浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2535-2544.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241071
小麦根际真菌分离及其抗菌活性
宋英俊( ), 蔡怡好, 张利霞, 吕淑芳, 李文文, 索晨美, 张昊, 侯典云, 赵杏利*(
), 蔡怡好, 张利霞, 吕淑芳, 李文文, 索晨美, 张昊, 侯典云, 赵杏利*( )
)
- 河南科技大学 农学院,河南 洛阳 471023
-
收稿日期:2024-12-07出版日期:2025-12-25发布日期:2026-01-09 -
作者简介:宋英俊(1996—),女,河南周口人,硕士研究生,研究方向为微生物多样性和生物防治。E-mail: 525879010@qq.com -
通讯作者:*赵杏利,E-mail: hellen1984@haust.edu.cn -
基金资助:河南省科技攻关项目(242102110227);河南省科技研发计划联合基金项目(222103810057)
Isolation of rhizosphere fungi from wheat and their antifungal activity
SONG Yingjun( ), CAI Yihao, ZHANG Lixia, LYU Shufang, LI Wenwen, SUO Chenmei, ZHANG Hao, HOU Dianyun, ZHAO Xingli*(
), CAI Yihao, ZHANG Lixia, LYU Shufang, LI Wenwen, SUO Chenmei, ZHANG Hao, HOU Dianyun, ZHAO Xingli*( )
)
- College of Agriculture, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan, China
-
Received:2024-12-07Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
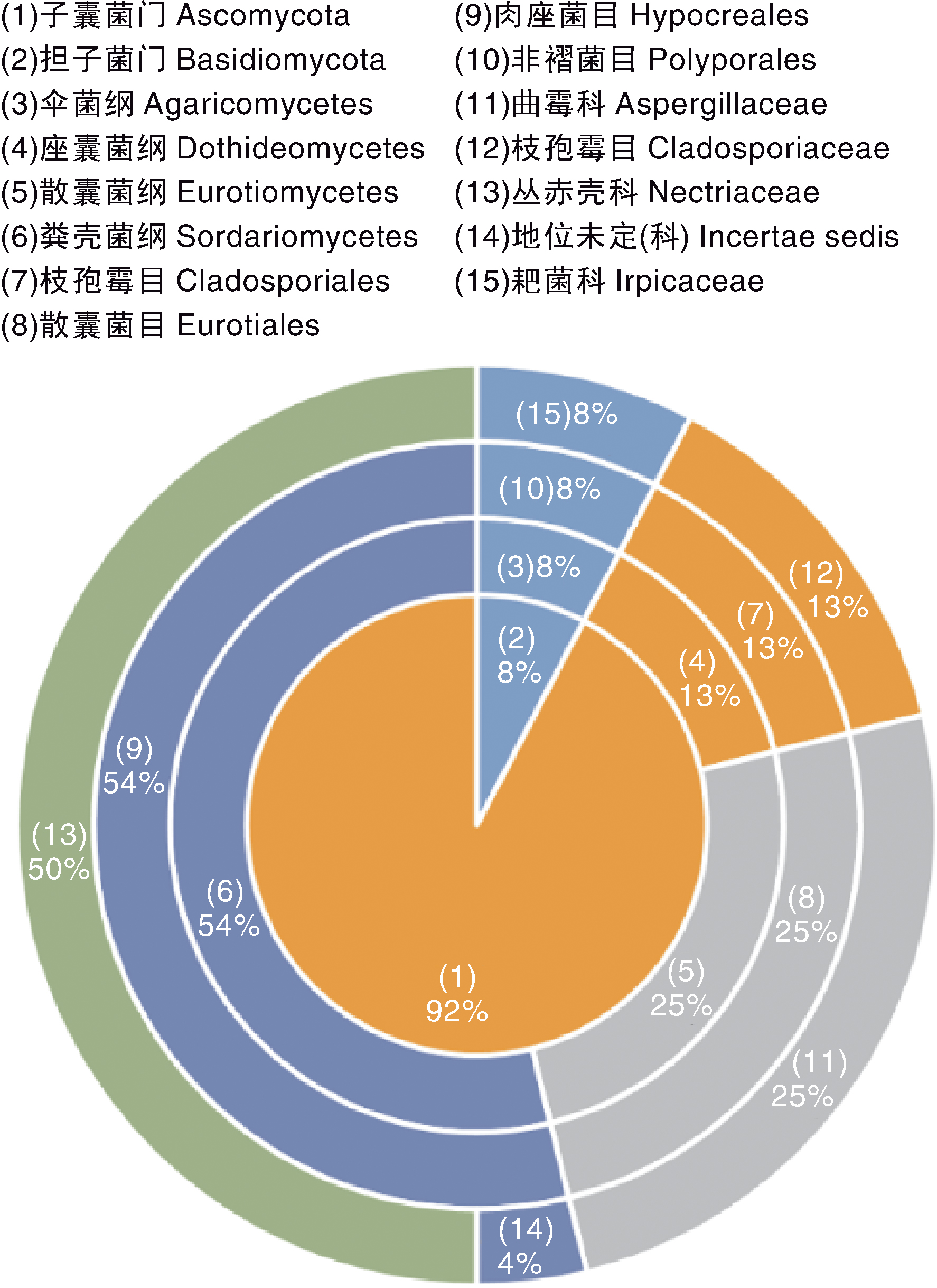
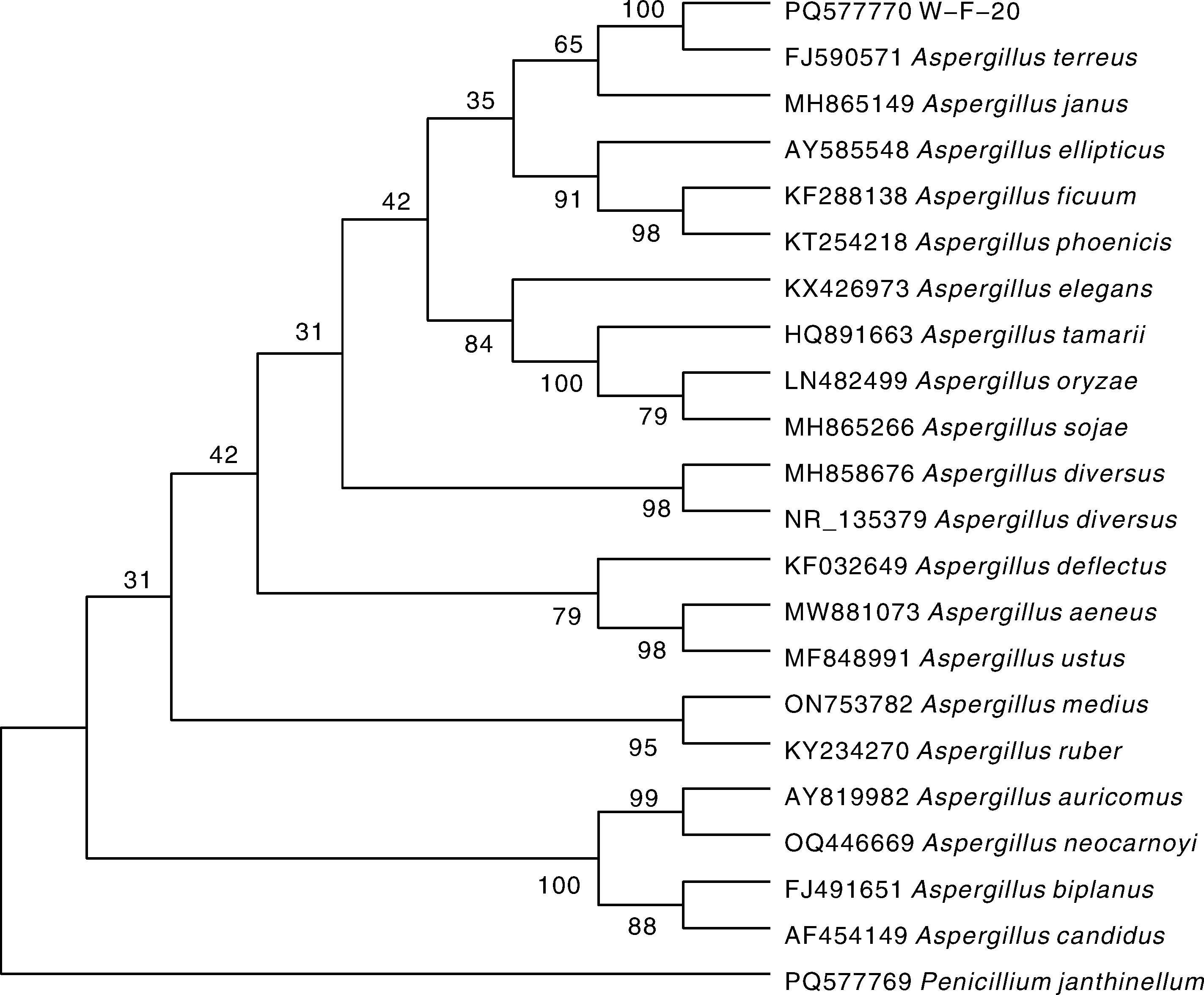
摘要: 根际微生物往往能促进植物的生长,保护植物免受病原菌的侵染,同时数量又远大于非根际微生物,因此从根际微生物出发,寻找防治根部病害的生防菌株是一个有效途径。小麦茎基腐病是近年来在黄淮小麦主产区日益严重的一种小麦土传真菌病害。本研究采用稀释平板法对小麦根际真菌进行分离,根据形态特征和ITS序列分析对获得的菌株进行分类地位的确定,通过平板对峙试验测定分离菌株对小麦茎基腐病病原菌的拮抗作用,并对拮抗性能较强菌株的抗菌谱进行测定。结果表明,本研究共分离获得52个菌株,分属于2门4纲4目5科6属的14种,鉴定到的6个属及其相对丰度分别为镰孢属(Fusarium)50.00%、曲霉属(Aspergillus)13.46%、枝孢属(Cladosporium) 13.46%、青霉属(Penicillium)11.54%、耙菌属(Irpex)7.69%和帚枝霉属(Sarocladium)3.85%。对小麦茎基腐病病原菌——假禾谷镰孢(Fusarium pseudograminearum)主要表现为基质竞争作用的菌株有28株,生长抑制率为17%~75%;主要表现为抗生作用的菌株有2株,分别为W-F-15和W-F-20,其中,土曲霉(Aspergillus terreus)W-F-20菌株的抗生作用最强,抑菌带宽度达15 mm,生长抑制率为62%。同时,W-F-20菌株对其他9种植物病原真菌也具有抗生作用,表现出广谱抗性。本研究为进一步开发利用防治小麦茎基腐病的真菌资源提供了理论支撑和基本材料。
中图分类号:
引用本文
宋英俊, 蔡怡好, 张利霞, 吕淑芳, 李文文, 索晨美, 张昊, 侯典云, 赵杏利. 小麦根际真菌分离及其抗菌活性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2535-2544.
SONG Yingjun, CAI Yihao, ZHANG Lixia, LYU Shufang, LI Wenwen, SUO Chenmei, ZHANG Hao, HOU Dianyun, ZHAO Xingli. Isolation of rhizosphere fungi from wheat and their antifungal activity[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2535-2544.
| 属 Genus | 菌株编号 Strain number | GenBank登录号 Accession number in GenBank | 最相关的菌株(登录号) Most closely related strain (accession number) | 一致性 Identity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 曲霉属Aspergillus | W-F-5 | PQ577766 | Aspergillus niger(MN429196) | 100.00 |
| 枝孢属Cladosporium | W-F-6 | PQ577767 | Cladosporium cladosporioides(OM237122) | 99.61 |
| 镰孢属Fusarium | W-F-4 | PQ577765 | Fusarium fujikuroi (MN871566) | 99.81 |
| 耙菌属Irpex | W-F-13 | PQ577768 | Irpex lacteus(MT085750) | 99.84 |
| 青霉属Penicillium | W-F-15 | PQ577769 | Penicillium janthinellum(KT779551) | 99.63 |
| 帚枝霉属Sarocladium | W-F-22 | PQ577771 | Sarocladium spinificis(MZ447507) | 99.82 |
表1 基于ITS序列的各属代表性菌株的分子鉴定结果
Table 1 Summary of representative rhizosphere fungi in each genus according to ITS sequences
| 属 Genus | 菌株编号 Strain number | GenBank登录号 Accession number in GenBank | 最相关的菌株(登录号) Most closely related strain (accession number) | 一致性 Identity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 曲霉属Aspergillus | W-F-5 | PQ577766 | Aspergillus niger(MN429196) | 100.00 |
| 枝孢属Cladosporium | W-F-6 | PQ577767 | Cladosporium cladosporioides(OM237122) | 99.61 |
| 镰孢属Fusarium | W-F-4 | PQ577765 | Fusarium fujikuroi (MN871566) | 99.81 |
| 耙菌属Irpex | W-F-13 | PQ577768 | Irpex lacteus(MT085750) | 99.84 |
| 青霉属Penicillium | W-F-15 | PQ577769 | Penicillium janthinellum(KT779551) | 99.63 |
| 帚枝霉属Sarocladium | W-F-22 | PQ577771 | Sarocladium spinificis(MZ447507) | 99.82 |
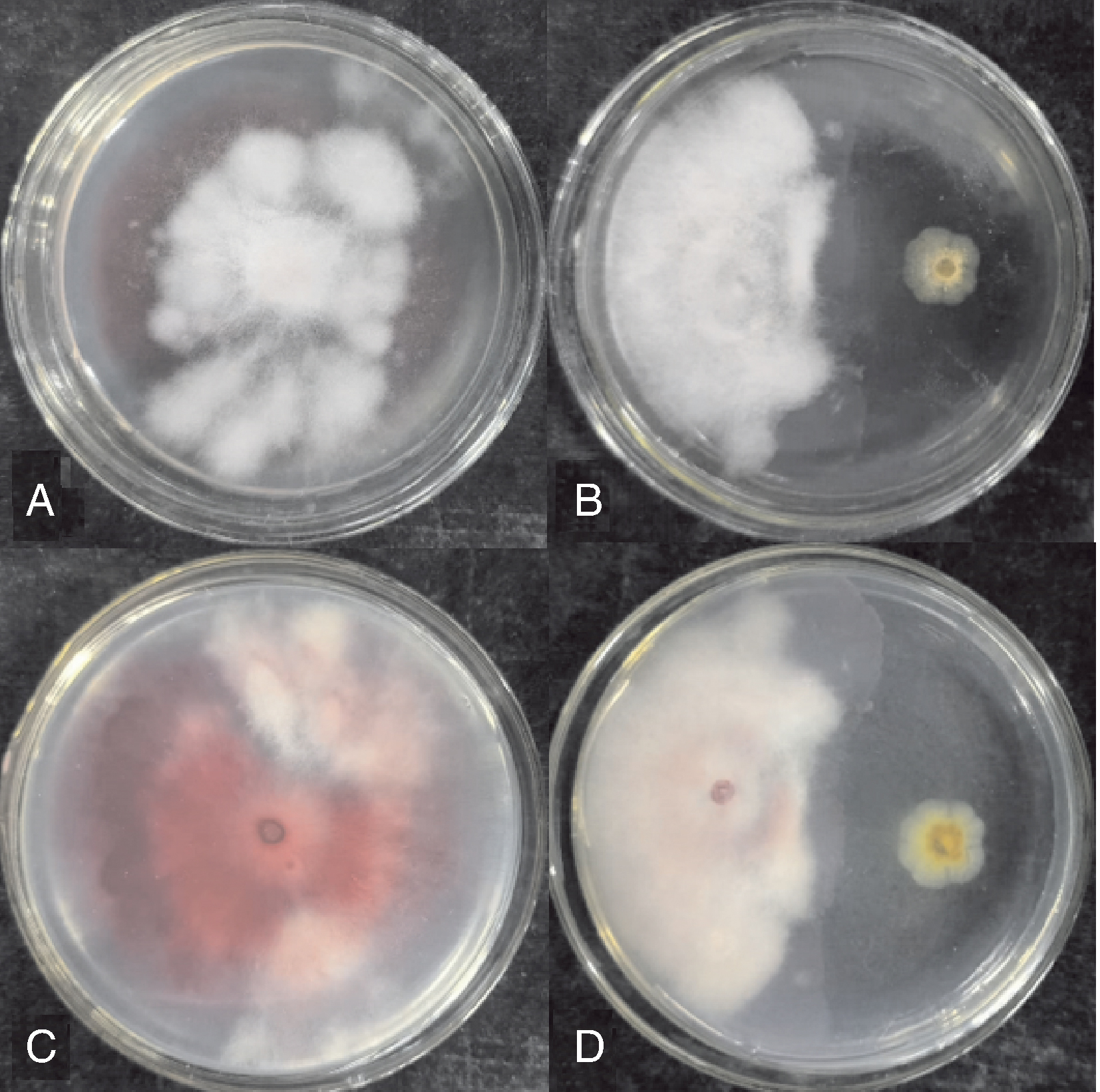
图3 菌株W-F-20对小麦茎基腐病病原菌的拮抗作用 A,对照(CK)正面照片;B,菌株W-F-20处理的正面照片;C,对照(CK)反面照片;D,菌株W-F-20处理的反面照片。
Fig.3 Antagonistic effect of strain W-F-20 on the pathogen of wheat crown rot A, Front view of the control (CK); B, Front view of the treatment with strain W-F-20; C, Back view of the control (CK); D, Back view of the treatment with strain W-F-20.
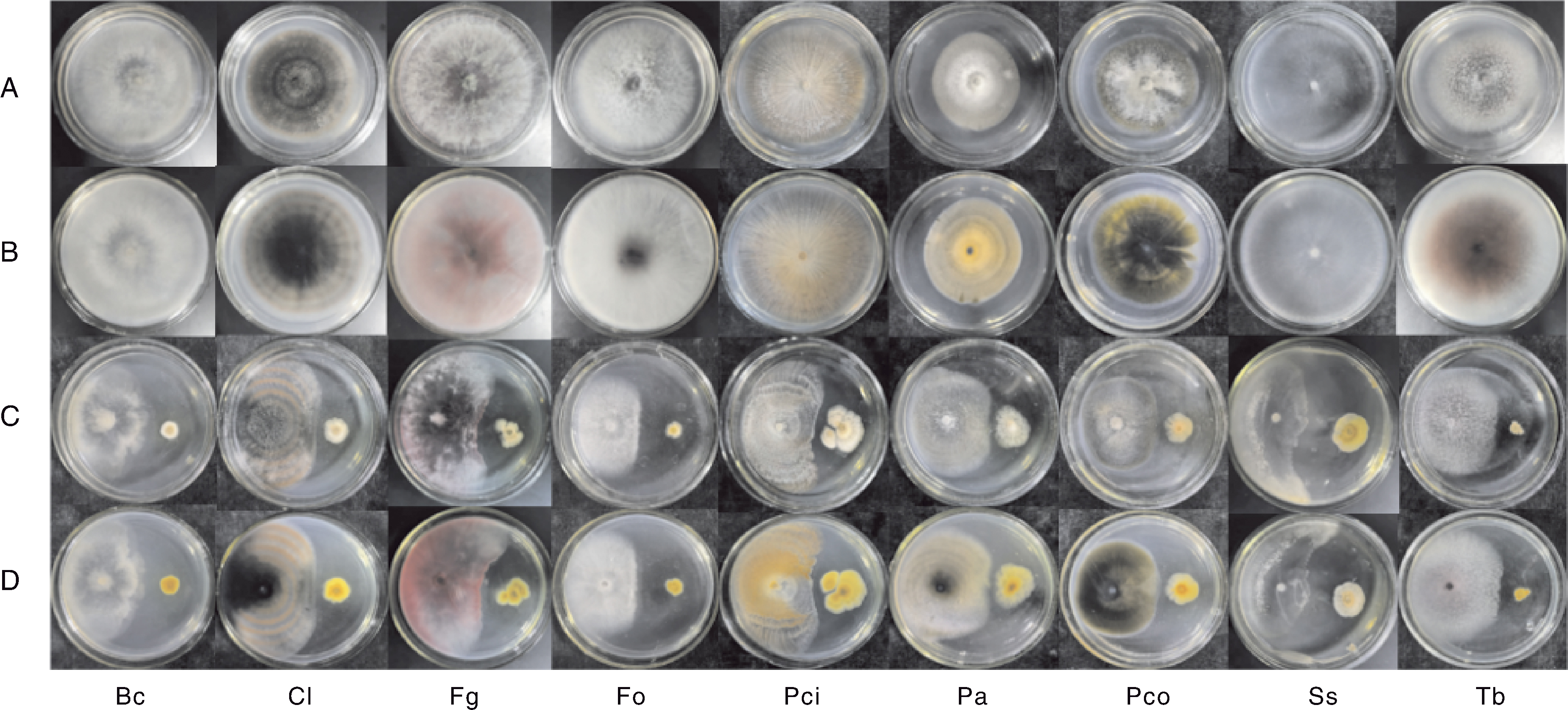
图4 菌株W-F-20对9种植物病原真菌的抗生作用 Bc,灰葡萄孢;Cl,新月弯孢;Fg,禾谷镰孢;Fo,尖镰孢;Pci,橘青霉;Pa,花生茎点霉;Pco,斑点叶点霉;Ss,核盘菌;Tb,根串珠霉。下同。A,对照(CK)正面照片;B,对照(CK)反面照片;C,菌株W-F-20处理的正面照片;D,菌株W-F-20处理的反面照片。
Fig.4 Antibiosis of W-F-20 strain against nine plant pathogenic fungi Bc, Botrytis cinerea; Cl, Curvularia lunata; Fg, Fusarium graminearum; Fo, Fusarium oxysporum; Pci, Penicillium citrinum; Pa, Phoma arachidicola; Pco, Phyllosticta commonsii, Ss, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum; Tb, Thielaviopsis basicola. The same as below. A, Front view of the control (CK); B, Back view of the control (CK); C, Front view of the treatment with strain W-F-20; D, Back view of the treatment with strain W-F-20.
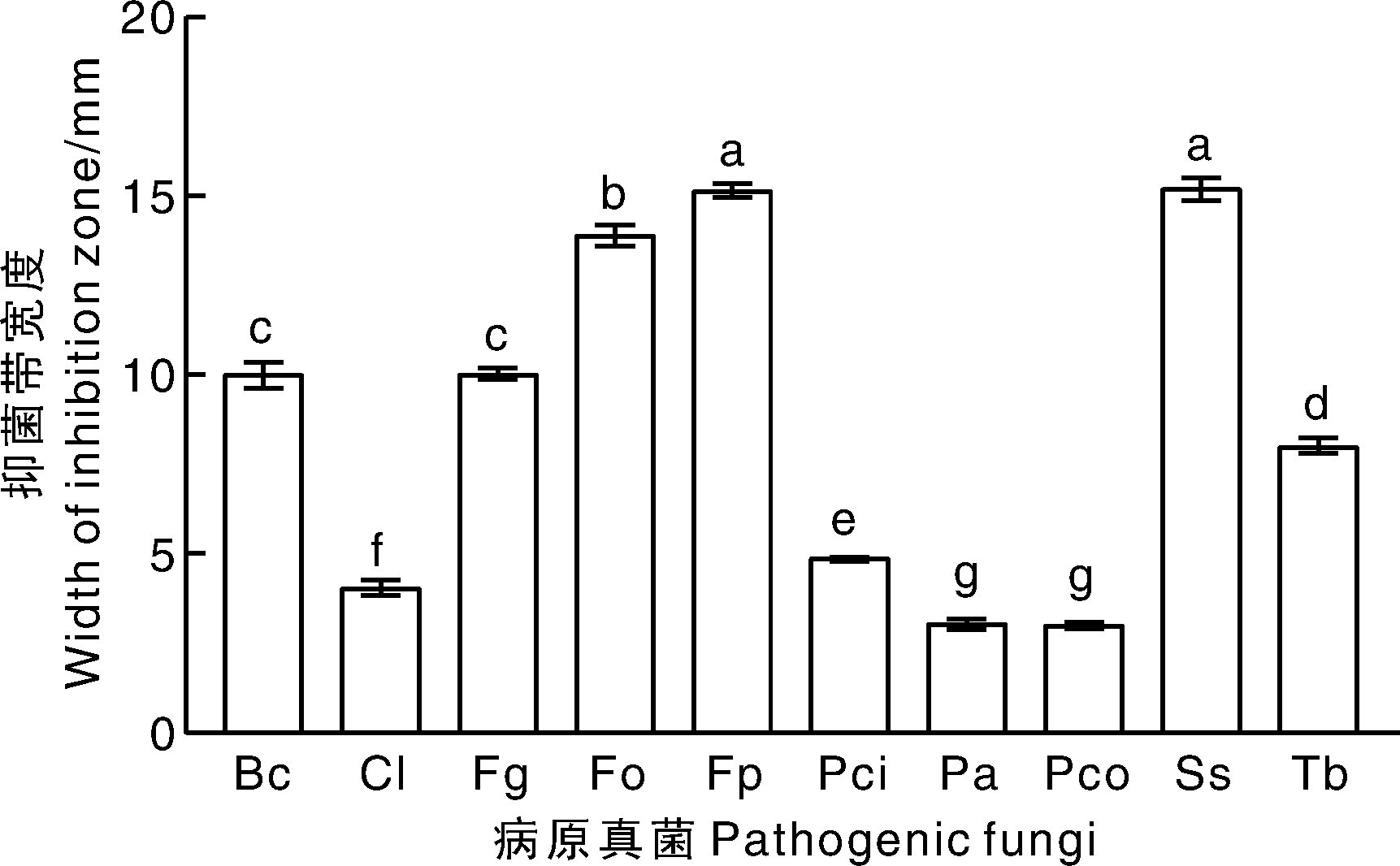
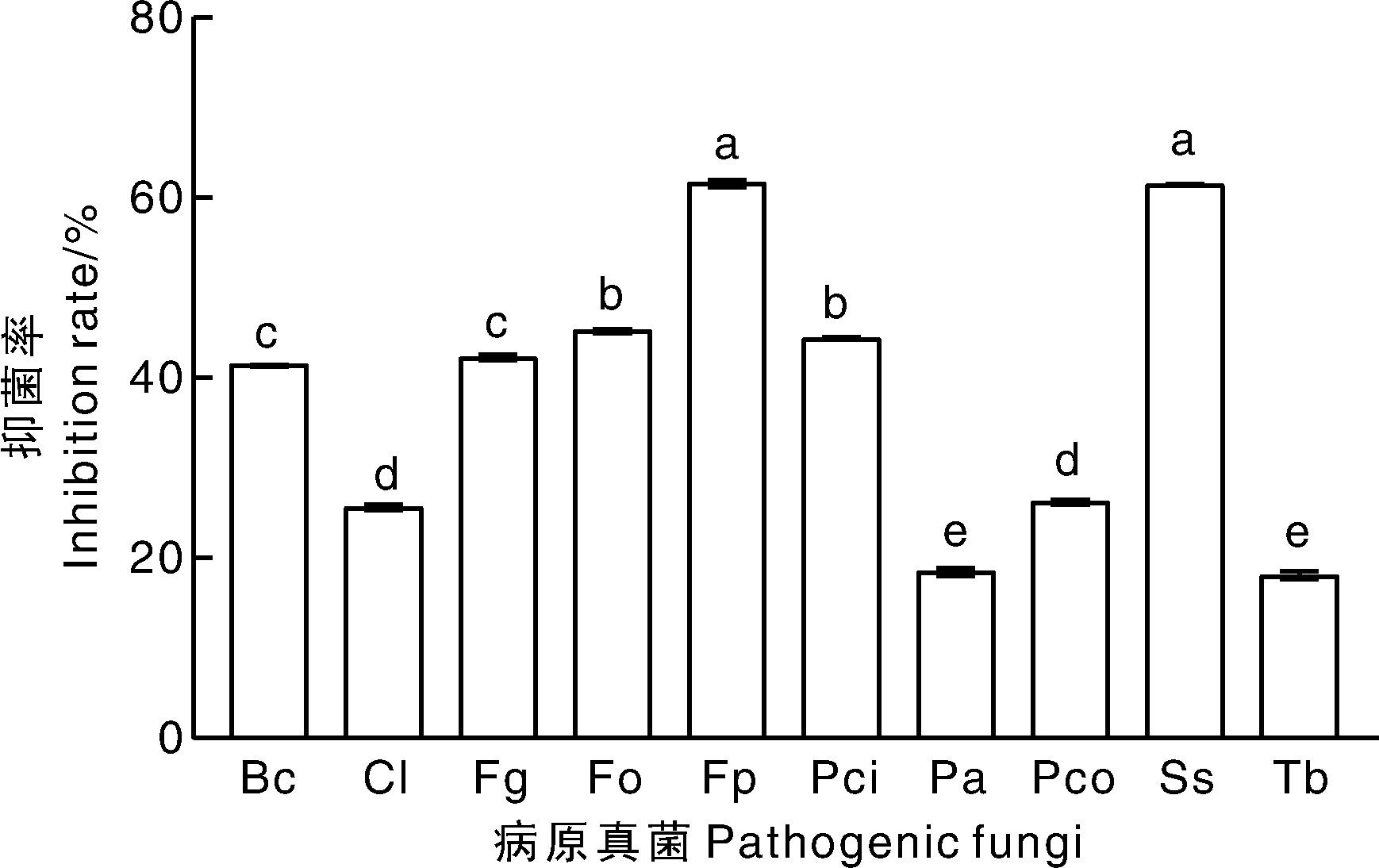
图5 菌株W-F-20对10种植物病原真菌的抑菌带宽度 Fp,假禾谷镰孢。柱上无相同字母的表示处理间差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.5 Inhibition width of W-F-20 strain against ten plant pathogenic fungi Fp, Fusarium pesudograminearum. Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant (p<0.05) difference within treatments. The same as below.
| [1] | SINHA A, SINGH L, RAWAT N. Current understanding of atypical resistance against fungal pathogens in wheat[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2022, 68: 102247. |
| [2] | 栾冬冬, 贾吉玉, 王光州, 等. 中国小麦茎基腐病的发生现状及防治策略[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(4): 512-520. |
| LUAN D D, JIA J Y, WANG G Z, et al. Occurrence status and control strategies of wheat crown rot in China[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(4): 512-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | SAVARY S, WILLOCQUET L, PETHYBRIDGE S J, et al. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2019, 3(3): 430-439. |
| [4] | NIU B, WANG W X, YUAN Z B, et al. Microbial interactions within multiple-strain biological control agents impact soil-borne plant disease[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 585404. |
| [5] | STENBERG J A, SUNDH I, BECHER P G, et al. When is it biological control?: a framework of definitions, mechanisms, and classifications[J]. Journal of Pest Science, 2021, 94(3): 665-676. |
| [6] | HUANG X F, CHAPARRO J M, REARDON K F, et al. Rhizosphere interactions: root exudates, microbes, and microbial communities[J]. Botany, 2014, 92(4): 267-275. |
| [7] | MEENA V S, MEENA S K, VERMA J P, et al. Plant beneficial rhizospheric microorganism (PBRM) strategies to improve nutrients use efficiency: a review[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2017, 107: 8-32. |
| [8] | 周益帆, 白寅霜, 岳童, 等. 植物根际促生菌促生特性研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2023, 50(2): 644-666. |
| ZHOU Y F, BAI Y S, YUE T, et al. Research progress on the growth-promoting characteristics of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria[J]. Microbiology China, 2023, 50(2): 644-666. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | LACAVA P T, BOGAS A C, DE PAULA NOGUEIRA CRUZ F. Plant growth promotion and biocontrol by endophytic and rhizospheric microorganisms from the tropics: a review and perspectives[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2022, 6: 796113. |
| [10] | 徐飞, 宋玉立, 周益林, 等. 2013—2016年河南省小麦茎基腐病的发生危害情况及特点[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(6): 126-132. |
| XU F, SONG Y L, ZHOU Y L, et al. Occurrence dynamics and characteristics of Fusariumroot and crown rot of wheat in Henan Province during 2013-2016[J]. Plant Protection, 2016, 42(6): 126-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | XU F, YANG G Q, WANG J M, et al. Spatial distribution of root and crown rot fungi associated with winter wheat in the North China Plain and its relationship with climate variables[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1054. |
| [12] | KANG R J, LI G N, ZHANG M J, et al. Expression of Fusarium pseudograminearum FpNPS9 in wheat plant and its function in pathogenicity[J]. Current Genetics, 2020, 66(1): 229-243. |
| [13] | 赵静雅, 彭梦雅, 张时雨, 等. C2H2锌指转录因子FpCzf7参与假禾谷镰孢的生长和致病性[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(8): 216-224. |
| ZHAO J Y, PENG M Y, ZHANG S Y, et al. Role of C2H2 zinc finger transcription factor FpCzf7 in the growth and pathogenicity of Fusarium pseudograminearum[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(8): 216-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 赵静雅, 夏荟清, 彭梦雅, 等. 假禾谷镰孢转录因子FpAPSES的鉴定与功能分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(16): 3428-3439. |
| ZHAO J Y, XIA H Q, PENG M Y, et al. Identification and functional analysis of transcription factors FpAPSES in Fusarium pseudograminearum[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(16): 3428-3439. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 李怡文, 李桂香, 黄中乔, 等. 假禾谷镰孢引起的小麦茎基腐病发生危害与防控研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2022, 24(5): 949-961. |
| LI Y W, LI G X, HUANG Z Q, et al. Research progress on the occurrence, damage and prevention of Fusarium crown rot caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum[J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2022, 24(5): 949-961. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 田秀, 黄路婷, 谢元贵, 等. 米槁果实不同发育时期根际土壤可培养真菌的动态变化[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(8): 1848-1854. |
| TIAN X, HUANG L T, XIE Y G, et al. Dynamic changes of cultivable fungi in rhizosphere soil during different developmental stages of Cinnamomum migao H. W. Li fruit[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(8): 1848-1854. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 方中达. 植病研究方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. |
| [18] | 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科技出版社, 1979. |
| [19] | ZHAO X L, HU Z J, HOU D Y, et al. Biodiversity and antifungal potential of endophytic fungi from the medicinal plant Cornus officinalis[J]. Symbiosis, 2020, 81(3): 223-233. |
| [20] | ZHAO X L, SONG P, HOU D Y, et al. Antifungal activity, identification and biosynthetic potential analysis of fungi against Rhizoctonia cerealis[J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2021, 71(1): 41. |
| [21] | CAMARGO J A. Can dominance influence stability in competitive interactions?[J]. Oikos, 1992, 64(3) : 605-609. |
| [22] | KUSARI P, KUSARI S, SPITELLER M, et al. Endophytic fungi harbored in Cannabis sativa L. diversity and potential as biocontrol agents against host plant-specific phytopathogens[J]. Fungal Diversity, 2013, 60(1): 137-151. |
| [23] | 贾南豫, 朱水英, 蒋栋, 等. 施用液体有机肥对干旱胁迫下玉米和小麦生长及根际微生物的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2024, 48(5): 1060-1069. |
| JIA N Y, ZHU S Y, JIANG D, et al. The effect of liquid organic fertilizer on the growth and rhizosphere microorganisms of corn and wheat under drought stress[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2024, 48(5): 1060-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | MOHAMED A H, ABD EL-MEGEED F H, HASSANEIN N M, et al. Native rhizospheric and endophytic fungi as sustainable sources of plant growth promoting traits to improve wheat growth under low nitrogen input[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2022, 8(2): 94. |
| [25] | MATAR N, MACADRÉ C, AMMAR G A G, et al. Identification of beneficial Lebanese Trichoderma spp. wheat endophytes[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1017890. |
| [26] | 陆宁海, 杨蕊, 郎剑锋, 等. 小麦根际土壤微生物数量对茎基腐病的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(22): 113-116. |
| LU N H, YANG R, LANG J F, et al. Influence of rhizosphere soil microorganisms quantity on wheat crown rot[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(22): 113-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 陈凯, 隋丽娜, 杨凯, 等. 两株木霉共培养发酵提高对小麦苗期茎基腐病的防治效果[J]. 植物病理学报, 2022, 52(3): 425-433. |
| CHEN K, SUI L N, YANG K, et al. Co-culturation of two Trichoderma strains enhanced control efficiency against wheat crown rot at seedling stage[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2022, 52(3): 425-433. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 扈进冬, 杨在东, 吴远征, 等. 哈茨木霉拌种对冬小麦生长、土传病害及根际真菌群落的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2021, 47(5): 35-40. |
| HU J D, YANG Z D, WU Y Z, et al. Effects of seed dressing treatment with Trichoderma harzianum on the growth of winter wheat seedlings, soil borne diseases and rhizosphere fungal community[J]. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(5): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | LIU L, JIN Y Q, LIAN H J, et al. Exploring the biocontrol potential of Phanerochaete chrysosporium against wheat crown rot[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2024, 10(9): 641. |
| [30] | YANG H, CUI S N, WEI Y L, et al. Antagonistic effects of Talaromyces muroii TM28 against Fusarium crown rot of wheat caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2024, 14: 1292885. |
| [31] | ZHAO X L, HOU D Y, XU J Q, et al. Antagonistic activity of fungal strains against Fusarium crown rot[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(3): 255. |
| [32] | 李思敏, 周金彩, 何蓉, 等. 海洋真菌Aspergillus terreus次生代谢产物研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2023, 35(10): 1732-1738. |
| LI S M, ZHOU J C, HE R, et al. Study on the secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungi Aspergillus terreus[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2023, 35(10): 1732-1738. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 安凡, 姜悦, 王宇, 等. 红树老鼠簕内生真菌Aspergillus terreus GXIMD 03158次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 41-48. |
| AN F, JIANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Studies on secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus GXIMD 03158 isolated from mangroves Acanthus ilicifolius L[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 王凤婷, 王岩, 孙颖, 等. 耐盐碱土曲霉SYAT-1的分离鉴定及抑制植物病原真菌特性研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2023, 39(2): 203-210. |
| WANG F T, WANG Y, SUN Y, et al. Isolation and identification of saline-alkali tolerant Aspergillus terreus SYAT-1 and its activities against plant pathogenic fungi[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2023, 39(2): 203-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 纪嵩岩, 邵长琪, 齐文康, 等. 枸杞根腐病病原鉴定及拮抗菌筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2283-2297. |
| JI S Y, SHAO C Q, QI W K, et al. Identification of Lycium barbarum root rot disease pathogens and biocontrol funguses against root rot disease[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(10): 2283-2297. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | 王妍, 张福军, 孙卓, 等. 防风枯萎病拮抗真菌的筛选鉴定及防效评价[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2023, 44(2): 263-269. |
| WANG Y, ZHANG F J, SUN Z, et al. Screening, identification and biological control effect of antagonistic fungus against fusarium wilt of Saposhnikovia divaricata[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2023, 44(2): 263-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [37] | 吕恒, 牛永春, 邓晖, 等. 根际真菌对黄瓜土传病害的抑制作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(12): 3759-3765. |
| LYU H, NIU Y C, DENG H, et al. Suppression of three soil-borne diseases of cucumber by a rhizosphere fungal strain[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(12): 3759-3765. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张均, 张博, 胡碧博, 刘京亮, 张晓宇, 李春阳, 熊盛婷, 郭彬彬, 王秀存, 马超. 小麦SWEET和SUT家族基因鉴定与表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1825-1839. |
| [2] | 潘鑫煜, 黄慧灵, 韩明明, 沈宁远, 赵旭东, 楼宝. 刺激隐核虫感染对小黄鱼肠道的组织结构、免疫水平与微生物组成的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2265-2274. |
| [3] | 刘胜男, 朱建义, 李明, 赵浩宇, 熊涛, 汤永禄, 周小刚, 李朝苏. 稻茬免耕带旋播种小麦的田间杂草防除效果与小麦产量[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(10): 2129-2137. |
| [4] | 杨晓雨, 马指挥, 魏青, 牛志鹏, 陈安琪, 胡正冲, 王林生. 一个小麦芒长基因的初步定位及候选基因预测[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(1): 14-23. |
| [5] | 沈峥嵘, 戴远兴, 郭留明, 汪芷瑶, 张恒木. 中国小麦花叶病毒(CWMV)外壳蛋白(CP)特异性抗体的制备与应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(9): 2042-2050. |
| [6] | 齐学礼, 李莹, 段俊枝. 耐盐基因在小麦耐盐基因工程中的应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(6): 1447-1457. |
| [7] | 李晶晶, 李闯, 路亚南, 郑文明. 小麦类硫素基因家族鉴定及表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(4): 729-737. |
| [8] | 张永彬, 李想, 满卫东, 刘明月, 樊继好, 胡皓然, 宋利杰, 刘玮佳. 融合Sentinel-1/2数据和机器学习算法的冬小麦产量估算方法研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(12): 2812-2822. |
| [9] | 刘永安, 黄业昌, 岳高红, 高锡腾, 邓立章, 潘彬荣. 优质小麦品种温麦10号籽粒蛋白质组学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(11): 2437-2446. |
| [10] | 娄渊根, 李闯, 李晶晶, 邢国珍, 路亚南, 郑文明. 小麦HP基因家族鉴定和分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(9): 2023-2032. |
| [11] | 余桂红, 宋桂成, 张鹏, 王化敦, 范祥云. 十八个小麦品种(系)拔节期耐渍性的综合评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(6): 1235-1242. |
| [12] | 杨凯, 陈凯, 李红梅, 赵忠娟, 扈进冬, 李纪顺, 杨合同. 哈茨木霉LTR-2与产脲节杆菌DnL1-1协同对小麦茎基腐病的防治效果与机理[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(6): 1385-1395. |
| [13] | 任开明, 王犇, 杨文俊, 樊永惠, 张文静, 马尚宇, 黄正来. 施氮对稻茬弱筋小麦生长特性、品质与产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(4): 769-779. |
| [14] | 鲁帅, 罗晓刚, 刘全伟, 张屹, 孟洋昊, 李洁, 张景来. 有机无机复混肥对小麦生长、土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(4): 922-930. |
| [15] | 白卫卫, 赵雪妮, 罗斌, 赵薇, 黄硕, 张晗. 基于YOLOv5的小麦种子发芽检测方法研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 445-454. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||