浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2066-2076.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240809
黄腐酸钾对甜瓜根区土壤微生态、根系形态及果实品质的影响
熊韬1( ), 闫淼1, 吴婷1, 马超2, 杨俊涛1, 胡国智1,*(
), 闫淼1, 吴婷1, 马超2, 杨俊涛1, 胡国智1,*( )
)
- 1.新疆农业科学院 哈密瓜研究中心,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830091
2.中化农业(新疆)生物科技有限公司玛纳斯公司,新疆 玛纳斯 832200
-
收稿日期:2024-09-18出版日期:2025-10-25发布日期:2025-11-13 -
作者简介:熊韬(1984—),男,新疆库车人,硕士,高级农艺师,研究方向为西甜瓜栽培生理。E-mail: bearxt@163.com -
通讯作者:胡国智,E-mail: hgz0901@126.com -
基金资助:新疆维吾尔自治区现代农业产业技术体系(XJARS-06);国家现代农业产业技术体系建设专项(CARS-25)
Effects of potassium fulvic acid on soil microecology, root morphology in root zone of melon and fruit quality
XIONG Tao1( ), YAN Miao1, WU Ting1, MA Chao2, YANG Juntao1, HU Guozhi1,*(
), YAN Miao1, WU Ting1, MA Chao2, YANG Juntao1, HU Guozhi1,*( )
)
- 1. Hami Melon Research Center, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Urumqi 830091, China
2. Sinochem Agriculture (Xinjiang) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Manas Company, Manas 832200, Xinjiang, China
-
Received:2024-09-18Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
摘要: 研究不同黄腐酸钾施用量对甜瓜根区土壤理化性质、土壤微生物数量、土壤酶活性变化、根系形态指标及果实品质的影响,明确黄腐酸钾的最佳施用量,为在甜瓜生产中科学合理使用黄腐酸钾肥料提供理论依据。选用甜瓜品种黄梦脆为试材,在常规施肥的基础上,设置5个黄腐酸钾施用水平(0、37.5、75.0、112.5、150.0 kg·hm-2,分别用CK、KT1、KT2、KT3、KT4表示),于幼苗期、伸蔓期、开花期、果实膨大期、成熟期追施。结果表明,与CK相比,施用黄腐酸钾显著提高了土壤中有机质及氮、磷、钾等主要养分的含量,提高了阳离子交换量,同时降低了土壤pH值,进一步改善了土壤理化性质和保水保肥能力;施用黄腐酸钾持续提高了微生物群落功能,土壤中可培养微生物总量、细菌、真菌数量均表现为KT3>KT4>KT2>KT1>CK,且KT3处理下土壤根区酶活性提升效果最佳;根系形态分析表明,黄腐酸钾促进了甜瓜根系生长发育,KT3处理效果最好,根系长度、根系体积、根系直径、根系表面积和根尖数分别较CK提高了36.27%、85.92%、39.59%、80.54%、83.80%;追施黄腐酸钾可以提高甜瓜的果实亮度、可溶性固形物含量、可溶性糖含量和维生素C含量,有效改善果实品质和商品性。由于在黄腐酸钾用量达到150.0 kg·hm-2时,各项指标均表现出下降的趋势。综合考虑,在本试验同等土壤状况和栽培条件下,黄腐酸钾最佳施用量为112.5 kg·hm-2。
中图分类号:
引用本文
熊韬, 闫淼, 吴婷, 马超, 杨俊涛, 胡国智. 黄腐酸钾对甜瓜根区土壤微生态、根系形态及果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(10): 2066-2076.
XIONG Tao, YAN Miao, WU Ting, MA Chao, YANG Juntao, HU Guozhi. Effects of potassium fulvic acid on soil microecology, root morphology in root zone of melon and fruit quality[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2066-2076.
| 处理 Treatment | 不同时期追施黄腐酸钾的用量Topdressing potassium fulvic acid quantity at different stages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 幼苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine extension stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 果实膨大期 Fruit expansion stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| KT1 | 3.750 | 5.625 | 9.375 | 9.375 | 9.375 |
| KT2 | 7.500 | 11.250 | 18.750 | 18.750 | 18.750 |
| KT3 | 11.250 | 16.875 | 28.125 | 28.125 | 28.125 |
| KT4 | 15.000 | 22.500 | 37.500 | 37.500 | 37.500 |
表1 各处理追施黄腐酸钾用量
Table 1 Topdressing potassium fulvic acid quantity of different treatments kg·hm-2
| 处理 Treatment | 不同时期追施黄腐酸钾的用量Topdressing potassium fulvic acid quantity at different stages | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 幼苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine extension stage | 开花期 Flowering stage | 果实膨大期 Fruit expansion stage | 成熟期 Maturity stage | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| KT1 | 3.750 | 5.625 | 9.375 | 9.375 | 9.375 |
| KT2 | 7.500 | 11.250 | 18.750 | 18.750 | 18.750 |
| KT3 | 11.250 | 16.875 | 28.125 | 28.125 | 28.125 |
| KT4 | 15.000 | 22.500 | 37.500 | 37.500 | 37.500 |
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质含量 Organic matter content/% | 碱解氮含量 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量 Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/ (cmol·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.93±0.40 d | 98.72±1.32 d | 38.28±0.91 d | 298.71±5.72 d | 8.57±0.05 d | 7.74±0.04 a |
| KT1 | 22.90±0.72 c | 102.15±1.11 c | 42.96±1.25 c | 376.05±15.47 c | 9.41±0.06 c | 7.72±0.02 a |
| KT2 | 24.93±0.19 b | 111.91±1.42 b | 44.41±0.50 c | 402.62±18.91 bc | 9.55±0.07 bc | 7.68±0.03 a |
| KT3 | 27.56±1.33 a | 121.45±1.26 a | 51.41±0.61 a | 468.29±26.92 a | 10.09±0.43 a | 7.48±0.06 b |
| KT4 | 26.15±1.05 ab | 113.34±1.44 b | 46.60±0.64 b | 442.02±63.86 ab | 9.83±0.11 ab | 7.55±0.07 b |
表2 不同处理对0~20 cm土壤理化性质的影响
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on physical and chemical properties of 0-20 cm soil
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质含量 Organic matter content/% | 碱解氮含量 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量 Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) | 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity/ (cmol·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.93±0.40 d | 98.72±1.32 d | 38.28±0.91 d | 298.71±5.72 d | 8.57±0.05 d | 7.74±0.04 a |
| KT1 | 22.90±0.72 c | 102.15±1.11 c | 42.96±1.25 c | 376.05±15.47 c | 9.41±0.06 c | 7.72±0.02 a |
| KT2 | 24.93±0.19 b | 111.91±1.42 b | 44.41±0.50 c | 402.62±18.91 bc | 9.55±0.07 bc | 7.68±0.03 a |
| KT3 | 27.56±1.33 a | 121.45±1.26 a | 51.41±0.61 a | 468.29±26.92 a | 10.09±0.43 a | 7.48±0.06 b |
| KT4 | 26.15±1.05 ab | 113.34±1.44 b | 46.60±0.64 b | 442.02±63.86 ab | 9.83±0.11 ab | 7.55±0.07 b |
| 处理 Treatment | 微生物总数 Microorganisms number/ (10 7 CFU·g-1 ) | 细菌数 Bacterial number/ (10 7 CFU·g-1 ) | 真菌数 Fungus number/ (104 CFU·g-1 ) | 放线菌数 Actinomycetes number/ (106 CFU·g-1 ) | 细菌数/真菌数 Ratio of bacterial number to fungus number/103 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.23±0.10 c | 1.87±0.05 d | 2.33±0.07 d | 3.98±0.10 c | 0.80±0.01 c |
| KT1 | 2.57±0.09 b | 2.08±0.11 c | 2.50±0.08 c | 4.08±0.07 c | 0.83±0.02 c |
| KT2 | 4.01±0.12 a | 3.41±0.07 b | 3.10±0.16 b | 4.99±0.16 b | 1.10±0.06 a |
| KT3 | 4.10±0.08 a | 3.88±0.05 a | 3.49±0.08 a | 5.65±0.12 a | 1.11±0.02 a |
| KT4 | 4.03±0.14 a | 3.52±0.03 b | 3.38±0.06 a | 5.66±0.06 a | 1.04±0.03 b |
表3 施用黄腐酸钾对甜瓜根际土壤微生物的影响
Table 3 Effects of potassium fulvic acid application on rhizosphere soil microorganisms of melon
| 处理 Treatment | 微生物总数 Microorganisms number/ (10 7 CFU·g-1 ) | 细菌数 Bacterial number/ (10 7 CFU·g-1 ) | 真菌数 Fungus number/ (104 CFU·g-1 ) | 放线菌数 Actinomycetes number/ (106 CFU·g-1 ) | 细菌数/真菌数 Ratio of bacterial number to fungus number/103 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.23±0.10 c | 1.87±0.05 d | 2.33±0.07 d | 3.98±0.10 c | 0.80±0.01 c |
| KT1 | 2.57±0.09 b | 2.08±0.11 c | 2.50±0.08 c | 4.08±0.07 c | 0.83±0.02 c |
| KT2 | 4.01±0.12 a | 3.41±0.07 b | 3.10±0.16 b | 4.99±0.16 b | 1.10±0.06 a |
| KT3 | 4.10±0.08 a | 3.88±0.05 a | 3.49±0.08 a | 5.65±0.12 a | 1.11±0.02 a |
| KT4 | 4.03±0.14 a | 3.52±0.03 b | 3.38±0.06 a | 5.66±0.06 a | 1.04±0.03 b |
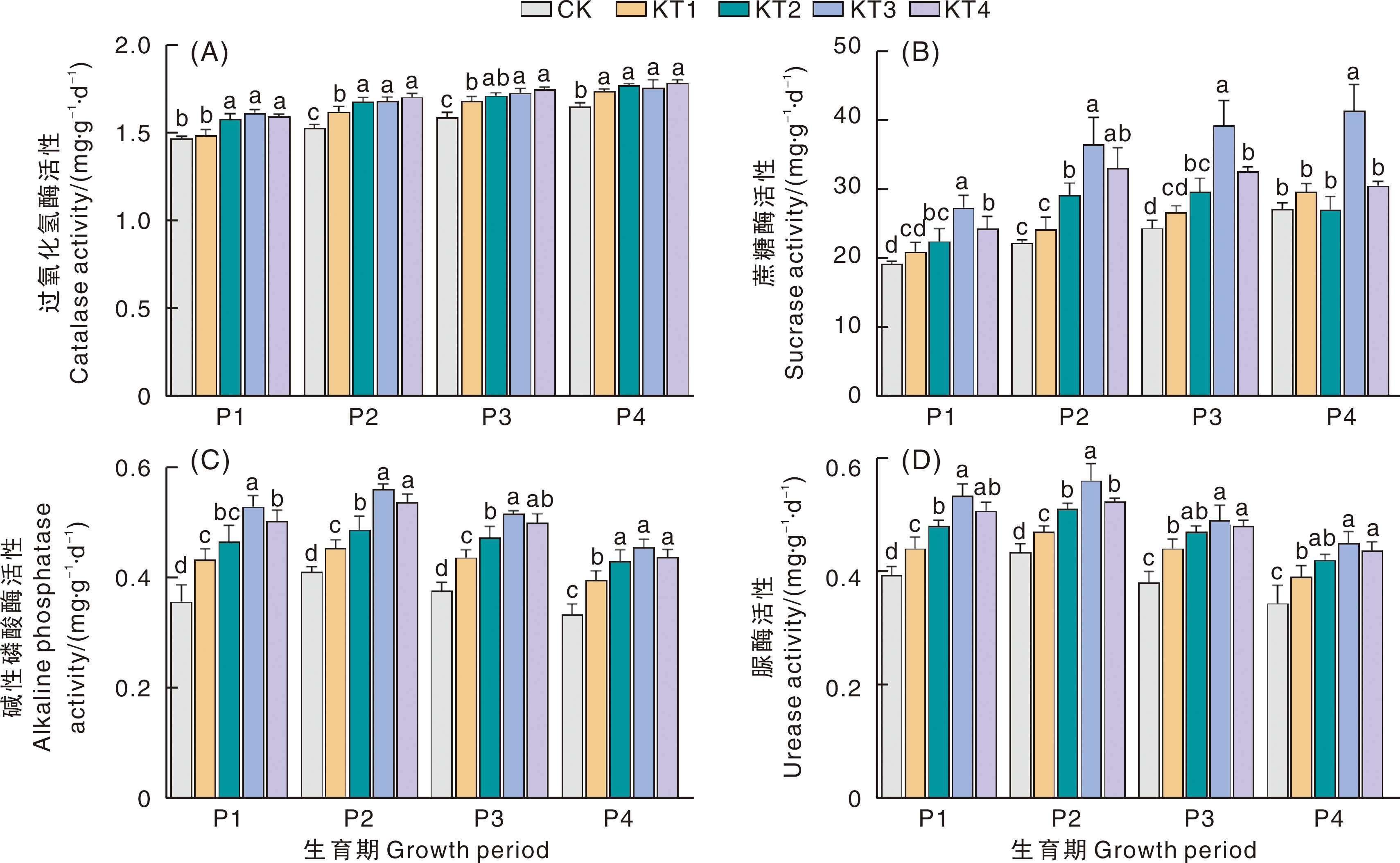
图1 黄腐酸钾对甜瓜根区土壤酶活性的影响 P1,P2,P3,P4分别代表伸蔓期、开花期、果实膨大期、成熟期。柱状图上无相同小写字母的表示同一生育期内各处理间差异显著(p<0.05)。
Fig.1 Effects of potassium fulvic acid on soil enzyme activity in melon root zone P1, P2, P3 and P4 represent vine extension stage, flowering stage, fruit expansion stage and maturity stage, respectively. Different lowercase letters above the columns represent statistically significant (p<0.05) differences among treatments during the same growth period.
| 处理 Treatment | 根系长度 Root length/cm | 根系体积 Root volume/cm3 | 根系直径 Root diameter/ mm | 根系表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 根尖数 Root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 386.90±14.01 d | 20.10±1.05 c | 1.97±0.29 d | 541.33±13.28 d | 273.23±22.89 d |
| KT1 | 410.34±11.89 c | 24.96±2.82 bc | 2.15±0.09 cd | 669.67±35.53 c | 341.48±24.65 c |
| KT2 | 455.58±12.07 b | 30.82±4.75 ab | 2.39±0.12 bc | 723.33±55.59 c | 424.61±10.80 b |
| KT3 | 527.21±7.92 a | 37.37±5.23 a | 2.75±0.01 a | 977.33±45.74 a | 502.21±22.16 a |
| KT4 | 511.47±4.69 a | 32.42±5.60 ab | 2.64±0.06 ab | 856.67±65.32 b | 457.73±28.13 b |
表4 黄腐酸钾对甜瓜根系形态的影响
Table 4 Effect of potassium fulvic acid on root morphology of melon
| 处理 Treatment | 根系长度 Root length/cm | 根系体积 Root volume/cm3 | 根系直径 Root diameter/ mm | 根系表面积 Root surface area/cm2 | 根尖数 Root tip number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 386.90±14.01 d | 20.10±1.05 c | 1.97±0.29 d | 541.33±13.28 d | 273.23±22.89 d |
| KT1 | 410.34±11.89 c | 24.96±2.82 bc | 2.15±0.09 cd | 669.67±35.53 c | 341.48±24.65 c |
| KT2 | 455.58±12.07 b | 30.82±4.75 ab | 2.39±0.12 bc | 723.33±55.59 c | 424.61±10.80 b |
| KT3 | 527.21±7.92 a | 37.37±5.23 a | 2.75±0.01 a | 977.33±45.74 a | 502.21±22.16 a |
| KT4 | 511.47±4.69 a | 32.42±5.60 ab | 2.64±0.06 ab | 856.67±65.32 b | 457.73±28.13 b |
| 处理 Treatment | L*值 L*value | C*值 C*value | 可溶性固形 物含量 Soluble solids content/% | 可溶性糖 含量 Soluble sugar content/% | 维生素C含量 Vitamin C content/ (mg·kg-1) | 可滴定酸含量 Titratable acidity content/% | 糖酸比 Sugar-acid ratio | 固酸比 Solid-to- acid ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 67.97± 1.45 c | 40.77± 0.78 b | 14.20± 0.30 c | 70.32± 1.90 c | 14.7± 1.2 c | 2.32± 0.03 a | 30.31± 0.61 d | 6.12± 0.19 d |
| KT1 | 70.95± 1.99 bc | 48.47± 6.10 ab | 15.23± 0.45 b | 73.50± 1.64 bc | 17.5± 1.7 c | 2.29± 0.02 a | 32.10± 1.00 cd | 6.65± 0.14 c |
| KT2 | 72.73± 2.30 ab | 50.23± 1.92 ab | 15.90± 0.40 b | 76.53± 1.15 b | 26.1± 3.4 b | 2.26± 0.04 a | 33.82± 0.38 c | 7.03± 0.28 bc |
| KT3 | 75.32± 1.50 a | 52.45± 6.03 a | 16.87± 0.31 a | 81.35± 1.91 a | 36.3± 3.8 a | 2.05± 0.07 c | 39.79± 2.00 a | 8.25± 0.36 a |
| KT4 | 72.27± 2.80 ab | 49.01± 6.77 ab | 15.80± 0.56 b | 81.14± 2.54 a | 36.6± 2.7 a | 2.19± 0.03 b | 37.12± 1.41 b | 7.23± 0.34 b |
表5 不同黄腐酸钾处理下甜瓜品质指标比较结果
Table 5 Comparison of quality indexes of melon under different potassium fulvic acid treatments
| 处理 Treatment | L*值 L*value | C*值 C*value | 可溶性固形 物含量 Soluble solids content/% | 可溶性糖 含量 Soluble sugar content/% | 维生素C含量 Vitamin C content/ (mg·kg-1) | 可滴定酸含量 Titratable acidity content/% | 糖酸比 Sugar-acid ratio | 固酸比 Solid-to- acid ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 67.97± 1.45 c | 40.77± 0.78 b | 14.20± 0.30 c | 70.32± 1.90 c | 14.7± 1.2 c | 2.32± 0.03 a | 30.31± 0.61 d | 6.12± 0.19 d |
| KT1 | 70.95± 1.99 bc | 48.47± 6.10 ab | 15.23± 0.45 b | 73.50± 1.64 bc | 17.5± 1.7 c | 2.29± 0.02 a | 32.10± 1.00 cd | 6.65± 0.14 c |
| KT2 | 72.73± 2.30 ab | 50.23± 1.92 ab | 15.90± 0.40 b | 76.53± 1.15 b | 26.1± 3.4 b | 2.26± 0.04 a | 33.82± 0.38 c | 7.03± 0.28 bc |
| KT3 | 75.32± 1.50 a | 52.45± 6.03 a | 16.87± 0.31 a | 81.35± 1.91 a | 36.3± 3.8 a | 2.05± 0.07 c | 39.79± 2.00 a | 8.25± 0.36 a |
| KT4 | 72.27± 2.80 ab | 49.01± 6.77 ab | 15.80± 0.56 b | 81.14± 2.54 a | 36.6± 2.7 a | 2.19± 0.03 b | 37.12± 1.41 b | 7.23± 0.34 b |
| 指标 Index | 有机质含量 Organic matter content | 碱解氮含量 Alkali- hydrolyzable nitrogen content | 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | 阳离子 交换量 Cation exchange capacity | pH值 pH value | 真菌数量 Fungus number | 细菌数量 Bacterial number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮含量 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content | 0.97** | |||||||
| 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | 0.97** | 0.96* | ||||||
| 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | 0.10** | 0.94* | 0.97** | |||||
| 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity | 0.98** | 0.91* | 0.96** | 0.99** | ||||
| pH值pH value | -0.90* | -0.92* | -0.93* | -0.90* | -0.85 | |||
| 真菌数量 Fungus number | 0.97** | 0.97** | 0.91* | 0.94* | 0.90* | -0.92* | ||
| 细菌数量 Bacterial number | 0.95* | 0.97** | 0.89* | 0.91* | 0.88 | -0.87 | 0.98** | |
| 放线菌数量 Actinomycetes number | 0.93* | 0.94* | 0.88 | 0.91* | 0.86 | -0.93* | 0.99** | 0.97** |
表6 黄腐酸钾处理下甜瓜根区土壤微生物数量与土壤养分之间的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis of soil microbial quantity and soil nutrients in melon root zone under potassium fulvic acid treatments
| 指标 Index | 有机质含量 Organic matter content | 碱解氮含量 Alkali- hydrolyzable nitrogen content | 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | 阳离子 交换量 Cation exchange capacity | pH值 pH value | 真菌数量 Fungus number | 细菌数量 Bacterial number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮含量 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content | 0.97** | |||||||
| 有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content | 0.97** | 0.96* | ||||||
| 速效钾含量 Available potassium content | 0.10** | 0.94* | 0.97** | |||||
| 阳离子交换量 Cation exchange capacity | 0.98** | 0.91* | 0.96** | 0.99** | ||||
| pH值pH value | -0.90* | -0.92* | -0.93* | -0.90* | -0.85 | |||
| 真菌数量 Fungus number | 0.97** | 0.97** | 0.91* | 0.94* | 0.90* | -0.92* | ||
| 细菌数量 Bacterial number | 0.95* | 0.97** | 0.89* | 0.91* | 0.88 | -0.87 | 0.98** | |
| 放线菌数量 Actinomycetes number | 0.93* | 0.94* | 0.88 | 0.91* | 0.86 | -0.93* | 0.99** | 0.97** |
| [1] | 胡波. 化肥减量条件下配施生物有机肥及氨基酸水溶肥对甜瓜生长及土壤肥力的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2019. |
| HU B. Effects of combined application of bio-organic fertilizer and amino acid water-soluble fertilizer on melon growth and soil fertility under the condition of chemical fertilizer reduction[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 徐小军, 张桂兰, 周亚峰, 等. 甜瓜设施栽培连作土壤的理化性质及生物活性[J]. 果树学报, 2016, 33(9): 1131-1138. |
| XU X J, ZHANG G L, ZHOU Y F, et al. Studies on the physical-chemical and biological properties of soils cropped continuously with melon under protected cultivation condition[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2016, 33(9): 1131-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 郑立伟, 赵阳阳, 王一冰, 等. 不同连作年限甜瓜种植土壤性质和微生物多样性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(1): 101-114. |
| ZHENG L W, ZHAO Y Y, WANG Y B, et al. Soil properties and microbial diversity in the muskmelon fields after continuous cropping for different years[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(1): 101-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 杨瑞秀. 甜瓜根系自毒物质在连作障碍中的化感作用及缓解机制研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2014. |
| YANG R X. Allelopathy and mitigation mechanism of autotoxic substances in melon root system in continuous cropping obstacles[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 包日在, 孔海民, 李岗, 等. 基施黄腐酸钾对大棚杨梅营养生长及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国南方果树, 2024, 53(3): 171-174. |
| BAO R Z, KONG H M, LI G, et al. Effects of basal application of potassium fulvic acid on the vegetative growth and fruit quality of bayberry in greenhouse[J]. South China Fruits, 2024, 53(3): 171-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 赵永长. 黄腐酸钾对干旱胁迫下烤烟生长的调控效应及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2017. |
| ZHAO Y C. Effect and mechanism of potassium fulvate on growth of flue-cured tobacco under drought stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 李瑞波. 生物腐植酸与生态农业[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| [8] | 陈海宁, 高文胜, 郑磊, 等. 硅钙钾镁肥与黄腐酸钾配施对酸化果园土壤化学性质及苹果产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(3): 82-87. |
| CHEN H N, GAO W S, ZHENG L, et al. Effects of silicon-calcium-potassium-magnesium fertilizer combined with fulvic acid potassium on soil chemical properties, yield and quality of fruit in apple orchard with acidified soils[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(3): 82-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 朱会调, 高登涛, 白茹, 等. 黄腐酸对土壤养分、葡萄品质和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(4): 672-681. |
| ZHU H T, GAO D T, BAI R, et al. Effects of fulvic acid on soil nutrients, grape quality and yield[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(4): 672-681. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 刘佳欢, 王倩, 罗人杰, 等. 黄腐酸肥料对小麦根际土壤微生物多样性和酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(10):1808-1816. |
| LIU J H, WANG Q, LUO R J, et al. Effects of fulvic acid fertilizer on microbial diversity and enzyme activity in wheat rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2019, 25(10):1808-1816. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 刘彩娟, 吕春雨, 艾希珍, 等. 黄腐酸对干旱胁迫下黄瓜光合特性及产量和品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(5): 1300-1310. |
| LIU C J, LYU C Y, AI X Z, et al. Effects of fulvic acid on photosynthetic characteristics, yield and quality of cucumber under drought stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(5): 1300-1310. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 段祥坤, 王建玉, 王志鹏. 黄腐酸钾对甜瓜新品系“14-64” 养分吸收、分配和产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(4): 146-154. |
| DUAN X K, WANG J Y, WANG Z P. Effects of potassium fulvic acid application on nutrition absorption, distribution and yield of melon line“14-64”[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(4): 146-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 孟阿静, 邵华伟, 唐蕾, 等. 施用不同类型黄腐酸对塔里木盆地密植骏枣产量和品质的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2022, 31(10): 1357-1364. |
| MENG A J, SHAO H W, TANG L, et al. Effects of different types of fulvic acid on yield and quality of dense planting Ziziphus jujuba Mill in Tarim basin[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 1357-1364. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 王吉平, 张野, 邓秀泉, 等. 黄腐酸钾对火龙果品质及果园土壤钾素形态的影响[J]. 热带农业科学, 2022, 42(10): 1-5. |
| WANG J P, ZHANG Y, DENG X Q, et al. Effects of potassium fulvic acid on the quality of pitaya fruit and the different forms of potassium in orchard soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2022, 42(10): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 禹坷, 王孝林, 张学斌, 等. 植物根系与益生菌相互作用的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(11): 2275-2287. |
| YU K, WANG X L, ZHANG X B, et al. Research progress on interactions between root and beneficial microbes[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(11): 2275-2287. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 林先贵. 土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010. |
| [17] | 王平, 李凤民, 刘淑英. 长期施肥对土壤生物活性有机碳库的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(1): 224-228. |
| WANG P, LI F M, LIU S Y. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil biologically active organic carbon pool[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(1): 224-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 李邵宇, 孙建, 王毅, 等. 青藏高原不同退化梯度草地土壤酶活性特征[J]. 草业科学, 2020, 37(12): 2389-2402. |
| LI S Y, SUN J, WANG Y, et al. Characteristics of soil enzyme activities in different degraded gradient grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(12): 2389-2402. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 谷明轩, 刘风珍, 孙伟, 等. 黄腐酸通过调控花生根系形态及活力促进幼苗生长[J]. 花生学报, 2023, 52(1): 63-71. |
| GU M X, LIU F Z, SUN W, et al. Fulvic acid promotes seedling growth by regulating root morphology and activity of peanut[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2023, 52(1): 63-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 黄小龙, 唐子燕, 刘济明, 等. 米槁根际微生物群落结构及其与土壤养分相关性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(10): 92-97. |
| HUANG X L, TANG Z Y, LIU J M, et al. Rhizosphere microbial community structure and its relationship with soil nutrients in Cinnamomum migao[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2023, 51(10): 92-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 戴雅婷, 闫志坚, 王慧, 等. 油蒿根际土壤微生物数量及其与土壤养分的关系[J]. 中国草地学报, 2012, 34(2): 71-75. |
| DAI Y T, YAN Z J, WANG H, et al. The relationships between the number of microorganisms in rhizospheric soil of Artemisia ordosica and soil nutrients[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2012, 34(2): 71-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 李娜. 矿源黄腐酸钾对化肥减量大豆生长和根际土壤养分的影响[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2023. |
| LI N. Effects of mineral potassium fulvate on soybean growth and rhizosphere soil nutrients reduced by chemical fertilizer[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 杨志桃. 外源腐殖酸对低温胁迫下厚皮甜瓜幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2022. |
| YANG Z T. Effects of exogenous humic acid on growth and physiological characteristics of muskmelon seedlings under low temperature stress[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 孙世君, 马博, 王逸轩, 等. 腐殖酸对盐胁迫下温室黄瓜根际土壤养分及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(5): 83-90. |
| SUN S J, MA B, WANG Y X, et al. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients and microbial community structure of greenhouse cucumber rhizosphere under salt stress[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(5): 83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 陈星星, 刘新社, 王盛荣. 腐殖酸对盐胁迫下土壤理化性质、微环境及苦瓜生长的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(17): 138-144. |
| CHEN X X, LIU X S, WANG S R. Influences of humic acid on soil physical and chemical properties, microenvironment and balsam pear growth under salt stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(17): 138-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 刘宇锋, 罗佳, 苏天明, 等. 外源腐殖酸对栽培基质性状和辣椒生长发育的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2016, 32(3): 647-655. |
| LIU Y F, LUO J, SU T M, et al. Physico-chemical properties of a soilless substrate and growth of pepper influenced by exogenous humic acid[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 32(3): 647-655. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 彭健健, 徐坚, 王晓晓, 等. 杨梅主产区土壤肥力空间异质性及其影响因素: 以浙江仙居和临海为例[J]. 果树学报, 2023, 40(7): 1421-1433. |
| PENG J J, XU J, WANG X X, et al. Spatial variation of soil fertility and its influencing factors in Myrica rubra region: a case study in Xianju County and Linhai City[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2023, 40(7): 1421-1433. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 韩剑宏, 孙一博, 张连科, 等. 生物炭与腐殖酸配施对盐碱土理化性质的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(6): 121-127. |
| HAN J H, SUN Y B, ZHANG L K, et al. Effect of biochar and humic acid on physical and chemical properties of saline-alkali soil[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(6): 121-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 张丽丽, 李继蕊, 毕焕改, 等. 不同土壤pH和磷水平下黄腐酸对番茄产量和根际土壤微生态的影响[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2021(11): 45-52. |
| ZHANG L L, LI J R, BI H G, et al. Effects of fulvic acid on tomato yield and hizosphere soil microecology under different soil pH and phosphorus levels[J]. China Vegetables, 2021(11): 45-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 智明, 黄占斌, 单瑞娟. 腐殖酸对土壤改良作用探讨[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2013, 38(3):109-111. |
| ZHI M, HUANG Z B, SHAN R J. Study on the effect of humic acid on soil improvement[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2013, 38(3):109-111. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | ZHANG Q, ZHOU W, LIANG G, et al. Distribution of soil nutrients, extracellular enzyme activities and microbial communities acrossparticle size fractions in a long-term fertilizer experiment[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2015, 94:59-71. |
| [32] | 孙希武, 彭福田, 肖元松, 等. 硅钙钾镁肥配施黄腐酸钾对土壤酶活性及桃幼树生长的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(4): 870-877. |
| SUN X W, PENG F T, XIAO Y S, et al. Effects of silicon, calcium, potassium and magnesium fertilizer combined with fulvic acid potassium on soil enzyme activity and the growth of young peach trees[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(4): 870-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 王鹏, 牟溥, 李云斌. 植物根系养分捕获塑性与根竞争[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(11): 1184-1196. |
| WANG P, MOU P, LI Y B. Review of root nutrient foraging plasticity and root competition of plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(11): 1184-1196. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 李亚杰, 罗磊, 姚彦红, 等. 黄腐酸菌肥与常规肥料配比对西北旱作区马铃薯根系形态及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 腐植酸, 2020(1): 93. |
| LI Y J, LUO L, YAO Y H, et al. Effects of the proportion of fulvic acid bacterial fertilizer and conventional fertilizer on potato root morphology and soil enzyme activity in northwest dry farming area[J]. Humic Acid, 2020(1): 93. (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 周丽平, 袁亮, 赵秉强, 等. 腐殖酸单侧刺激对玉米根系生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(2): 339-349. |
| ZHOU L P, YUAN L, ZHAO B Q, et al. Effects of single-sided application of humic acid on maize root growth[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(2): 339-349. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | CANELLAS L P, OLIVARES F L. Production of border cells and colonization of maize root tips by Herbaspirillum seropedicae are modulated by humic acid[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 417(1): 403-413. |
| [37] | CANELLAS L P, PICCOLO A, DOBBSS L B, et al. Chemical composition and bioactivity properties of size-fractions separated from a vermicompost humic acid[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 78(4): 457-466. |
| [38] | 吴芳纯. 1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸、黄腐酸对巴氏杜氏藻类胡萝卜素成分积累的影响[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021. |
| WU F C. Effects of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid and fulvic acid on the accumulation of carotene in Dunaliella pasteurella[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 贺世雄, 杨蕾, 齐安民, 程籍, 王敏, 李英奎, 洪林. 中间砧对3种杂柑叶片光合特性、理化指标和果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1680-1693. |
| [2] | 张顺昌, 徐继根, 符成悦, 蒲占湑, 胡丽鹏, 吴昊, 李俊兵, 辛亮, 雷元军. 喷施氨基酸钙对红美人杂柑果皮龟裂与品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1706-1715. |
| [3] | 王呈阳, 刘洁雅, 吴敏怡, 谢博伊, 洪德成, 冷锋, 吴国泉. 钙处理对涝害下寒香蜜葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(7): 1451-1458. |
| [4] | 项缨, 丛建民, 潘丹红, 陶永刚. 春大棚有机种植不同品种番茄的生育进程分析和综合评价研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1252-1261. |
| [5] | 王丽, 陈立明, 王鹏飞, 张彬, 穆霄鹏. 有机肥配施菌肥对欧李果实品质和土壤性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 820-830. |
| [6] | 孙鹂, 张淑文, 俞浙萍, 郑锡良, 梁森苗, 任海英, 戚行江. 腐殖酸钾对杨梅土壤改良和生长结实的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(8): 1878-1886. |
| [7] | 朱学慧, 谢辉, 韩守安, 王敏, 白世践, 马云龙, 王艳蒙, 麦斯乐, 潘明启, 张雯. 两种植物生长调节剂对无核白鸡心葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(6): 1309-1319. |
| [8] | 汪颖, 王尖, 冯子珊, 汪宝根, 吴新义, 鲁忠富, 孙玉燕, 董文其, 李国景, 吴晓花. 瓠瓜果实品质性状因子分析和综合评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 334-343. |
| [9] | 罗莎莎, 王如月, 甄紫怡, 吴嘉龙, 徐业勇, 巴合提牙儿·克热木, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 灌溉时间和灌溉量对杏李裂果率与果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 365-372. |
| [10] | 马玲, 张镇武, 方英姿, 吴慧欣, 邢承华. 减氮配施生物炭对椪柑生长发育与土壤特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(12): 2739-2747. |
| [11] | 夏智杰, 张雷, 宋江华, 傅敏, 张立新. 安徽甜瓜和栝楼蔓枯病的病原菌鉴定及其有效药剂筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 168-176. |
| [12] | 岳宗伟, 李嘉骁, 孙向阳, 刘国梁, 李素艳, 王晨晨, 查贵超, 魏宁娴. 化肥有机肥配施对土壤性质、樱桃果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(9): 2192-2201. |
| [13] | 寿伟松, 何艳军, 沈佳, 许昕阳. 甜瓜SWEET基因家族的全基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(7): 1591-1603. |
| [14] | 李苹芳, 姚协丰, 徐锦华, 朱凌丽, 羊杏平. 甜瓜果实发育相关SWEET糖转运蛋白基因的鉴定与功能初步分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 308-318. |
| [15] | 方明雅, 余宏伟, 武雅娴, 韩文炎, 李鑫, 刘海河. 外源表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对甜瓜幼苗白粉病抗性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(1): 138-145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

