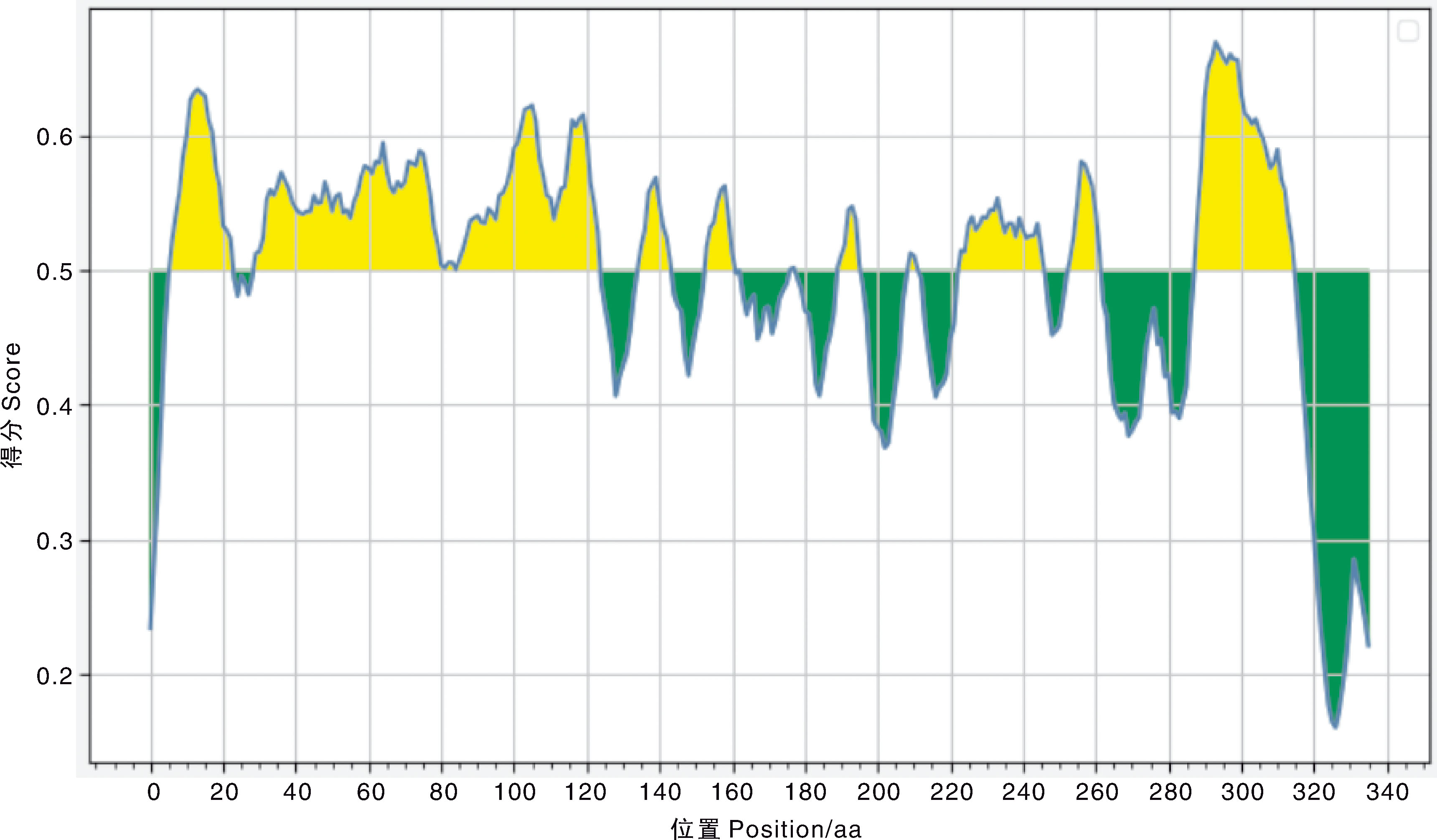
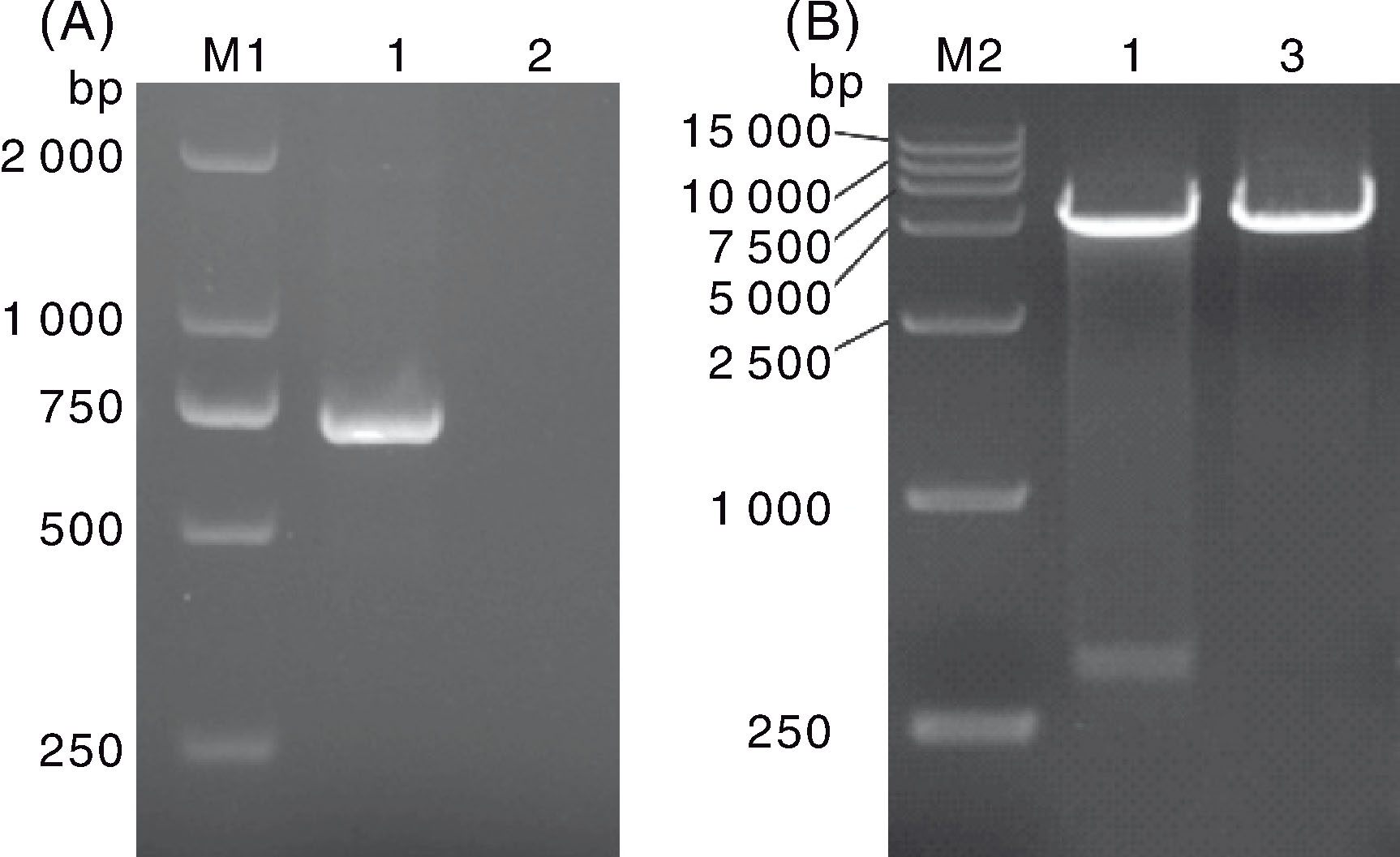
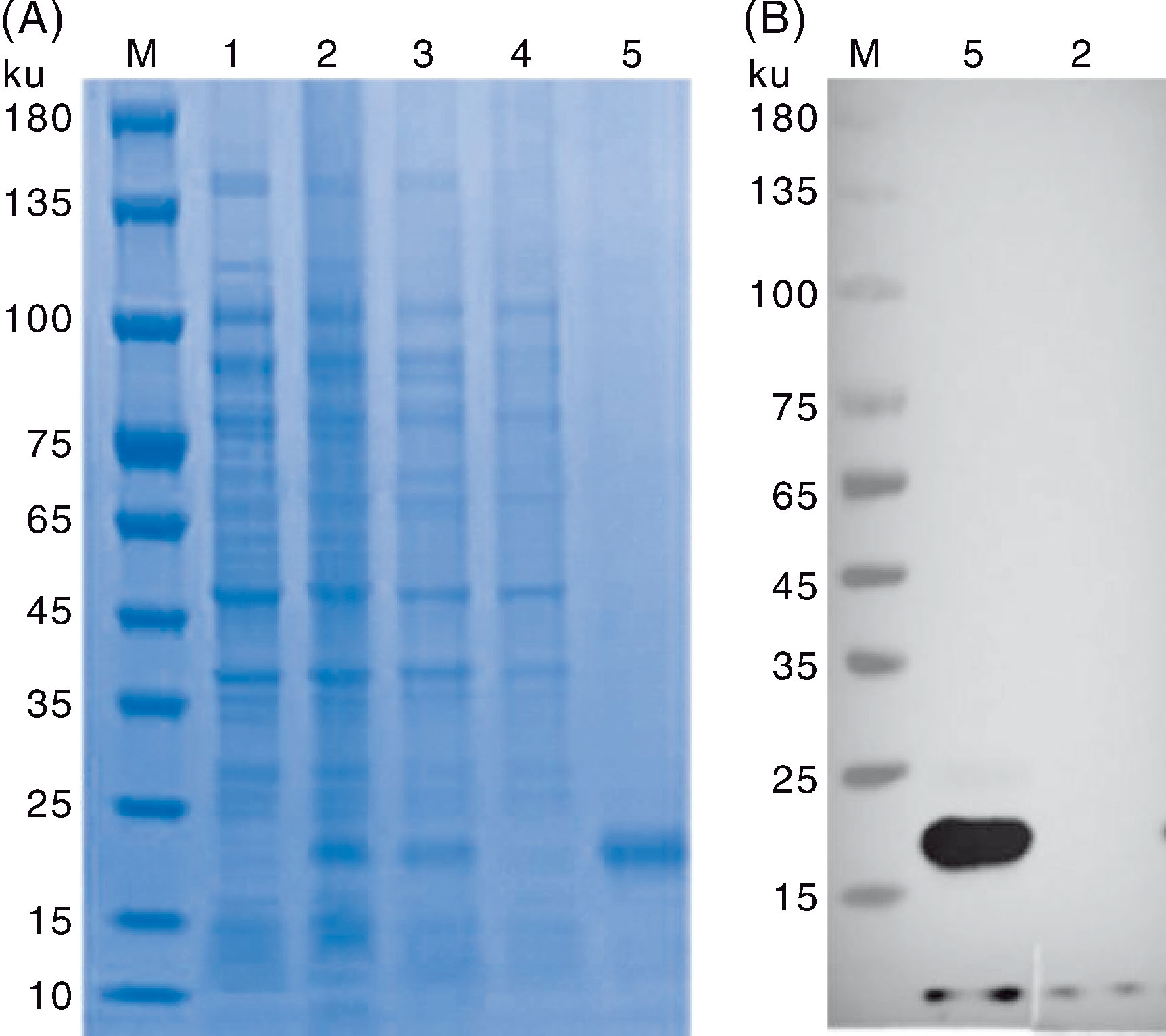
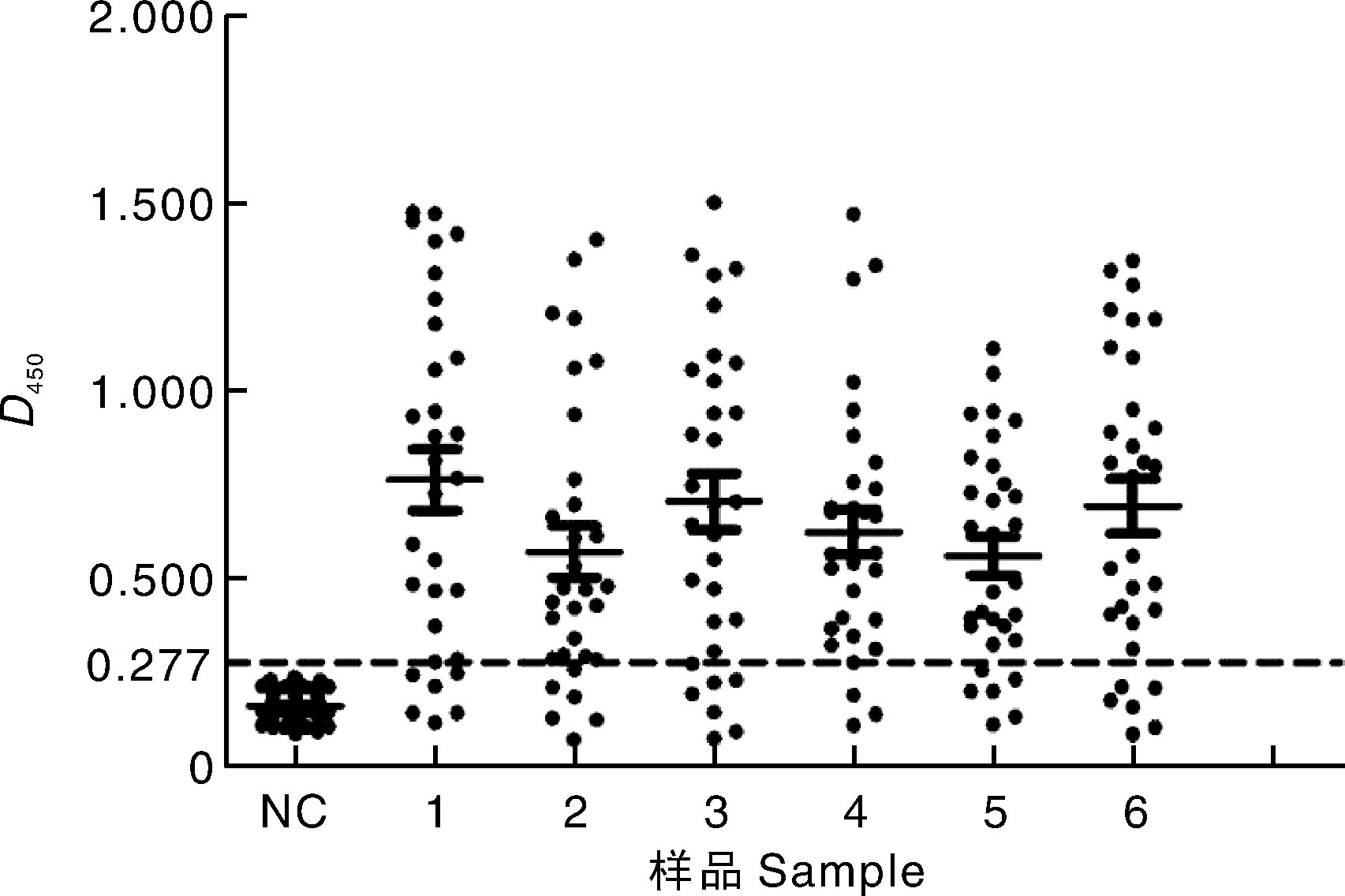
| [1] |
BERTELLONI F, CECCHERELLI R, MARZONI M, et al. Molecular detection of Avipox virus in wild birds in central Italy[J]. Animals, 2022, 12(3): 338.
|
| [2] |
MATOS M, BILIC I, PALMIERI N, et al. Epidemic of cutaneous fowlpox in a naïve population of chickens and turkeys in Austria: detailed phylogenetic analysis indicates co-evolution of fowlpox virus with reticuloendotheliosis virus[J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2022, 69(5): 2913-2923.
|
| [3] |
姜绍全, 王金亮, 秦燕. 海兰褐蛋鸡痘病毒的分离与鉴定[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2015, 36(1): 36-37.
|
|
JIANG S Q, WANG J L, QIN Y. Isolation and identification of poxvirus from hailan brown laying hens[J]. Shandong Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 36(1): 36-37. (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
KIM T J, SCHNITZLEIN W M, MCALOOSE D, et al. Characterization of an avianpox virus isolated from an Andean condor (Vultur gryphus)[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2003, 96(3): 237-246.
|
| [5] |
YEHIA N, ELSAYED S, AL-SAEED F A, et al. Current situation and genomic characterization of fowlpox virus in lower Egypt during 2022[J]. Poultry Science, 2023, 102(8): 102769.
|
| [6] |
AFONSO C L, TULMAN E R, LU Z, et al. The genome of fowlpox virus[J]. Journal of Virology, 2000, 74(8): 3815-3831.
|
| [7] |
WELI S C, TRYLAND M. Avipoxviruses: infection biology and their use as vaccine vectors[J]. Virology Journal, 2011, 8: 49.
|
| [8] |
赵宏吉, 张金花, 司朵朵, 等. 山羊痘病毒G9蛋白的原核表达及间接ELISA方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2021, 43(3): 280-284.
|
|
ZHAO H J, ZHANG J H, SI D D, et al. Prokaryotic expression of G9 protein of GTPV and establishment of an indirect ELISA[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 43(3): 280-284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
叶伟成, 云涛, 朱寅初, 等. 基于番鸭细小病毒VP3蛋白的间接ELISA方法建立[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(11): 2740-2745, 2750.
|
|
YE W C, YUN T, ZHU Y C, et al. Establishment of indirect ELISA assay based on VP3 protein of Muscovy duck parvovirus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(11): 2740-2745, 2750. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
OJEDA S, DOMI A, MOSS B. Vaccinia virus G9 protein is an essential component of the poxvirus entry-fusion complex[J]. Journal of Virology, 2006, 80(19): 9822-9830.
|
| [11] |
GRAY R D M, ALBRECHT D, BEERLI C, et al. Nanoscale polarization of the entry fusion complex of vaccinia virus drives efficient fusion[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2019, 4(10): 1636-1644.
|
| [12] |
FOO C H, WHITBECK J C, PONCE-DE-LEÓN M, et al. The myristate moiety and amino terminus of vaccinia virus l1 constitute a bipartite functional region needed for entry[J]. Journal of Virology, 2012, 86(10): 5437-5451.
|
| [13] |
SHINODA K, WYATT L S, MOSS B. The neutralizing antibody response to the vaccinia virus A28 protein is specifically enhanced by its association with the H2 protein[J]. Virology, 2010, 405(1): 41-49.
|
| [14] |
ADEBAJO M C, ADEMOLA S I, OLUWASEUN A. Seroprevalence of fowl pox antibody in indigenous chickens in jos north and south council areas of Plateau state, Nigeria: implication for vector vaccine[J]. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012, 2012(1): 154971.
|
| [15] |
MOCKETT A P A, SOUTHEE D J, TOMLEY F M, et al. Fowlpox virus: its structural proteins and immunogens and the detection of viral-specific antibodies by ELISA[J]. Avian Pathology, 1987, 16(3): 493-504.
|
| [16] |
雪鹏, 刘悦竹, 姜世金, 等. 用间接ELISA检测鸡痘病毒抗体的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2005, 41(6): 15-16.
|
|
WANG X P, LIU Y Z, JIANG S J, et al. Establishment and application of an indirect ELISA to detect antibodies against poultry pox[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2005, 41(6): 15-16. (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
张体银, 孙蕾, 孙学辉, 等. 应用间接ELISA检测鸡痘病毒抗体方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2005, 27(6): 540-543.
|
|
ZHANG T Y, SUN L, SUN X H, et al. Development of indirect ELISA for detection of antibodies against fowlpox virus[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2005, 27(6): 540-543. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [18] |
纪朋艳, 卢广林. 检测鸡痘病毒抗体间接ELISA方法的建立[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2012(23): 94-95.
|
|
JI P Y, LU G L. Establishment of indirect ELISA for detection of fowlpox virus antibody[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2012(23): 94-95. (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
张琪, 庞文静, 付明哲, 等. 山羊痘病毒ORF103蛋白的原核表达及间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2017, 47(5): 537-543.
|
|
ZHANG Q, PANG W J, FU M Z, et al. Prokaryotic expression of ORF103 protein of capripox virus and establishment of indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against the virus[J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2017, 47(5): 537-543. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [20] |
VENKATESAN G, KUMAR TELI M, SANKAR M, et al. Expression and evaluation of recombinant P32 protein based ELISA for sero-diagnostic potential of capripox in sheep and goats[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2018, 37: 48-54.
|
| [21] |
DASHPRAKASH M, VENKATESAN G, KUMAR A, et al. Prokaryotic expression, purification and evaluation of goatpox virus ORF117 protein as a diagnostic antigen in indirect ELISA to detect goatpox[J]. Archives of Virology, 2019, 164(4): 1049-1058.
|
| [22] |
邓舜洲, 蒋新华, 冷闯, 等. 猪痘病毒P35基因的原核表达及间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2013, 33(10): 1488-1492.
|
|
DENG S Z, JIANG X H, LENG C, et al. Establishment of an indirect ELISA for detection of antibodies against swinepox virus with the recombinant P35 as the coating antigen[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2013, 33(10): 1488-1492. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [23] |
朱俊达, 王爽, 任书凝, 等. 基于猴痘病毒A27L蛋白的间接ELISA抗体检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2022, 58(10): 1-7.
|
|
ZHU J D, WANG S, REN S N, et al. Establishment of indirect ELISA method for detection of monkeypox virus antibody based on A27L protein[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 58(10): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
 ), 朱寅初1, 叶加林2, 张存1, 陈柳1, 倪征1, 付媛1, 霍苏馨1, 云涛1,*(
), 朱寅初1, 叶加林2, 张存1, 陈柳1, 倪征1, 付媛1, 霍苏馨1, 云涛1,*( )
)
 ), ZHU Yinchu1, YE Jialin2, ZHANG Cun1, CHEN Liu1, NI Zheng1, FU Yuan1, HUO Suxin1, YUN Tao1,*(
), ZHU Yinchu1, YE Jialin2, ZHANG Cun1, CHEN Liu1, NI Zheng1, FU Yuan1, HUO Suxin1, YUN Tao1,*( )
)