浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2545-2553.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241094
青海省海东市设施番茄根结线虫病原鉴定
- 1.青海大学 农业病虫害综合治理重点实验室,农业农村部西宁农作物病虫害科学观测实验站,青海 西宁 810016
2.海东市平安区蔬菜技术服务中心,青海 海东 810699
-
收稿日期:2024-12-17出版日期:2025-12-25发布日期:2026-01-09 -
作者简介:*闫佳会,E-mail:15209787170@163.com
鲍梦楠(2000—),女,河南洛阳人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物病理学。E-mail:15737982286@163.com -
通讯作者:闫佳会 -
基金资助:青海省中央引导地方科技发展资金项目(2024ZY025)
Identification of Meloidogyne spp. infecting tomato in Haidong City, Qinghai Province, China
BAO Mengnan1( ), LI Jinbin1, ZHANG Xian2, YAN Jiahui1,*(
), LI Jinbin1, ZHANG Xian2, YAN Jiahui1,*( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Agricultural Integrated Pest Management of Qinghai Province, Xining Crop Diseases and Insect Pests Scientific Observation Experimental Station of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Qinghai University, Xining 810016, China
2. Vegetable Technology Service Center, Ping’an District, Haidong City, Haidong 810699, Qinghai, China
-
Received:2024-12-17Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09 -
Contact:YAN Jiahui
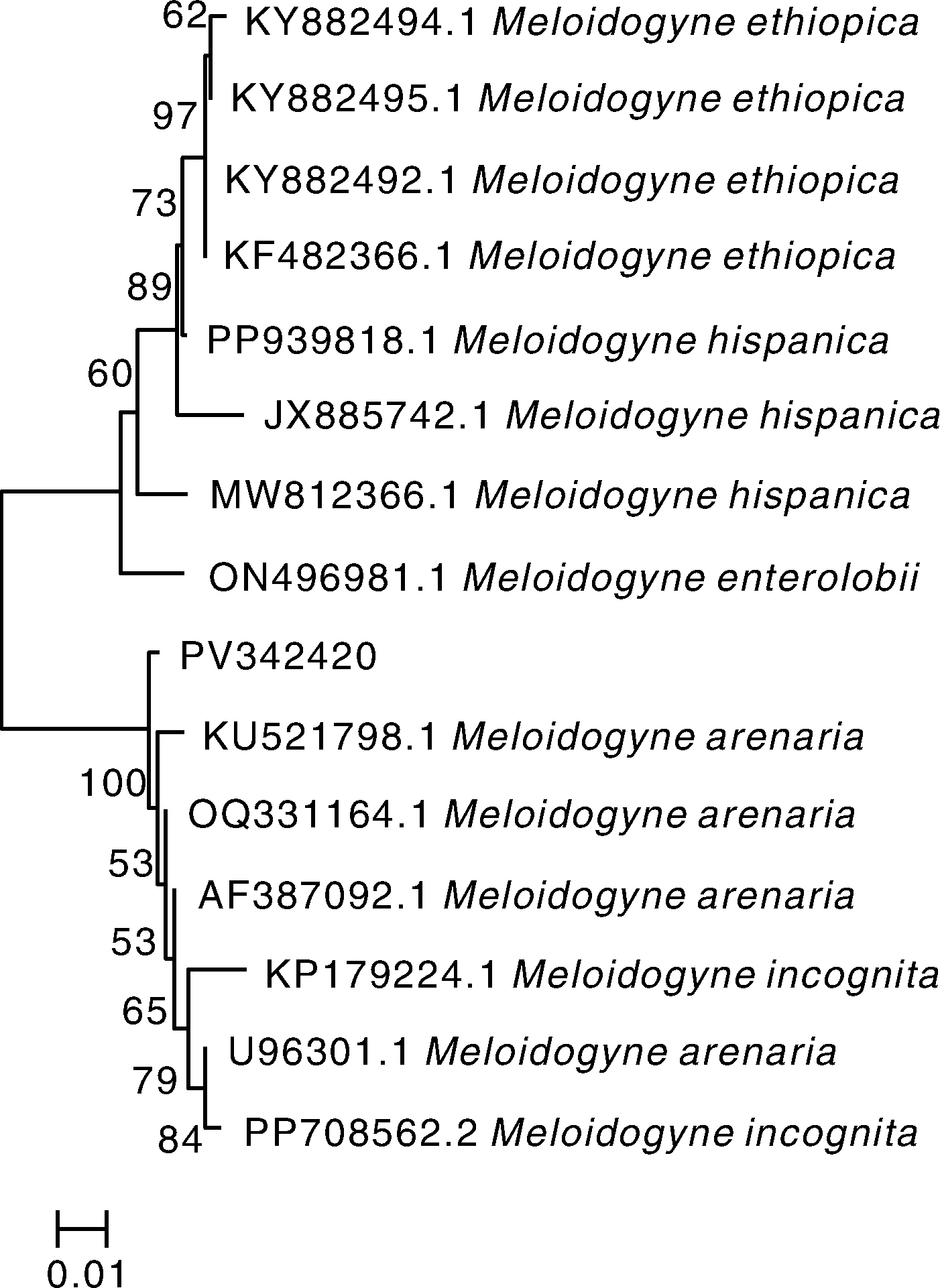
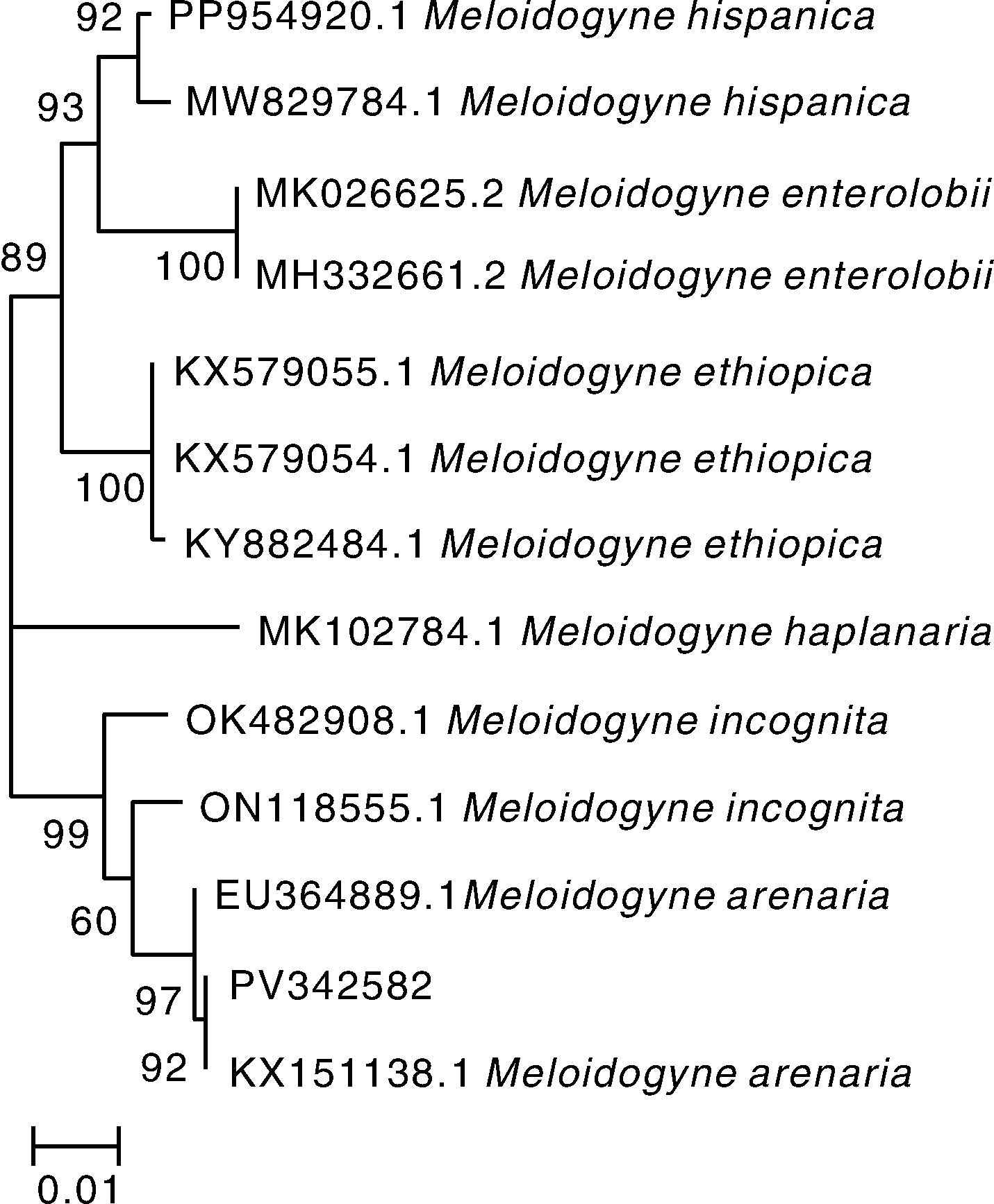
摘要: 为明确青海省海东市平安区农鑫种植专业合作社番茄大棚中根结线虫(Meloidogyne spp.)的种类,本研究采用形态学与分子生物学方法对该线虫群体进行种类鉴定,并通过室内盆栽接种试验测定其对番茄的致病性。结果表明,该群体雌虫的体值与会阴花纹特征均与花生根结线虫(Meloidogyne arenaria)基本一致;利用花生根结线虫特异序列扩增标记(SCAR)引物Far/Rar进行PCR扩增,获得长度为420 bp的特异性条带。基于rDNA ITS区与28S rRNA D2A/D3B区序列构建的系统发育树显示,该线虫群体与其他花生根结线虫序列聚为一支,同源性高于95%。综合形态学与分子生物学鉴定结果,确定引起该地区番茄根结线虫病的病原为花生根结线虫(M. arenaria)。盆栽接种试验表明,接种该线虫后番茄植株表现为植株矮小、茎秆细弱、叶片黄化;接种30 d后根部可见明显根结,经分离鉴定确认为花生根结线虫。本研究首次在青海省发现并报道了花生根结线虫,为该地区番茄根结线虫病的科学防控提供了依据。
中图分类号:
引用本文
鲍梦楠, 李劲斌, 张宪, 闫佳会. 青海省海东市设施番茄根结线虫病原鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2545-2553.
BAO Mengnan, LI Jinbin, ZHANG Xian, YAN Jiahui. Identification of Meloidogyne spp. infecting tomato in Haidong City, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2545-2553.
| 目标片段 Target region | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5'→3') Sequence(5'→3') | 扩增长度 Amplification size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ | 退火时间 Annealing time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rDNA ITS | 18S | TTGATTACGTCCCTGCCCTTT | 771 | 55 | 45 |
| 26S | TTTCACTCGCCGTTACTACGG | ||||
| 28S rDNA | D2A | ACAAGTACCGTGAGGGAAAGTTG | 754 | 56 | 45 |
| D3B | TCGGAAGGAACCAGCTACTA | ||||
| SCAR标记 | Far | TCGGCGATAGAGGTAAATGAC | 420 | 61 | 27 |
| SCAR marker | Rar | TCGGCGATAGACACTACAACT |
表1 本研究所用引物信息
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 目标片段 Target region | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5'→3') Sequence(5'→3') | 扩增长度 Amplification size/bp | 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ | 退火时间 Annealing time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rDNA ITS | 18S | TTGATTACGTCCCTGCCCTTT | 771 | 55 | 45 |
| 26S | TTTCACTCGCCGTTACTACGG | ||||
| 28S rDNA | D2A | ACAAGTACCGTGAGGGAAAGTTG | 754 | 56 | 45 |
| D3B | TCGGAAGGAACCAGCTACTA | ||||
| SCAR标记 | Far | TCGGCGATAGAGGTAAATGAC | 420 | 61 | 27 |
| SCAR marker | Rar | TCGGCGATAGACACTACAACT |
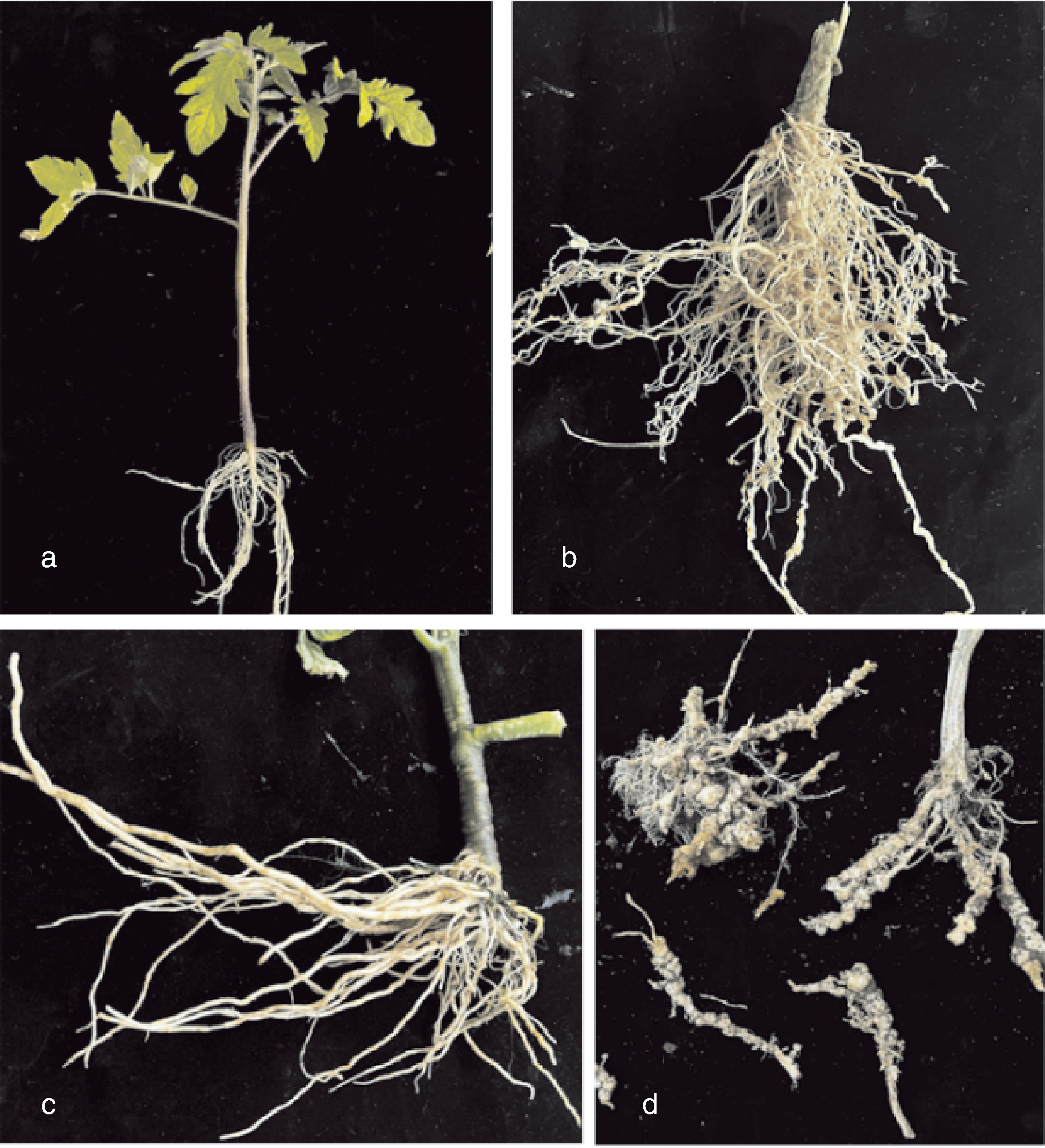
图1 番茄根结线虫病发病症状 a,发病前期地上部表现缺素;b,发病前期根部出现根结;c,健康番茄植株根部; d,发病后期根部变为褐色并腐烂。
Fig.1 Symptoms of tomato plants infected with root-knot nematodes a, Aboveground symptoms of nutrient deficiency at the early stage of disease; b, Root knots in the root system at the early stage; c, Roots of healthy tomato plant; d, Roots turning brown and rotting at the late stage of disease.
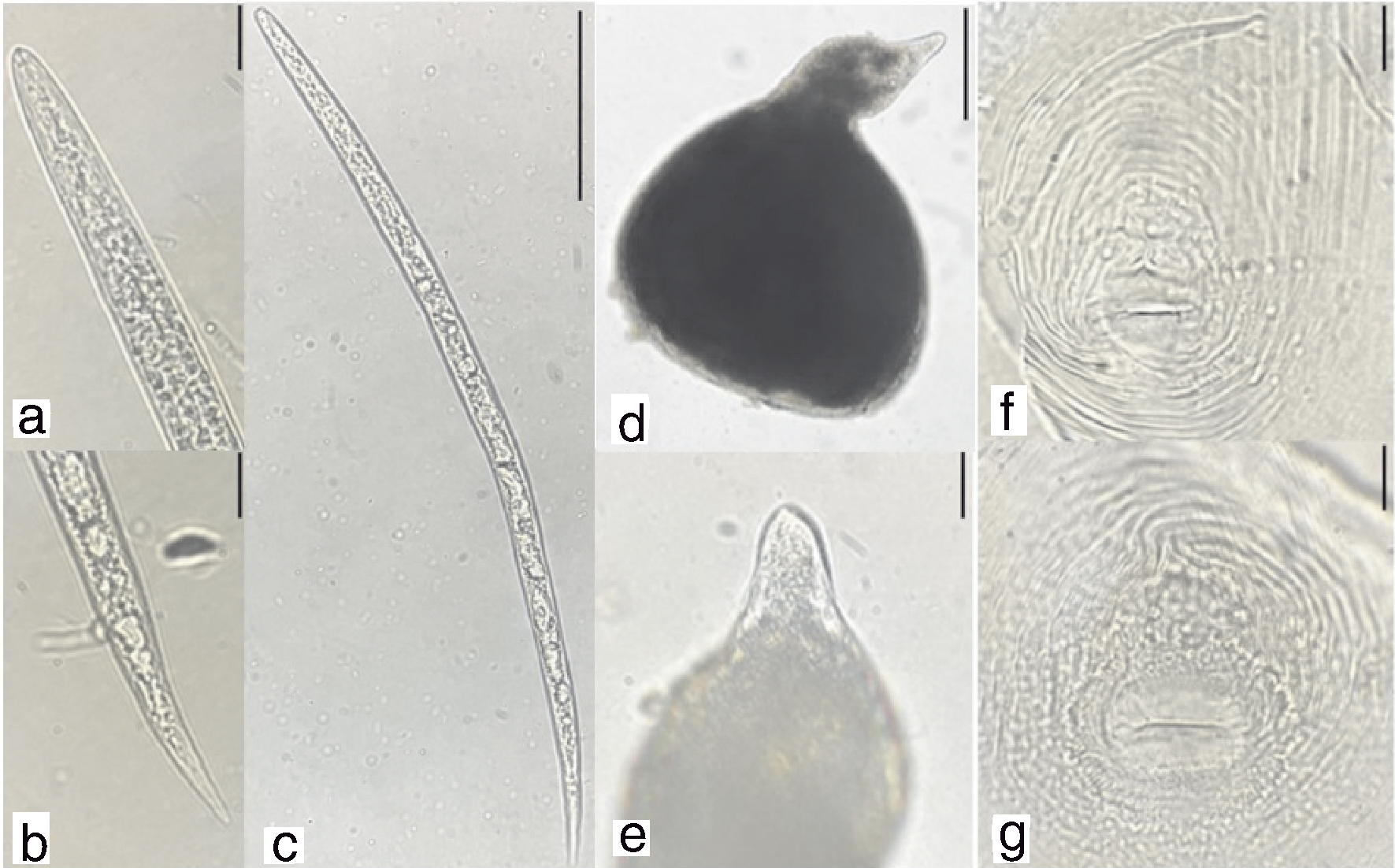
图2 番茄根结线虫群体形态学特征 a,二龄幼虫头部;b,二龄幼虫尾部;c,二龄幼虫整体;d,雌虫;e,雌虫体前端;f和g,会阴花纹。比例尺:a、b、e、f、g为10 μm,c、d为100 μm。
Fig.2 Morphological characteristics of the root-knot nematode population in tomato a, Anterior region of J2; b, Tail region of J2; c, Entire body of J2; d, Female; e, Anterior region of female; f and g, Perineal pattern. Scale bars: a, b, e, f, g=10 μm, c and d=100 μm.
| 样本 Sample | 体长 Body length/μm | 体宽 Body width/μm | 口针长 Stylet length/μm | 背食道腺开口到口 针基部球的距离 Distance from dorsal esophageal gland opening to the stylet knot/μm | 尾长 Tail length/ μm | 体长/体宽 Body length/ Body width | 体长/尾长 Body length/ Tail length | 尾长/肛门 处虫体宽 Tail length/ Anal body diameter | 中食道 球宽 Metacorpus width/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雌虫 Female (n=20) | 571.33± 78.61 (455.51~ 696.03) | 403.45± 59.21 (302.02~ 492.74) | 12.48± 1.50 (10.09~ 14.80) | 3.98±0.57 (3.09~4.98) | — | — | — | — | 30.23± 6.33 (21.48~ 39.42) |
| 二龄幼虫 Second-stage juveniles(J2) (n=20) | 413.53± 32.64 (372.52~ 486.10) | — | 11.33± 1.35 (8.90~ 13.12) | 9.23±2.64 (5.04~14.42) | 31.19± 2.97 (22.50~ 40.38) | 31.30± 2.63 | 16.34± 1.68 | 5.10± 1.03 | — |
表2 根结线虫群体雌虫与二龄幼虫的体值
Table 2 Morphometric parameters of female and second-stage juveniles (J2) of root-knot nematode population
| 样本 Sample | 体长 Body length/μm | 体宽 Body width/μm | 口针长 Stylet length/μm | 背食道腺开口到口 针基部球的距离 Distance from dorsal esophageal gland opening to the stylet knot/μm | 尾长 Tail length/ μm | 体长/体宽 Body length/ Body width | 体长/尾长 Body length/ Tail length | 尾长/肛门 处虫体宽 Tail length/ Anal body diameter | 中食道 球宽 Metacorpus width/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 雌虫 Female (n=20) | 571.33± 78.61 (455.51~ 696.03) | 403.45± 59.21 (302.02~ 492.74) | 12.48± 1.50 (10.09~ 14.80) | 3.98±0.57 (3.09~4.98) | — | — | — | — | 30.23± 6.33 (21.48~ 39.42) |
| 二龄幼虫 Second-stage juveniles(J2) (n=20) | 413.53± 32.64 (372.52~ 486.10) | — | 11.33± 1.35 (8.90~ 13.12) | 9.23±2.64 (5.04~14.42) | 31.19± 2.97 (22.50~ 40.38) | 31.30± 2.63 | 16.34± 1.68 | 5.10± 1.03 | — |
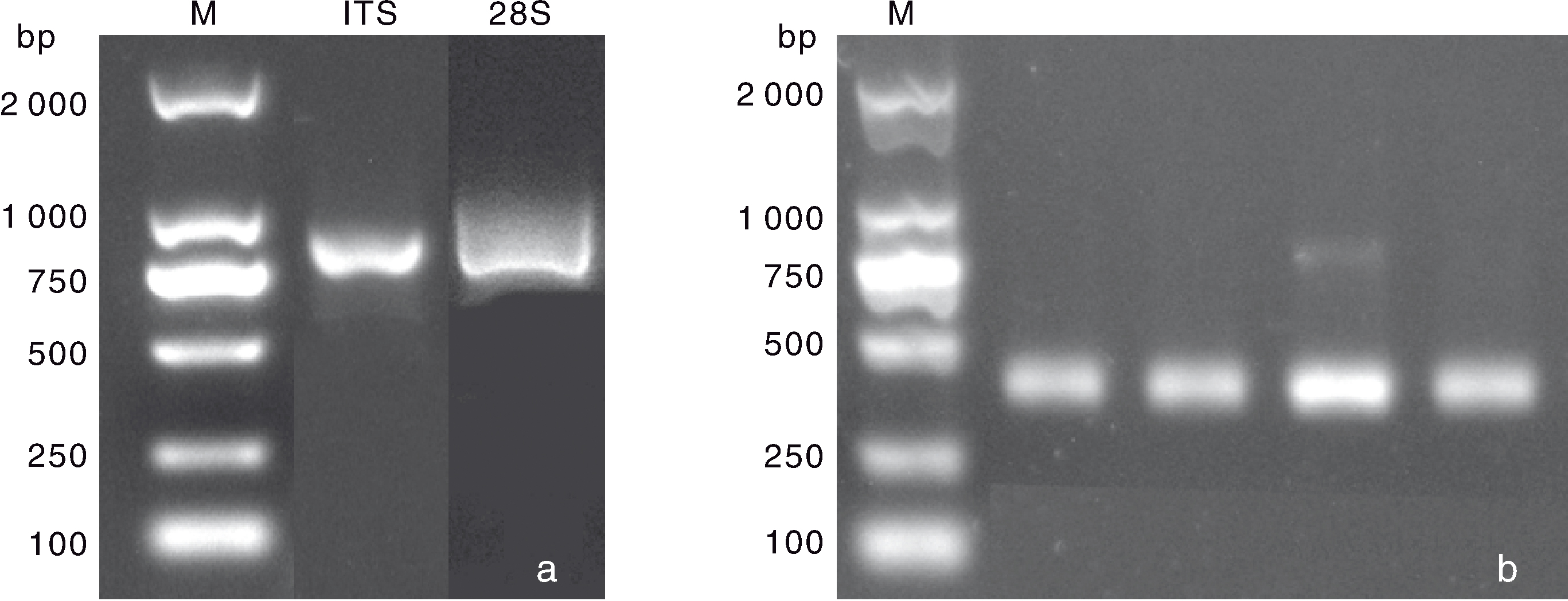
图3 番茄群体根结线虫分子生物学鉴定结果 a,根结线虫rDNA ITS与28S rDNA D2/D3区扩增结果;b,花生根结线虫SCAR标记引物(Far/Rar)扩增结果。
Fig.3 Molecular biological identification results of root-knot nematodes in tomato population a, Amplification of rDNA ITS and 28S rDNA D2/D3 regions in root-knot nematodes; b, Amplification with the M. arenaria-specific SCAR primers Far/Rar.
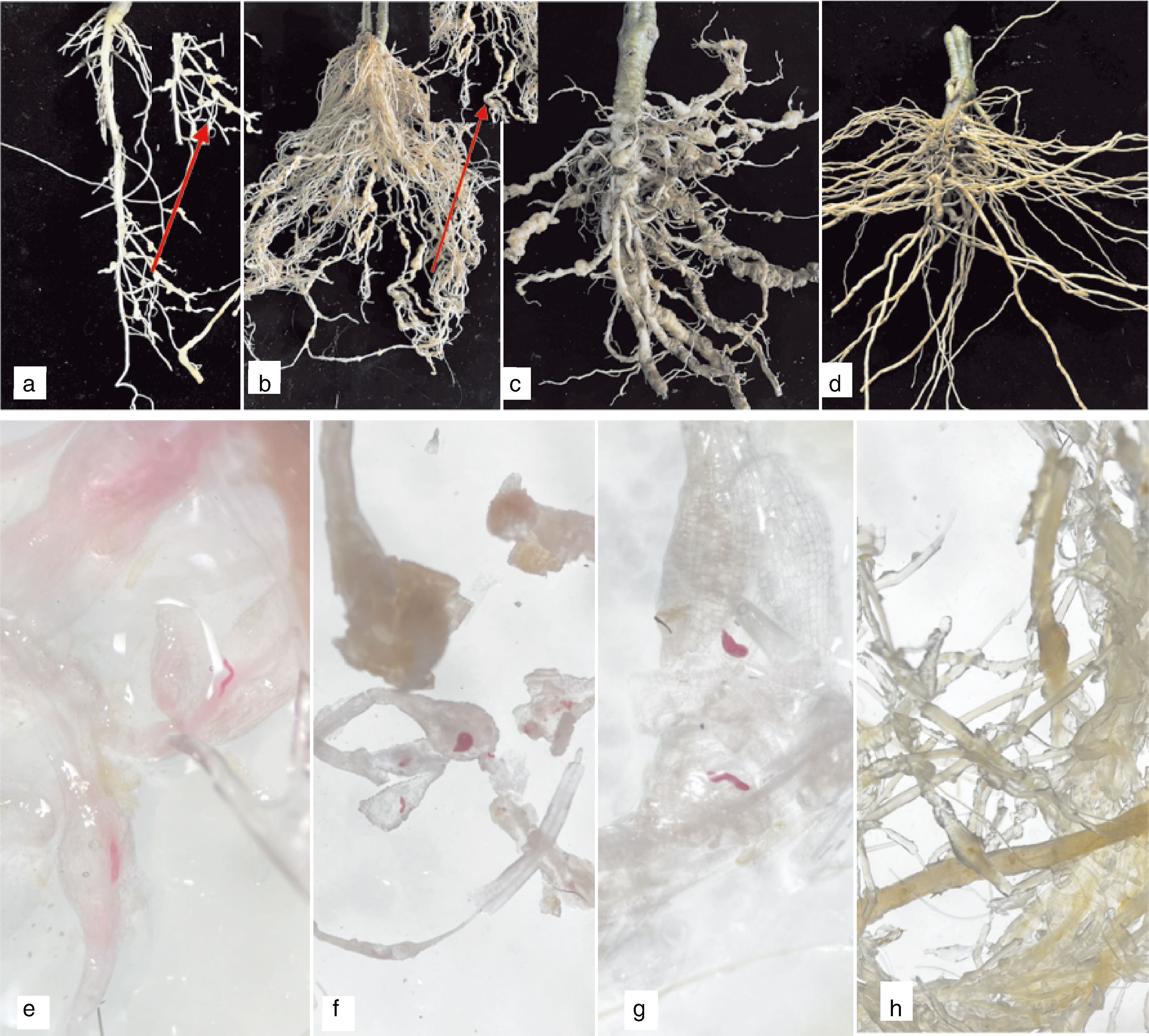
图6 盆栽番茄接种根结线虫后的根部症状与染色结果 a,接种40 d后番茄根部症状;b,接种70 d后番茄根部症状;c,侵染后期番茄根部症状;d,健康植株根部;e~h,根系染色结果。
Fig.6 Root symptoms and staining results of potted tomato plants following root-knot nematode inoculation a, Tomato roots on 40 days post-inoculation; b, Tomato roots on 70 days post-inoculation; c, Roots at late infection stage; d, Roots of healthy plants; e-h, Root staining results.
| [1] | 曹秀伟. 海东市乐都区设施蔬菜发展对策[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2022(4): 110-114. |
| CAO X W. Development countermeasures of protected vegetables in Ledu District of Haidong City[J]. China Vegetables, 2022(4): 110-114. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 钟应霞. 青海省设施农业生产经营情况调查与分析[J]. 青海农技推广, 2023(3): 39-40. |
| ZHONG Y X. Investigation and analysis on the production and management of protected agriculture in Qinghai Province[J]. Qinghai Agro-Technology Extension, 2023(3): 39-40. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | TAPIA-VÁZQUEZ I, MONTOYA-MARTÍNEZ A C, DE LOS SANTOS-VILLALOBOS S, et al. Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) a threat to agriculture in Mexico: biology, current control strategies, and perspectives[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 38(2): 26. |
| [4] | LONG H B, SUN Y F, CHEN Y, et al. Occurrence of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) on peppers in Hainan, China, and M. enterolobii and M. incognita resistance of common cultivars[J]. Plant Disease, 2023, 107(10): 3148-3154. |
| [5] | 付博, 王家哲, 李英梅, 等. 陕西猕猴桃根结线虫病综合防控措施[J]. 西北园艺, 2024(4): 36-37. |
| FU B, WANG J Z, LI Y M, et al. Comprehensive control measures of kiwifruit root-knot nematode disease in Shaanxi Province[J]. Northwest Horticulture, 2024(4): 36-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | XU C L, ZHAO C B, DING S, et al. First report of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne arenaria infesting roots of Anubias barteri in Guangdong, China[J]. Plant Disease, 2012, 96(5): 773. |
| [7] | CAO Y, LI C B, MA G M, et al. First report of Meloidogyne arenaria infecting maize in Guizhou Province of China[J]. Plant Disease, 2023, 107(10): 3321. |
| [8] | 罗佳, 杭晓宁, 汝学娟, 等. 重庆番茄根结线虫病的病原种类鉴定[J]. 分子植物育种, 2024, 22(2): 512-516. |
| LUO J, HANG X N, RU X J, et al. Identification of pathogen species of root knot nematode on tomato in Chongqing[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2024, 22(2): 512-516. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 安丽婷, 石明明, 倪春辉, 等. 甘肃省胡萝卜根结线虫病病原鉴定[J]. 西北农业学报, 2024, 33(1): 183-190. |
| AN L T, SHI M M, NI C H, et al. Identification of carrot root-knot nematode pathogen in Gansu Province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 183-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 秦瑞峰, 李春杰, 郭文秀, 等. 山东省临沂地区中草药丹参根结线虫的种类鉴定[J]. 土壤与作物, 2023, 12(2): 161-169. |
| QIN R F, LI C J, GUO W X, et al. Species identification of Chinese herbal medicine Danshen root-knot nematodes in Linyi region, Shandong Province[J]. Soils and Crops, 2023, 12(2): 161-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 魏佩瑶, 潘嵩, 刘晨, 等. 西安市鄠邑区设施西瓜根结线虫种类鉴定及药剂防治研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(1): 83-90. |
| WEI P Y, PAN S, LIU C, et al. Pathogen identification and chemical control techniques against root-knot nematode disease of facility watermelon in Huyi District of Xi’an City[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(1): 83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | WANG X Z, WANG L F, PIAO C G, et al. First report of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne arenaria on Atractylodis macrocephalae in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2012, 96(10): 1583. |
| [13] | 石明明, 李惠霞, 刘永刚, 等. 甘肃省党参根结线虫病发生、分布及病原种类鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2022, 48(3): 181-191. |
| SHI M M, LI H X, LIU Y G, et al. Occurrence, distribution and species identification of the root-knot nematode disease of Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu, China[J]. Plant Protection, 2022, 48(3): 181-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 陈京环, 石明明, 乔万强, 等. 甘肃省黄芩根结线虫病病原种类鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2024, 50(2): 202-210. |
| CHEN J H, SHI M M, QIAO W Q, et al. Identification of pathogens of root-knot nematode disease of Scutellaria baicalensis in Gansu Province[J]. Plant Protection, 2024, 50(2): 202-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李芳. 玉米根线虫病的发生与防治[J]. 乡村科技, 2019(22): 85-86. |
| LI F. Occurrence and control of maize root nematode disease[J]. Rural Science and Technology, 2019, (22): 85-86. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 徐幸, 卓富彦, 杨芳, 等. 中国南方稻田及其周边环境根结线虫种类鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2023, 49(6): 95-103. |
| XU X, ZHUO F Y, YANG F, et al. Identification of root-knot nematode species from paddy fields and surrounding environment in southern China[J]. Plant Protection, 2023, 49(6): 95-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 赵传波, 郑小玲, 阮兆英, 等. 深圳市蔬菜基地根结线虫的种类和分布[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2015, 34(2): 41-48. |
| ZHAO C B, ZHENG X L, RUAN Z Y, et al. Identification and population distribution of Meloidogyne species from the vegetable base in Shenzhen City[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015, 34(2): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 练冬梅, 赖正锋, 姚运法, 等. 黄秋葵根结线虫病的病原鉴定[J]. 福建农业科技, 2019, 50(3): 40-42. |
| LIAN D M, LAI Z F, YAO Y F, et al. Pathogen identification of root-knot nematode on okra[J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 50(3): 40-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 曹业凡, 汪来发, 王曦茁, 等. 九叶青花椒根结线虫病的病原鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 2019, 45(5): 242-246. |
| CAO Y F, WANG L F, WANG X Z, et al. Identification of root-knot nematode on Zanthoxylum armatum var. novemfolius[J]. Plant Protection, 2019, 45(5): 242-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 宫远福. 东北地区根结线虫的种类分布及南方根结线虫氯离子通道基因分析[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. |
| GONG Y F. Species distribution of root-knot nematodes in northeast China and analysis of chloride channel genes in Meloidogyne incognita[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 王兴松, 李恩星, 杨诗瀚, 等. 根结线虫病对烟草植株根际土壤微生物群落及其功能的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(6): 993-1003. |
| WANG X S, LI E X, YANG S H, et al. Effects of root-knot nematode disease on microbial community and function in rhizosphere soil of tobacco plants[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 40(6): 993-1003. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 陈立杰, 魏峰, 段玉玺, 等. 温湿度对南方根结线虫卵孵化和二龄幼虫的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2009, 35(2): 48-52. |
| CHEN L J, WEI F, DUAN Y X, et al. Effects of temperature and moisture on egg hatching and the second instars of Meloidogyne incognita[J]. Plant Protection, 2009, 35(2): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 刘丽, 颜世翠, 姚良同, 等. 一种番茄根结线虫人工培养和保存的优化方法[J]. 山东农业科学, 2012, 44(11): 117-120. |
| LIU L, YAN S C, YAO L T, et al. An optimized artificial culture and preservation method for tomato root-knot nematodes[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 44(11): 117-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 钟雪超. 土壤线虫的分离方法[J]. 环境, 2012(S1): 147,149. |
| ZHONG X C. Isolation method of soil nematodes[J]. Environment, 2012(S1): 147,149. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 段玉玺. 植物线虫学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 95-146. |
| [26] | 张绍升. 植物线虫病害诊断与治理[M]. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 1999: 84-88. |
| [27] | 谢辉. 植物线虫分类学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005: 243-247. |
| [28] | 陶冶. 南方果蔬根结线虫鉴定及其基于线粒体基因组系统发育分析[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2018. |
| TAO Y. Identification of root-knot nematodes parasitizing vegetables and fruits in Southern China and phylogenetic analysis based on their mitochondrial genomes[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 王炳太. 植物根结线虫病发生规律分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(22): 122-123. |
| WANG B T. Analysis on occurrence regularity of plant root-knot nematodes[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016(22): 122-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 崔爱华, 袁升凯, 冷鹏, 等. 设施甜瓜根结线虫病的发生规律与综合防控技术[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2020, 33(1): 82-83. |
| CUI A H, YUAN S K, LENG P, et al. Occurrence regularity and comprehensive prevention and control technology of facility Meloidogyne incognita chitwood[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2020, 33(1): 82-83. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 尤作将, 王萍. 花生根结线虫病综合防治技术[J]. 现代农村科技, 2022(9): 41. |
| YOU Z J, WANG P. Integrated control techniques of peanut root-knot nematode disease[J]. Modern Rural Science and Technology, 2022(9): 41. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 雷敬超, 黄惠琴. 南方根结线虫生物防治研究进展[J]. 中国生物防治, 2007(S1): 76-81. |
| LEI J C, HUANG H Q. Research advance on biological control of the Meloidogyne incognita[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2007(S1): 76-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 李星星, 尚嘉彦, 袁海琪, 等. 不同药剂对南方根结线虫的室内生物活性测定[J]. 农业灾害研究, 2023, 13(8): 31-33. |
| LI X X, SHANG J Y, YUAN H Q, et al. Laboratory bioactivity determination of Meloidogyne incognita with different nematicides[J]. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2023, 13(8): 31-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 鲁毅, 张毅, 周玲. 10.5%阿维菌素·噻唑膦颗粒剂防治黄瓜根结线虫病田间药效试验[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2018, 64(5): 34-36. |
| LU Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU L. Field efficacy experiment on 10.5% avermectins·fosthiazate particle against root-knot nematode in cucumber[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 64(5): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 项缨, 丛建民, 潘丹红, 陶永刚. 春大棚有机种植不同品种番茄的生育进程分析和综合评价研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1252-1261. |
| [2] | 刘朋飞, 张舒涵, 洪凯, 邵越, 楼兵干. 浙江省番茄溃疡病病原菌分离与鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1293-1300. |
| [3] | 马献, 尤雨薇, 康娟, 王国琴, 郑蕊, 苏建宇, 岳思君. 枸杞采后致腐病原菌的分离鉴定与天然抑菌剂筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1327-1335. |
| [4] | 季梦婷, 陈长江, 朱玲, 詹梦琳, 肖顺, 蔡学清. 无花果细菌性叶斑病病原鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(5): 1097-1106. |
| [5] | 狄延翠, 嵇泽琳, 王媛媛, 娄世浩, 张涛, 国志信, 申顺善, 朴凤植, 杜南山, 董晓星, 董韩. 番茄SlMYB52基因鉴定、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 808-819. |
| [6] | 巩鑫鑫, 刘瑞玲, 韩延超, 孟祥红, 郜海燕, 陈杭君. 四种食用菌采后主要病原菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(2): 456-465. |
| [7] | 丁莹莹, 杨林平, 杨庆, 张子晨, 蔡霖颖, 杨康, 李琛, 刘惠文, 鲍光彬, 王晴, 王桂军. 两株新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及其致病性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2458-2467. |
| [8] | 肖毓淼, 马巧梅, 张思法, 何勇, 赵振卿. 鱼蛋白水解物对番茄幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2504-2515. |
| [9] | 闫沛玉, 张生银, 陈亮, 刘斌. 不同水肥耦合对设施栽培番茄生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2516-2524. |
| [10] | 解雨佳, 李镇江, 沙飞宇, 张琳, 仝雅娜, 乔长晟, 曹伟锋. 草莓内生菌的分离筛选及其功能特性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2525-2534. |
| [11] | 王同林, 邵志勇, 聂智星, 郭赛赛, 刘丽红, 汪俏梅, 郑积荣. 基于德尔菲法及层次分析法构建鲜食番茄品质评价体系[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2583-2592. |
| [12] | 李腾飞, 杨桂玲, 阮美颖, 褚田芬, 秦华, 邓美华. 不同肥药管理对设施番茄生产系统土壤健康与番茄性状的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(1): 145-158. |
| [13] | 谷瑞, 宋翠玲, 钱春花. 融合沙漏结构与改进坐标注意力的轻量级番茄叶片病害识别模型[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(1): 217-230. |
| [14] | 韩清宇, 程林润, 李月红, 仇智灵, 后猛, 楼兵干. 六十份甘薯种质资源对基腐病的抗性评价与抗病相关指标分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1616-1625. |
| [15] | 李亚妮, 陈卫良, 毛碧增. 温郁金根茎腐烂病的病原鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(5): 1086-1093. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||