| [1] |
刘文达. 绣球花在园林景观中的应用探究[J]. 南方农业, 2020, 14(21): 43-44.
|
|
LIU W D. Application of Hydrangea in landscape architecture[J]. South China Agriculture, 2020, 14(21): 43-44.
|
| [2] |
朱嘉润, 王凤兰, 李永红, 等. 华南地区绣球花栽培技术及园林应用[J]. 现代农业科技, 2024(5): 81-84.
|
|
ZHU J R, WANG F L, LI Y H, et al. Cultivation techniques and garden application of Hydrangea in South China[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024(5): 81-84.
|
| [3] |
KUMLA J, SUWANNARACH N, LIU Y S, et al. Survey of edible Amanita in northern Thailand and their nutritional value, total phenolic content, antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2023, 9(3): 343.
|
| [4] |
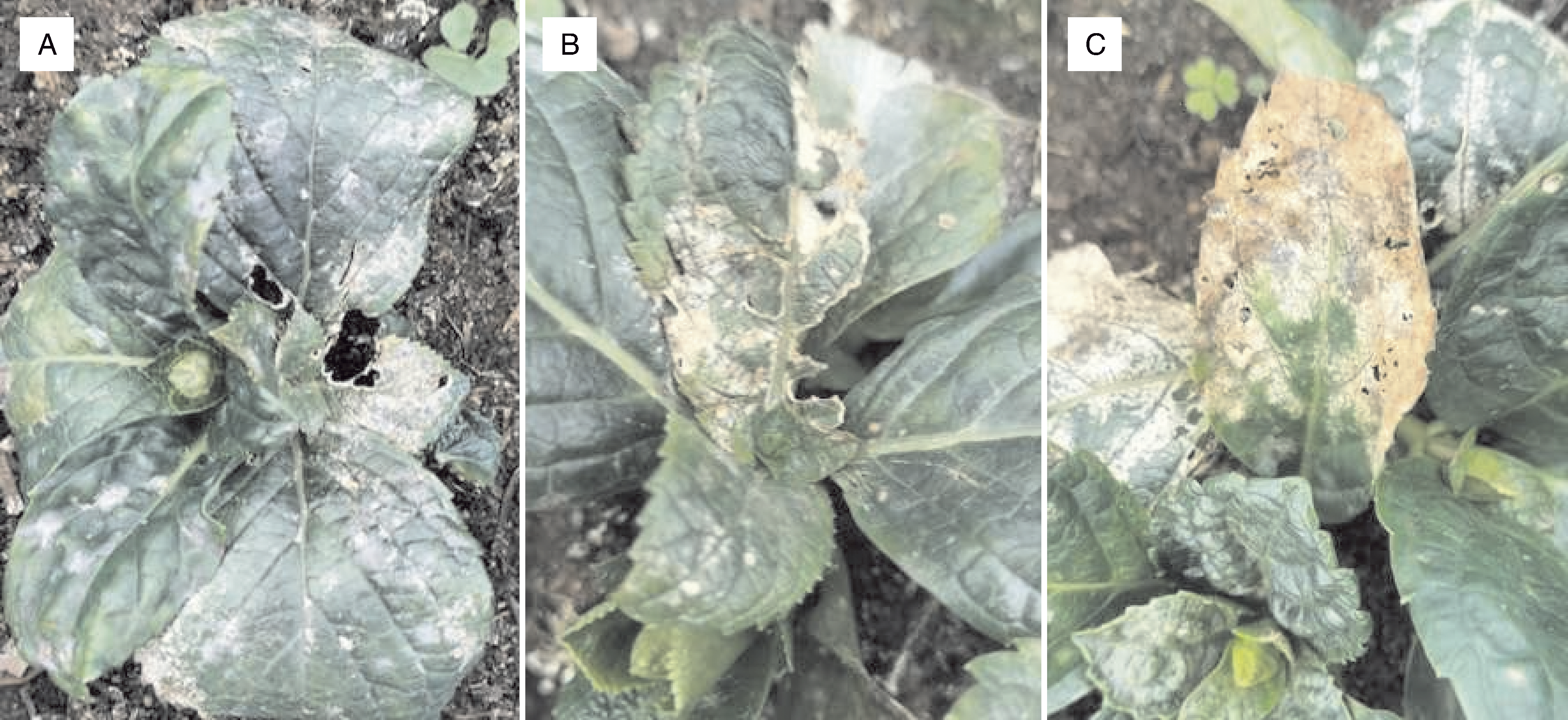
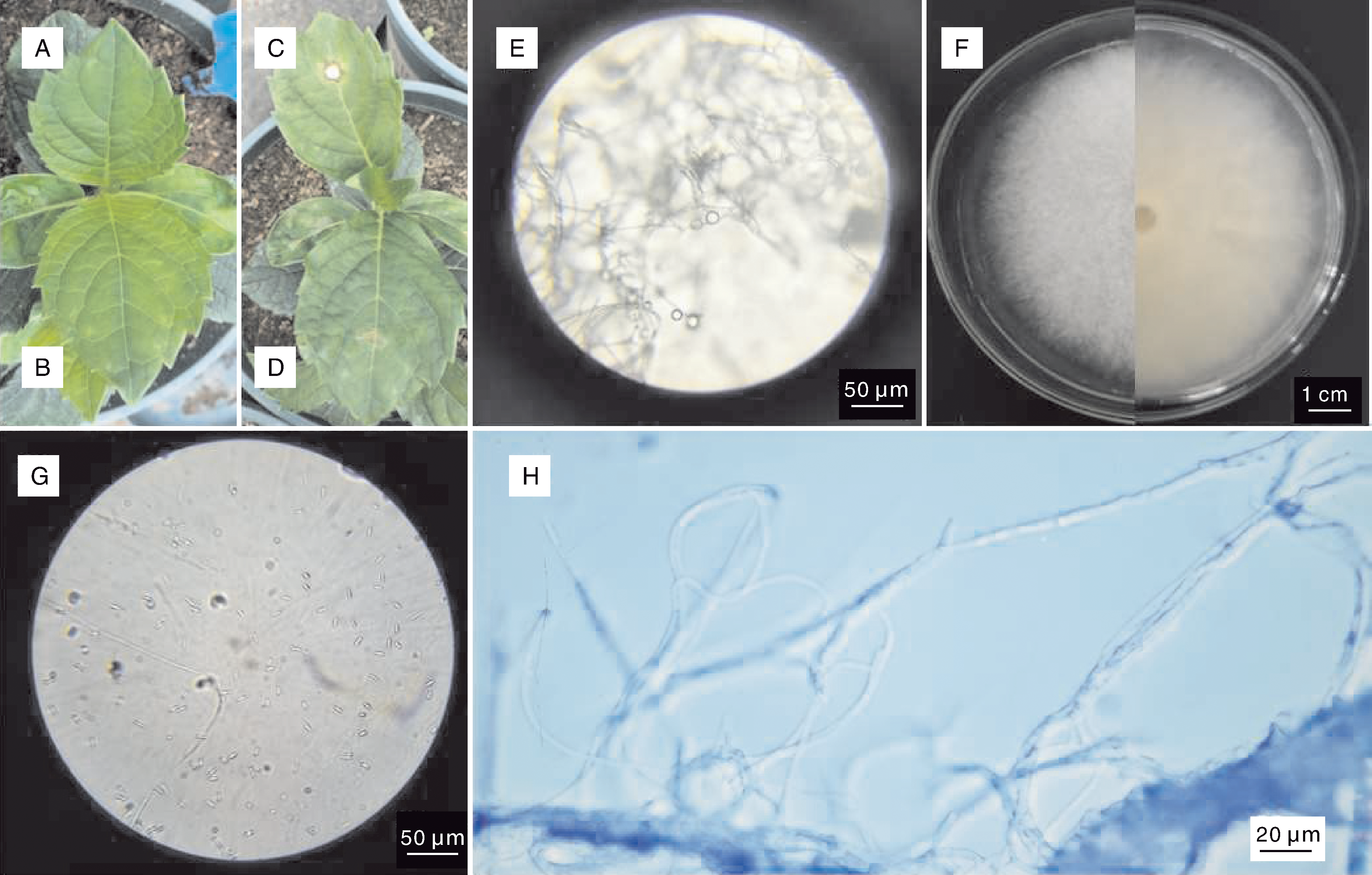
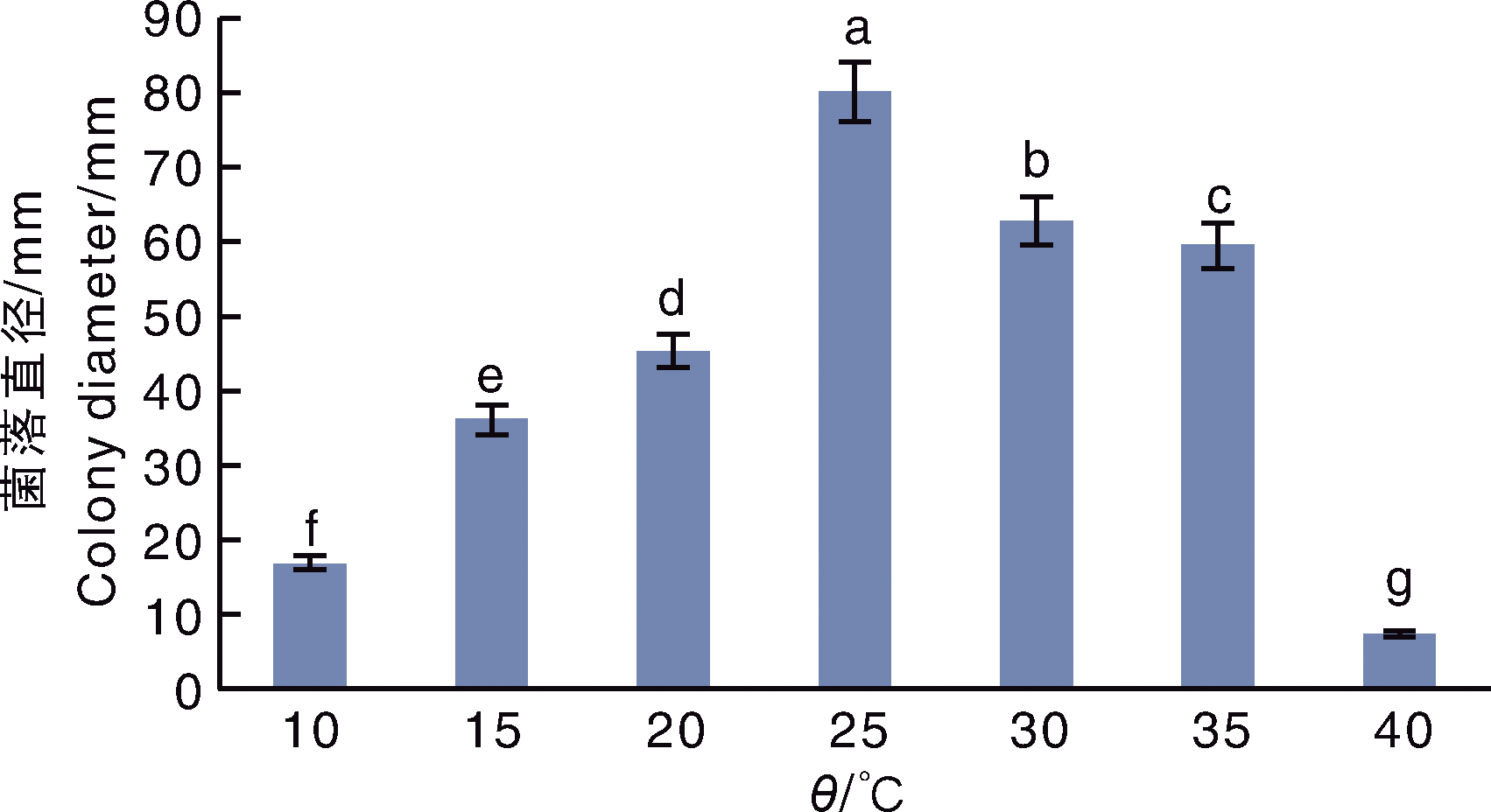
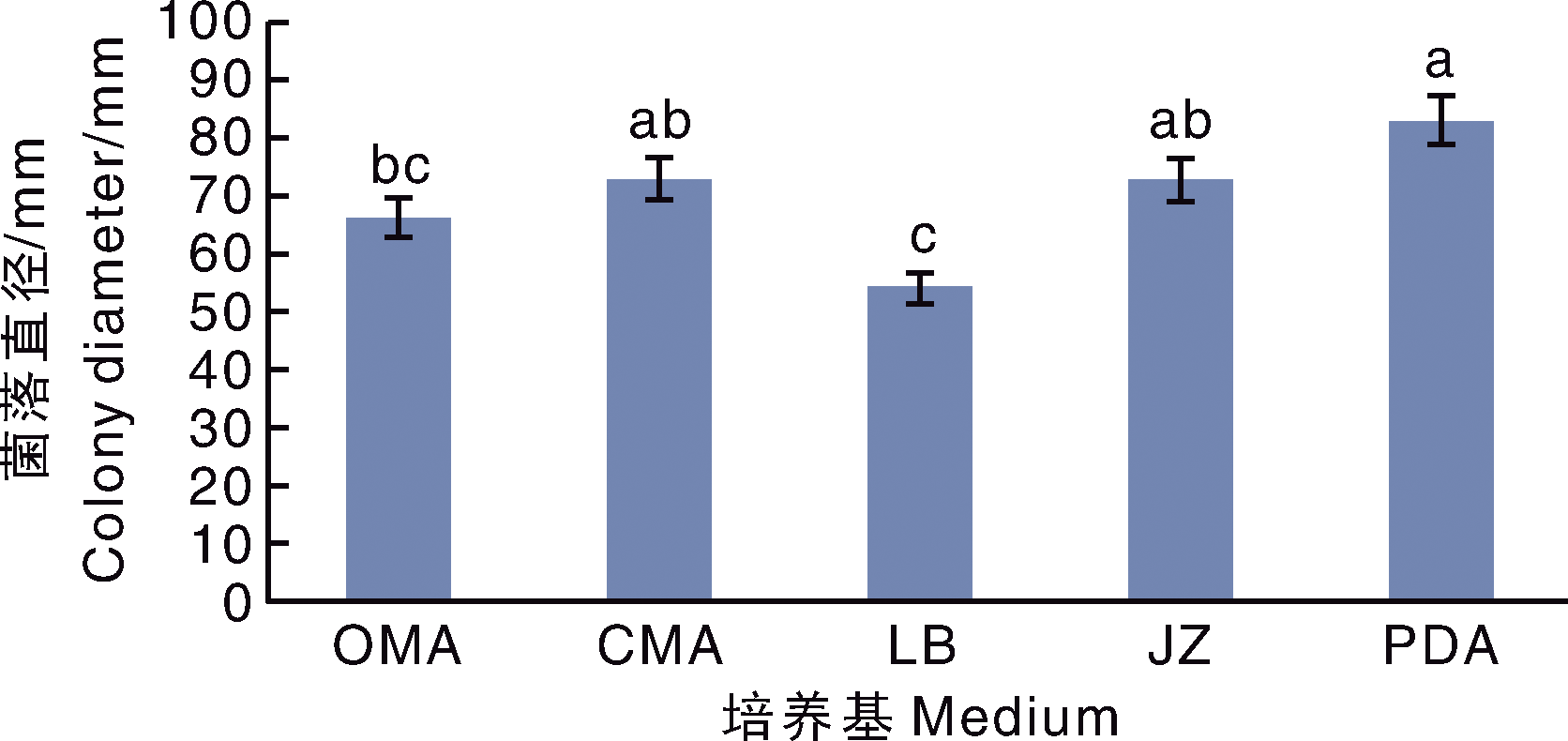
杨婷, 曹春玲, 周逸文, 等. 绣球叶斑病病原菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 植物病理学报, 2025, 55(2): 352-355.
|
|
YANG T, CAO C L, ZHOU Y W, et al. Isolation and identification of the pathogen causing leaf spot on Hydrangea macrophylla[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2024, 55(2): 352-355.
|
| [5] |
HU Y F, LUO X X, XU Z H, et al. First report of anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum siamense on Hydrangea macrophylla in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2023, 107(9):2853.
|
| [6] |
FANG T J, SHANG W J, BAI L C, et al. First report of Golovinomyces orontii causing Hydrangea macrophylla powdery mildew in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China[J]. Plant Disease, 2021, 105(9):2730.
|
| [7] |
GU X, LIU W, JI K W, et al. First Reports of Cladosporium tenuissimum causing leaf spots on Hydrangea macrophylla in Anhui Province in China[J]. Plant Disease, 2024, 108(5):1392.
|
| [8] |
MMBAGA M T, LI Y, KIM M S. First report of Myrothecium roridum causing leaf spot on garden Hydrangea in the United States[J]. Plant Disease, 2010, 94(10): 1266.
|
| [9] |
GARIBALDI A, GILARDI G, MINERDI D, et al. First report of leaf spot caused by Phoma exigua on Hydrangea macrophylla in Italy[J]. Plant Disease, 2006, 90(8): 1113.
|
| [10] |
PARK M J, CHO S E, PARK J H, et al. First report of powdery mildew caused by Oidium hortensiae on mophead Hydrangea in Korea[J]. Plant Disease, 2012, 96(7): 1072.
|
| [11] |
GARIBALDI A, GILARDI G, FRATI S, et al. First report of leaf spot caused by Alternaria alternata on Hydrangea macrophylla in Italy[J]. Plant Disease, 2007, 91(6): 767.
|
| [12] |
GARIBALDI A, BERTETTI D, GULLINO M L. First report of a leaf spot caused by Alternaria compacta on Hydrangea anomala subsp. petiolaris in Italy[J]. Plant Disease, 2008, 92(1): 173.
|
| [13] |
杨苗, 张杰, 白嘉伟, 等. 雾灵山国家级自然保护区大型真菌物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1229-1235.
|
|
YANG M, ZHANG J, BAI J W, et al. Species diversity of macrofungi in the Wuling Mountain National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2021, 29(9): 1229-1235.
|
| [14] |
刘升乔, 邓洪平, 胡亚萍, 等. 湖北竹溪大型真菌资源及生态分布研究[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(6): 52-59.
|
|
LIU S Q, DENG H P, HU Y P, et al. Study on ecological distribution of macrofungus resources in Zhuxi Hubei[J]. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(6): 52-59.
|
| [15] |
GUO J X, BOWATTE S, HOU F J. Diversity of endophytic bacteria and fungi in seeds of Elymus nutans growing in four locations of Qinghai Tibet Plateau, China[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 459(1): 49-63.
|
| [16] |
张纹浩. 中国西南地区鹅膏属物种资源研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2023.
|
|
ZHANG W H. The species resources of Amanita in southwestern China[D]. Kunming: Kunming Medical University, 2023.
|
| [17] |
王凡, 卞晓春, 刘陈玮, 等. 南通市蚕豆赤斑病病原菌鉴定及其抑菌药剂筛选[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2024, 40(10): 1810-1817.
|
|
WANG F, BIAN X C, LIU C W, et al. Identification and screening of antifungal agents for the pathogen causing broad bean chocolate spot in Nantong City[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 40(10): 1810-1817.
|
| [18] |
程亮, 秦健, 黎炎, 等. 冬瓜苗期立枯病病原鉴定及防治药剂筛选[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2024(6): 74-80.
|
|
CHENG L, QIN J, LI Y, et al. Identification of pathogen causing damping off at seeding stage of wax gourd and screening of control fungicides[J]. China Vegetables, 2024(6): 74-80.
|
 ), 张玉1, 温联好1, 刘光炎1, 周梅1, 李正敏1, 熊海燕1, 杨振翼2, 杨曾华2, 童译2, 王超1,*(
), 张玉1, 温联好1, 刘光炎1, 周梅1, 李正敏1, 熊海燕1, 杨振翼2, 杨曾华2, 童译2, 王超1,*( )
)
 ), ZHANG Yu1, WEN Lianhao1, LIU Guangyan1, ZHOU Mei1, LI Zhengmin1, XIONG Haiyan1, YANG Zhenyi2, YANG Zenghua2, TONG Yi2, WANG Chao1,*(
), ZHANG Yu1, WEN Lianhao1, LIU Guangyan1, ZHOU Mei1, LI Zhengmin1, XIONG Haiyan1, YANG Zhenyi2, YANG Zenghua2, TONG Yi2, WANG Chao1,*( )
)