浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 95-104.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250376
爪哇虫草菌ZN-S21的培养特征及其对南亚果实蝇的室内杀虫活性
王璐瑶1( ), 周湘怡1, 王国荣2, 陈梦丽1, 吴慧明1,*(
), 周湘怡1, 王国荣2, 陈梦丽1, 吴慧明1,*( )
)
- 1.浙江农林大学 现代农学院,浙江省作物病虫生物学与生态调控重点实验室,浙江 杭州 311300
2.杭州市萧山区农业和林业技术推广中心,浙江 杭州 311699
-
收稿日期:2025-05-14出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:吴慧明,E-mail:wuhm@zafu.edu.cn
王璐瑶,研究方向为蔬菜害虫生物防治。E-mail:wangluyao0777@163.com -
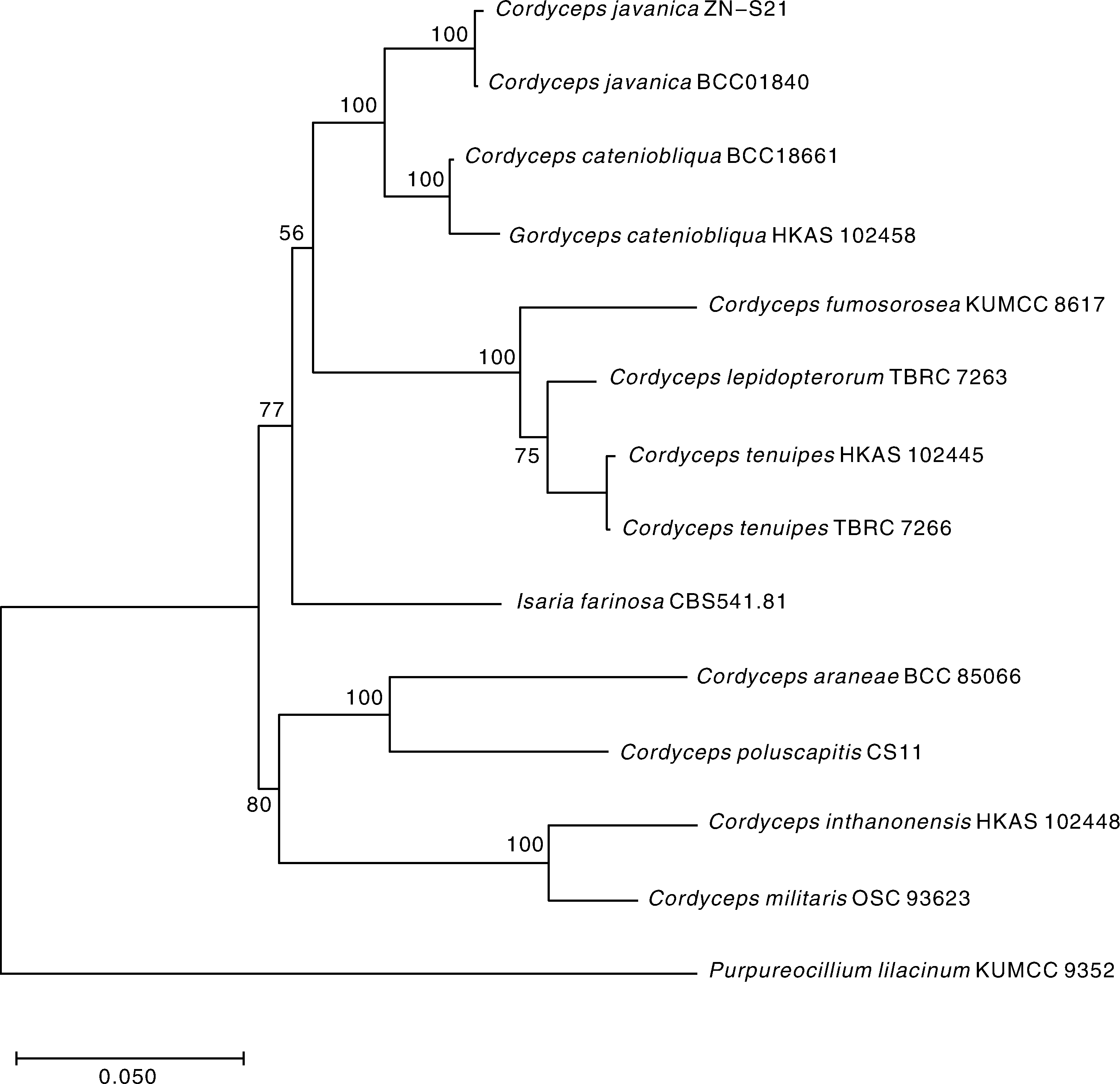
通讯作者:吴慧明 -
基金资助:浙江省“三农九方”科技协作计划“揭榜挂帅”项目(2023SNJF036)
Cultural characteristics of Cordyceps javanica strain ZN-S21 and its indoor insecticidal activity against Bactrocera tau
WANG Luyao1( ), ZHOU Xiangyi1, WANG Guorong2, CHEN Mengli1, WU Huiming1,*(
), ZHOU Xiangyi1, WANG Guorong2, CHEN Mengli1, WU Huiming1,*( )
)
- 1. Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Biology and Ecological Regulation of Crop Pathogens and Insects, College of Advanced Agricultural Sciences, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Agricultural and Forestry Technology Extension Center of Xiaoshan District, Hangzhou City, Hangzhou 311699, China
-
Received:2025-05-14Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:WU Huiming
摘要:
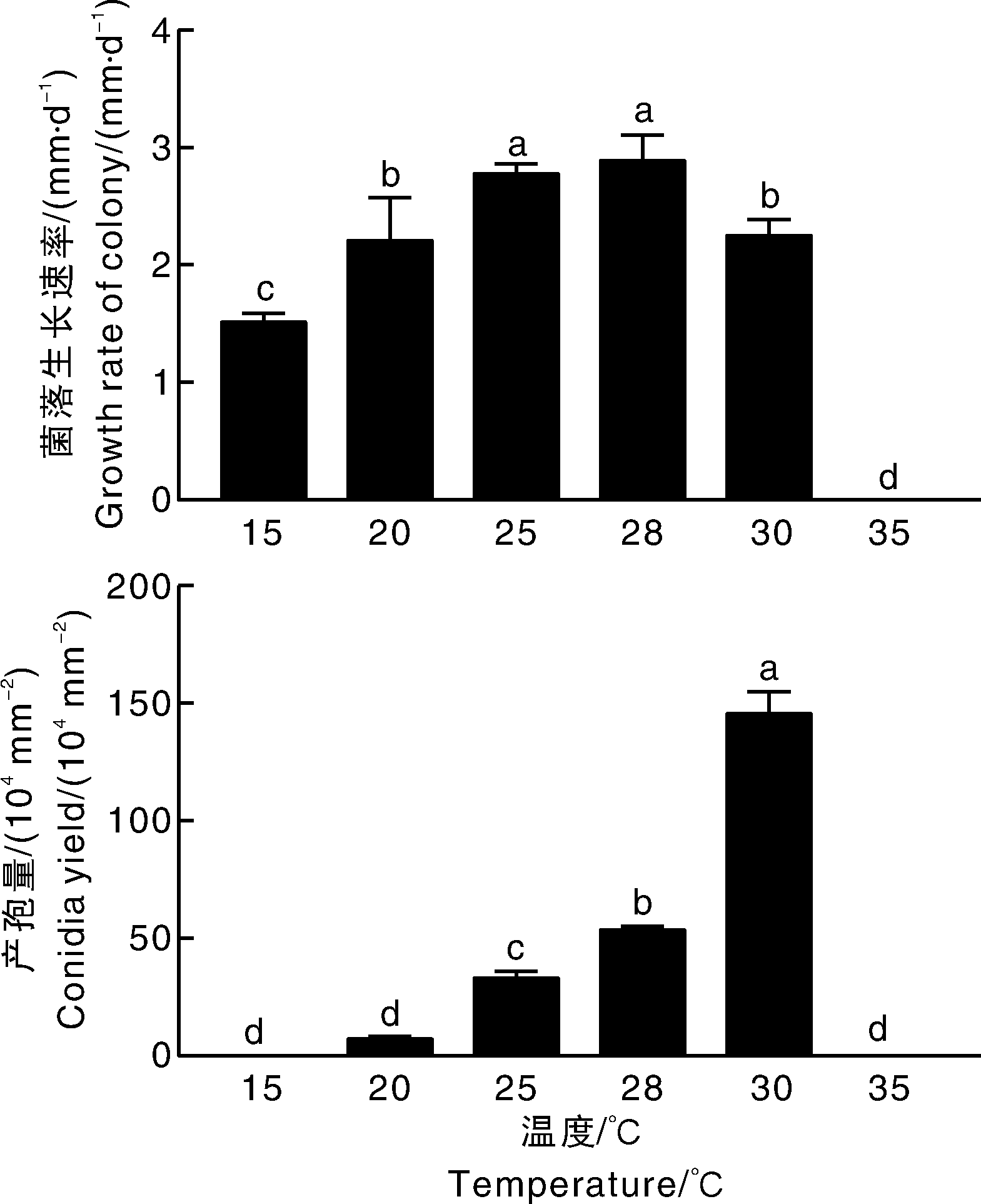
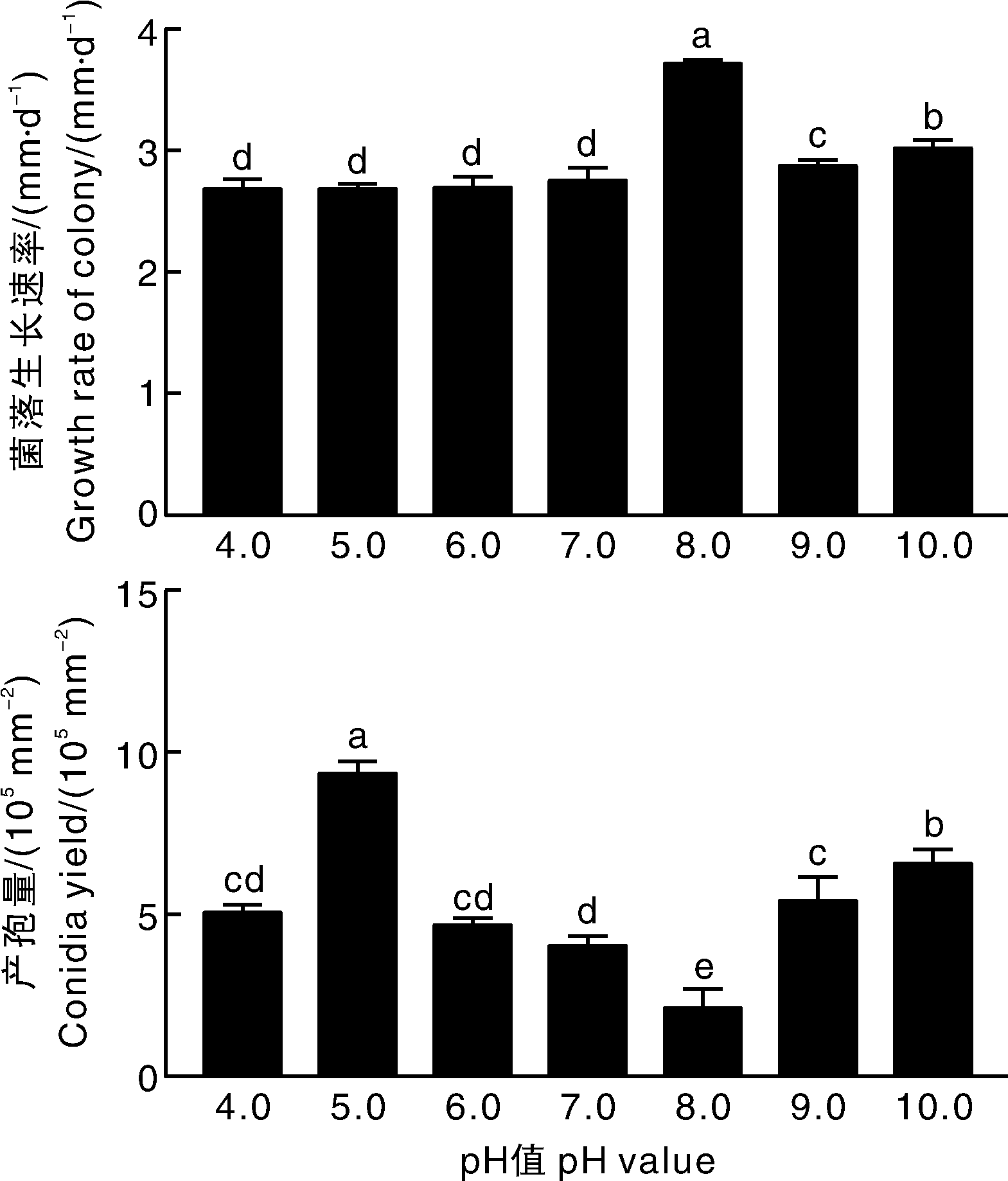
南亚果实蝇(Bactrocera tau)是一种重要检疫性害虫。为了明确田间分离得到的生防菌株ZN-S21对南亚果实蝇的防治潜力,本文通过形态学和多基因系统发生树对菌株ZN-S21的系统分类进行鉴定,研究了菌株ZN-S21的培养特征,并测定了不同环境条件下ZN-S21对南亚果实蝇三龄幼虫的室内杀虫活性。 结果显示: 菌株ZN-S21为爪哇虫草菌(Cordyceps javanica),在温度30 ℃、pH值为5.0的PSA培养基上菌落生长速率较快,产孢量较大。该菌在室内防治南亚果实蝇的最适条件为温度30 ℃、孢子浓度1×108 mL-1,土壤相对含水量90%,土壤pH值7.0。爪哇虫草菌ZN-S21对南亚果实蝇三龄幼虫具有较强的杀虫活性,在南亚果实蝇种群控制方面极具潜力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王璐瑶, 周湘怡, 王国荣, 陈梦丽, 吴慧明. 爪哇虫草菌ZN-S21的培养特征及其对南亚果实蝇的室内杀虫活性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 95-104.
WANG Luyao, ZHOU Xiangyi, WANG Guorong, CHEN Mengli, WU Huiming. Cultural characteristics of Cordyceps javanica strain ZN-S21 and its indoor insecticidal activity against Bactrocera tau[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 95-104.
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5'→3') Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| ITS[ | ITS5 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |
| LSU[ | LR5 | ATCCTGAGGGAAACTTC |
| LROR | GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC | |
| TEF1[ | 985F | GCTCCYGGHCAYCGTGAYTTYAT |
| 2218R | ATGACACCRACRGCRACRGTYTG | |
| RPB1[ | CRPB1 | CCWGGYTTYATCAAGAARGT |
| RPB1Cr | CCNGCDATNTCRTTRTCCATRTA |
表1 PCR引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers for PCR
| 基因 Gene | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5'→3') Sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|
| ITS[ | ITS5 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |
| LSU[ | LR5 | ATCCTGAGGGAAACTTC |
| LROR | GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC | |
| TEF1[ | 985F | GCTCCYGGHCAYCGTGAYTTYAT |
| 2218R | ATGACACCRACRGCRACRGTYTG | |
| RPB1[ | CRPB1 | CCWGGYTTYATCAAGAARGT |
| RPB1Cr | CCNGCDATNTCRTTRTCCATRTA |
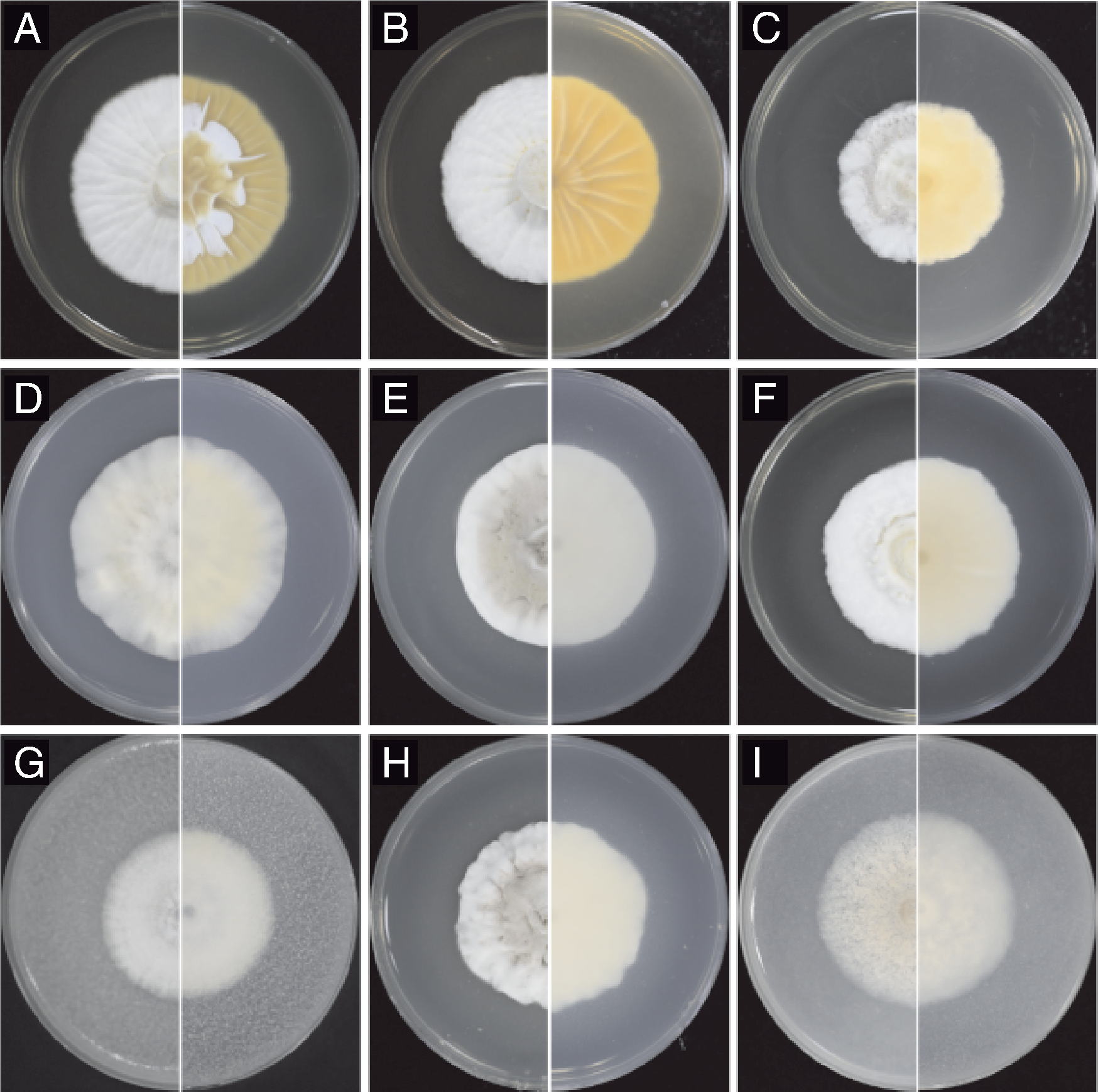
图1 菌株ZN-S21在SDAY(A)、SMAY(B)、MEA(C)、Czapek(D)、PSA(E)、PPDA(F)、CMA(G)、PDA(H)、OMA(I)培养基上的菌落形态
Fig.1 Colony morphology of strain ZN-S21 on culture media of SDAY (A), SMAY (B), MEA (C), Czapek (D), PSA (E), PPDA (F), CMA (G), PDA (H), OMA (I)
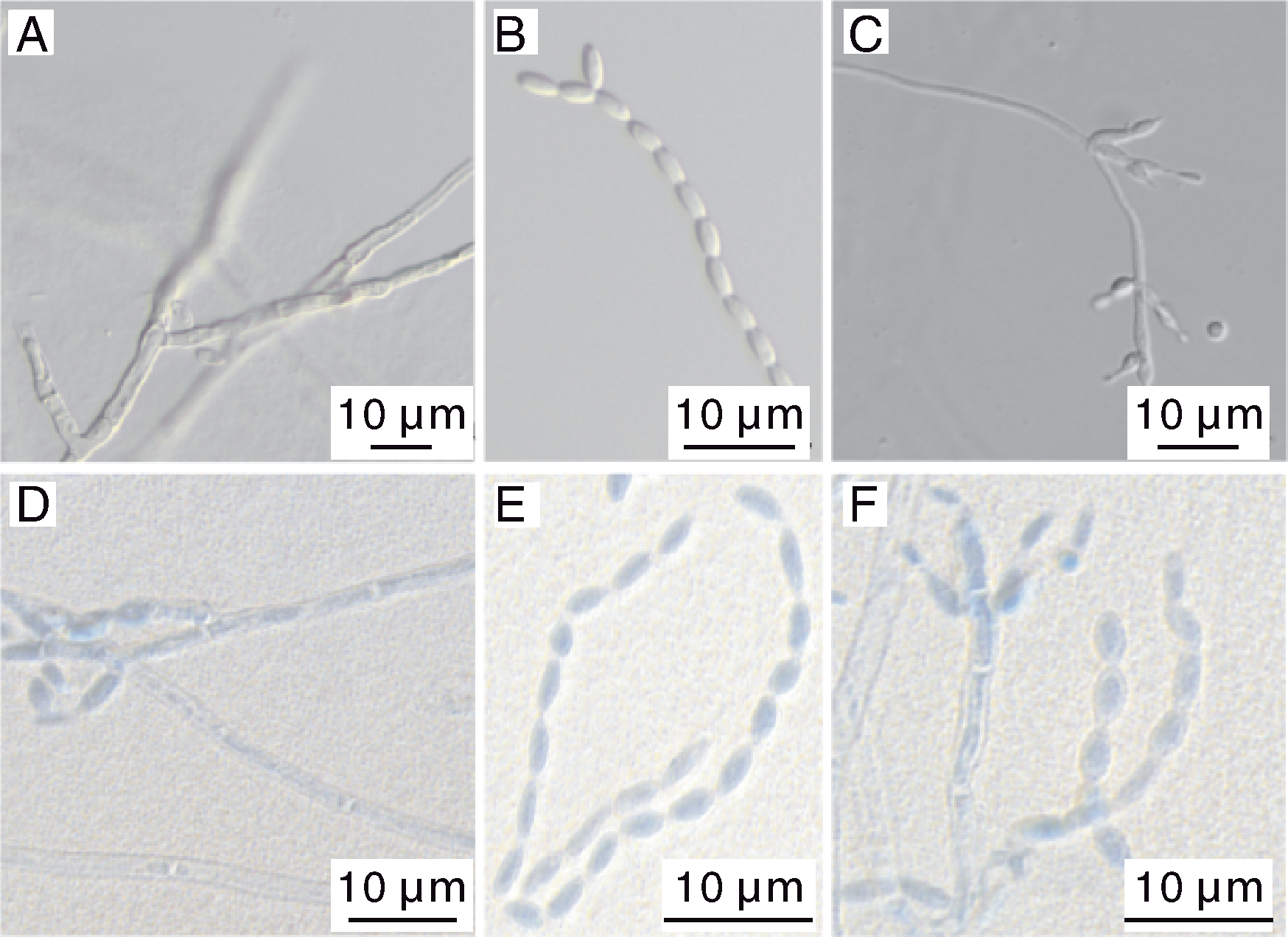
图2 菌株ZN-S21在PDA培养基上的形态学特征 A,菌株ZN-S21的菌丝;B,菌株ZN-S21的分生孢子;C,菌株ZN-S21的产孢结构;D,菌株ZN-S21染色后的菌丝形态;E,菌株ZN-S21染色后的分生孢子;F,菌株ZN-S21染色后的产孢结构。
Fig.2 Morphological characteristics of strain ZN-S21 on PDA medium A, Mycelia of strain ZN-S21; B, Conidia of strain ZN-S21; C, Sporogenous structure of strain ZN-S21; D, Mycelia of strain ZN-S21 after staining; E, Conidia of strain ZN-S21 after staining; F, Sporogenous structure of strain ZN-S21 after staining.
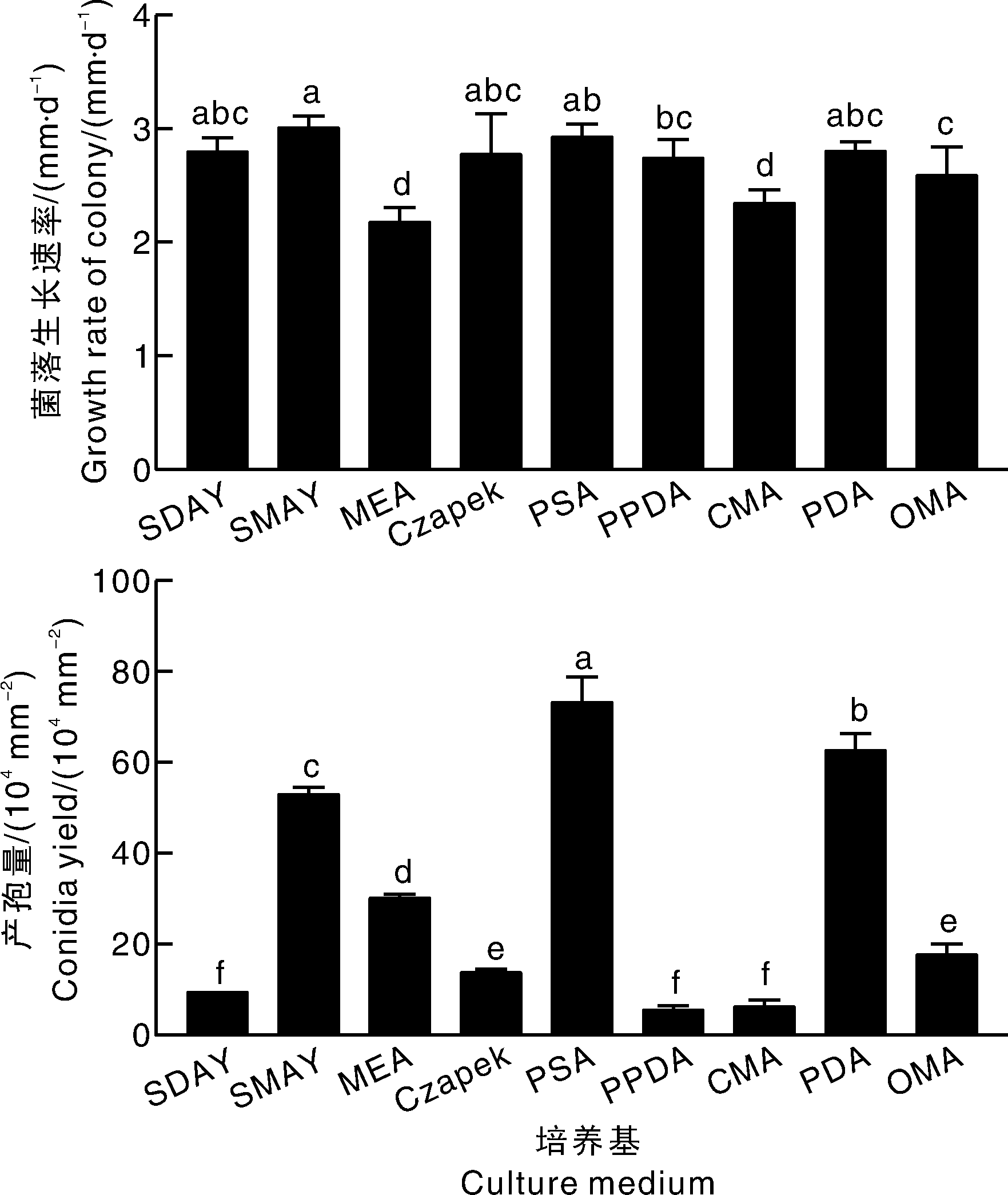
图4 菌株ZN-S21在不同培养基上的菌落生长速率和产孢量 柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.4 Growth rate of colony and conidia yield of strain ZN-S21 on different media Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference at p<0.05. The same as below.
| 编号No. | A/℃ | B/mL-1 | C/% | D | Y/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 1×106 | 30 | 5.0 | 26.14±1.97 d |
| 2 | 20 | 1×107 | 60 | 7.0 | 37.50±5.21 c |
| 3 | 20 | 1×108 | 90 | 9.0 | 27.27±3.94 d |
| 4 | 25 | 1×106 | 60 | 9.0 | 26.14±1.97 d |
| 5 | 25 | 1×107 | 90 | 5.0 | 55.68±0.00 ab |
| 6 | 25 | 1×108 | 30 | 7.0 | 28.41±3.41 d |
| 7 | 30 | 1×106 | 90 | 7.0 | 60.23±1.97 a |
| 8 | 30 | 1×107 | 30 | 9.0 | 53.41±1.97 b |
| 9 | 30 | 1×108 | 60 | 5.0 | 38.64±0.01 c |
| k1 | 30.30 | 37.50 | 35.98 | 37.12 | |
| k2 | 36.74 | 48.86 | 31.06 | 42.05 | |
| k3 | 47.73 | 28.41 | 47.73 | 35.61 | |
| R | 17.43 | 20.45 | 16.67 | 6.44 |
表2 正交试验设计与结果
Table 2 Orthogonal experiment design and results
| 编号No. | A/℃ | B/mL-1 | C/% | D | Y/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 1×106 | 30 | 5.0 | 26.14±1.97 d |
| 2 | 20 | 1×107 | 60 | 7.0 | 37.50±5.21 c |
| 3 | 20 | 1×108 | 90 | 9.0 | 27.27±3.94 d |
| 4 | 25 | 1×106 | 60 | 9.0 | 26.14±1.97 d |
| 5 | 25 | 1×107 | 90 | 5.0 | 55.68±0.00 ab |
| 6 | 25 | 1×108 | 30 | 7.0 | 28.41±3.41 d |
| 7 | 30 | 1×106 | 90 | 7.0 | 60.23±1.97 a |
| 8 | 30 | 1×107 | 30 | 9.0 | 53.41±1.97 b |
| 9 | 30 | 1×108 | 60 | 5.0 | 38.64±0.01 c |
| k1 | 30.30 | 37.50 | 35.98 | 37.12 | |
| k2 | 36.74 | 48.86 | 31.06 | 42.05 | |
| k3 | 47.73 | 28.41 | 47.73 | 35.61 | |
| R | 17.43 | 20.45 | 16.67 | 6.44 |
| 孢子浓度 Spore concentration/mL-1 | 累计校正死亡率Corrected accumulative mortality/% | LT50/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 10 d | 15 d | ||
| 1.0×104 | 4.44±3.85 b | 5.75±1.99 d | 10.34±3.45 d | 16.09±3.98 e | 18.97±7.31 e | 41.72±13.77 a |
| 1.0×105 | 6.67±0 b | 9.20±1.99 d | 33.33±1.99 c | 51.72±0.01 d | 51.72±0.01 d | 12.61±0.10 b |
| 1.0×106 | 6.67±0 b | 22.99±1.99 c | 39.08±1.99 b | 63.22±1.99 c | 65.52±0.01 c | 10.08±0.09 b |
| 1.0×107 | 11.11±1.92 a | 28.74±1.99 b | 42.53±1.99 b | 67.82±1.99 b | 72.41±0.01 b | 9.05±0.10 b |
| 1.0×108 | 13.33±0 a | 35.63±1.99 a | 51.72±3.45 a | 79.31±0.01 a | 84.48±2.44 a | 7.50±0.12 b |
表3 接种菌株ZN-S21后南亚果实蝇三龄幼虫的累计校正死亡率
Table 3 Corrected accumulative mortality of 3rd instar larvae of Bactrocera tau with inoculation of strain ZN-S21
| 孢子浓度 Spore concentration/mL-1 | 累计校正死亡率Corrected accumulative mortality/% | LT50/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 10 d | 15 d | ||
| 1.0×104 | 4.44±3.85 b | 5.75±1.99 d | 10.34±3.45 d | 16.09±3.98 e | 18.97±7.31 e | 41.72±13.77 a |
| 1.0×105 | 6.67±0 b | 9.20±1.99 d | 33.33±1.99 c | 51.72±0.01 d | 51.72±0.01 d | 12.61±0.10 b |
| 1.0×106 | 6.67±0 b | 22.99±1.99 c | 39.08±1.99 b | 63.22±1.99 c | 65.52±0.01 c | 10.08±0.09 b |
| 1.0×107 | 11.11±1.92 a | 28.74±1.99 b | 42.53±1.99 b | 67.82±1.99 b | 72.41±0.01 b | 9.05±0.10 b |
| 1.0×108 | 13.33±0 a | 35.63±1.99 a | 51.72±3.45 a | 79.31±0.01 a | 84.48±2.44 a | 7.50±0.12 b |
| t/d | LC50/mL-1 | LC50的95%置信区间/mL-1 95% Confidence interval of LC50/mL-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3.669×108 | 6.970×105~1.931×108 |
| 5 | 7.468×108 | 1.171×108~4.763×109 |
| 7 | 3.039×107 | 2.403×106~3.844×108 |
| 10 | 4.655×105 | 1.022×105~2.120×106 |
| 15 | 2.945×105 | 9.378×104~9.251×105 |
表4 菌株ZN-S21对南亚果实蝇的致死中浓度(LC50)
Table 4 Median lethal concentration (LC50) of strain ZN-S21 against the 3rd instar larvae of Bactrocera tau
| t/d | LC50/mL-1 | LC50的95%置信区间/mL-1 95% Confidence interval of LC50/mL-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3.669×108 | 6.970×105~1.931×108 |
| 5 | 7.468×108 | 1.171×108~4.763×109 |
| 7 | 3.039×107 | 2.403×106~3.844×108 |
| 10 | 4.655×105 | 1.022×105~2.120×106 |
| 15 | 2.945×105 | 9.378×104~9.251×105 |
| [1] | 李小珍, 刘映红, 贺智勇. 南亚果实蝇对六种果实的趋性和产卵选择性[J]. 昆虫知识, 2007, 44(1): 82-85. |
| LI X Z, LIU Y H, HE Z Y. Taxis response and selective propensity of Bactrocera tau to six host fruits[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 2007, 44(1): 82-85. | |
| [2] | 张艳, 陈俊谕. 南亚果实蝇国内研究进展[J]. 热带农业科学, 2018, 38(11): 70-77. |
| ZHANG Y, CHEN J Y. Recent advances in research of Bactrocera(Zeugodacus) tau (Walker) in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2018, 38(11): 70-77. | |
| [3] | 袁伊旻, 张雨童, 李文静, 等. 探析南亚果实蝇研究进展[J]. 林业科技情报, 2021, 53(3): 15-17. |
| YUAN Y M, ZHANG Y T, LI W J, et al. Research progress of Bactrocera tau (Walker)[J]. Forestry Science and Technology Information, 2021, 53(3): 15-17. | |
| [4] | 曾宪儒, 覃江梅, 龙秀珍, 等. 我国主要瓜类实蝇的生物防治研究进展[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2019, 56(3): 416-425. |
| ZENG X R, QIN J M, LONG X Z, et al. Advances in research on the biological control of the major gourd fly species in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2019, 56(3): 416-425. | |
| [5] | 张燕南, 毕司进, 李悦, 等. 球孢白僵菌菌株GZGY对茶黄螨致病力及生长发育的影响[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2023, 60(6): 1835-1840. |
| ZHANG Y N, BI S J, LI Y, et al. Effects of the Beauveria bassiana GZGY strain on the pathogenicity and reproduction of Polyphagotarsonemus latus[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2023, 60(6): 1834-1840. | |
| [6] | SHIN T Y, LEE M R, PARK S E, et al. Pathogenesis-related genes of entomopathogenic fungi[J]. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2020, 105(4): e21747. |
| [7] | 潘志萍, 翟欣. 球孢白僵菌对橘小实蝇实验种群的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2015, 41(3): 60-63. |
| PAN Z P, ZHAI X. Effects of Beauveria bassiana on experimental populations of Bactrocera dorsalis[J]. Plant Protection, 2015, 41(3): 60-63. | |
| [8] | ONSONGO S K. Evaluation of entomopathogenic fungal isolate(s) for management of melon fruit fly (Zeugodacus cucurbitae) (Coquillette)[D]. Embu: University of Embu, 2019. |
| [9] | SOOKAR P, BHAGWANT S, ALLYMAMOD M N. Mortality in tephritid fruit fry puparia and adults caused by Metarhizium anisopliae, Paecilomyces fumosoroseus and Beauveria bassiana[J]. University of Mauritius Research Journal, 2016, 16(1): 281-298. |
| [10] | 孙燕, 袁盛勇, 李红丽, 等. 蜡蚧轮枝菌对南瓜实蝇室内毒力测定[J]. 南方农业学报, 2013, 44(10): 1662-1666. |
| SUN Y, YUAN S Y, LI H L, et al. Determination of virulence of Verticillium lecanii against Bactrocera tau[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2013, 44(10): 1662-1666. | |
| [11] | KEPLER R M, LUANGSA-ARD J J, HYWEL-JONES N L, et al. A phylogenetically-based nomenclature for Cordycipitaceae (Hypocreales)[J]. IMA Fungus, 2017, 8(2): 335-353. |
| [12] | XING P X, DIAO H L, WANG D, et al. Identification, pathogenicity, and culture conditions of a new isolate of Cordyceps javanica (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) from soil[J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 2023, 116(1): 98-107. |
| [13] | SHIMAZU M, TAKATSUKA J. Isaria javanica (anamorphic Cordycipitaceae) isolated from gypsy moth larvae, Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae), in Japan[J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2010, 45(3): 497-504. |
| [14] | OU D, ZHANG L-H, GUO C-F, et al. Identification of a new Cordyceps javanica fungus isolate and its toxicity evaluation against Asian citrus psyllid[J]. MicrobiologyOpen, 2019, 8(6): e00760. |
| [15] | 陈名, 张大敏, 彭凡, 等. 用于防治假眼小绿叶蝉的爪哇棒束孢可湿性粉剂的研制[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2014, 30(1): 51-57. |
| CHEN M, ZHANG D M, PENG F, et al. Wettable powder development of Isaria javanica for control of the lesser green leafhopper, Empoasca vitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2014, 30(1): 51-57. | |
| [16] | 李洋. 2021年国内新登记的生物农药品种[J]. 世界农药, 2022, 44(2): 1-8. |
| LI Y. New biopesticides registered in China in 2021[J]. World Pesticide, 2022, 44(2): 1-8. | |
| [17] | 林俨, 刘玉军, 汪婷, 等. 几株类棒束孢菌株分类地位的修订[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(12): 4555-4563. |
| LIN Y, LIU Y J, WANG T, et al. Revision of taxonomic status of several Isaria-like strains[J]. Microbiology China, 2021, 48(12): 4555-4563. | |
| [18] | WHITE T J, BRUNS T, LEE S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics[M]// PCR protocols. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1990: 315-322. |
| [19] | VILGALYS R, HESTER M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1990, 172(8): 4238-4246. |
| [20] | REHNER S A, BUCKLEY E. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-alpha sequences: evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs[J]. Mycologia, 2005, 97(1): 84-98. |
| [21] | CASTLEBURY L A, ROSSMAN A Y, SUNG G H, et al. Multigene phylogeny reveals new lineage for Stachybotrys chartarum, the indoor air fungus[J]. Mycological Research, 2004, 108(8): 864-872. |
| [22] | LI X L, ZHANG J J, LI D D, et al. Toxicity of Beauveria bassiana to Bactrocera dorsalis and effects on its natural predators[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2024, 15: 1362089. |
| [23] | USMAN M, GULZAR S, WAKIL W, et al. Virulence of entomopathogenic fungi to Rhagoletis pomonella(Diptera: Tephritidae) and interactions with entomopathogenic nematodes[J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 2020, 113(6): 2627-2633. |
| [24] | 汤永玉, 吴国星, 李冉, 等. 响应面法优化爪哇虫草菌的培养条件及其对斜纹夜蛾的毒力和保护酶活性影响[J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(12): 4555-4573. |
| TANG Y Y, WU G X, LI R, et al. Response surface methodology-based optimization of culture conditions of Cordyceps javanica with effects on virulence and protective enzyme activity of Spodoptera litura[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63(12): 4555-4573. | |
| [25] | 齐禹哲, 闫芳芳, 李成军, 等. 烟草甲幼虫高毒力病原真菌的筛选[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2021, 42(5): 57-62. |
| QI Y Z, YAN F F, LI C J, et al. Screening for highly virulent entomopathogenic fungi against Lasioderma serricorne(Fabricius) larvae[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2021, 42(5): 57-62. | |
| [26] | 叶峻豪, 何景超, 魏燕华, 等. 1株白僵菌分离鉴定、生物学特性及对草地贪夜蛾幼虫影响[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 44(5): 103-111. |
| YE J H, HE J C, WEI Y H, et al. Isolation, identification, biological characteristics, and insecticidal activity of a Beauveria bassiana strain against Spodoptera frugiperda larvae[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 44(5): 103-111. | |
| [27] | 刘全俊, 易璟, 吴国星, 等. 一株咖啡灭字脊虎天牛幼虫虫生真菌鉴定、培养及致病力研究[J]. 西部林业科学, 2022, 51(5): 89-96. |
| LIU Q J, YI J, WU G X, et al. The identification, cultivation and pathogenicity of an entomogenous fungus in larvae of Xylotrechus quadripes chevrolat[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2022, 51(5): 89-96. | |
| [28] | SHAH R, AL-SADI A M, NASSER AL-SABAHI J, et al. Efficacy of an Omani strain of Cordyceps javanicaand its culture filtrate against whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) under laboratory conditions[J]. All Life, 2020, 13(1): 615-622. |
| [29] | 王文秀. 美国白蛾昆虫病原真菌爪哇虫草Cordyceps javanica BE01鉴定及致病机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2022. |
| WANG W X. Identification of the entomopathogenic fungus Cordyceps javanica BE01 isolated from Hyphantria cunea and study on its pathogenic mechanism[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2022. | |
| [30] | 袁盛勇, 孔琼, 孙燕, 等. 球孢白僵菌对南瓜实蝇致病力的测定[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(9): 158-160. |
| YUAN S Y, KONG Q, SUN Y, et al. Determination of pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana to Bactrocera cucurbitae[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(9): 158-160. | |
| [31] | RIZAL L M, FURLONG M J, WALTER G H. Responses of diamondback moth to diverse entomopathogenic fungi collected from non-agricultural habitat: effects of dose, temperature and starvation[J]. Fungal Biology, 2022, 126(10): 648-657. |
| [32] | 潘志萍, 李敦松, 曾玲. 环境因子对球孢白僵菌侵染桔小实蝇致病力的影响[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2008, 30(1): 11-15. |
| PAN Z P, LI D S, ZENG L. Effects of environmental factors on the pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana to Bactrocera dorsalis(Hendel)[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2008, 30(1): 11-15. | |
| [33] | EKESI S, MANIANIA N K, LUX S A. Effect of soil temperature and moisture on survival and infectivity of Metarhizium anisopliae to four tephritid fruit fly puparia[J]. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 2003, 83(2): 157-167. |
| [34] | SOOKAR P, BHAGWANT S, AWUOR OUNA E. Isolation of entomopathogenic fungi from the soil and their pathogenicity to two fruit fly species (Diptera: Tephritidae)[J]. Journal of Applied Entomology, 2008, 132(9/10): 778-788. |
| [1] | 朱为静, 吴佳, 洪春来, 朱凤香, 洪磊东, 张涛, 张硕, 诸惠芬. 秸秆覆盖对土壤水热肥及蟠桃产量和品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1924-1932. |
| [2] | 肖立涵, 辛美果, 卢文静, 叶沁, 张岑, 肖朝耿, 谌迪. 不同贮藏条件对3种花粉源蜂王浆品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(5): 1161-1167. |
| [3] | 冷猛, 姚地慧, 龙凯, 赵海燕, 杨茂发, 于晓飞. 不同温度对益蝽过冷却点和冰点的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(3): 624-629. |
| [4] | 林勇, 代伟伟, 鲍恩财, 王强, 柏宗春, 夏礼如, 张姚, 孙玉伦, 欧阳礼虎. 层叠式笼养肉鸭舍夏季风机运行模式优化与计算流体力学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(3): 666-675. |
| [5] | 孙楠, 闫国超, 何勇, 朱祝军. 葫芦科作物叶片硅含量测定方法的优化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 338-345. |
| [6] | 黄秋伟, 毛立彦, 檀小辉, 王丽萍, 刘功德, 彭继飞, 龙凌云. 贮藏温度对广西旱藕采后重要品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 346-354. |
| [7] | 马波, 陶震, 周瑞, 王雪, 吕茜茜, 孙士红, 王寒, 高金秋, 张楚涵, 陈凤清. 花叶万年青功能成分提取条件优化与活性探究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(2): 383-393. |
| [8] | 清源, 方志荣, 姚昕, 尹胜. 不同贮藏温度下印度块菌净菜品质变化及其货架期研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(11): 2698-2709. |
| [9] | 张志国, 丛琳, 张世杰, 李荣光, 邹维娜, 迟法安, 张宝, 姜玉萍. 根区温度对萱草生长发育及其开花的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(5): 1005-1014. |
| [10] | 黄雷, 李光庆, 姚雪琴, 刘春晴, 谢祝捷, 耿春女. 基因型和环境对不同生育期花椰菜霜霉病的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(8): 1420-1426. |
| [11] | 张芳, 王佩欣, 何勇, 骆慧枫, 寿国忠. 基于物联网的阳台微型温室作物生长环境因子探究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2020, 32(2): 234-242. |
| [12] | 余纯, 许冬, 黄维, 雷明洪, 万鹏. 月相和温度对棉红铃虫成虫种群动态的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(2): 260-267. |
| [13] | 黄惠群, 蔡文昌, 张健瑜, 李灿, 曾和平. 炭化温度对牛粪生物炭结构性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(9): 1561-1568. |
| [14] | 朱作艺, 张玉, 王君虹, 李雪, 王伟. 不同贮藏条件下大黄鱼生物胺变化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(9): 1592-1598. |
| [15] | 张青. 贮藏温度对越心和章姬草莓果实品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(4): 600-606. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||