 02 | 0.806 56 |
| 胞质DNA感知通路Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 0.811 59 | 0.760 06 | 0.985 52 |
表3 健康组和感染组小黄鱼不同组织中免疫相关信号通路及其p值变化
Table 3 Changes of key signaling pathways and their p-values in different tissues of healthy group and infected group of little yellow croakers
| 信号通路 Signaling pathway | p值p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TLT vs CLT | TGT vs CGT | TST vs CST | |
| ECM受体相互作用ECM-receptor interaction | 0.053 83 | 1.55×10-5 | 1.80×10-4 |
| 类固醇生物合成Steroid biosynthesis | 4.68×10-5 | 0.204 51 | 0.709 55 |
| 药物代谢-细胞色素P450 Drug metabolism-cytochrome P450 | 0.001 61 | 0.760 06 | 0.093 75 |
| 过氧化物酶体Peroxisome | 0.006 07 | 0.638 46 | 0.540 21 |
| JAK-STAT信号通路JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 0.513 82 | 8.80×10-4 | 0.074 86 |
| 细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 0.719 27 | 2.50×10-5 | 0.014 39 |
| 黏着斑Focal adhesion | 0.749 86 | 3.10×10-4 | 0.125 39 |
| 吞噬体Phagosome | 0.950 17 | 0.009 32 | 0.804 68 |
| 肌动蛋白细胞骨架的调节Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 0.987 48 | 0.042 31 | 0.944 52 |
| NOD样受体信号通路NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.632 37 | 0.137 23 | 0.460 77 |
| RIG-I样受体信号通路RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.788 59 | 0.405 46 | 0.955 60 |
| Toll样受体信号通路Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 0.937 22 | 0.513 55 | 0.968 32 |
| MAPK信号通路MAPK signaling pathway | 0.999 00 | 0.854 76 | 0.800 23 |
| 内吞作用Endocytosis | 0.998 29 | 0.849 45 | 0.998 04 |
| 钙信号通路Calcium signaling pathway | 0.996 86 | 0.464 02 | 0.806 56 |
| 胞质DNA感知通路Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 0.811 59 | 0.760 06 | 0.985 52 |
| [1] | 李建生, 林龙山, 程家骅. 东海北部秋季小黄鱼分布特征及其与底层温度和盐度的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2009, 16(3): 348-356. |
| LI J S, LIN L S, CHENG J H. Distribution characteristic of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis Bleeker) and its relationship with bottom water temperature and salinity in the northern East China Sea in autumn[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2009, 16(3): 348-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 楼宝, 詹炜, 陈睿毅, 等. 小黄鱼全人工繁育技术研究[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 35(5): 361-365. |
| LOU B, ZHAN W, CHEN R Y, et al. Studies on techniques of the artificial breeding of Larimichthys polyactis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University(Natural Science), 2016, 35(5): 361-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张晓华, 钟英斌, 陈吉祥. 哈维氏弧菌的生物学特性、流行病学及检测技术[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 37(5): 740-748. |
| ZHANG X H, ZHONG Y B, CHEN J X. The biological characteristics, epidemiology and detection techniques of Vibrio harveyi[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2007, 37(5): 740-748. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 吴雅婷, 汪笑宇, 汤青平, 等. 半滑舌鳎体表溃疡症细菌性病原的分离鉴定及组织病理学研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(6): 135-143. |
| WU Y T, WANG X Y, TANG Q P, et al. Isolation and identification of bacterial etiology and histopathological study of surface ulcer of Cynoglossus semilaevis[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(6): 135-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 范文辉, 黄倢, 王秀华, 等. 养殖大菱鲆溃疡症病原菌的分离鉴定及系统发育分析[J]. 微生物学报, 2005, 45(5): 665-670. |
| FAN W H, HUANG J, WANG X H, et al. Identification and phylogenetic study of pathogenic bacteria causing ulcer disease of cultured Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2005, 45(5): 665-670. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 毛芝娟, 刘国勇, 陈昌福. 大黄鱼溃疡病致病菌的初步分离与鉴定[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2002, 29(2): 178-181. |
| MAO Z J, LIU G Y, CHEN C F. Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria causing ulcerosis in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea)[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2002, 29(2): 178-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 苏杭. 养殖凡纳滨对虾病原菌(哈维氏弧菌)的分离鉴定与防治[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2010. |
| SU H. Isolation and identification of Vibrio harveyi in cultured Litopenaeus vannamei and its prevention and treatment[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | ISHIMARU K, MUROGA K. Taxonomical re-examination of two pathogenic Vibrio species isolated from milkfish and swimming crab[J]. Fish Pathology, 1997, 32(1): 59-64. |
| [9] | 潘晓艺, 沈锦玉, 尹文林, 等. 哈维氏弧菌黑鲷分离株BK-1培养条件优化研究[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2005, 24(3): 240-243. |
| PAN X Y, SHEN J Y, YIN W L, et al. Studies on the optimal culture conditions of Vibrio harveyi BK-1 from Sparus macrocephalus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University, 2005, 24(3): 240-243. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 陈献稿, 吴淑勤, 石存斌, 等. 斜带石斑鱼病原菌(哈维氏弧菌)的分离与鉴定[J]. 中国水产科学, 2004, 11(4): 313-317. |
| CHEN X G, WU S Q, SHI C B, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogenetic Vibrio harveyi from estuary cod Epinephelus coioides[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2004, 11(4): 313-317. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 李营, 王波, 张培玉, 等. 哈维氏弧菌引起的条纹海马表皮溃疡综合征的研究[J]. 水产学报, 2019, 43(5): 1298-1307. |
| LI Y, WANG B, ZHANG P Y, et al. Research on epidermis ulcer syndrome caused by Vibrio harveyi in Hippocampus erectus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(5): 1298-1307. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李文悦, 左志晗, 张晶晶, 等. 半滑舌鳎溃疡病病原菌的分离、鉴定及其致病性分析[J]. 水产学报, 2020, 44(4): 672-680. |
| LI W Y, ZUO Z H, ZHANG J J, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogens of ulcer disease in Cynoglossus semilaevis[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2020, 44(4): 672-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 戴瑜来, 吕永林, 李凯, 等. 大黄鱼溃疡病的组织病理和超微病理研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(5): 174-179. |
| DAI Y L, LYU Y L, LI K, et al. Histopathological and ultrapathological study on ulcer disease of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(5): 174-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 徐晓津, 徐斌, 王军, 等. 哈维氏弧菌人工感染大黄鱼的组织病理学研究[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 48(2): 281-286. |
| XU X J, XU B, WANG J, et al. Histopathological studies on Pseudosciaena crocea artificially challenged with Vibrio harveyi[J]. Journal of Xiamen University(Natural Science), 2009, 48(2): 281-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 许悦, 王印庚, 周永灿, 等. 海南地区养殖石斑鱼皮肤溃疡病病原的分离、鉴定、药敏分析及病理学研究[J]. 海南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 36(2): 153-163. |
| XU Y, WANG Y G, ZHOU Y C, et al. Isolation, identification, and pathogen analysis of skin-ulcer disease in cultured groupers in Hainan Province[J]. Natural Science Journal of Hainan University, 2018, 36(2): 153-163. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | DASH S, DAS S K, SAMAL J, et al. Epidermal mucus, a major determinant in fish health: a review[J]. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, 2018, 19(2): 72-81. |
| [17] | SOMAMOTO T, NAKANISHI T. Mucosal delivery of fish vaccines: local and systemic immunity following mucosal immunisations[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2020, 99: 199-207. |
| [18] | 张永安, 孙宝剑, 聂品. 鱼类免疫组织和细胞的研究概况[J]. 水生生物学报, 2000, 24(6): 648-654. |
| ZHANG Y A, SUN B J, NIE P. Immune tissues and cells of fish: a review[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2000, 24(6): 648-654. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | DALMO R A, INGEBRIGTSEN K, BØGWALD J. Non-specific defence mechanisms in fish, with particular reference to the reticuloendothelial system (RES)[J]. Journal of Fish Diseases, 1997, 20(4): 241-273. |
| [20] | 吴迪. 鰤鱼诺卡氏菌分离、培养及感染对小黄鱼免疫应答初步研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2023. |
| WU D. Isolation and culture of Nocardia seriolae and preliminary study on immune reponse of infection to Larimichthys polyactis[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | SUTHERLAND T E, DYER D P, ALLEN J E. The extracellular matrix and the immune system: a mutually dependent relationship[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6633): eabp8964. |
| [22] | 龚非力. 医学免疫学[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| [23] | TURNER M D, NEDJAI B, HURST T, et al. Cytokines and chemokines: at the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2014, 1843(11): 2563-2582. |
| [24] | GAO D X, LEI W, WANG C S, et al. RNA-sequencing analysis of the spleen and gill of Takifugu rubripes in response to Vibrio harveyi infection[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2022, 8: 813988. |
| [25] | CHUPHAL B, RAI U, ROY B. Teleost NOD-like receptors and their downstream signaling pathways: a brief review[J]. Fish and Shellfish Immunology Reports, 2022, 3: 100056. |
| [26] | 庞纪彩. 尼罗罗非鱼Toll样受体信号通路基因表达研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016. |
| PANG J C. Expression analysis of TLR signaling pathway genes of Nile Tilapia[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 丁云磊, 孙英杰, 王晓旭, 等. RIG-I样受体信号通路及其调控研究进展[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2014, 22(5): 72-79. |
| DING Y L, SUN Y J, WANG X X, et al. Advances in signaling pathways and regulation of RIG-I-like receptor[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2014, 22(5): 72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 潘鑫煜, 黄慧灵, 韩明明, 沈宁远, 赵旭东, 楼宝. 刺激隐核虫感染对小黄鱼肠道的组织结构、免疫水平与微生物组成的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2265-2274. |
| [2] | 杨蕾, 汪小福, 魏巍, 陈笑芸, 彭城, 徐晓丽, 徐俊锋. 昆虫抗白僵菌免疫应答及其在害虫防治中的应用潜力[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(4): 825-836. |
| [3] | 聂红丽, 成琪璐, 孙万春, 马进川, 林辉, 马军伟. 小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris)对泰乐菌素的胁迫响应与耐受性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2316-2327. |
| [4] | 何雨, 刘峰, 张天乐, 楼宝, 魏福亮, 叶挺. 高温胁迫对小黄鱼肝脏组织结构和细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 58-66. |
| [5] | 郭丹丹, 刘峰, 牛宝龙, 楼宝. 基于线粒体Cytb基因和D-loop区的野生与养殖小黄鱼群体遗传多样性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(9): 1856-1865. |
| [6] | 樊利虹, 郭红瑞, 吴江, 易军, 马晓平, 苟丽萍, 谢跃, 叶刚, 左之才. 牛源皮特不动杆菌对小鼠的致病性分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(2): 230-238. |
| [7] | 王元红, 鲁智敏, 张学琪, 刘自敏, 胡子慧, 杨侃侃, 刘红梅, 潘玲, 彭开松, 李永东, 王勇. 一株J亚型禽白血病病毒的分离鉴定及其gp85基因的序列分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(5): 709-715. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||