浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2340-2353.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250009
衢州市柑橘园碳排放与碳储量现状评价
沈佳瑜1,2( ), 邓燕3, 张姬雯4, 彭国方5, 吴群6, 朱齐超3, 张卫峰1,2,3, 李贝3,*(
), 邓燕3, 张姬雯4, 彭国方5, 吴群6, 朱齐超3, 张卫峰1,2,3, 李贝3,*( )
)
- 1.安徽农业大学 资源与环境学院,安徽 合肥 230036
2.农田生态保育与养分资源高效利用安徽省重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230036
3.中国农业大学 资源与环境学院,北京 100083
4.衢州市农业特色产业发展中心,浙江 衢州 324000
5.常山县大宝山柑桔专业合作社,浙江 常山 324204
6.衢州市农业林业科学研究院,浙江 衢州 324003
-
收稿日期:2024-12-31出版日期:2025-11-25发布日期:2025-12-08 -
作者简介:沈佳瑜(1999—),女,江苏海门人,硕士研究生,研究方向为果园碳排放。E-mail:3256495855@qq.com -
通讯作者:*李贝,E-mail: libei90@cau.edu.cn -
基金资助:衢州市农业农村局项目(衢农合2022-31)
Evaluation of carbon emissions and storage status of citrus orchard in Quzhou City, China
SHEN Jiayu1,2( ), DENG Yan3, ZHANG Jiwen4, PENG Guofang5, WU Qun6, ZHU Qichao3, ZHANG Weifeng1,2,3, LI Bei3,*(
), DENG Yan3, ZHANG Jiwen4, PENG Guofang5, WU Qun6, ZHU Qichao3, ZHANG Weifeng1,2,3, LI Bei3,*( )
)
- 1. College of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Anhui Key Laboratory of Farmland Ecological Conservation and Efficient Utilization of Nutrient Resources, Hefei 230036, China
3. College of Resources and Environment, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China
4. Quzhou Agricultural Characteristic Industry Development Center, Quzhou 324000, Zhejiang, China
5. Dabaoshan Citrus Professional Cooperative of Changshan County, Changshan 324204, Zhejiang, China
6. Quzhou Agricultural Forestry Science Research Institute, Quzhou 324003, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2024-12-31Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
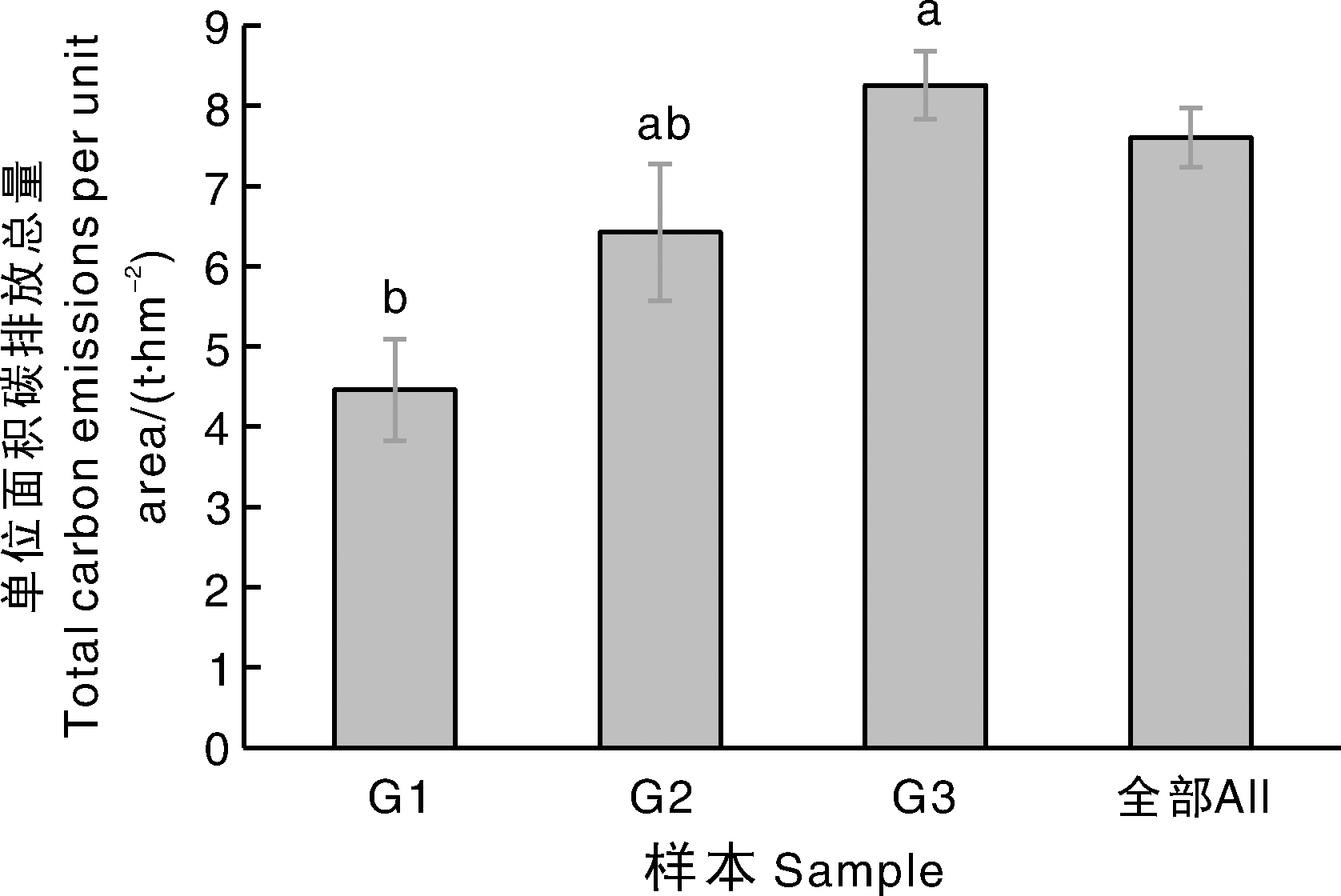
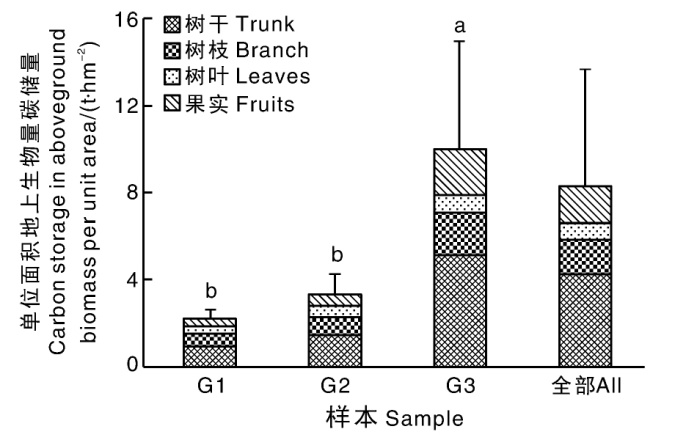
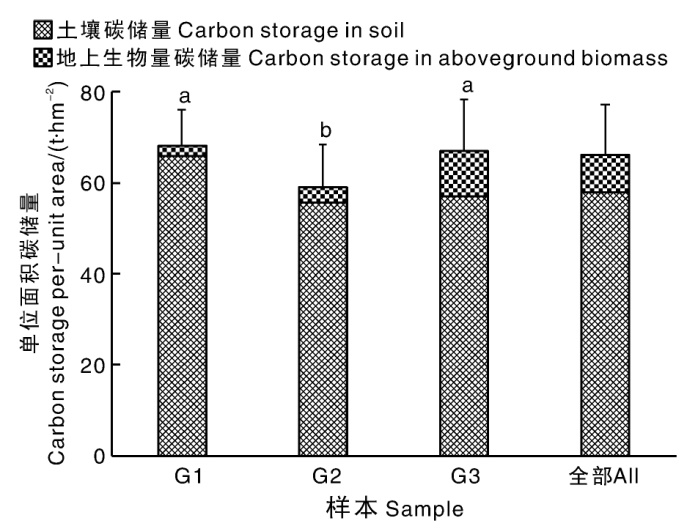
摘要: 为给柑橘园的低碳发展提供科学依据,本文以浙江省衢州市柑橘园为研究对象,采用生命周期评价方法,针对投入品生产运输、田间施肥管理和果园固碳等建立柑橘园碳核算方法,并对衢州市柑橘园的碳排放和碳储量现状进行评价。结果表明:衢州市柑橘园以≥20年树龄为主,平均产量为43.35 t·hm-2;单位面积碳排放总量(以CO2当量计)为7.61 t ·hm-2,其中,氮肥生产运输排放的占比最大,为41.66%;单位面积碳储量为66.18 t·hm-2。0~30 cm土层的土壤碳储量是碳汇的主体,占87.43%。不同树龄柑橘园的碳排放和碳储量有所差异,主要与不同树龄果园的施肥和管理差异有关。未来,应进一步优化果园管理,通过减少化肥施用和增加有机肥替代比例,进一步提升柑橘园的减排固碳能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
沈佳瑜, 邓燕, 张姬雯, 彭国方, 吴群, 朱齐超, 张卫峰, 李贝. 衢州市柑橘园碳排放与碳储量现状评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2340-2353.
SHEN Jiayu, DENG Yan, ZHANG Jiwen, PENG Guofang, WU Qun, ZHU Qichao, ZHANG Weifeng, LI Bei. Evaluation of carbon emissions and storage status of citrus orchard in Quzhou City, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2340-2353.
| 基径 Base diameter/cm | 树干占比 Proportion of trunk | 树根占比 Proportion of roots | 树枝占比 Proportion of branches | 树叶占比 Proportion of leaves | 果实占比 Proportion of fruits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4~<12 | 31.90 | 25.70 | 18.91 | 12.40 | 11.09 |
| 12~<20 | 36.09 | 29.98 | 13.26 | 6.37 | 14.30 |
| 20~<24 | 37.56 | 32.21 | 12.63 | 3.82 | 13.78 |
表1 不同基径柑橘树体各部分干基生物量占全株干基生物量的比例
Table 1 Proportion of dry biomass of different parts of citrus trees in the total dry biomass with varied base diameters %
| 基径 Base diameter/cm | 树干占比 Proportion of trunk | 树根占比 Proportion of roots | 树枝占比 Proportion of branches | 树叶占比 Proportion of leaves | 果实占比 Proportion of fruits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4~<12 | 31.90 | 25.70 | 18.91 | 12.40 | 11.09 |
| 12~<20 | 36.09 | 29.98 | 13.26 | 6.37 | 14.30 |
| 20~<24 | 37.56 | 32.21 | 12.63 | 3.82 | 13.78 |
| 样本 Sample | 样本量 Sample size | 面积 Area/hm2 | 树龄 Tree-age | 种植密度 Planting density/hm-2 | 基径 Base diameter/cm | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 11 | 3.34±6.32 a | 3.1±1.0 b | 867.3±171.9 a | 3.14±0.95 c | 25.98±18.95 b |
| G2 | 11 | 0.10±0.07 a | 6.9±2.0 b | 737.7±154.4 ab | 6.91±1.97 b | 41.25±15.91 a |
| G3 | 73 | 1.07±5.47 a | 23.3±7.7 a | 702.3±197.3 b | 14.77±2.05 a | 45.69±20.44 a |
| 全部All | 95 | 1.22±5.28 | 19.1±10.3 | 725.5±195.7 | 12.51±4.65 | 43.35±20.24 |
表2 调研柑橘园的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of the surveyed citrus orchards
| 样本 Sample | 样本量 Sample size | 面积 Area/hm2 | 树龄 Tree-age | 种植密度 Planting density/hm-2 | 基径 Base diameter/cm | 产量 Yield/(t·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 11 | 3.34±6.32 a | 3.1±1.0 b | 867.3±171.9 a | 3.14±0.95 c | 25.98±18.95 b |
| G2 | 11 | 0.10±0.07 a | 6.9±2.0 b | 737.7±154.4 ab | 6.91±1.97 b | 41.25±15.91 a |
| G3 | 73 | 1.07±5.47 a | 23.3±7.7 a | 702.3±197.3 b | 14.77±2.05 a | 45.69±20.44 a |
| 全部All | 95 | 1.22±5.28 | 19.1±10.3 | 725.5±195.7 | 12.51±4.65 | 43.35±20.24 |
| 指标 Index | 不同样本的用量Usage in different samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | 全部All | |
| 化肥N用量 | 150.30±118.81 b | 297.20±161.15 ab | 428.45±236.40 a | 381.05±236.37 |
| Usage of N in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 化肥P2O5用量 | 153.93±134.54 b | 266.52±132.88 ab | 420.49±237.26 a | 371.80±235.83 |
| Usage of P2O5 in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 化肥K2O用量 | 186.40±179.45 b | 297.20±161.15 ab | 422.66±229.75 a | 380.78±230.70 |
| Usage of K2O in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥N用量 | 69.84±70.55 a | 49.70±117.95 a | 41.91±108.73 a | 46.04±105.57 |
| Usage of N in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥P用量 | 30.27±28.23 a | 21.44±49.02 a | 25.60±92.04 a | 25.66±82.67 |
| Usage of P in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥K用量 | 31.83±48.98 a | 18.29±41.55 a | 23.00±93.47 a | 23.48±84.51 |
| Usage of K in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥C用量 | 861.49±1 112.75 a | 566.55±1 236.52 a | 508.90±1 561.92 a | 556.40±1 475.01 |
| Usage of C in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 除草剂用量Usage of herbicide/(kg·hm-2) | 2.84±3.40 a | 2.13±1.88 a | 1.73±1.70 a | 1.90±1.99 |
| 杀虫剂用量Usage of pesticide/(kg·hm-2) | 0.89±0.42 a | 1.05±0.31 a | 1.11±0.64 a | 1.08±0.59 |
| 杀菌剂用量Usage of fungicide/(kg·hm-2) | 0.97±0.76 a | 0.61±0.82 a | 0.81±1.09 a | 0.80±1.02 |
| 耗油量Fuel consumption/(kg·hm-2) | 64.55±58.76 a | 54.55±31.66 a | 62.23±43.44 a | 61.61±43.89 |
| 耗电量Electricity consumption/(kW·h·hm-2) | 323.18±274.94 b | 548.18±236.92 a | 361.23±273.26 ab | 378.47±274.17 |
表3 调研柑橘园的投入品用量
Table 3 Consumption of inputs of surveyed citrus orchards
| 指标 Index | 不同样本的用量Usage in different samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | 全部All | |
| 化肥N用量 | 150.30±118.81 b | 297.20±161.15 ab | 428.45±236.40 a | 381.05±236.37 |
| Usage of N in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 化肥P2O5用量 | 153.93±134.54 b | 266.52±132.88 ab | 420.49±237.26 a | 371.80±235.83 |
| Usage of P2O5 in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 化肥K2O用量 | 186.40±179.45 b | 297.20±161.15 ab | 422.66±229.75 a | 380.78±230.70 |
| Usage of K2O in chemical fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥N用量 | 69.84±70.55 a | 49.70±117.95 a | 41.91±108.73 a | 46.04±105.57 |
| Usage of N in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥P用量 | 30.27±28.23 a | 21.44±49.02 a | 25.60±92.04 a | 25.66±82.67 |
| Usage of P in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥K用量 | 31.83±48.98 a | 18.29±41.55 a | 23.00±93.47 a | 23.48±84.51 |
| Usage of K in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 有机肥C用量 | 861.49±1 112.75 a | 566.55±1 236.52 a | 508.90±1 561.92 a | 556.40±1 475.01 |
| Usage of C in organic fertilizer/(kg·hm-2) | ||||
| 除草剂用量Usage of herbicide/(kg·hm-2) | 2.84±3.40 a | 2.13±1.88 a | 1.73±1.70 a | 1.90±1.99 |
| 杀虫剂用量Usage of pesticide/(kg·hm-2) | 0.89±0.42 a | 1.05±0.31 a | 1.11±0.64 a | 1.08±0.59 |
| 杀菌剂用量Usage of fungicide/(kg·hm-2) | 0.97±0.76 a | 0.61±0.82 a | 0.81±1.09 a | 0.80±1.02 |
| 耗油量Fuel consumption/(kg·hm-2) | 64.55±58.76 a | 54.55±31.66 a | 62.23±43.44 a | 61.61±43.89 |
| 耗电量Electricity consumption/(kW·h·hm-2) | 323.18±274.94 b | 548.18±236.92 a | 361.23±273.26 ab | 378.47±274.17 |
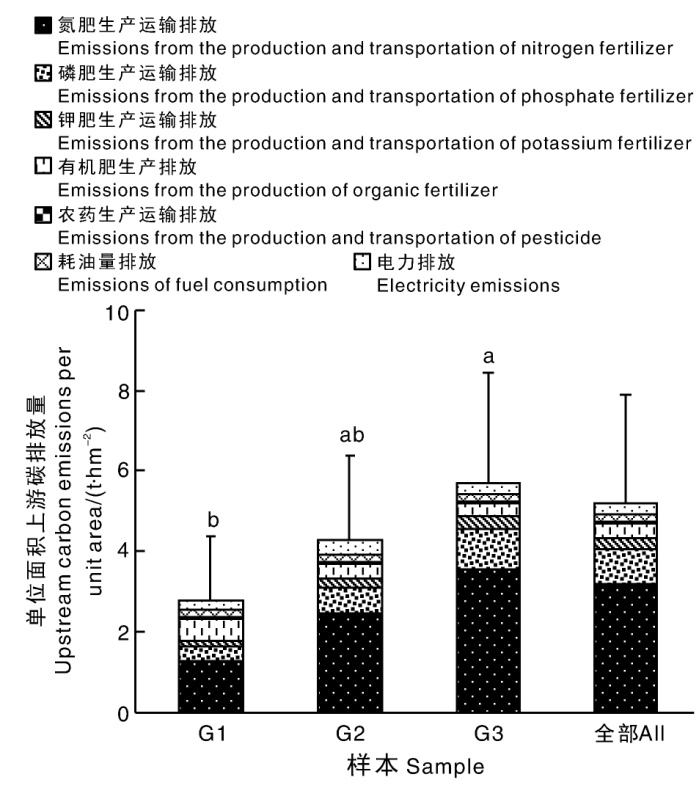
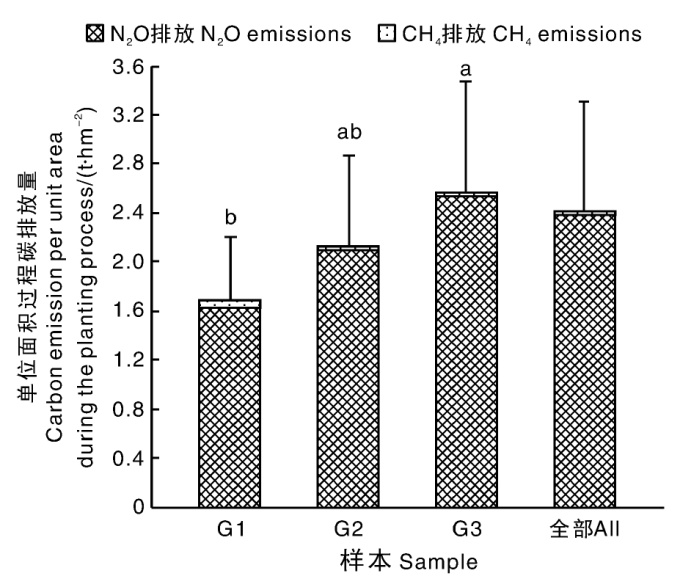
图1 调研柑橘园的单位面积上游碳排放量 柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.1 Upstream carbon emissions per unit area of surveyed citrus orchards Data marked without the same letters indicate significant difference at p<0.05. The same as below.
| [1] | 彭奎, 郑煜, 何蓉, 等. 重庆市烟草玉米轮作系统碳足迹研究: 基于生命周期评价[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2025, 42(1): 228-236. |
| PENG K, ZHENG Y, HE R, et al. Carbon footprint of the tobacco-maize cropping system in Chongqing: based on life cycle assessment[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2025, 42(1): 228-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | World Meteorological Organization. State of the Climate 2024 Update for COP29[R/OL]. [2024-12-31]. https://library.wmo.int/viewer/69075/downloadfile=State-Climate-2024-Update-COP29_en.pdf&type=pdf&navigator=1. |
| [3] | 石岳, 杨晨, 朱江玲, 等. 中国及省域碳排放、陆地碳汇及其相对减排贡献, 1980—2020[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2024, 54(12): 2459-2478. |
| SHI Y, YANG C, ZHU J L, et al. Estimation of national and provincial carbon emissions, terrestrial carbon sinks and their relative contribution to emission reductions during 1980-2020[J]. Scientia Sinica(Vitae), 2024, 54(12): 2459-2478. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | PIERRE F, MICHAEL O, JONES MATTHEW W, et al. Global carbon budget 2022[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2022, 14(11): 4811-4900. |
| [5] | 商燕, 奥布力·塔力普, 娜迪拉·阿不都热苏力。 中国省域能源消费碳排放强度的时空演变及影响因素研究[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 44(1): 11-17. |
| SHANG Y, AOBULI T, NADILA A. Spatial and temporal evolution of carbon emission intensity of energy consumption in provincial areas of China and the influencing factors[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2025, 44(1): 11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 温源远, 张建宇, 于晓龙, 等. 全球碳排放碳市场现状趋势及对我国的影响[J]. 中国投资(中英文), 2024(S5): 70-74. |
| WEN Y Y, ZHANG J Y, YU X L, et al. Trend of global carbon emission market and its impact on China[J]. China Investment, 2024(S5): 70-74. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 范紫月, 齐晓波, 曾麟岚, 等. 中国农业系统近40年温室气体排放核算[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(23): 9470-9482. |
| FAN Z Y, QI X B, ZENG L L, et al. Accounting of greenhouse gas emissions in the Chinese agricultural system from 1980 to 2020[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(23): 9470-9482. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | CHEN X H, MA C C, ZHOU H M, et al. Identifying the main crops and key factors determining the carbon footprint of crop production in China, 2001-2018[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 172: 105661. |
| [9] | HU G W, MU X Z, XU M, et al. Potentials of GHG emission reductions from cold chain systems: case studies of China and the United States[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 239: 118053. |
| [10] | 王少剑, 周诗洁, 方创琳. 1980—2020年中国陆地生态系统碳储量时空格局与演进规律[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2024, 54(10): 3323-3339. |
| WANG S J, ZHOU S J, FANG C L. Spatial-temporal patterns and evolution of carbon storage in China’s terrestrial ecosystems from 1980 to 2020[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 2024, 54(10): 3323-3339. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 周广胜, 周梦子, 周莉, 等. 中国陆地生态系统增汇潜力研究展望[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(31): 3625-3632. |
| ZHOU G S, ZHOU M Z, ZHOU L, et al. Advances in the carbon sink potential of terrestrial ecosystems in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(31): 3625-3632. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | XU L, YU G R, HE N P, et al. Carbon storage in China’s terrestrial ecosystems: a synthesis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 2806. |
| [13] | 杨元合, 石岳, 孙文娟, 等. 中国及全球陆地生态系统碳源汇特征及其对碳中和的贡献[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2022, 52(4): 534-574. |
| YANG Y H, SHI Y, SUN W J, et al. Terrestrial carbon sinks in China and around the world and their contribution to carbon neutrality[J]. Scientia Sinica(Vitae), 2022, 52(4): 534-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 童荣鑫, 梁迅, 关庆锋, 等. 2000—2020年中国陆地土壤碳储量及土地管理碳汇核算[J]. 地理学报, 2023, 78(9): 2209-2222. |
| TONG R X, LIANG X, GUAN Q F, et al. Estimation of soil carbon storage change from land use and management at a high spatial resolution in China during 2000-2020[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2023, 78(9): 2209-2222. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 林清山. 柑橘林碳汇潜力和生态服务价值研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2010. |
| LIN Q S. A study on carbon sink potential of tangerine plantation and its ecological service value[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 刘世荣, 王晖, 李海奎, 等. 碳中和目标下中国森林碳储量、碳汇变化预估与潜力提升途径[J]. 林业科学, 2024, 60(4): 157-172. |
| LIU S R, WANG H, LI H K, et al. Projections of China’s forest carbon storage and sequestration and ways of their potential capacity enhancement[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2024, 60(4): 157-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 中国国际发展知识中心. 生态系统碳汇发展的国际进展与中国展望[R/OL]. [2024-12-31]. https://zhongguoguojifazhanzhishizhongxin0514.pdf. |
| [18] | 国家统计局. 中国第三产业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2023. |
| [19] | 黄国华, 宁心怡, 卢玉鹏, 等. 基于果园生草模式的固碳潜力及影响研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2023(14): 146-153. |
| HUANG G H, NING X Y, LU Y P, et al. Research progress on carbon sequestration potential and its effects based on grass planting model in the orchard[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023(14): 146-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | YANG X, HOU H J, XU Y J, et al. Divergent pattern of soil CO2, CH4 and N2O emissions in 18-year citrus orchard and Camellia oleifera plantations converted from natural shrub forests[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 175: 104447. |
| [21] | 马艳婷, 赵志远, 冯天宇, 等. 有机无机肥配施对苹果园温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(9): 2039-2048. |
| MA Y T, ZHAO Z Y, FENG T Y, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions from an apple orchard with the mixed application of organic and chemical fertilizers[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(9): 2039-2048. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | PENG X L, CHEN D Y, ZHEN J B, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and drivers of the global warming potential of vineyards under different irrigation and fertilizer management practices[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 950: 175447. |
| [23] | YANG Y Y, QI C J, GU Y M, et al. Use efficiency, reduction potential, and effects of fertilizers on carbon emissions in China’s major citrus regions[J]. Agriculture, 2024, 14(11): 1971. |
| [24] | 金相乐. 农田和果园不同施肥措施下作物产量、土壤N2O排放的模拟与碳足迹计量评价[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023. |
| JIN X L. Simulation of crop yield and soil N2O emissions under different fertilization regimes and carbon footprint measurement evaluation in farmland and orchard[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 张雅诗, 刘立生, 任凤玲, 等. 幼龄果园套种西瓜施肥模式碳足迹评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2024, 14(5): 1479-1487. |
| ZHANG Y S, LIU L S, REN F L, et al. Evaluation of the carbon footprint of watermelon fertilization regimes in young orchards[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2024, 14(5): 1479-1487. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | XU P S, LI Z T, WANG J Y, et al. Fertilizer-induced nitrous oxide emissions from global orchards and its estimate of China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2022, 328: 107854. |
| [27] | LIU H F, LIU G H, LI Y, et al. Effects of land use conversion and fertilization on CH4 and N2O fluxes from typical hilly red soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(20): 20269-20280. |
| [28] | 康福蓉. 氮肥运筹对柑橘园氨挥发与氮素淋洗的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022. |
| KANG F R. Study on the effects of nitrogen management on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen leaching in citrus orchard[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | ZHANG B G, LI Q, CAO J, et al. Reducing nitrogen leaching in a subtropical vegetable system[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 241: 133-141. |
| [30] | 吴志丹, 王义祥, 翁伯琦, 等. 福州地区7年生柑橘果园生态系统的碳氮储量[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 37(3): 316-319. |
| WU Z D, WANG Y X, WENG B Q, et al. Organic carbon and nitrogen storage in 7 years old citrus orchard ecosystem in Fuzhou, China[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 37(3): 316-319. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [31] | 林清山, 洪伟, 吴承祯, 等. 永春县柑橘林生态系统的碳储量及其动态变化[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(2): 309-316. |
| LIN Q S, HONG W, WU C Z, et al. Organic carbon storage and its dynamic change in citrus ecosystem in Yongchun, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(2): 309-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | WU T, WANG Y, YU C J, et al. Carbon sequestration by fruit trees: Chinese apple orchards as an example[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(6): e38883. |
| [33] | ROSEMARY A. Carbon storage in orchards[D]. Bangor, Wales, UK: Bangor University, 2013 |
| [34] | WANG Y X, WENG B Q, YE J, et al. Carbon sequestration in a nectarine orchard as affected by green manure in China[J]. European Journal of Horticultural Science, 2015, 80(5): 208-215. |
| [35] | 衢州市统计局, 国家统计局衢州调查队. 衢州统计年鉴: 2022[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2023. |
| [36] | 朱晓龙, 周明强, 孙灵. 衢州市柑橘绿色高效栽培管理技术[J]. 果农之友, 2024(5): 68-70. |
| ZHU X L, ZHOU M Q, SUN L. Green and efficient cultivation and management techniques of citrus in Quzhou City[J]. Fruit Growers’ Friend, 2024(5): 68-70. (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | XIANG Y Z, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Factors shaping soil organic carbon stocks in grass covered orchards across China: a meta-analysis[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 807: 150632. |
| [38] | 衢州市统计局, 国家统计局衢州调查队. 衢州市统计年鉴: 2020[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. |
| [39] | 张明洁, 张京红, 李文韬, 等. 热带果类农产品碳足迹核算研究: 以海南芒果为例[J]. 热带农业科学, 2023, 43(4): 57-62. |
| ZHANG M J, ZHANG J H, LI W T, et al. Estimate of carbon footprint accounting of tropical fruit agricultural products: taking Hainan mango as an example[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2023, 43(4): 57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [40] | 吴海燕, 仇欢欢, 周倩. 基于生命周期评价法的我国油菜碳足迹核算与时空变化分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 2024, 56(4): 1341-1350. |
| WU H Y, QIU H H, ZHOU Q. Carbon footprint accounting and spatiotemporal changes of Chinese rapeseed by province based on life cycle assessment method[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2025, 56(4): 1341-1350. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [41] | ZHANG W F, DOU Z X, HE P, et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(21): 8375-8380. |
| [42] | 陈舜, 逯非, 王效科. 中国主要农作物种植农药施用温室气体排放估算[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(9): 2560-2569. |
| CHEN S, LU F, WANG X K. Estimate of greenhouse gases emission from pesticides usage in China’s major crops[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(9): 2560-2569. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [43] | CHEN X P, CUI Z L, FAN M S, et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 486-489. |
| [44] | 袁京, 刘燕, 唐若兰, 等. 畜禽粪便堆肥过程中碳氮损失及温室气体排放综述[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(11): 2428-2438, 2590. |
| YUAN J, LIU Y, TANG R L, et al. A review of carbon and nitrogen losses and greenhouse gas emissions during livestock manure composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(11): 2428-2438, 2590. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [45] | 陈中督, 徐春春, 纪龙, 等. 长江中游地区稻麦生产系统碳足迹及氮足迹综合评价[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(7): 1125-1133. |
| CHEN Z D, XU C C, JI L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation for carbon and nitrogen footprints of rice-wheat rotation system in Middle Yangtze River Basin[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(7): 1125-1133. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [46] | 国家应对气候变化战略研究和国际合作中心. 2011年和2012年中国区域电网平均二氧化碳排放因子[R]. 北京: 国家应对气候变化战略研究和国际合作中心, 2014. |
| [47] | ZHANG X Y, FANG Q C, ZHANG T, et al. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: a meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(2): 888-900. |
| [48] | 吴晓莲, 程玥晴, 罗友进, 等. 重庆三峡库区柑橘果园系统碳储量及碳汇潜能研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2014, 27(2): 693-698. |
| WU X L, CHENG Y Q, LUO Y J, et al. Carbon sequestration and storage of citrus orchard system in Three Gorges Reservoir Region of Chongqing[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 27(2): 693-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [49] | The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories[EB/OL]. [2024-12-31]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/2019-refinement-to-the-2006-ipcc-guidelines-for-national-greenhouse-gas-inventories. |
| [50] | CHEN X H, XU X Z, LU Z Y, et al. Carbon footprint of a typical pomelo production region in China based on farm survey data[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277: 124041. |
| [51] | 王文赞, 韩建, 倪玉雪, 等. 有机肥替代化肥氮对苹果产量、品质及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(3): 437-448. |
| WANG W Z, HAN J, NI Y X, et al. Effects of substituting chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer on apple yield, quality, and greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(3): 437-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [52] | XUN Z F, XU T Y, REN B H, et al. Nitrogen fertilization of lawns enhanced soil nitrous oxide emissions by increasing autotrophic nitrification[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 943920. |
| [53] | 赵健宇, 杨开静, 王凤新. 滴头流量对土壤甲烷吸收扩散转化及马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(13): 97-106. |
| ZHAO J Y, YANG K J, WANG F X. Effects of emitter flow rates of drip irrigation on methane uptake, diffusion, transformation in the soil and potato yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(13): 97-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [54] | 赵环宇. 我国柑橘生产的环境代价及氮素优化措施研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2023. |
| ZHAO H Y. Study on environmental cost and nitrogen optimization measures of Chinese citrus production[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [55] | 许修柱. 琯溪蜜柚生产中的碳排放及优化施肥的综合效应评价[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2019. |
| XU X Z. Comprehensive evaluation of carbon emission and optimum fertilization in Guanxi pomelo production[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [56] | 詹鹏杰. 三峡库区典型柑橘园土壤有机碳固持潜力及碳足迹分析[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022. |
| ZHAN P J. Analysis of soil organic carbon sequestration potential and carbon footprint of citrus orchards in the three gorges reservoir area[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [57] | 李志坚, 李燕青, 李壮. 柑橘园养分管理技术[J]. 果树实用技术与信息, 2023(10): 19-22. |
| LI Z J, LI Y Q, LI Z. Nutrient management techniques in citrus orchards[J]. Guoshu Shiyong Jishu Yu Xinxi, 2023(10): 19-22. (in Chinese) | |
| [58] | 李旭. 减氮施肥对柑橘树体氮素含量、果实品质产量和氮肥利用的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| LI X. Effects of reduced nitrogen fertilization on nitrogen content, fruit yield and nitrogen fertilizer utilization of citrus trees[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [59] | 朱志军. 渭北苹果园施肥制度对氨挥发和温室气体排放的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. |
| ZHU Z J. Effects of fertilization system on ammonia volatilization and greenhouse gas emission in Weibei apple orchard[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [60] | 张卫强, 许修柱, 陈晓辉, 等. 优化施肥对琯溪蜜柚产量、品质和碳排放的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(6): 82-90. |
| ZHANG W Q, XU X Z, CHEN X H, et al. Effect of optimized fertilization on Guanxi pomelo’s yield, quality, and carbon emission[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(6): 82-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [61] | 罗自威, 陶晶霞, 侯凯捷, 等. 养分优化管理实现蜜柚高产高效和降低碳排放[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(4): 688-700. |
| LUO Z W, TAO J X, HOU K J, et al. Optimized nutrient management improves fruit yield and fertilizer use efficiency and reduces carbon emissions in pomelo production[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(4): 688-700. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [62] | 朱教君, 高添, 于立忠, 等. 森林生态系统碳汇: 概念、时间效应与提升途径[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(9): 2313-2321. |
| ZHU J J, GAO T, YU L Z, et al. Carbon sink of forest ecosystems: concept, time effect and improvement approaches[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(9): 2313-2321. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [63] | 胡彦婷, 管东生, 王浩, 等. 广州常绿阔叶林和果园生态系统碳储量[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(11): 2873-2879. |
| HU Y T, GUAN D S, WANG H, et al. Carbon storage of evergreen broad-leaved forest and orchard ecosystems in Guangzhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(11): 2873-2879. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [64] | 叶小曼, 魏天兴, 于欢, 等. 黄土丘陵区典型森林生态系统碳储量及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 2025, 44(5): 1409-1416. |
| YE X M, WEI T X, YU H, et al. Carbon storage and influencing factors of typical forest ecosystems in loess hilly region[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2025, 44(5): 1409-1416. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [65] | 朱苑维, 罗婧, 陈玉娟, 等. 广州市海珠区万亩果园主要生态系统的碳密度及其分配特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(1): 164-169. |
| ZHU Y W, LUO J, CHEN Y J, et al. Carbon density and distribution of main ecosystems in Ten-Thousand-Mu Orchard at Haizhu District, Guangzhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(1): 164-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [66] | 陈绍民, 杨硕欢, 张保成, 等. 不同水肥条件下夏玉米/冬小麦农田生态系统碳平衡研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(5): 229-238. |
| CHEN S M, YANG S H, ZHANG B C, et al. Carbon balance in summer maize/winter wheat farmland ecosystem under different water and fertilizer conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(5): 229-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [67] | 赵牧秋, 史云峰. 三亚地区芒果园生态系统碳储量及其分布特征[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014, 42(4): 1088-1090. |
| ZHAO M Q, SHI Y F. Carbon storage and distribution in mango plantation ecosystems in Sanya[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(4): 1088-1090. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [68] | 张佳佳, 雷蕾, 肖文发, 等. 三峡库区经济林土壤有机碳特征[J]. 陆地生态系统与保护学报, 2022(1): 22-30. |
| ZHANG J J, LEI L, XIAO W F, et al. Soil organic carbon characteristics of economic forest in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Terrestrial Ecosystem and Conservation, 2022(1): 22-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [69] | 刘春荣, 王登亮, 胡燕芳, 等. 衢州市柑橘园土壤养分调查[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2019, 60(2): 234-236, 240. |
| LIU C R, WANG D L, HU Y F, et al. Status of soil nutrients in citrus orchards of Quzhou City[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 60(2): 234-236, 240. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [70] | 马创举, 刘春荣, 吴雪珍, 等. 衢州市桔园土壤管理现状与改进提升对策[J]. 中国果业信息, 2023, 40(3): 65-69. |
| MA C J, LIU C R, WU X Z, et al. Present situation and improvement countermeasures of soil management in orange orchard in Quzhou City[J]. China Fruit News, 2023, 40(3): 65-69. (in Chinese) | |
| [71] | 尹献远, 张鑫, 徐霄, 等. 有机肥料对衢州市不同类型土壤肥力的影响效果[J]. 南方农业, 2024, 18(4): 82-84. |
| YIN X Y, ZHANG X, XU X, et al. The effect of organic fertilizer on different soil fertility in Quzhou City[J]. South China Agriculture, 2024, 18(4): 82-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [72] | 王高起, 袁丹, 吴萍, 等. 深层土壤有机碳储量、稳定性以及对人类活动响应的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2025, 33(3): 435-448. |
| WANG G Q, YUAN D, WU P, et al. Research advances on deep soil organic carbon storage, stability and responses to human activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2025, 33(3): 435-448. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [73] | WRIGHT A L, HONS F M. Tillage impacts on soil aggregation and carbon and nitrogen sequestration under wheat cropping sequences[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2005, 84(1): 67-75. |
| [74] | 李景, 吴会军, 武雪萍, 等. 长期保护性耕作提高土壤大团聚体含量及团聚体有机碳的作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(2): 378-386. |
| LI J, WU H J, WU X P, et al. Impact of long-term conservation tillage on soil aggregate formation and aggregate organic carbon contents[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(2): 378-386. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [75] | 李景, 吴会军, 武雪萍, 等. 长期免耕和深松提高了土壤团聚体颗粒态有机碳及全氮含量[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(2): 334-344. |
| LI J, WU H J, WU X P, et al. Long-term conservation tillage enhanced organic carbon and nitrogen contents of particulate organic matter in soil aggregates[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(2): 334-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [76] | 李文慧, 陈浩楠, 南雄雄, 等. 宁夏旱区枸杞/覆盖作物种植体系对土壤活性有机碳库的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(5): 1324-1332. |
| LI W H, CHEN H N, NAN X X, et al. Effects of cropping system of Lycium barbarum L. and cover crops on soil labile organic carbon pool in an arid region of Ningxia[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(5): 1324-1332. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [77] | 马小雯, 顾艾节, 李丹, 等. 奉贤区不同树龄桃树的碳汇价值分析[J]. 上海农业科技, 2022(3): 22-23. |
| MA X W, GU A J, LI D, et al. Analysis of carbon sequestration value of peach trees with different age in Fengxian District[J]. Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(3): 22-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [78] | 刘伟, 罗玲, 钟奇, 等. 生草和地布覆盖对攀枝花地区芒果园土壤性质及果实品质的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021, 27(2): 261-270. |
| LIU W, LUO L, ZHONG Q, et al. Effects of grass planting and ground fabric mulching on soil properties and fruit quality in mango orchards in Panzhihua, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2021, 27(2): 261-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [79] | 秦秦, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 等. 猕猴桃园行间生草对土壤养分的影响及有效性评价[J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(1): 68-76. |
| QIN Q, SONG K, SUN L J, et al. Effect of inter-row sod system on the contents and availability of soil nutrients in a kiwifruit orchard[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(1): 68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [80] | 杨露, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 生草改善果园土壤肥力和苹果树体营养的效果[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. |
| YANG L, MAO Y F, HU Y L, et al. Effects of orchard grass on soil fertility and apple tree nutrition[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [81] | 吴东, 黄志霖, 肖文发, 等. 三峡库区典型退耕还林模式水土保持功能研究[J]. 中国水土保持, 2017(1): 33-37. |
| WU D, HUANG Z L, XIAO W F, et al. Soil and water conservation functions of typical returning farmland to forest mode of the three-gorge reservoir area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2017(1): 33-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 周聃, 刘梅, 张政, 邹松保, 倪蒙, 原居林. 虾蟹混养池塘的温室气体排放及其影响因子[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1872-1880. |
| [2] | 易明, 孙宏, 沈琦, 汤江武. 异位发酵床技术在畜禽粪污处理中的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1390-1396. |
| [3] | 龚娜, 刘国丽, 陈珣, 马晓颖, 肇莹, 肖军. 一株野生肺形侧耳的鉴定及其液体发酵培养基的优化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(11): 2535-2545. |
| [4] | 董捷, 曾咪. 基于碳汇收益和木材收益损失的碳汇造林补偿标准研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(4): 790-800. |
| [5] | 陈丽荣, 陈丽娟, 朱震锋, 韩丽晶, 曹玉昆. 基于交易视角的天然林资源保护工程区林业碳汇项目开发潜力——以黑龙江森工天保工程区为例[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(5): 944-954. |
| [6] | 甄伟, 庄鸿源, 米松华. 中国农业中间投入温室气体排放与减排潜力[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(11): 2185-2194. |
| [7] | 梁林波, 王仕玉, 杨建华, 张雨思. 杯鞘石斛链格孢病菌生物学特性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(11): 1862-1867. |
| [8] | 孙仲奇1,裘娟萍1,陆建卫2,赵春田1,*. 碳源对多粘类芽孢杆菌生长和多粘菌素E合成的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(8): 1343-. |
| [9] | 米松华1,黄祖辉2,*,朱奇彪1,黄河啸1,李宝值1 . 稻田温室气体减排成本收益分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(4): 707-. |
| [10] | 金群力, 范丽军, 冯伟林, 宋婷婷, 沈颖越, 田芳芳, 蔡为明. 不同栽培原料配方及装瓶容重对金针菇生长发育的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(11): 1874-1880. |
| [11] | 赵佩文, 王新, 吴逸飞, 姚晓红, 柳永, 孙宏, 葛向阳, 汤江武. 不同碳源促进污染水体氮素转化的微生态过程[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(11): 1915-1921. |
| [12] | 车阳,赵春田,裘娟萍. 碳源对加纳链霉菌合成默诺霉素的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(8): 1355-. |
| [13] | 黄锦法;王国峰;石艳平;*;倪雄伟 . 嘉兴市农业碳汇及低碳农业技术应用策略[J]. , 2012, 24(2): 0-274. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||