浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 54-66.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250366
异形根孢囊霉对镉胁迫下番茄生长和基因表达的影响
刘俊丽1( ), 江建锋2, 董祥伟2, 杨海峻2, 包晓琪1,3, 付晨曦1, 郭彬1, 童文彬2,*(
), 江建锋2, 董祥伟2, 杨海峻2, 包晓琪1,3, 付晨曦1, 郭彬1, 童文彬2,*( )
)
- 1.浙江省农业科学院 环境资源与土壤肥料研究所,农产品质量安全全国重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310021
2.衢州市衢江区农业技术推广中心,浙江 衢州 324022
3.浙江工业大学 环境学院,浙江 杭州 310014
-
收稿日期:2025-03-14出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:童文彬,E-mail:zjqztwb@163.com
刘俊丽,研究方向为微生物与植物互作机制及其生态应用。E-mail:liujunli@zaas.ac.cn -
通讯作者:童文彬 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42007120);农产品质量安全全国重点实验室财政专项(10417000024CE0601G)
The influence of Rhizophagus irregularis on the growth and gene expression of tomato under cadmium stress
LIU Junli1( ), JIANG Jianfeng2, DONG Xiangwei2, YANG Haijun2, BAO Xiaoqi1,3, FU Chenxi1, GUO Bin1, TONG Wenbin2,*(
), JIANG Jianfeng2, DONG Xiangwei2, YANG Haijun2, BAO Xiaoqi1,3, FU Chenxi1, GUO Bin1, TONG Wenbin2,*( )
)
- 1. Institute of Environment, Resource, Soil and Fertilizer, State Key Laboratory for Quality and Safety of Agro-Products, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
2. Qujiang District Agricultural Technology Promotion Center, Quzhou 324022, Zhejiang, China
3. College of Environment, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China
-
Received:2025-03-14Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:TONG Wenbin
摘要:
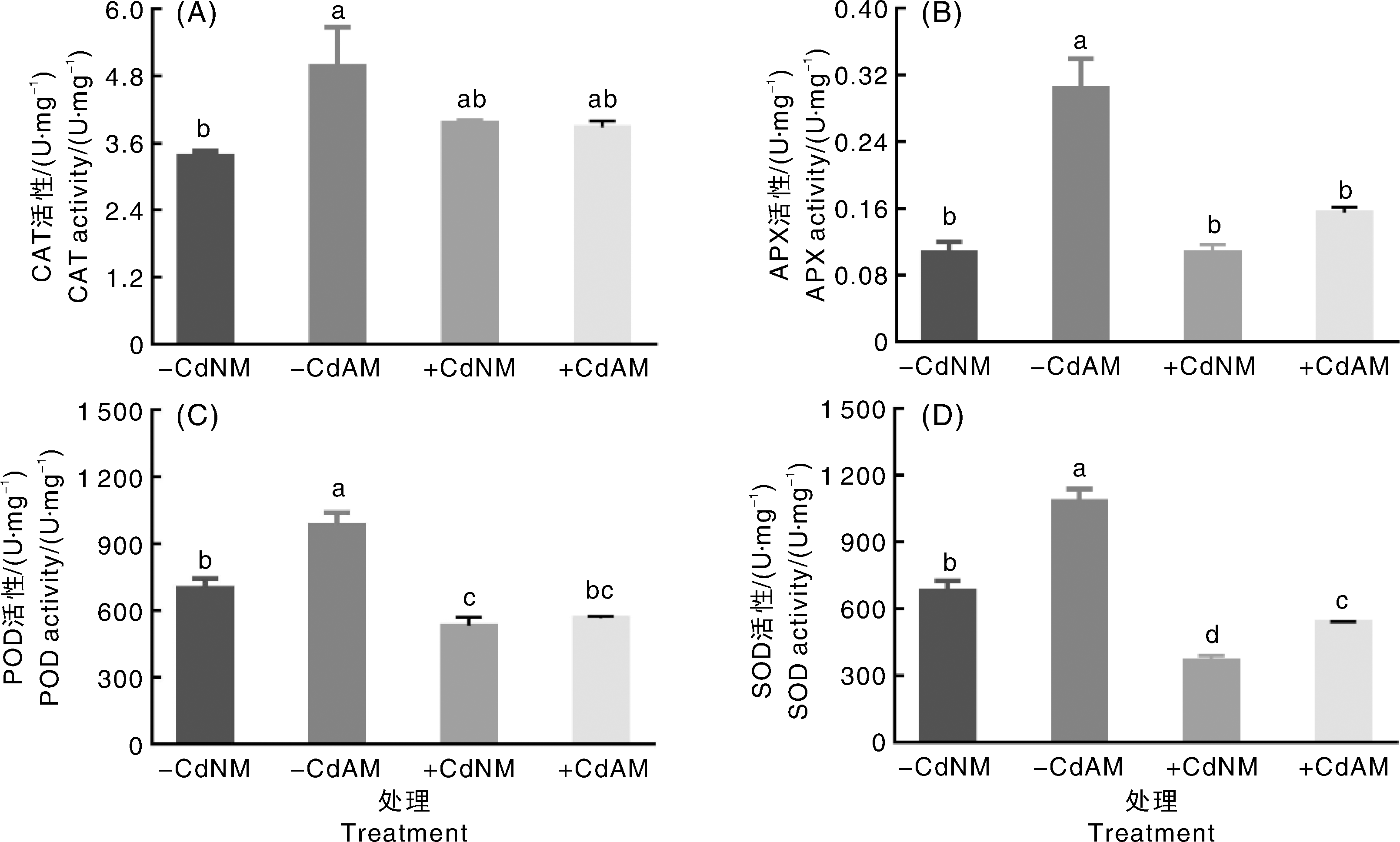
丛枝菌根真菌(arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, AMF)在调控植物镉(cadmium, Cd)耐性中具有重要作用,但其对番茄生长与Cd积累的分子机制尚不明确。为探究接种AMF提高番茄Cd耐性的机制,采用砂培试验,研究100 μmol·L-1 Cd胁迫下接种异形根孢囊霉(Rhizophagus irregularis, Ri)对番茄生长、Cd含量、抗氧化酶活性、根组织细胞超微结构与基因表达的影响,并通过GO(Gene Ontology)和KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)分析差异表达基因(differential expressed gene, DEG)的富集特征。结果表明,Cd胁迫抑制番茄生长,显著降低根部过氧化物酶(POD)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的活性,并导致细胞超微结构严重损伤。与未接种Ri相比,Cd胁迫下接种Ri的番茄地上部生物量显著增加27%,根部和地上部Cd含量分别显著降低40%与38%,根部抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)和SOD活性分别显著提高45.27%与46.35%,同时细胞超微结构损伤得到缓解。GO富集分析显示,对照处理与单独Cd处理、单独Cd处理与Cd+Ri共处理2个比较组的差异表达基因在生物学过程(代谢、应激响应等)、细胞组分(膜、细胞器等)和分子功能(催化、转运、抗氧化活性等)3个分支均显著富集,且接种Ri组在各分支中涉及的DEG数量更多。KEGG富集分析表明,对照处理与单独Cd处理的DEG显著富集于110条代谢通路,单独Cd处理与Cd+Ri共处理的DEG显著富集于118条代谢通路,主要包括苯丙氨酸代谢、植物激素信号转导和ABC转运蛋白等关键途径。热图分析显示,含有LysM结构域基因(上调14倍)、PDR基因(上调12.6倍)与多个激酶基因(上调倍数>9)的特异性高表达,是AMF介导重金属解毒的重要分子特征。本研究表明,Ri可能通过协同调控苯丙氨酸代谢、ABC转运蛋白、植物激素信号转导和防御反应等多个关键通路,构建系统的重金属胁迫响应网络,增强番茄对Cd胁迫的生理适应性,从而促进生长并提高抗逆性。研究结果可为利用AMF降低作物Cd累积的技术应用提供理论基础与候选基因资源。
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘俊丽, 江建锋, 董祥伟, 杨海峻, 包晓琪, 付晨曦, 郭彬, 童文彬. 异形根孢囊霉对镉胁迫下番茄生长和基因表达的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 54-66.
LIU Junli, JIANG Jianfeng, DONG Xiangwei, YANG Haijun, BAO Xiaoqi, FU Chenxi, GUO Bin, TONG Wenbin. The influence of Rhizophagus irregularis on the growth and gene expression of tomato under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 54-66.
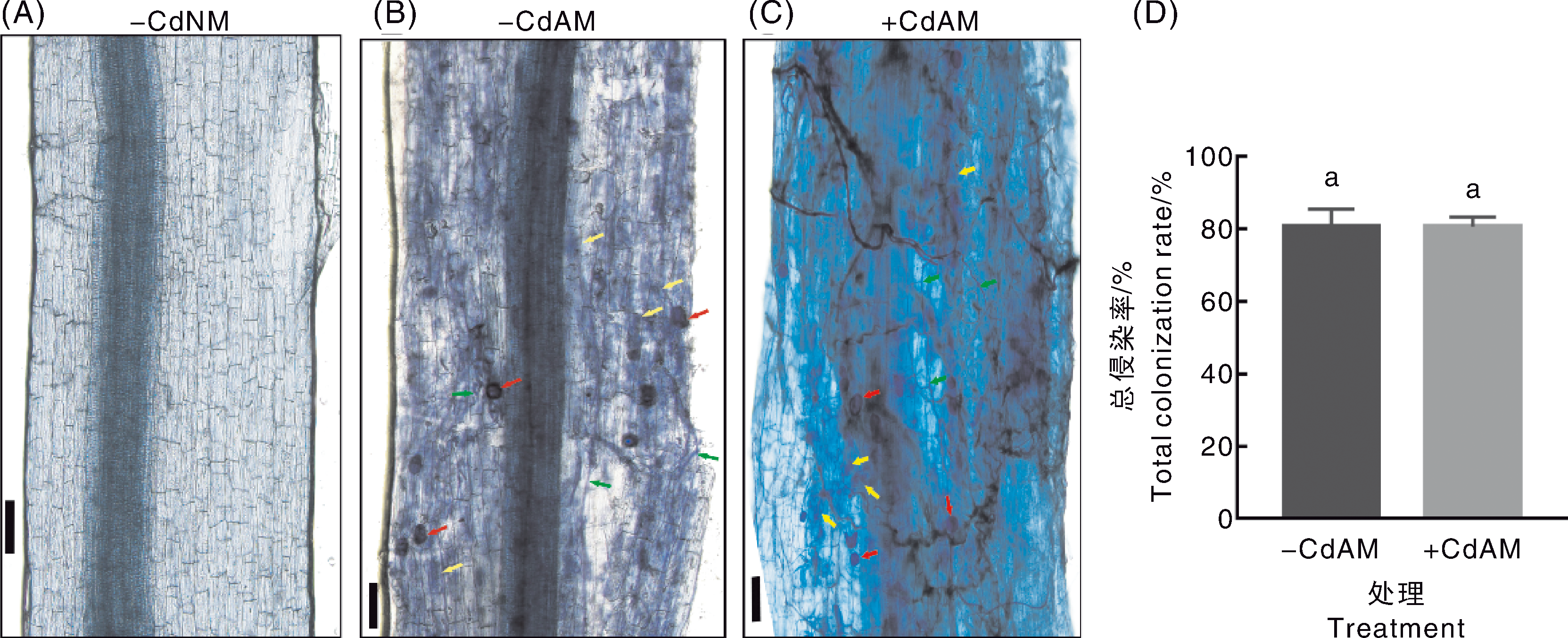
图1 Cd胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌与番茄的共生关系 A~C,番茄根部菌丝、泡囊与丛枝等结构的显微观察;红色箭头指示泡囊,黄色箭头指示丛枝,绿色箭头指示根外菌丝,标尺=100 μm。D,番茄根部的总侵染率;数据为平均值±标准误(n=3),无相同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(p<0.05,Duncan检验)。-CdNM,未添加Cd、不接种菌根真菌;-CdAM,未添加Cd、接种菌根真菌;+CdAM,添加Cd、接种菌根真菌。下同。
Fig.1 Symbiotic relationship between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and tomato under cadmium stress A-C, Microscopic observation of structures such as hyphae, vesicles and arbuscular branches in tomato roots; red arrows indicate vesicles, yellow arrows indicate arbuscular branches, green arrows indicate extraradical hyphae, scale bar=100 μm. D, Total colonization rate of tomato roots; data were mean±standard error (n=3), data marked without the same lowercase letter indicated significant differences (p<0.05, Duncan’s test).-CdNM, no Cd added, no mycorrhizal fungi inoculated;-CdAM, no Cd added, mycorrhizal fungi inoculated;+CdAM, Cd added, mycorrhizal fungi inoculated. The same as below.
| 处理 Teatment | 根部生物量/g Root biomass/g | 地上部生物量/g Shoot biomass/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| -CdNM | 0.014±0.001 b | 0.221±0.011 b | 0.061±0.003 a |
| -CdAM | 0.020±0.001 a | 0.304±0.028 a | 0.067±0.004 a |
| +CdNM | 0.014±0.002 b | 0.164±0.016 c | 0.089±0.022 a |
| +CdAM | 0.012±0.001 b | 0.208±0.002 b | 0.058±0.004 a |
表1 不同处理下番茄单株生物量(干重)
Table 1 Biomass (dry weight) per plant of tomato under different treatments
| 处理 Teatment | 根部生物量/g Root biomass/g | 地上部生物量/g Shoot biomass/g | 根冠比 Root shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| -CdNM | 0.014±0.001 b | 0.221±0.011 b | 0.061±0.003 a |
| -CdAM | 0.020±0.001 a | 0.304±0.028 a | 0.067±0.004 a |
| +CdNM | 0.014±0.002 b | 0.164±0.016 c | 0.089±0.022 a |
| +CdAM | 0.012±0.001 b | 0.208±0.002 b | 0.058±0.004 a |
| 处理 Teatment | 根部Cd含量/ (mg·g-1) Cd content in root/(mg·g-1) | 地上部Cd含量/ (mg·g-1) Cd content in shoot/(mg·g-1) | 镉转运系数 Transfer coefficient of cadmium |
|---|---|---|---|
| -CdNM | 0.004±0 c | 0.001±0 c | — |
| -CdAM | 0.003±0.001 c | 0.001±0 c | — |
| +CdNM | 3.473±0.530 a | 0.118±0.013 a | 0.035±0.003 a |
| +CdAM | 2.073±0.236 b | 0.073±0.007 b | 0.036±0.001 a |
表2 不同处理下番茄植株镉含量与转运系数
Table 2 Cd content and transfer coefficient in tomato plants under different treatments
| 处理 Teatment | 根部Cd含量/ (mg·g-1) Cd content in root/(mg·g-1) | 地上部Cd含量/ (mg·g-1) Cd content in shoot/(mg·g-1) | 镉转运系数 Transfer coefficient of cadmium |
|---|---|---|---|
| -CdNM | 0.004±0 c | 0.001±0 c | — |
| -CdAM | 0.003±0.001 c | 0.001±0 c | — |
| +CdNM | 3.473±0.530 a | 0.118±0.013 a | 0.035±0.003 a |
| +CdAM | 2.073±0.236 b | 0.073±0.007 b | 0.036±0.001 a |
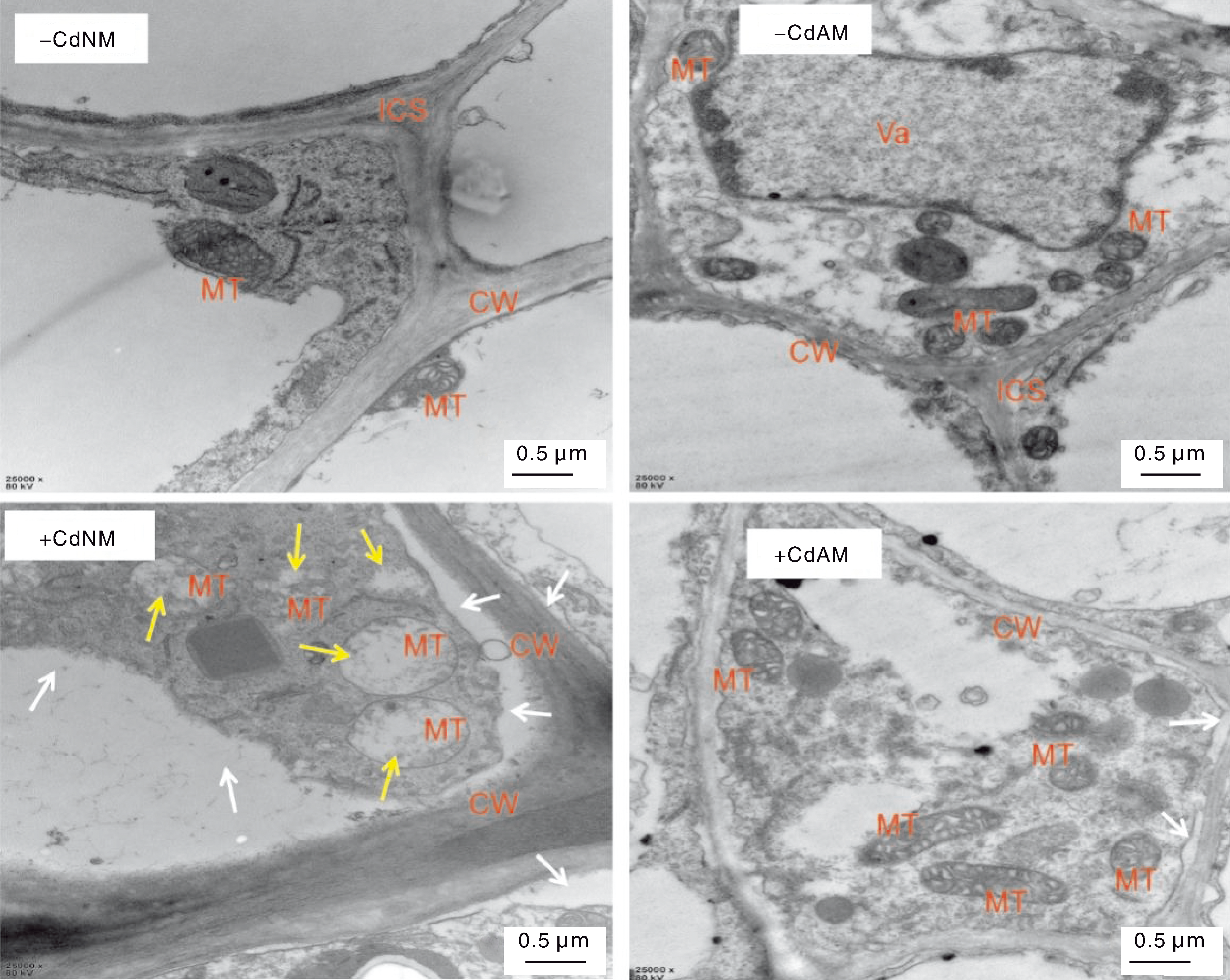
图3 不同处理下番茄根组织细胞的超微结构 MT,线粒体;CW,细胞壁;ICS,细胞间隙;Va,液泡。白色箭头指示质壁分离,黄色箭头指示线粒体空泡化。
Fig.3 Ultrastructure of tomato root tissue cells under different treatments MT, Mitochondria; CW, Cell wall; ICS, Intercellular space; Va, Vacuole. White arrows indicate plasmolysis, yellow arrows indicate mitochondrial vacuolization.
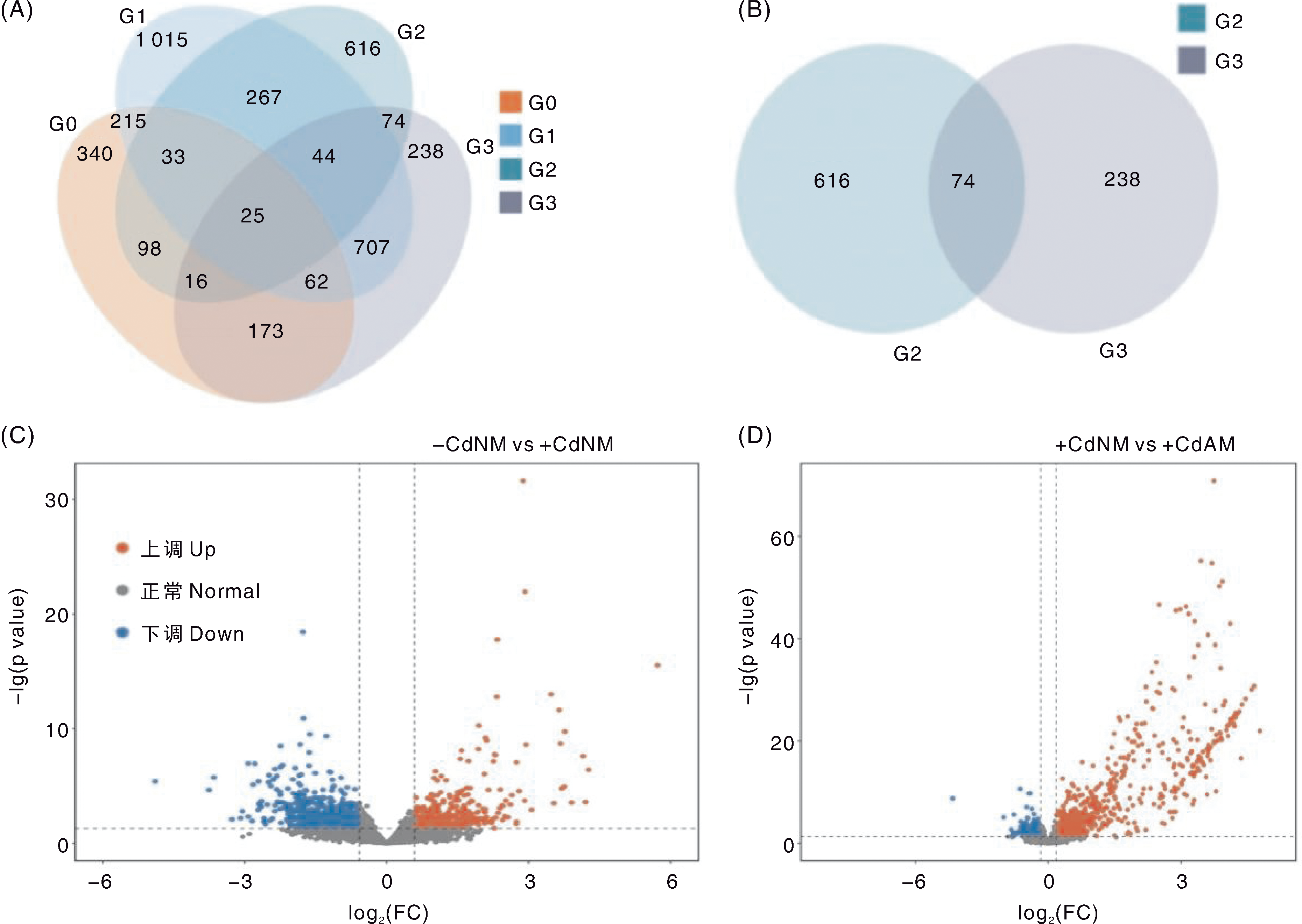
图4 不同处理番茄根系中的差异表达基因 A,不同处理番茄根系差异表达基因的韦恩图;G0、G1、G2和G3分别表示+CdAM与-CdAM、-CdAM与-CdNM、+CdNM与-CdNM,以及+CdAM与+CdNM对比组间的差异表达基因。B,G2与G3两个对比组差异表达基因的韦恩图。C和D分别为-CdNM vs+CdNM与+CdNM vs+CdAM对比组的基因表达火山图。FC,差异倍数。
Fig.4 Differentially expressed genes in tomato roots under different treatments A, Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in tomato roots under different treatments; G0, G1, G2, and G3 represent differentially expressed genes between the comparison groups+CdAM vs-CdAM,-CdAM vs-CdNM,+CdNM vs-CdNM, and+CdAM vs+CdNM, respectively. B, Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in the two comparison groups G2 and G3. C and D are gene expression volcano plots for the comparison groups-CdNM vs+CdNM and+CdNM vs+CdAM, respectively. FC, Fold change.
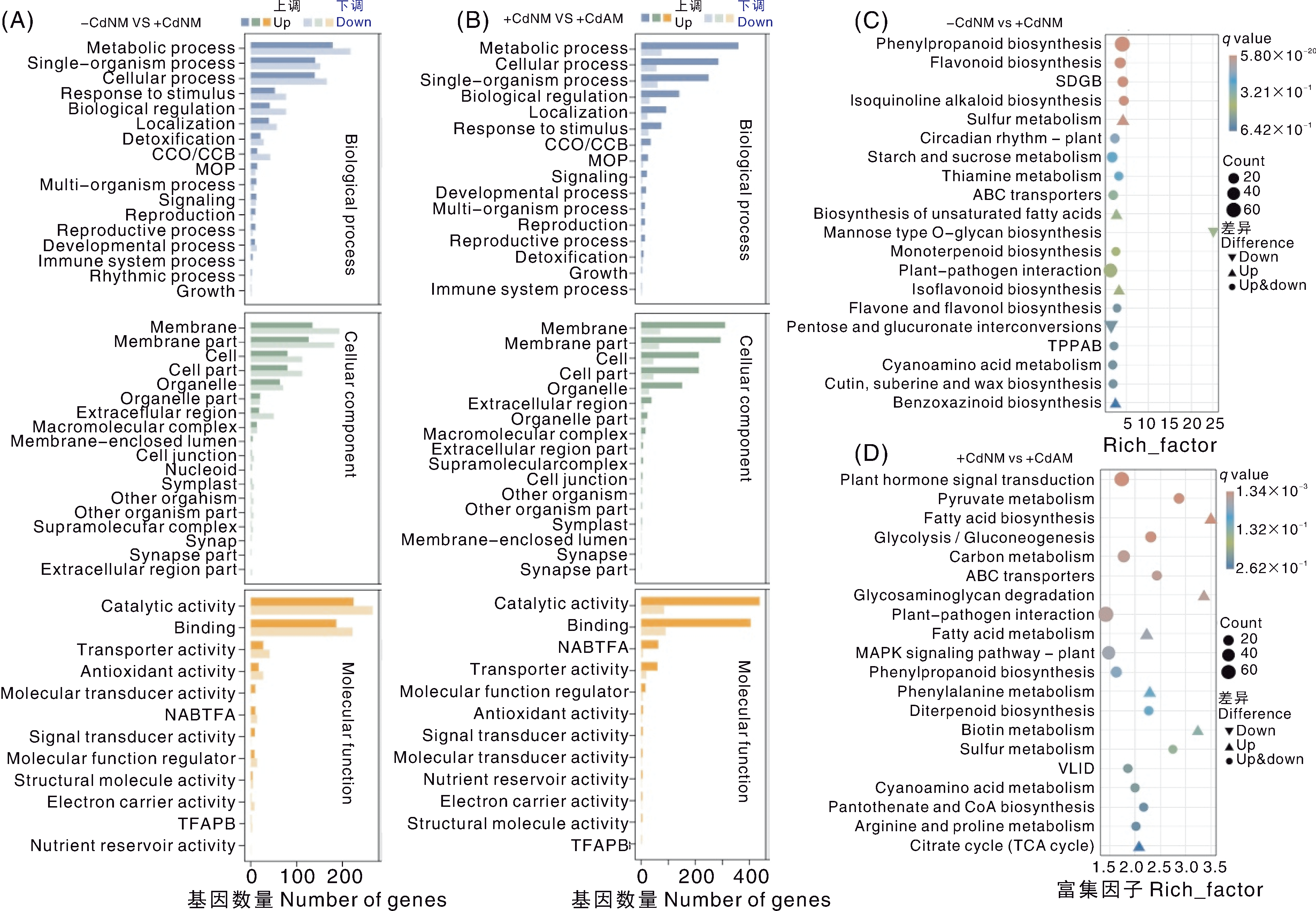
图5 差异表达基因的GO与KEGG富集分析 Metabolic process,代谢过程;Single-organism process,单生物过程;Cellular process,细胞过程;Response to stimulus,刺激响应;Biological regulation,生物调节;Localization,定位;Detoxification,解毒;Multi-organism process,多生物过程;Signaling,信号传导;Reproduction,繁殖;Reproductive process,生殖过程;Developmental process,发育过程;Immune system process,免疫系统过程;Rhythmic process,节律过程;Growth,生长;Membrane,膜;Membrane part,膜部分;Cell,细胞;Cell part,细胞部分;Organelle part,细胞器部分;Extracellular region,细胞外区域;Macromolecular complex,大分子复合物;Membrane-enclosed lumen,膜包被腔;Cell junction,细胞连接;Nucleoid,类核;Symplast,共质体;Other organism,其他生物体;Other organism part,其他生物体部分;Supramolecular complex,超分子复合物;Synapse,突触;Synapse part,突触部分;Extracellular region part,细胞外区域部分;Catalytic activity,催化活性;Binding,结合;Transporter activity,转运蛋白活性;Antioxidant activity,抗氧化活性;Molecular transducer activity,分子转导活性;Signal transducer activity,信号转导活性;Molecular function regulator,分子功能调节因子;Structural molecule activity,结构分子活性;Electron carrier activity,电子载体活性;Nutrient reservoir activity,营养储存活性。Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis,苯丙烷类生物合成;Flavonoid biosynthesis,类黄酮生物合成;Isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis,异喹啉类生物碱生物合成;Sulfur metabolism,硫代谢;Circadian rhythm-plant,植物昼夜节律;Starch and sucrose metabolism,淀粉和蔗糖代谢;Thiamine metabolism,硫胺素代谢;ABC transporters,ABC转运蛋白;Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids,不饱和脂肪酸生物合成;Mannose type O-glycan biosynthesis,甘露糖型O-聚糖生物合成;Monoterpenoid biosynthesis,单萜类生物合成;Plant-pathogen interaction,植物-病原体互作;Isoflavonoid biosynthesis,异黄酮类生物合成;Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis,黄酮与黄酮醇生物合成;Pentose and glucuronate interconversions,戊糖与葡萄糖醛酸相互转化;Cyanoamino acid metabolism,氰基氨基酸代谢;Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis,角质、木栓质与蜡生物合成;Benzoxazinoid biosynthesis,苯并恶嗪类生物合成;Plant hormone signal transduction,植物激素信号转导;Pyruvate metabolism,丙酮酸代谢;Fatty acid biosynthesis,脂肪酸生物合成;Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis,糖酵解/糖异生;Carbon metabolism,碳代谢; Glycosaminoglycan degradation,糖胺聚糖降解; Fatty acid metabolism,脂肪酸代谢;MAPK signaling pathway-plant,植物MAPK信号通路;Phenylalanine metabolism,苯丙氨酸代谢;Diterpenoid biosynthesis,二萜类生物合成;Biotin metabolism,生物素代谢;Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis,泛酸与辅酶A生物合成;Arginine and proline metabolism,精氨酸与脯氨酸代谢;Citrate cycle (TCA cycle),柠檬酸循环。 A和B分别为-CdNM vs+CdNM比较组与+CdNM vs+CdAM比较组差异表达基因的GO富集分析。CCO/CCB,细胞组分组成或生物发生;MOP,多细胞生物过程;NABTFA,核酸结合转录因子活性;TFAPB,转录因子活性、蛋白质结合。C和D分别为-CdNM vs+CdNM比较组与+CdNM vs+CdAM比较组差异表达基因的KEGG富集分析。图中展示了q值最小的前20个通路;TPPAB,托烷类、哌啶类和吡啶类生物碱的生物合成;SDGB,二苯乙烯类、二芳基庚烷类和姜酚类物质的生物合成;VLID,缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸的降解。
Fig.5 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes A and B, Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from the comparison groups -CdNM vs +CdNM and +CdNM vs +CdAM, respectively. CCO/CCB, Cellular component organization or biogenesis; MOP, Multicellular organismal process; NABTFA, Nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity; TFAPB, Transcription factor activity, protein binding. C and D, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of DEGs from the same comparison groups. The figure shows the top 20 pathways with the smallest q-values. TPPAB, Tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis; SDGB, Stilbenoid, diarylheptanoid and gingerol biosynthesis; VLID, Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation.
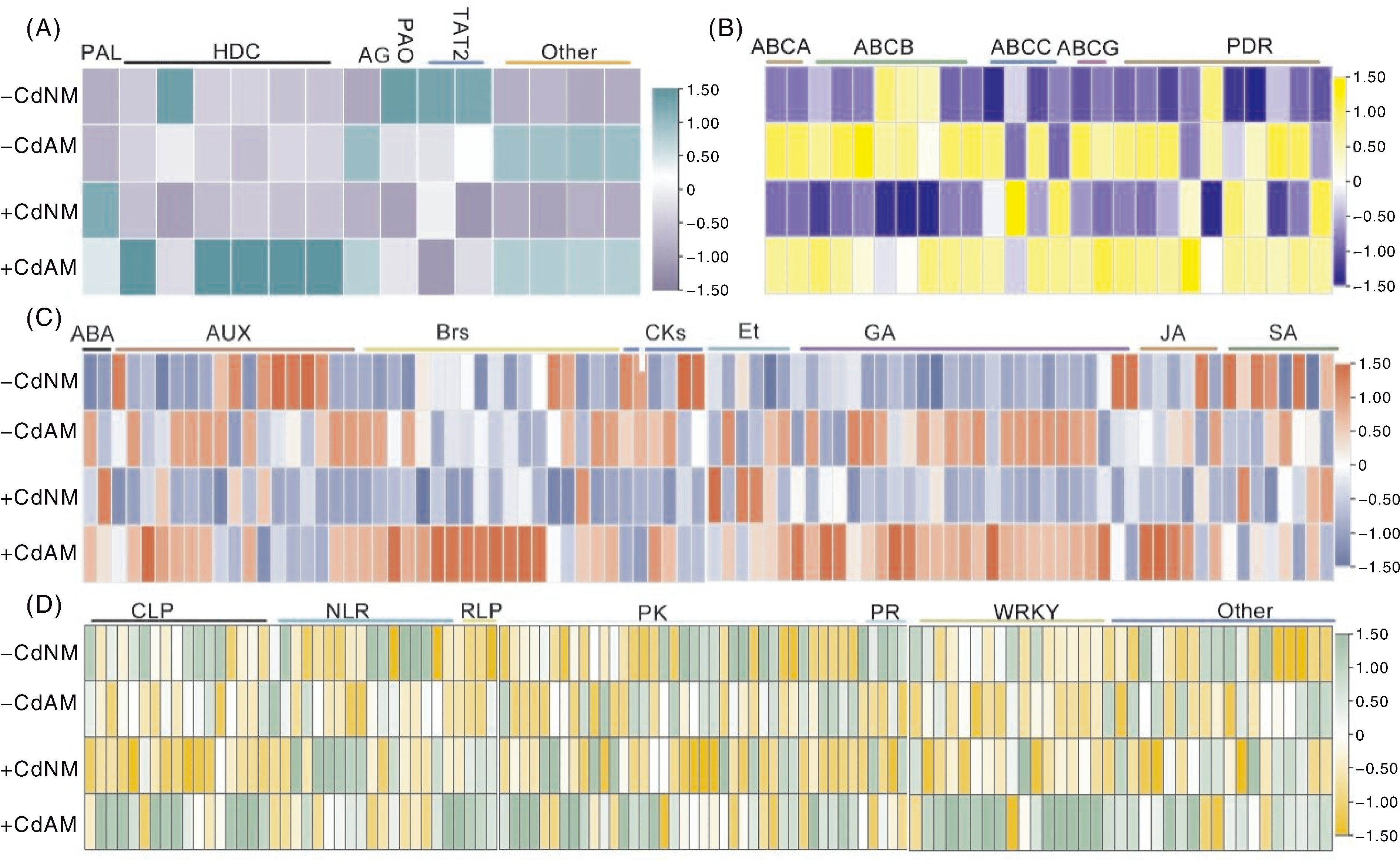
图6 苯丙氨酸代谢途径(A)、ABC转运蛋白家族基因(B)、植物激素信号转导(C)和植物-病原菌互作(D)相关差异表达基因热图 A,苯丙氨酸代谢途径差异表达基因热图。PAL,苯丙氨酸解氨酶基因;HDC,组氨酸脱羧酶基因;AG,酰胺酶基因;PAO,初级胺氧化酶基因;TAT2,氨基酸转移酶基因;Other,其他基因。B,ABC家族基因差异表达基因热图。ABCA、ABCB、ABCC、ABCG分别表示ABC家族A、B、C和G亚家族基因;PDR,多效药物耐性基因,属于ABCG亚家族。C,植物激素信号转导差异表达基因热图。ABA,脱落酸相关基因;AUX,生长素相关基因;Brs,油菜素内酯相关基因;CK,细胞分裂素相关基因;Et,乙烯相关基因;GA,赤霉素相关基因;JA,茉莉酸相关基因;SA,水杨酸相关基因。D,植物-病原菌互作差异表达基因热图。CLP,钙结合蛋白家族基因;NLR,NLR家族基因;RLP,受体类似蛋白基因;PK,蛋白激酶基因;PR,病程相关蛋白基因;WRKY,WRKY转录因子基因;Other,其他基因。数据为log2|FPKM平均值+1|(n=3),标尺表示颜色对应的数值范围。
Fig.6 Heatmap of differentially expressed genes related to phenylalanine metabolism (A), ABC transporter family gene (B), plant hormone signal transduction (C) and plant-pathogen interaction (D) A, Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to phenylalanine metabolism pathway. PAL, Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene; HDC, Histidine decarboxylase gene; AG, Amidase gene; PAO, Primary amine oxidase gene; TAT2, Aminotransferase gene; Other, Other genes. B, Heatmap of DEGs associated with ABC transporter family genes. ABCA/B/C/G represent subfamilies A, B, C and G of ABC transporter family genes, respectively; PDR, Pleiotropic drug resistance gene (belonging to ABCG subfamily). C, Heatmap of DEGs involved in plant hormone signal transduction. ABA, Abscisic acid gene; AUX, Auxin gene; Brs, Brassinosteroids gene; CK, Cytokinins gene; Et, Ethylene gene; GA, Gibberellins gene; JA, Jasmonic acid gene; SA, Salicylic acid gene. D, Heatmap of DEGs related to plant-pathogen interaction. CLP, Calmodulin-like protein gene; NLR, NLR family gene; RLP, Receptor-like protein gene; PK, Protein kinase gene; PR, Pathogenesis-related protein gene; WRKY, WRKY transcription factor gene; Other, Other genes. Data are presented as log2|FPKM mean+1| (n=3), the scale bar is the numerical range corresponding to the color in the heatmap.
| [1] | 翟夜雨, 黄五星, 袁岐山, 等. 植物镉毒害与硒对镉胁迫的缓解作用研究进展[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2023, 57(3): 372-382. |
| ZHAI Y Y, HUANG W X, YUAN Q S, et al. Research progress on plant cadmium toxicity and the alleviation effect of selenium on cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2023, 57(3): 372-382. | |
| [2] | 陈瑾芬, 胡淑宝, 秦艺鸣, 等. 植物对镉胁迫响应的分子机制研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2025, 53(3): 1-9. |
| CHEN J F, HU S B, QIN Y M, et al. Research progress on the molecular mechanism of plant response to cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 53(3): 1-9. | |
| [3] | 彭佳师, 王娅婷, 王梦琦, 等. 植物重金属镉积累调控机制及其应用研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2024, 60(2): 185-210. |
| PENG J S, WANG Y T, WANG M Q, et al. Research and regulation of cadmium uptake, transport and accumulation in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2024, 60(2): 185-210. | |
| [4] | 李娜, 王剑峰, 龚记熠, 等. 植物响应镉胁迫的生理、分子和根际微生态机制研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(24): 1-11. |
| LI N, WANG J F, GONG J Y, et al. Research progress on physiological, molecular and rhizosphere microecological mechanisms of plant response to cadmium stress[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(24): 1-11. | |
| [5] | 段世龙, 严文辉, 冯固, 等. 植物根系/菌根途径获取养分的碳磷互惠机制[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(6): 1160-1167. |
| DUAN S L, YAN W H, FENG G, et al. Carbon-phosphorus reciprocal mechanism for plants to acquire nutrients through the root/mycorrhizal pathway[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(6): 1160-1167. | |
| [6] | LI X, ZHENG D, ZHANG N L, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-mediated resistance to salt spray in Cinnamomum camphora seedlings enhanced by leaf functional traits[J]. Soil Ecology Letters, 2023, 6(3): 230211. |
| [7] | 张嘉慧, 邢佳佳, 彭丽媛, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌提高感染青枯菌番茄根际土壤细菌群落多样性和稳定性及有益菌属相对丰度[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(1): 120-131. |
| ZHANG J H, XING J J, PENG L Y, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves diversity and stability of bacterial community and abundance of beneficial bacteria genus in the rhizosphere of tomato infected with Ralstonia solanacearum[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(1): 120-131. | |
| [8] | JIN W H, TU J Y, WU Q F, et al. Moso bamboo expansion decreased soil heterotrophic respiration but increased arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelial respiration in a subtropical broadleaved forest[J]. Forest Ecosystems, 2023, 10: 100116. |
| [9] | WANG Y H, SHAO C L, QIU Y J, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi protect a subtropical tree species exposed to simulated acid rain by accelerating photosynthetic ability, antioxidant enzymes and osmolyte accumulation[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 15(5): 1036-1048. |
| [10] | SHI W G, ZHANG Y H, CHEN S L, et al. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of heavy metal accumulation in nonmycorrhizal versus mycorrhizal plants[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2019, 42(4): 1087-1103. |
| [11] | CHEN B D, NAYUKI K, KUGA Y, et al. Uptake and intraradical immobilization of cadmium by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as revealed by a stable isotope tracer and synchrotron radiation μX-ray fluorescence analysis[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2018, 33(3): 257-263. |
| [12] | ZHANG Q M, GONG M G, XU S S, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate arsenic toxicity in Sophora viciifolia Hance. by improving the growth, photosynthesis, reactive oxygen species and gene expression of phytochelatin synthase[EB/OL]. ( 2021-01-04)[2025-01-20]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-137602/v1. |
| [13] | ZHANG X F, HU Z H, YAN T X, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate Cd phytotoxicity by altering Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms in Zea mays[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 352-360. |
| [14] | ZHUANG X L, LIU S Y, XU S Z, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate cadmium phytotoxicity by regulating cadmium mobility, physiological responses, and gene expression patterns in Malus hupehensis Rehd[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, 26(4): 1418. |
| [15] | ZHU Q Y, XU P X, LEI L L, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals decreased accumulation and toxicity of Cd in upland rice inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 177: 104501. |
| [16] | AHMED D A E, SLIMA D F, AL-YASI H M, et al. Risk assessment of trace metals in Solanum lycopersicum L. (tomato) grown under wastewater irrigation conditions[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(14): 42255-42266. |
| [17] | SU L H, XIE Y D, HE Z Q, et al. Network response of two cherry tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cultivars to cadmium stress as revealed by transcriptome analysis[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 222: 112473. |
| [18] | PAN J, CAO S, XU G F, et al. Comprehensive analysis reveals the underlying mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in kenaf cadmium stress alleviation[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 314: 137566. |
| [19] | WANG Y P, HUANG J, GAO Y Z. Arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization alters subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Medicago sativa L. and resists cadmium toxicity[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e48669. |
| [20] | DAS D, PARIES M, HOBECKER K, et al. PHOSPHATE STARVATION RESPONSE transcription factors enable arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 477. |
| [21] | BALZERGUE C, CHABAUD M, BARKER D G, et al. High phosphate reduces host ability to develop arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis without affecting root calcium spiking responses to the fungus[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4: 426. |
| [22] | LIU J L, CHEN J D, XIE K, et al. A mycorrhiza-specific H+-ATPase is essential for arbuscule development and symbiotic phosphate and nitrogen uptake[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(4): 1069-1083. |
| [23] | LIU J L, BAO X Q, QIU G Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SlNRAMP genes in tomato under nutrient deficiency and cadmium stress during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(15): 8269. |
| [24] | BAO X Q, LIU J L, QIU G Y, et al. The effect of Rhizophagus intraradices on cadmium uptake and OsNRAMP5 gene expression in rice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, 26(4): 1464. |
| [25] | 刘月芹, 高小朋, 贺晓龙. 提高温度对灵芝抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 延安大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(4): 27-31. |
| LIU Y Q, GAO X P, HE X L. Effects of increasing temperature on antioxidant activity of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Journal of Yanan University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 39(4): 27-31. | |
| [26] | LIU D, ZHENG K Y, WANG Y, et al. Harnessing an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus to improve the adaptability of a facultative metallophytic poplar (Populus yunnanensis) to cadmium stress: physiological and molecular responses[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 424: 127430. |
| [27] | 宋西娇, 陈浙, 何步远, 等. 西瓜花叶病毒和小西葫芦黄花叶病毒复合侵染南瓜的透射电镜诊断[J]. 电子显微学报, 2015, 34(2): 126-131. |
| SONG X J, CHEN Z, HE B Y, et al. Electron microscopic diagnosis of multiple pathogen of watermelon mosaic virus and Zucchini yellow mosaic virus in infected Cucurbita moschata[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2015, 34(2): 126-131. | |
| [28] | 杨慧, 金良韵, 姬曼, 等. 不同树脂对特殊生物样品包埋效果的比较[J]. 分析仪器, 2019(5): 46-51. |
| YANG H, JIN L Y, JI M, et al. Comparison of embedding effects of two resins on special biological specimens[J]. Analytical Instrumentation, 2019(5): 46-51. | |
| [29] | CHEN C J, WU Y, LI J W, et al. TBtools-II: a “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(11): 1733-1742. |
| [30] | LUO N, LI X, CHEN A Y, et al. Does arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus affect cadmium uptake and chemical forms in rice at different growth stages[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 599: 1564-1572. |
| [31] | JIANG Q Y, ZHUO F, LONG S H, et al. Can arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce Cd uptake and alleviate Cd toxicity of Lonicera japonica grown in Cd-added soils[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21805. |
| [32] | LI H, WANG H X, ZHAO J N, et al. Physio-biochemical and transcriptomic features of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi relieving cadmium stress in wheat[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(12): 2390. |
| [33] | GU L J, ZHAO M L, GE M, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals comprehensive responses to cadmium stress in maize inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 186: 109744. |
| [34] | ZHOU Y, FU J Y, YE Y Q, et al. Physiological and molecular response mechanisms of tomato seedlings to cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) stress[J]. PeerJ, 2024, 12: e18533. |
| [35] | 刘伟, 樊文华, 刘奋武, 等. 施磷对镉胁迫下黄瓜苗期光合作用及抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(3): 596-604. |
| LIU W, FAN W H, LIU F W, et al. Effects of phosphorus on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme system of cucumber seedlings under cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(3): 596-604. | |
| [36] | TAN X H, WANG D P, ZHANG X W, et al. A pair of LysM receptors mediates symbiosis and immunity discrimination in Marchantia[J]. Cell, 2025, 188(5): 1330-1348. |
| [37] | FU S, LU Y S, ZHANG X, et al. The ABC transporter ABCG36 is required for cadmium tolerance in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(20): 5909-5918. |
| [38] | TAKAHASHI R, ISHIMARU Y, SHIMO H, et al. The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2012, 35(11): 1948-1957. |
| [39] | CAO L, LIU L Y, ZHANG C, et al. The MYC2 and MYB43 transcription factors cooperate to repress HMA2 and HMA4 expression, altering cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 479: 135703. |
| [40] | KAUSHIK S, RANJAN A, SINGH A K, et al. Methyl jasmonate reduces cadmium toxicity by enhancing phenol and flavonoid metabolism and activating the antioxidant defense system in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan)[J]. Chemosphere, 2024, 346: 140681. |
| [41] | LI Y, ZHANG S N, BAO Q L, et al. Jasmonic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity through regulating the antioxidant response and enhancing the chelation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 304: 119178. |
| [42] | WANG H R, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG J M, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus regulates cadmium accumulation, migration, transport, and tolerance in Medicago sativa[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 435: 129077. |
| [43] | LIU J L, QIU G Y, LIU C, et al. Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone, combats abiotic stresses in plants[J]. Life, 2022, 12(6): 886. |
| [44] | SAPARA K K, KHEDIA J, AGARWAL P, et al. SbMYB15 transcription factor mitigates cadmium and nickel stress in transgenic tobacco by limiting uptake and modulating antioxidative defence system[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2019, 46(8): 702-714. |
| [1] | 徐燕, 李素娟, 陈光, 徐盛春, 王剑. 大豆耐盐与耐镉胁迫共性基因的挖掘[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 1-16. |
| [2] | 朱长松, 纳琦婷, 张梦卓, 曹慧, 刘诗颖, 张正科, 孟兰环. SlCHRC基因对高温环境下番茄花耐热性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 67-75. |
| [3] | 裴惠民, 巫明明, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 金月, 朱仪, 侯建军, 朱国富, 叶胜海. 低镉水稻基因功能与新品种培育研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 2012-2020. |
| [4] | 师阳阳, 吕丽霞, 脱登峰. 低温弱光胁迫下AMF和PGPR对紫罗兰生长及营养吸收的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1694-1705. |
| [5] | 张若楠, 门小明, 秦凯鹏, 王彬彬, 吴杰, 丁向彬, 徐子伟, 齐珂珂. 绿嘉黑猪的不同杂交组合生长性能、胴体品质、产肉性能和收益比较研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1203-1211. |
| [6] | 项缨, 丛建民, 潘丹红, 陶永刚. 春大棚有机种植不同品种番茄的生育进程分析和综合评价研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1252-1261. |
| [7] | 刘朋飞, 张舒涵, 洪凯, 邵越, 楼兵干. 浙江省番茄溃疡病病原菌分离与鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1293-1300. |
| [8] | 邹俊燕, 王筠竹, 赵婉秋, 尹志浩, 杜建科, 孙崇波. 兰科植物原球茎和类原球茎研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1372-1389. |
| [9] | 苏扬, 商小兰, 钱忠明, 吴林根, 黄佳琦, 庄海峰, 赵宇飞, 党洪阳, 徐立军. 腐熟剂与生物炭协同强化秸秆还田对土壤质量和水稻生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(5): 1139-1148. |
| [10] | 胡心柔, 王梅, 张雅芬, 蔡为明, 金群力. 非生物胁迫对灵芝生长发育及其响应机制的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(5): 1182-1190. |
| [11] | 狄延翠, 嵇泽琳, 王媛媛, 娄世浩, 张涛, 国志信, 申顺善, 朴凤植, 杜南山, 董晓星, 董韩. 番茄SlMYB52基因鉴定、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 808-819. |
| [12] | 任安琪, 黄依然, 万映伶, 刘燕. 生长素对芍药花茎表型和解剖结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(3): 591-602. |
| [13] | 任元龙, 马蓉, 王晓卓, 张雪艳. 叶面喷施褪黑素对甘蓝幼苗干旱胁迫的缓解作用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(2): 338-348. |
| [14] | 肖毓淼, 马巧梅, 张思法, 何勇, 赵振卿. 鱼蛋白水解物对番茄幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2504-2515. |
| [15] | 闫沛玉, 张生银, 陈亮, 刘斌. 不同水肥耦合对设施栽培番茄生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2516-2524. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||