浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2179-2189.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241040
基于LC-MS/MS的桑叶5种生物活性物质的同时检测
任晓蓉1,2( ), 王新全2, 张善英3, 王萌3, 朱鸿明1, 章程辉1,*(
), 王新全2, 张善英3, 王萌3, 朱鸿明1, 章程辉1,*( ), 齐沛沛2,*(
), 齐沛沛2,*( )
)
- 1.海南大学 食品科学与工程学院,海南 海口 570100
2.浙江省农业科学院 农产品质量安全与营养研究所,浙江 杭州 310021
3.海南大学 植物保护学院,海南 海口 570100
-
收稿日期:2024-11-29出版日期:2025-10-25发布日期:2025-11-13 -
作者简介:任晓蓉(1998—),女,山西太原人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农产品加工与质量安全。E-mail:renxiaorong101@163.com -
通讯作者:章程辉,E-mail:zchlm@163.com;齐沛沛,E-mail:qipeipei@zaas.ac.cn -
基金资助:海南省重点研发项目(ZDYF2022XDNY198)
Simultaneous determination of five bioactive substances in mulberry leaves by LC-MS/MS
REN Xiaorong1,2( ), WANG Xinquan2, ZHANG Shanying3, WANG Meng3, ZHU Hongming1, ZHANG Chenghui1,*(
), WANG Xinquan2, ZHANG Shanying3, WANG Meng3, ZHU Hongming1, ZHANG Chenghui1,*( ), QI Peipei2,*(
), QI Peipei2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Food Science and Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou 570100, China
2. Institute of Agricultural Product Quality and Nutrition, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
3. College of Plant Protection, Hainan University, Haikou 570100, China
-
Received:2024-11-29Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
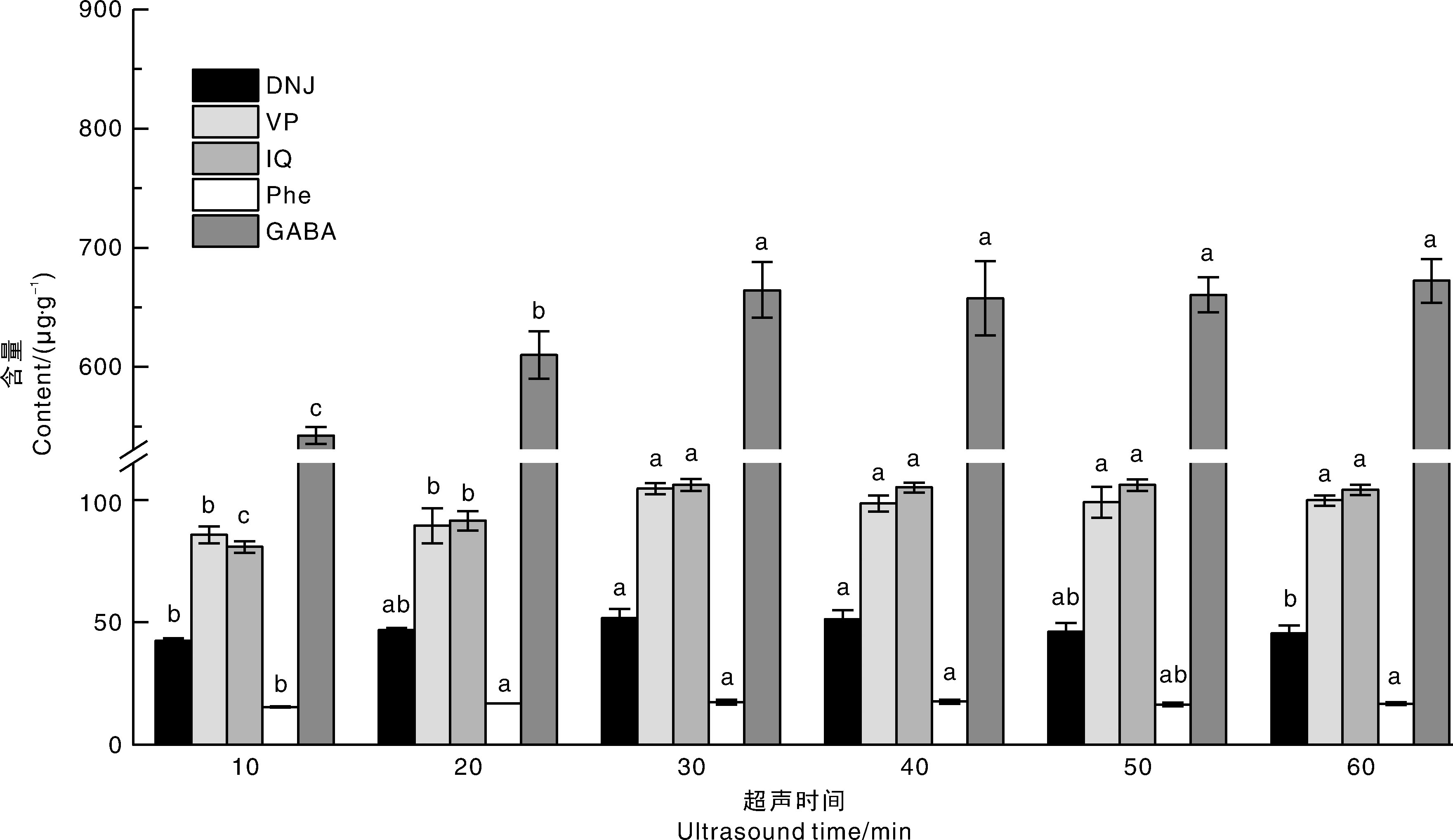
摘要: 为建立准确、快速、同步测定桑叶中1-脱氧野尻霉素(1-deoxynojirimycin, DNJ)、芦丁(rutin, VP)、异槲皮苷(isoquercitrin, IQ)、苯丙氨酸(phenylalanine, Phe)和γ-氨基丁酸(γ-aminobutyric acid, GABA)这5种生物活性物质的分析方法,本研究系统考察了提取溶剂、料液比和超声时间对5种生物活性物质提取效果的影响,确定了最佳的样品前处理方法,并采用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)进行分析。样品前处理方法优化结果表明,以90%甲醇水溶液为提取溶剂,料液比为1∶12(g·mL-1),超声提取时间为30 min,重复提取2次时,5种生物活性物质提取效果更佳。方法验证结果表明,在1~200 μg·kg-1范围内目标物的线性关系良好(r ≥ 0.998 6),5种生物活性物质的检出限为0.47~0.93 μg·kg-1,定量限为1.56~3.10 μg·kg-1,添加回收率为76.0%~99.5%,相对标准偏差均小于13%,展现出良好的灵敏度、回收率和精密度。采用该方法分析实际桑叶样品,发现不同叶位的桑叶样品中5种生物活性物质的含量均存在显著(p<0.05)差异,DNJ、Phe和GABA在芽尖中含量最高,随着叶位下移而逐渐降低,VP和IQ含量变化趋势则相反,说明该方法可以为准确评估桑叶中生物活性物质的含量变化和桑叶资源精准化开发提供技术支撑。
中图分类号:
引用本文
任晓蓉, 王新全, 张善英, 王萌, 朱鸿明, 章程辉, 齐沛沛. 基于LC-MS/MS的桑叶5种生物活性物质的同时检测[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(10): 2179-2189.
REN Xiaorong, WANG Xinquan, ZHANG Shanying, WANG Meng, ZHU Hongming, ZHANG Chenghui, QI Peipei. Simultaneous determination of five bioactive substances in mulberry leaves by LC-MS/MS[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2179-2189.
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 分子式 Molecular Formula | 先驱离子 Precursor ion(m/z) | 产物离子 Product ions(m/z) | 锥孔电压 Conce voltage/V | 碰撞能量 Collision energy/eV | 保留时间 Retention time/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | C6H13NO4 | 164 | 69*/80 | 50 | 23/22 | 0.72 |
| VP | C27H30O16 | 611 | 303*/465 | 50 | 25/10 | 3.07 |
| IQ | C21H20O12 | 463 | 300*/255 | 50 | 25/54 | 3.09 |
| Phe | C9H11NO2 | 166 | 120*/103 | 50 | 13/29 | 2.76 |
| GABA | C4H9NO2 | 104 | 87*/69 | 50 | 8/15 | 0.76 |
表1 五种生物活性物质的信息与质谱分析参数
Table 1 The information and mass spectrometric analysis parameters of 5 bioactive substances
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 分子式 Molecular Formula | 先驱离子 Precursor ion(m/z) | 产物离子 Product ions(m/z) | 锥孔电压 Conce voltage/V | 碰撞能量 Collision energy/eV | 保留时间 Retention time/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | C6H13NO4 | 164 | 69*/80 | 50 | 23/22 | 0.72 |
| VP | C27H30O16 | 611 | 303*/465 | 50 | 25/10 | 3.07 |
| IQ | C21H20O12 | 463 | 300*/255 | 50 | 25/54 | 3.09 |
| Phe | C9H11NO2 | 166 | 120*/103 | 50 | 13/29 | 2.76 |
| GABA | C4H9NO2 | 104 | 87*/69 | 50 | 8/15 | 0.76 |
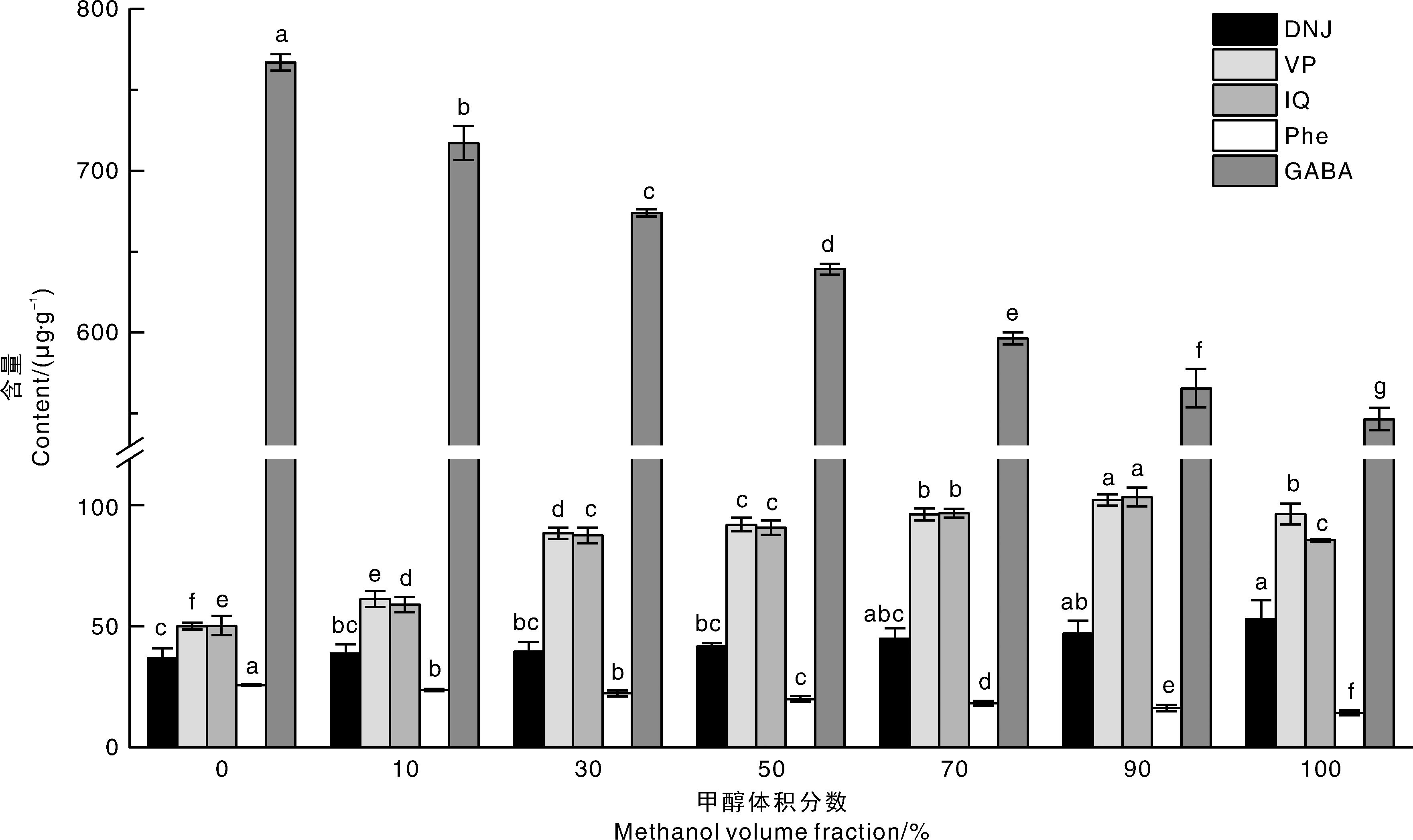
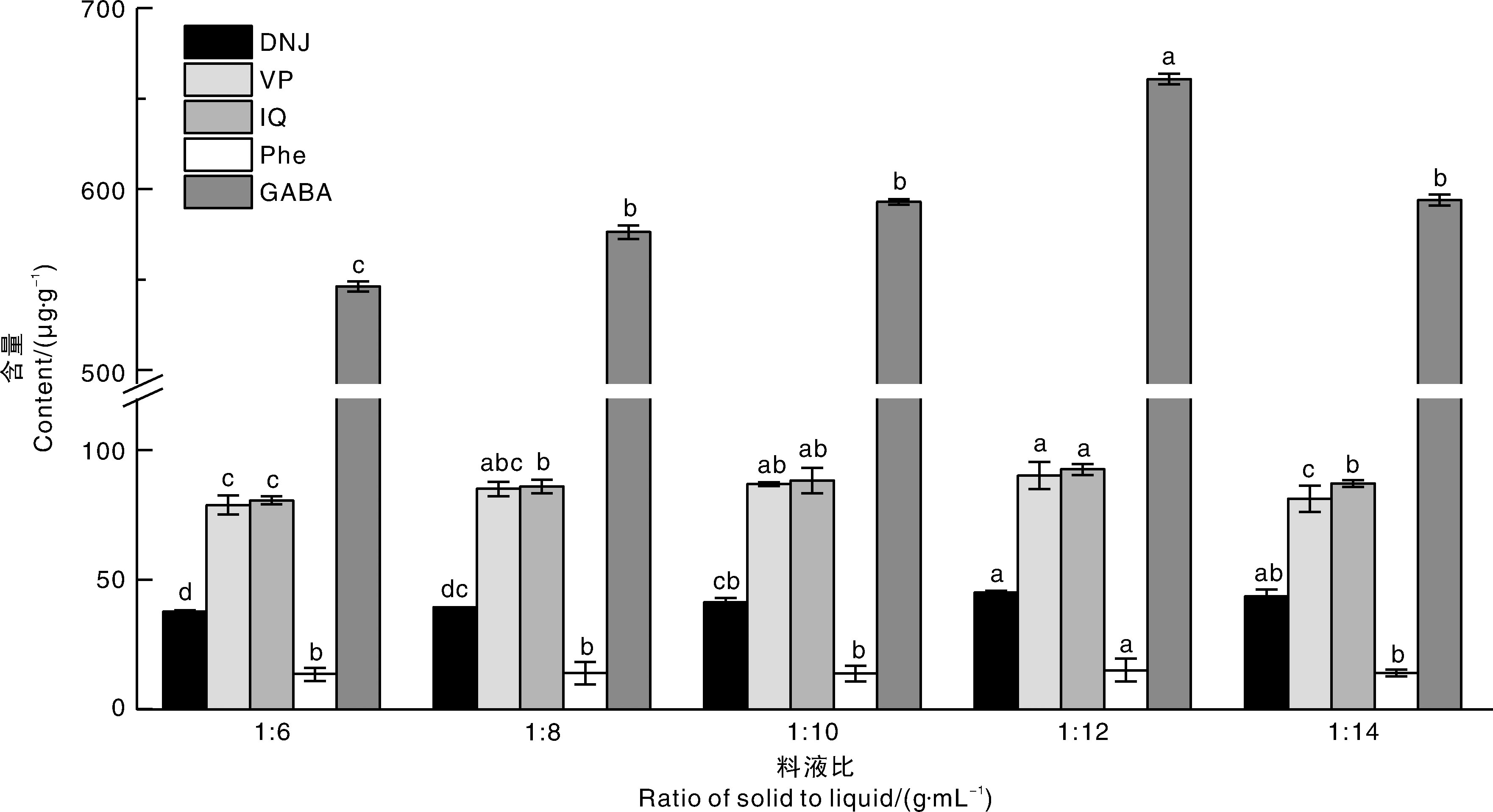
图1 不同甲醇体积分数下5种生物活性物质的含量 DNJ,1-脱氧野尻霉素;VP,芦丁;IQ,异槲皮苷;Phe,苯丙氨酸;GABA,γ-氨基丁酸。相同指标上无相同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.1 Contents of five bioactive substances under different methanol volume fractions DNJ, 1-Deoxynojirimycin; VP, Rutin; IQ, Isoquercitrin; Phe, Phenylalanine; GABA, γ-Aminobutyric acid. Different lowercase letters for the same index indicate significant differences between treatments (p<0.05). The same as below.
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 线性方程 Linear equation | 线性范围 Linear range/(μg·kg-1) | 相关系数 r | 检测限 LOD/(μg·kg-1) | 定量限 LOQ/(μg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | Y=782X+1 408 | 1~200 | 0.999 7 | 0.78 | 2.59 |
| VP | Y=918X+1 516 | 1~200 | 0.998 6 | 0.67 | 2.25 |
| IQ | Y=824X+600 | 1~200 | 0.998 8 | 0.47 | 1.56 |
| Phe | Y=11730X+91 353 | 1~200 | 0.998 9 | 0.67 | 2.24 |
| GABA | Y=1716X+1 677 | 1~200 | 0.999 4 | 0.93 | 3.10 |
表2 五种生物活性物质的线性回归方程、相关系数、检出限(LOD)和定量限(LOQ)
Table 2 Regression equations, correlation coefficients, detection limit (LOD) and quantification limit(LOQ) of five bioactive substances
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 线性方程 Linear equation | 线性范围 Linear range/(μg·kg-1) | 相关系数 r | 检测限 LOD/(μg·kg-1) | 定量限 LOQ/(μg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | Y=782X+1 408 | 1~200 | 0.999 7 | 0.78 | 2.59 |
| VP | Y=918X+1 516 | 1~200 | 0.998 6 | 0.67 | 2.25 |
| IQ | Y=824X+600 | 1~200 | 0.998 8 | 0.47 | 1.56 |
| Phe | Y=11730X+91 353 | 1~200 | 0.998 9 | 0.67 | 2.24 |
| GABA | Y=1716X+1 677 | 1~200 | 0.999 4 | 0.93 | 3.10 |
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 本底检出值 Background/(μg·g-1) | 添加值 Added/(μg·g-1) | 检测值 Found/(μg·g-1) | 平均回收率 Average recovery/% | 相对标准偏差 RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | 22.5±0.6 | 16 | 35.3±0.9 | 80.0 | 7.4 |
| 22.5±0.6 | 20 | 38.6±1.2 | 80.9 | 7.3 | |
| 22.5±0.6 | 24 | 40.7±1.5 | 76.0 | 8.0 | |
| VP | 19.9±0.3 | 32 | 48.6±0.5 | 89.9 | 1.8 |
| 19.9±0.3 | 40 | 56.4±2.5 | 91.4 | 6.7 | |
| 19.9±0.3 | 48 | 65.1±1.2 | 94.3 | 2.6 | |
| IQ | 23.6±0.8 | 32 | 51.6±0.8 | 87.5 | 2.7 |
| 23.6±0.8 | 40 | 57.1±4.2 | 83.7 | 12.6 | |
| 23.6±0.8 | 48 | 61.7±1.0 | 79.6 | 2.6 | |
| Phe | 20.3±0.3 | 16 | 32.8±1.5 | 77.9 | 12.1 |
| 20.3±0.3 | 20 | 36.5±0.4 | 80.6 | 2.5 | |
| 20.3±0.3 | 24 | 40.8±0.1 | 85.3 | 0.2 | |
| GABA | 547.7±9.7 | 560 | 1 105.1±4.6 | 99.5 | 0.8 |
| 547.7±9.7 | 700 | 1 228.6±71.8 | 97.3 | 10.6 | |
| 547.7±9.7 | 840 | 1 334.1±31.9 | 93.6 | 4.1 |
表3 不同加标水平下桑叶样品中5种生物活性物质的回收率
Table 3 Recoveries of five bioactive substances from mulberry leaves at different spike levels (n=3)
| 生物活性物质 Bioactive substances | 本底检出值 Background/(μg·g-1) | 添加值 Added/(μg·g-1) | 检测值 Found/(μg·g-1) | 平均回收率 Average recovery/% | 相对标准偏差 RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | 22.5±0.6 | 16 | 35.3±0.9 | 80.0 | 7.4 |
| 22.5±0.6 | 20 | 38.6±1.2 | 80.9 | 7.3 | |
| 22.5±0.6 | 24 | 40.7±1.5 | 76.0 | 8.0 | |
| VP | 19.9±0.3 | 32 | 48.6±0.5 | 89.9 | 1.8 |
| 19.9±0.3 | 40 | 56.4±2.5 | 91.4 | 6.7 | |
| 19.9±0.3 | 48 | 65.1±1.2 | 94.3 | 2.6 | |
| IQ | 23.6±0.8 | 32 | 51.6±0.8 | 87.5 | 2.7 |
| 23.6±0.8 | 40 | 57.1±4.2 | 83.7 | 12.6 | |
| 23.6±0.8 | 48 | 61.7±1.0 | 79.6 | 2.6 | |
| Phe | 20.3±0.3 | 16 | 32.8±1.5 | 77.9 | 12.1 |
| 20.3±0.3 | 20 | 36.5±0.4 | 80.6 | 2.5 | |
| 20.3±0.3 | 24 | 40.8±0.1 | 85.3 | 0.2 | |
| GABA | 547.7±9.7 | 560 | 1 105.1±4.6 | 99.5 | 0.8 |
| 547.7±9.7 | 700 | 1 228.6±71.8 | 97.3 | 10.6 | |
| 547.7±9.7 | 840 | 1 334.1±31.9 | 93.6 | 4.1 |
| 叶位 Leaf position | 含量Content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | VP | IQ | Phe | GABA | |
| 芽尖Bud | 318.4±35.7 a | 7.1±0.9 c | 3.7±0.5 c | 62.8±4.3 a | 583.8±22.2 a |
| 上叶位Apical leaf | 253.5±18.1 b | 8.0±0.7 c | 4.2±0.4 c | 41.3±1.0 b | 547.3±26.3 b |
| 中叶位Middle leaf | 194.7±2.9 c | 13.9±1.5 b | 7.9±0.2 b | 22.3±0.9 c | 546.7±15.7 b |
| 下叶位Basal leaf | 154.1±10.0 d | 18.9±1.9 a | 11.1±1.0 a | 21.2±1.8 c | 496.0±5.7 c |
表4 不同叶位桑叶中5种生物活性物质的含量
Table 4 Content of 5 bioactive substances in mulberry leaves at different leaf positionsμg·g-1
| 叶位 Leaf position | 含量Content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNJ | VP | IQ | Phe | GABA | |
| 芽尖Bud | 318.4±35.7 a | 7.1±0.9 c | 3.7±0.5 c | 62.8±4.3 a | 583.8±22.2 a |
| 上叶位Apical leaf | 253.5±18.1 b | 8.0±0.7 c | 4.2±0.4 c | 41.3±1.0 b | 547.3±26.3 b |
| 中叶位Middle leaf | 194.7±2.9 c | 13.9±1.5 b | 7.9±0.2 b | 22.3±0.9 c | 546.7±15.7 b |
| 下叶位Basal leaf | 154.1±10.0 d | 18.9±1.9 a | 11.1±1.0 a | 21.2±1.8 c | 496.0±5.7 c |
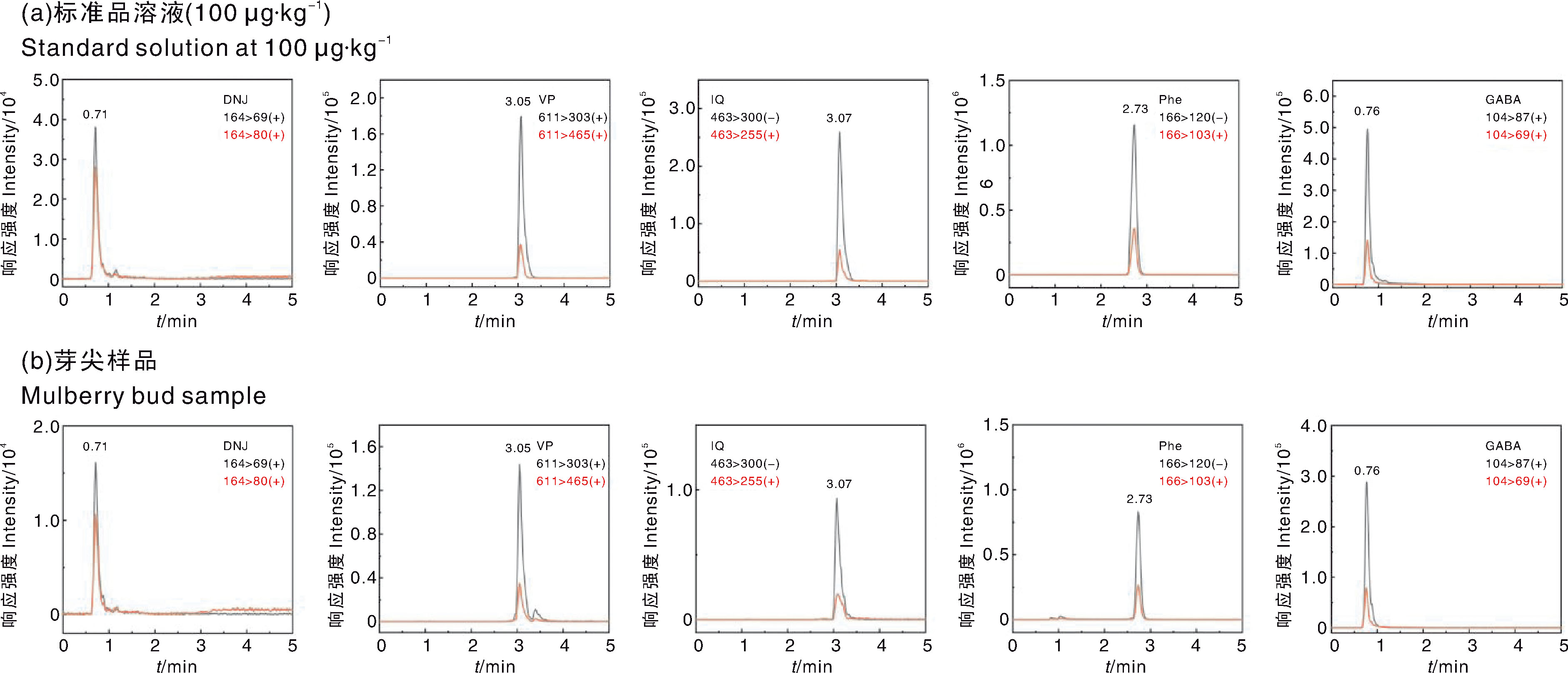
图4 五种生物活性物质标准品(100 μg·kg-1)(a)和桑树芽尖样品(b)的MRM色谱图
Fig.4 MRM chromatogram of five bioactive substances standard solution (100 μg·kg-1) (a) and mulberry bud sample(b)
| [1] | 杨虎, 沈浩. 中国传统桑树资源利用变迁及其当代生态价值探微[J]. 蚕业科学, 2021, 47(4): 374-379. |
| YANG H, SHEN H. Changes of traditional mulberry resource utilization in China and its contemporary ecological value[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica, 2021, 47(4): 374-379. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | LI Y G, XU W Y, ZHANG F, et al. The gut microbiota-produced indole-3-propionic acid confers the antihyperlipidemic effect of mulberry-derived 1-deoxynojirimycin[J]. mSystems, 2020, 5(5): e00313-20. |
| [3] | LI Y G, ZHONG S, YU J Q, et al. The mulberry-derived 1-deoxynojirimycin (DNJ) inhibits high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hypercholesteremia and modulates the gut microbiota in a gender-specific manner[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2019, 52: 63-72. |
| [4] | MA Q T, LI Y Q, ZHAO R X, et al. Therapeutic mechanisms of mulberry leaves in type 2 diabetes based on metabolomics[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2022, 13: 954477. |
| [5] | LIN Z W, GAN T T, HUANG Y Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of mulberry leaf flavonoids in vitro and in vivo[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(14): 7694. |
| [6] | HOU D Z, TANG J, FENG Q Q, et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): a comprehensive review of dietary sources, enrichment technologies, processing effects, health benefits, and its applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2024, 64(24): 8852-8874. |
| [7] | BAI H X, JIANG W, YAN R N, et al. Comparing the effects of three processing methods on the efficacy of mulberry leaf tea: Analysis of bioactive compounds, bioavailability and bioactivity[J]. Food Chemistry, 2023, 405: 134900. |
| [8] | LEE X Y, TAN J S, CHENG L H. Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) enrichment in plant-based food: a mini review[J]. Food Reviews International, 2023, 39(8): 5864-5885. |
| [9] | 吴潇, 胡杨, 蒙小玉, 等. 不同有机溶剂提取翠冠梨果皮蜡质效果比较研究[J]. 果树学报, 2023, 40(12): 2562-2573. |
| WU X, HU Y, MENG X Y, et al. Comparison of cuticular wax extraction from pear fruit by different organic solvents[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2023, 40(12): 2562-2573. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 张朝阳, 马明, 李金霖, 等. 以丙酮为溶剂提取纯化槐米中芦丁的工艺研究[J]. 化学研究, 2024, 35(1): 29-39. |
| ZHANG C Y, MA M, LI J L, et al. Study on extraction and purification technique of rutin from Sophora japonica L. using acetone as solvent[J]. Chemical Research, 2024, 35(1): 29-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王玲玲, 边祥雨, 高蔚娜, 等. 植物类黄酮提取纯化技术研究进展[J]. 营养学报, 2019, 41(6): 606-610. |
| WANG L L, BIAN X Y, GAO W N, et al. Advances in extraction and purification techniques for flavonoids in plants[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2019, 41(6): 606-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李雅琪, 余涛, 李继洋, 等. 几种现代检测技术在桑叶活性成分和有害物质残留分析中的应用[J]. 蚕业科学, 2020, 46(5): 642-649. |
| LI Y Q, YU T, LI J Y, et al. Application of several modern detection methods to analysis of active ingredient and residue of harmful substance in mulberry leaf[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica, 2020, 46(5): 642-649. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 孔维涓, 庞道睿, 杜冰, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合GC-O分析不同叶位桑叶挥发性风味物质[J]. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(16): 282-291. |
| KONG W J, PANG D R, DU B, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor substances in different leaf positions of mulberry leaves using HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with GC-O[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(16): 282-291. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | LING X, HU Y F, HU Y M, et al. Analysis of chlorogenic acid and two flavonoids in mulberry leaves of different harvest periods and origins and HPLC fingerprint study for quality control[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2024, 132: 106284. |
| [15] | 王梅, 黄晓梅, 幸秭余, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时测定桑叶中9种多酚类成分含量[J]. 食品工程, 2024(2): 66-68. |
| WANG M, HUANG X M, XING Z Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of nine polyphenols in mulberry leaves by HPLC[J]. Food Engineering, 2024(2): 66-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 何聪杰, 李舸远. HPLC法测定桑叶和金银花中绿原酸及四种黄酮类化合物[J]. 海峡药学, 2023, 35(9): 25-32. |
| HE C J, LI G Y. Determination of chlorogenic acid and four flavonoids from Flos lonicerae and mulberry leaf by HPLC[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal, 2023, 35(9): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 侯建波, 谢文, 钱艳, 等. 固相萃取-液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定蜂蜜中16种黄酮类化合物和阿魏酸[J]. 色谱, 2020, 38(5): 529-537. |
| HOU J B, XIE W, QIAN Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of 16 flavonoids and ferulic acid in honey by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2020, 38(5): 529-537. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | SCHNURR C, BUCKETT L, BITENC J, et al. Quantification of mulberrin and morusin in mulberry and other food plants via stable isotope dilution analysis using LC-MS/MS[J]. Food Chemistry, 2025, 473: 143061. |
| [19] | DEMIR S, KOYU H, YILMAZ M A, et al. Antityrosinase activity and LC-MS/MS analysis of optimized ultrasound-assisted condition extracts and fractions from strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.)[J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 2024, 32(2): 194-212. |
| [20] | JIN X, ACKAH M, WANG L, et al. Magnesium nutrient application induces metabolomics and physiological responses in mulberry (Morus alba) plants[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(11): 9650. |
| [21] | DENG F H, LIANG Y H, LEI Y L, et al. Development and identification of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from mulberry leaves[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(21): 3917. |
| [22] | 王瑞娴, 楚渠, 禚苏, 等. 不同桑品种的桑叶多酚和黄酮含量的测定[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2019, 65(1): 78-80. |
| WANG R X, CHU Q, ZHUO S, et al. Determination of polyphenol and flavone in leaves of different mulberry varieties[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 65(1): 78-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | YU Y F, HUANG J Z, DENG Z H, et al. Soil application of Bacillus subtilis regulates flavonoid and alkaloids biosynthesis in mulberry leaves[J]. Metabolites, 2024, 14(4): 180. |
| [24] | PANYATIP P, PADUMANONDA T, YONGRAM C, et al. Impact of tea processing on tryptophan, melatonin, phenolic and flavonoid contents in mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves: quantitative analysis by LC-MS/MS[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(15): 4979. |
| [25] | 钟石, 吴伟杰, 霍进喜, 等. HPLC法测定桑叶1-脱氧野尻霉素(DNJ)含量的方法学研究[J]. 蚕桑通报, 2022, 53(3): 15-20. |
| ZHONG S, WU W J, HUO J X, et al. Methodological study on the determination of 1-DNJ in mulberry leaf with HPLC[J]. Bulletin of Sericulture, 2022, 53(3): 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | ZHANG L L, BAI Y L, SHU S L, et al. Simultaneous quantitation of nucleosides, nucleobases, amino acids, and alkaloids in mulberry leaf by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2014, 37(11): 1265-1275. |
| [27] | 白娟, 朱倩云, 白华, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时测定桑叶中绿原酸及4种黄酮类成分的含量[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2020, 31(4): 469-472. |
| BAI J, ZHU Q Y, BAI H, et al. Simultaneous determination of chlorogenic acid and four flavonoids in Mori folium by HPLC[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2020, 31(4): 469-472. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 倪沁, 朱柏羽, 蒋浣竹, 等. 桑叶中1-脱氧野尻霉素的提取、分离及纯化方法研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2017, 38(20): 199-203. |
| NI Q, ZHU B Y, JIANG H Z, et al. Review on the methods of extraction, isolation and purification of 1-deoxynojirimycin in mulberry leaf[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(20): 199-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 沈维治, 廖森泰, 刘吉平, 等. 用二次回归正交旋转组合设计优化桑叶多酚的提取工艺[J]. 蚕业科学, 2009, 35(3): 594-598. |
| SHEN W Z, LIAO S T, LIU J P, et al. Optimization of polyphenol extraction from mulberry leaves using quadratic regression rotational combinational design[J]. Science of Sericulture, 2009, 35(3): 594-598. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | 曹小雪, 吉绍长, 匡雯婕, 等. 甲醇-水溶剂中L-苯丙氨酸结晶热力学[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1255-1262. |
| CAO X X, JI S C, KUANG W J, et al. Crystallization thermodynamics of L-phenylalanine in methanol-water solvent[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(4): 1255-1262. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 马强, 张涛, 沐万孟, 等. γ-氨基丁酸结晶热力学的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2010, 31(2): 77-79. |
| MA Q, ZHANG T, MU W M, et al. Crystallization thermodynamics of γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2010, 31(2): 77-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 郑燕菲, 韦凤, 韦金田. 单性木兰多糖的提取及其抗氧化稳定性能[J]. 化学工程, 2024, 52(9): 14-19. |
| ZHENG Y F, WEI F, WEI J T. Extraction and antioxidant stability of polysaccharide from Magnolia kwangsiensis Figlar & Noot[J]. Chemical Engineering(China), 2024, 52(9): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 蒲俊松. 桑叶生物碱的检测提取及含量分析[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016. |
| PU J S. Determination, extraction and concentration analysis of alkaloid in mulberry leaves[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | YUSOFF I M, MAT TAHER Z, RAHMAT Z, et al. A review of ultrasound-assisted extraction for plant bioactive compounds: phenolics, flavonoids, thymols, saponins and proteins[J]. Food Research International, 2022, 157: 111268. |
| [35] | ARANDA-LEDESMA N E, AGUILAR-ZÁRATE P, BAUTISTA-HERNÁNDEZ I, et al. The optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction for bioactive compounds from Flourensia cernua and Jatropha dioica and the evaluation of their functional properties[J]. Horticulturae, 2024, 10(7): 709. |
| [36] | 董智丹, 王宝林, 黄氏玄庄, 等. 油茶枯饼总黄酮提取工艺优化、含量测定及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 饲料研究, 2024, 47(11): 89-95. |
| DONG Z D, WANG B L, HUANG S X Z, et al. Optimization of extraction technology, content determination, and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Camellia oleifera cake[J]. Feed Research, 2024, 47(11): 89-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 李有贵, 林天宝, 钟石, 等. 桑叶1-脱氧野尻霉素生长分布规律研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2014, 26(5): 1240-1245. |
| LI Y G, LIN T B, ZHONG S, et al. Study on the growth and distribution of 1-deoxynojirimycin in mulberry leaf[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2014, 26(5): 1240-1245. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 徐斌, 张东阳, 刘利, 等. 高效液相色谱荧光检测法测定22种桑叶中1-脱氧野尻霉素含量的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(20): 1-3. |
| XU B, ZHANG D Y, LIU L, et al. Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin in 22 kinds of mulberry leaves using high-performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(20): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | LOU D S, ZOU F M, YAN H, et al. Factors influencing the biosynthesis of 1-deoxynojirimycin in Morus alba L[J]. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2011, 6(13): 2998-3006. |
| [40] | CHEN Q B, MAN C, LI D N, et al. Arogenate dehydratase isoforms differentially regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(12): 1609-1619. |
| [41] | YANG Z, LUO Y W, XIA X Y, et al. Dehydrogenase MnGutB1 catalyzes 1-deoxynojirimycin biosynthesis in mulberry[J]. Plant Physiology, 2023, 192(2): 1307-1320. |
| [42] | SHEN N, WANG T F, GAN Q, et al. Plant flavonoids: classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 383: 132531. |
| [43] | LI Z X, YANG W J, AHAMMED G J, et al. Developmental changes in carbon and nitrogen metabolism affect tea quality in different leaf position[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 106: 327-335. |
| [1] | 孙凤婷, 王旭, 韩新雨, 许振岚, 吴声敢, 黄浩, 汤涛, 盛清, 王强, 沈国强, 赵学平. 复硝酚钠对铁皮石斛中黄酮含量和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 934-942. |
| [2] | 裘丞军, 侯轩, 陈凯, 吴望君, 周炜, 段友刚. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定畜禽排泄物中15种喹诺酮类药物[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1519-1529. |
| [3] | 王晓梅, 骆玉琴, 赵学平, 陆兰菲, 方楠, 王祥云, 蒋金花, 何红梅, 张昌朋, 王强. 氟吡菌酰胺在铁皮石斛中的残留与膳食风险[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1666-1676. |
| [4] | 陈恒辉, 王军峰, 韩延超, 陈慧芝, 吴伟杰, 丁玉庭, 童川, 郜海燕. 干燥方式对桑叶枸杞固体饮料品质的影响及其口感优化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 205-214. |
| [5] | 吉小凤, 王小骊, 吕文涛, 周忠静, 吴钰潇, 杨华. 加速溶剂萃取-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定婴幼儿配方乳粉中17种磺胺类药物残留[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(1): 175-183. |
| [6] | 赵宇洪, 何文, 李根, 王强, 谢锐, 王燕, 陈清, 王小蓉. 四川地区琯溪蜜柚及其芽变品种的果实品质[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(5): 995-1004. |
| [7] | 张春荣, 郭钤, 孔丽萍, 吴园园, 林琴, 许振岚, 汤涛. 固相萃取/超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定白术中井冈霉素和丙环唑残留量[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(12): 2750-2758. |
| [8] | 黄胜佳, 叶霜, 刘新亚, 席利娟, 汪志辉, 付佳玲. 不同肥料对黄果柑果实酚类物质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(1): 91-98. |
| [9] | 林静, 张顺, 蔡挺, 曹慧, 刘鹏, 荀凯, 乐元洁. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱技术同时测定大蒜中10种农药残留[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(1): 159-166. |
| [10] | 刘泽静,薛生玲,夏雪,田玉肖,张芬,陈清,汤浩茹,孙勃*. 鱼腥草不同部位生物活性物质和抗氧化能力分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(6): 992-. |
| [11] | 黄渝岚1,2,兰柳燕2,胡盛沪2,张超兰2,冯健玲2,唐健1,黎晓峰1,2,*. 有机肥和铁肥对水稻土上桑叶失绿病的效应研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(11): 1984-. |
| [12] | 李有贵,林天宝,钟石,吕志强,计东风*. 桑叶1\|脱氧野尻霉素生长分布规律研究 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2014, 26(5): 1240-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||