Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2449-2457.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240672
• Crop Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of rice blast resistance in rice varieties from regional trials in Zhejiang Province of China from 2014 to 2023
HAO Zhongna1( ), QIU Haiping1, CHAI Rongyao1, HAN Zhanyu2, ZHANG Zhen1, WANG Yanli1, WANG Jiaoyu1, LIU Xin2,*(
), QIU Haiping1, CHAI Rongyao1, HAN Zhanyu2, ZHANG Zhen1, WANG Yanli1, WANG Jiaoyu1, LIU Xin2,*( )
)
- 1. Zhejiang National Test Station for Resistance Identification of Crop Variety, Institute of Plant Protection and Microbiology, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
2. Seed Management Station of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310020, China
-
Received:2024-07-23Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HAO Zhongna, QIU Haiping, CHAI Rongyao, HAN Zhanyu, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Yanli, WANG Jiaoyu, LIU Xin. Analysis of rice blast resistance in rice varieties from regional trials in Zhejiang Province of China from 2014 to 2023[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2449-2457.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240672
| 水稻类型 Rice type | 每年的水稻品种数量Number of rice varieties in different years | 合计 Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| 早籼稻Early indica rice | 24 | 13 | 12 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 27 | 223 |
| 单季杂交籼稻Single-season hybrid indica rice | 27 | 37 | 24 | 25 | 34 | 34 | 28 | 36 | 34 | 38 | 317 |
| 单季籼粳杂交稻Single-season hybrid indica-japonica rice | 26 | 26 | 36 | 24 | 24 | 36 | 39 | 50 | 51 | 51 | 363 |
| 单季晚粳稻Single-season late japonica rice | 13 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 23 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 27 | 205 |
| 连作杂交晚籼稻Continuous cropping hybrid late indica rice | 25 | 28 | 12 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 158 |
| 连作晚粳稻Continuous cropping late japonica rice | 12 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 126 |
| 连作籼粳杂交稻Continuous cropping indica-japonica hybrid rice | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 62 |
| 特早熟晚粳稻Especially early maturing late japonica rice | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 |
| 特早熟籼稻Especial early maturing indica rice | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| 合计Total | 134 | 135 | 109 | 111 | 129 | 173 | 169 | 179 | 175 | 184 | 1 498 |
Table 1 Rice varieties in regional trials in Zhejiang Province from 2014-2023
| 水稻类型 Rice type | 每年的水稻品种数量Number of rice varieties in different years | 合计 Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| 早籼稻Early indica rice | 24 | 13 | 12 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 27 | 223 |
| 单季杂交籼稻Single-season hybrid indica rice | 27 | 37 | 24 | 25 | 34 | 34 | 28 | 36 | 34 | 38 | 317 |
| 单季籼粳杂交稻Single-season hybrid indica-japonica rice | 26 | 26 | 36 | 24 | 24 | 36 | 39 | 50 | 51 | 51 | 363 |
| 单季晚粳稻Single-season late japonica rice | 13 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 23 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 27 | 205 |
| 连作杂交晚籼稻Continuous cropping hybrid late indica rice | 25 | 28 | 12 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 158 |
| 连作晚粳稻Continuous cropping late japonica rice | 12 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 126 |
| 连作籼粳杂交稻Continuous cropping indica-japonica hybrid rice | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 62 |
| 特早熟晚粳稻Especially early maturing late japonica rice | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 |
| 特早熟籼稻Especial early maturing indica rice | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| 合计Total | 134 | 135 | 109 | 111 | 129 | 173 | 169 | 179 | 175 | 184 | 1 498 |
| 年份 | 菌株来源 | 菌株编号(生理小种) |
|---|---|---|
| Year | Source of strain | Number of strain (physiologic race ) |
| 2014 | 籼稻Indica rice | 14-12(ZA1)、14-24(ZA9)、14-28(ZB1)、14-15(ZB5)、14-22(ZB13)、14-20(ZC5)、14-27(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 14-36(ZA15)、14-39(ZA41)、14-41(ZA59)、14-32(ZA63)、14-35(ZB15) | |
| 2015 | 籼稻Indica rice | 15-173(ZA1)、15-116(ZA13)、15-133(ZB1)、15-166(ZB5)、15-176(ZB13)、15-117(ZC13)、15-143(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 15-114(ZA35)、15-108(ZA51)、15-53(ZB1)、15-13(ZC15)、15-105(ZD1) | |
| 2016 | 籼稻Indica rice | 16-158(ZA1)、16-59(ZA33)、16-150(ZB1)、16-164(ZB5)、16-163(ZB13)、16-36(ZC13)、16-176(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 16-56(ZA19)、16-174(ZA59)、16-166(ZB9)、16-82(ZC11)、16-122(ZD3) | |
| 2017 | 籼稻Indica rice | 17-57(ZA1)、17-49(ZA5)、17-36(ZA33)、17-1(ZB1)、17-21(ZB13)、17-20(ZC13)、17-34(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 17-87(ZA1)、17-63(ZA33)、17-60(ZA49)、17-18(ZC15)、17-54(ZE3)、17-230(ZF1) | |
| 2018 | 籼稻Indica rice | 18-59(ZA1)、18-60(ZA5)、18-65(ZA9)、18-2(ZB1)、18-68(ZB13)、18-127(ZC13)、18-13(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 18-51(ZA1)、18-73(ZA33)、18-75(ZA49)、18-64(ZC15)、18-56(ZD3)、18-20(ZE3)、18-11(ZF1) | |
| 2019 | 籼稻Indica rice | 19-12(ZA33)、19-2(ZB13)、19-4(ZC13)、19-3(ZC15)、19-20(ZE3) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 19-28(ZA1)、19-34(ZA9)、19-25(ZB1)、19-37(ZC13)、19-46(ZD3)、19-54(ZE3)、19-23(ZG1) | |
| 2020 | 籼稻Indica rice | 20-10(ZB7)、20-4(ZB32)、20-1(ZC13)、20-13(ZC15)、20-18(ZE3) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 20-20(ZA1)、20-23(ZA49)、20-27(ZB25)、20-32(ZC15)、20-39(ZE1)、20-54(ZE3)、20-33(ZG1) | |
| 2021 | 籼稻Indica rice | 21-20(ZA33)、21-16(ZB1)、21-100(ZB9)、21-11(ZB13)、21-9(ZC1)、21-83(ZC5) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 21-145(ZA1)、21-138(ZA33)、21-148(ZA49)、21-142(ZB1)、21-164(ZB13)、21-126(ZC1)、21-135(ZG1) | |
| 2022 | 籼稻Indica rice | 22-28(ZB1)、22-48(ZB11)、22-41(ZB13)、22-13(ZC1)、22-6(ZC13) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 22-51(ZA1)、22-73(ZA33)、22-75(ZA49)、22-53(ZB1)、22-91(ZB13)、22-80(ZC1)、22-71(ZG1) | |
| 2023 | 籼稻Indica rice | 23-145(ZA1)、23-160(ZA17)、23-140(ZB1)、23-164(ZB3)、23-116(ZB5)、23-66(ZD5) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 23-291(ZA1)、23-311(ZA9)、23-329(ZA13)、23-319(ZA25)、23-376(ZB1)、23-323(ZB5) |
Table 2 Information of strains used for identification of rice leaf blast
| 年份 | 菌株来源 | 菌株编号(生理小种) |
|---|---|---|
| Year | Source of strain | Number of strain (physiologic race ) |
| 2014 | 籼稻Indica rice | 14-12(ZA1)、14-24(ZA9)、14-28(ZB1)、14-15(ZB5)、14-22(ZB13)、14-20(ZC5)、14-27(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 14-36(ZA15)、14-39(ZA41)、14-41(ZA59)、14-32(ZA63)、14-35(ZB15) | |
| 2015 | 籼稻Indica rice | 15-173(ZA1)、15-116(ZA13)、15-133(ZB1)、15-166(ZB5)、15-176(ZB13)、15-117(ZC13)、15-143(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 15-114(ZA35)、15-108(ZA51)、15-53(ZB1)、15-13(ZC15)、15-105(ZD1) | |
| 2016 | 籼稻Indica rice | 16-158(ZA1)、16-59(ZA33)、16-150(ZB1)、16-164(ZB5)、16-163(ZB13)、16-36(ZC13)、16-176(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 16-56(ZA19)、16-174(ZA59)、16-166(ZB9)、16-82(ZC11)、16-122(ZD3) | |
| 2017 | 籼稻Indica rice | 17-57(ZA1)、17-49(ZA5)、17-36(ZA33)、17-1(ZB1)、17-21(ZB13)、17-20(ZC13)、17-34(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 17-87(ZA1)、17-63(ZA33)、17-60(ZA49)、17-18(ZC15)、17-54(ZE3)、17-230(ZF1) | |
| 2018 | 籼稻Indica rice | 18-59(ZA1)、18-60(ZA5)、18-65(ZA9)、18-2(ZB1)、18-68(ZB13)、18-127(ZC13)、18-13(ZC15) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 18-51(ZA1)、18-73(ZA33)、18-75(ZA49)、18-64(ZC15)、18-56(ZD3)、18-20(ZE3)、18-11(ZF1) | |
| 2019 | 籼稻Indica rice | 19-12(ZA33)、19-2(ZB13)、19-4(ZC13)、19-3(ZC15)、19-20(ZE3) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 19-28(ZA1)、19-34(ZA9)、19-25(ZB1)、19-37(ZC13)、19-46(ZD3)、19-54(ZE3)、19-23(ZG1) | |
| 2020 | 籼稻Indica rice | 20-10(ZB7)、20-4(ZB32)、20-1(ZC13)、20-13(ZC15)、20-18(ZE3) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 20-20(ZA1)、20-23(ZA49)、20-27(ZB25)、20-32(ZC15)、20-39(ZE1)、20-54(ZE3)、20-33(ZG1) | |
| 2021 | 籼稻Indica rice | 21-20(ZA33)、21-16(ZB1)、21-100(ZB9)、21-11(ZB13)、21-9(ZC1)、21-83(ZC5) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 21-145(ZA1)、21-138(ZA33)、21-148(ZA49)、21-142(ZB1)、21-164(ZB13)、21-126(ZC1)、21-135(ZG1) | |
| 2022 | 籼稻Indica rice | 22-28(ZB1)、22-48(ZB11)、22-41(ZB13)、22-13(ZC1)、22-6(ZC13) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 22-51(ZA1)、22-73(ZA33)、22-75(ZA49)、22-53(ZB1)、22-91(ZB13)、22-80(ZC1)、22-71(ZG1) | |
| 2023 | 籼稻Indica rice | 23-145(ZA1)、23-160(ZA17)、23-140(ZB1)、23-164(ZB3)、23-116(ZB5)、23-66(ZD5) |
| 粳稻Japonica rice | 23-291(ZA1)、23-311(ZA9)、23-329(ZA13)、23-319(ZA25)、23-376(ZB1)、23-323(ZB5) |
| 病级 | 抗性类型 | 单穗损失率 | 穗瘟发病率 | 穗瘟损失率 | 稻瘟病综合指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease grade | Resistance type | Loss rate per panicle/% | Incidence of panicle blast/% | Loss rate of panicle blast/% | Composite index |
| 0 | 高抗Highly resistant | 0 | 0 | 0 | <0.1 |
| 1 | 抗Resistant | ≤5.0 | ≤5.0 | ≤5.0 | 0.1~2.0 |
| 3 | 中抗Moderately resistant | 5.1~20.0 | 5.1~10.0 | 5.1~15.0 | 2.1~4.0 |
| 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible | 20.1~50.0 | 10.1~25.0 | 15.1~30.0 | 4.1~6.0 |
| 7 | 感Susceptible | 50.1~70.0 | 25.1~50.0 | 30.1~50.0 | 6.1~7.5 |
| 9 | 高感Highly susceptible | ≥70.1 | ≥50.1 | ≥50.1 | 7.6~9.0 |
Table 3 Grading standard for rice resistance to panicle blast and composite evaluation
| 病级 | 抗性类型 | 单穗损失率 | 穗瘟发病率 | 穗瘟损失率 | 稻瘟病综合指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease grade | Resistance type | Loss rate per panicle/% | Incidence of panicle blast/% | Loss rate of panicle blast/% | Composite index |
| 0 | 高抗Highly resistant | 0 | 0 | 0 | <0.1 |
| 1 | 抗Resistant | ≤5.0 | ≤5.0 | ≤5.0 | 0.1~2.0 |
| 3 | 中抗Moderately resistant | 5.1~20.0 | 5.1~10.0 | 5.1~15.0 | 2.1~4.0 |
| 5 | 中感Moderately susceptible | 20.1~50.0 | 10.1~25.0 | 15.1~30.0 | 4.1~6.0 |
| 7 | 感Susceptible | 50.1~70.0 | 25.1~50.0 | 30.1~50.0 | 6.1~7.5 |
| 9 | 高感Highly susceptible | ≥70.1 | ≥50.1 | ≥50.1 | 7.6~9.0 |
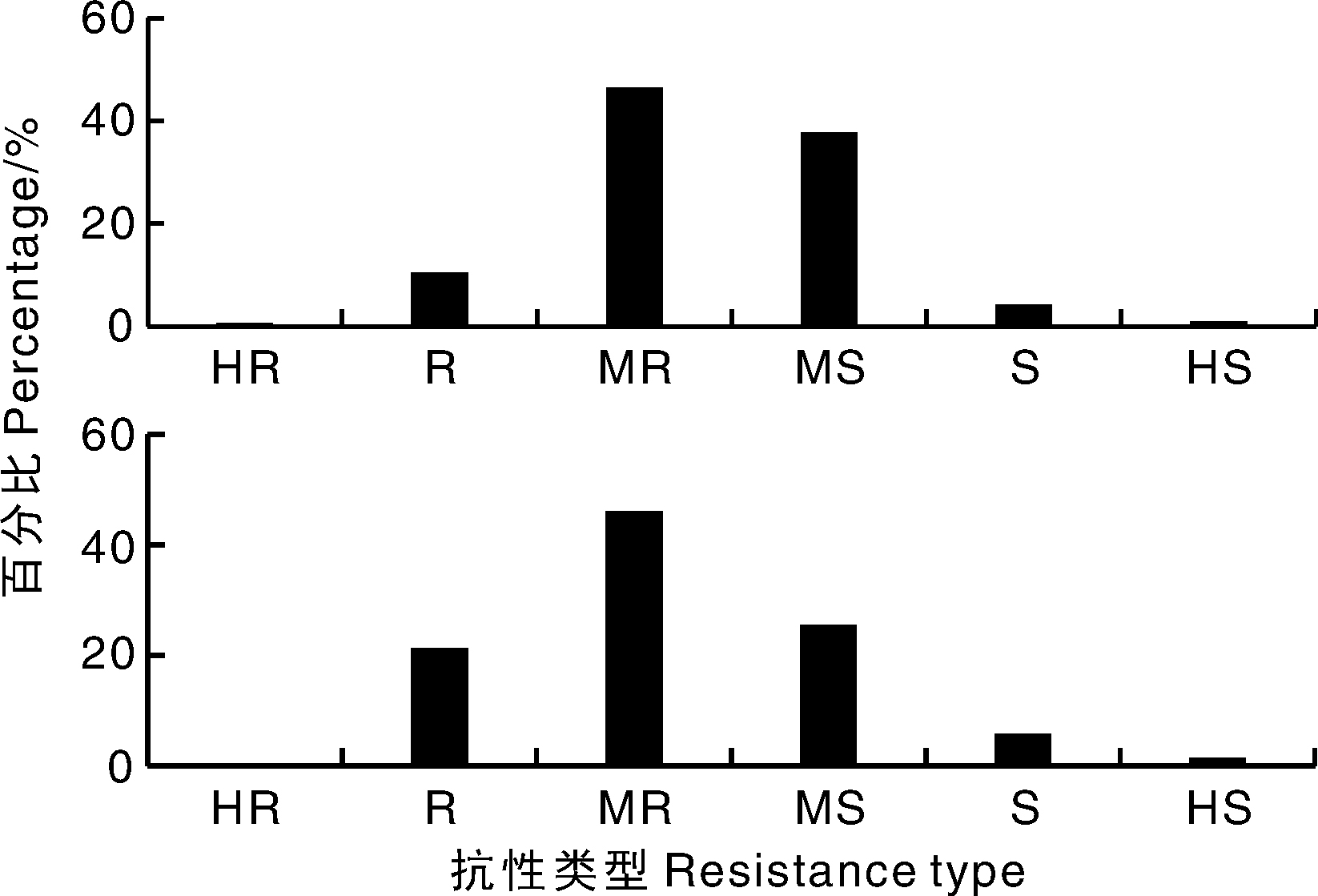
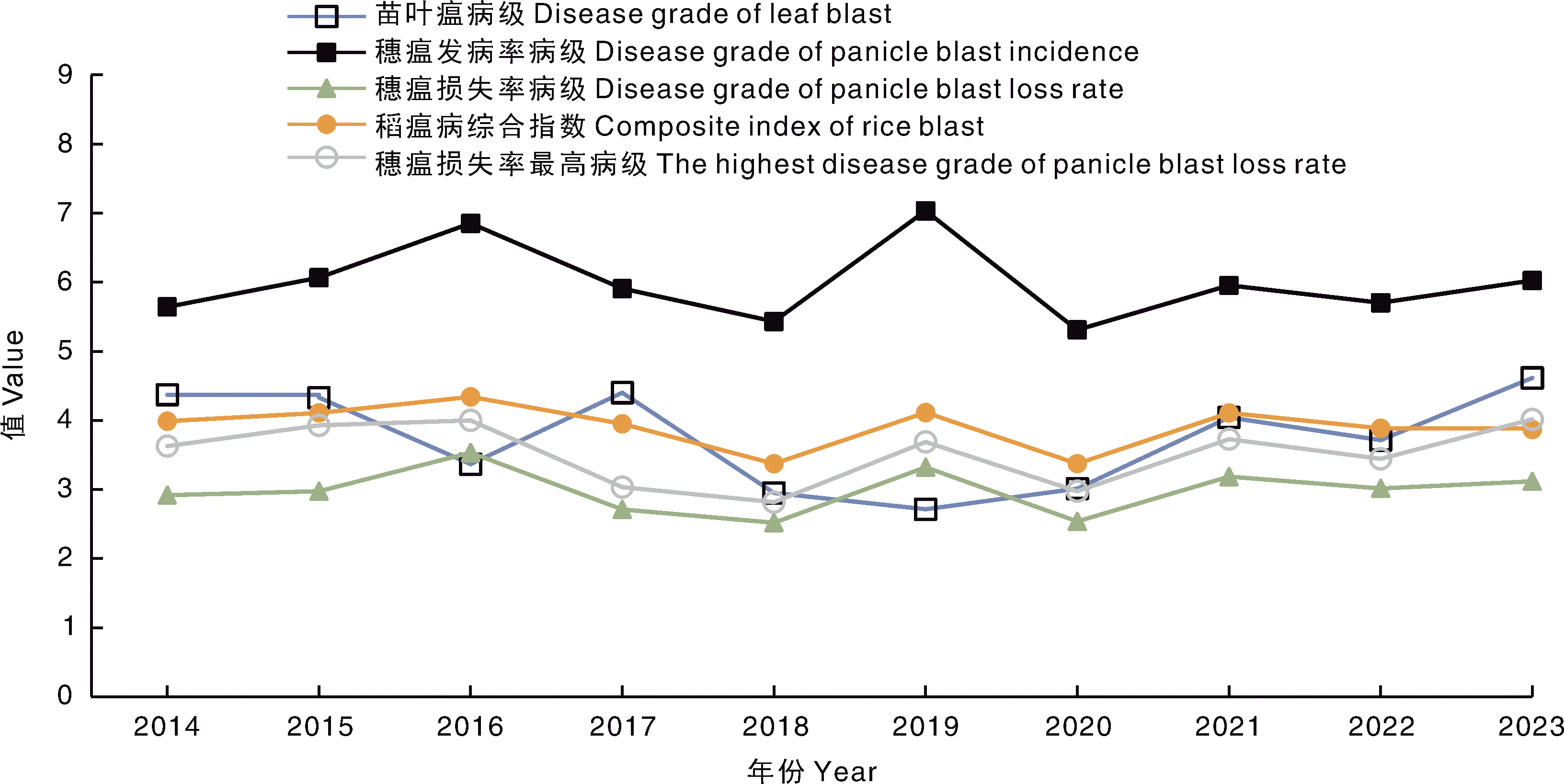
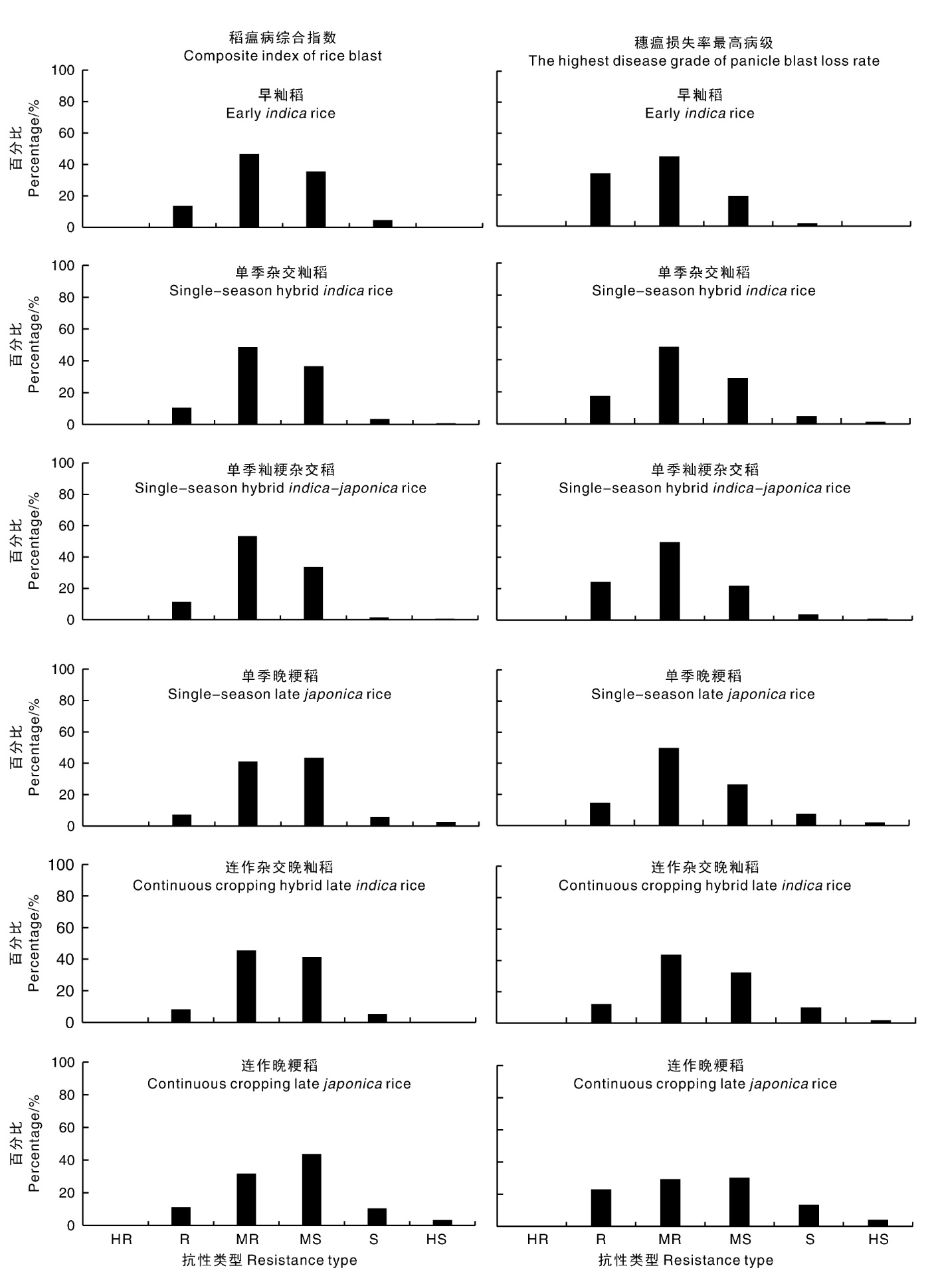
Fig.2 Distribution of overall resistance types of rice varieties based on the composite index of rice blast (top) and the highest disease grade of panicle blast loss rate (bottom) HR, Highly resistant; R, Resistant; MR, Moderately resistant; MS, Moderately susceptible; S, Susceptible; HS, Highly susceptible. The same as below.
| [1] | 鄂志国, 孙红伟, 林海, 等. 浙江育成和审定水稻品种分析(1980—2019)[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(3): 542-548. |
| E Z G, SUN H W, LIN H, et al. Analysis of rice varieties bred and certified in Zhejiang Province, China(1980-2019)[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(3): 542-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 施俊生, 王仁杯, 郁晓敏, 等. 浙江省水稻审定品种主要性状分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2019, 60(6): 865-866, 868. |
| SHI J S, WANG R B, YU X M, et al. Character analysis of approval rice varieties in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 60(6): 865-866, 868. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 杨仕华, 廖琴, 谷铁城, 等. 南方稻区国家水稻品种区域试验进展及建议[J]. 中国种业, 2009, 12: 12-14. |
| YANG S H, LIAO Q, GU T C, et al. Progress and suggestions on regional trials of national rice varieties in southern rice-growing areas[J]. China Seed Industry, 2009, 12: 12-14. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 郝中娜, 毛雪琴, 柴荣耀, 等. 国家长江中下游稻区品种区域试验籼稻稻瘟病抗性分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(2): 152-157. |
| HAO Z N, MAO X Q, CHAI R Y, et al. Analysis of resistance to rice blast in indica rice varieties from rice regional trials in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(2): 152-157. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 鄂志国, 程本义, 孙红伟, 等. 近40年我国水稻育成品种分析[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(6): 523-531. |
| E Z G, CHENG B Y, SUN H W, et al. Analysis on Chinese improved rice varieties in recent four decades[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(6): 523-531. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 沈文杰, 陈晴晴, 胡逸群, 等. 安徽省水稻区试品种(系)稻瘟病抗性鉴定和评价[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(6): 1338-1341. |
| SHEN W J, CHEN Q Q, HU Y Q, et al. Identification and evaluation of rice blast resistance of rice varieties from regional trials in Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(6): 1338-1341. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 齐中强, 于俊杰, 张荣胜, 等. 江苏省2016—2020年水稻新品种(系)和主栽品种对稻瘟病的抗病性评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(1): 91-96. |
| QI Z Q, YU J J, ZHANG R S, et al. Identification and evaluation of resistance of new rice cultivars(lines) and main cultivars to rice blast in Jiangsu Province from 2016 to 2020[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(1): 91-96. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 李莉, 刘晓梅, 姜兆远, 等. 2015—2019年吉林省水稻区试品种(系)稻瘟病抗性鉴定与评价[J]. 东北农业科学, 2020, 45(5): 43-46. |
| LI L, LIU X M, JIANG Z Y, et al. Identification and evaluation of blast resistance of rice varieties (lines) in the regional test in Jilin Province from 2015 to 2019[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 45(5): 43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 姜秀英, 于永梅, 魏松红, 等. 2016—2020年辽宁省水稻区域试验参试品种(系)稻瘟病抗性评述[J]. 北方水稻, 2024, 54(1): 12-16. |
| JIANG X Y, YU Y M, WEI S H, et al. Evaluation of resistance to rice blast in rice varieties (lines) from regional trails in Liaoning Province from 2016 to 2020[J]. Northern Rice, 2024, 54(1): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 中华人民共和国农业部.水稻品种试验稻瘟病抗性鉴定与评价技术规程: NY/T 2646—2014[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. |
| [11] | 陶荣祥, 陈建明, 廖琴. 水稻病虫害田间手册:病虫害鉴别与抗性鉴定[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2006. |
| [12] | HAO Z N, QIU H P, ZHANG Z, et al. Mass cultivation of conidia of Pyricularia oryzae[J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2022, 104: 363-368. |
| [13] | International Rice Research Institute (IRRI). Standard evaluation system for rice (SES)[M]. Manila: IRRI, 2002. |
| [14] | 肖丹凤, 张佩胜, 王玲, 等. 中国稻瘟病菌种群分布及优势生理小种的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(3): 312-320. |
| XIAO D F, ZHANG P S, WANG L, et al. Research progress on populations and physiological race distribution of rice blast pathogen(Magnaporthe grisea) in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2013, 27(3): 312-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | ZHU L, SUN J, WU G C, et al. Identification of rice varieties and determination of their geographical origin in China using Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 82: 175-182. |
| [16] | 郝中娜, 张红志, 朱旭东, 等. 籼、粳稻上分离的稻瘟病菌致病性分析[J]. 植物保护学报, 2006, 33(4): 337-340. |
| HAO Z N, ZHANG H Z, ZHU X D, et al. Pathogenicity analysis of Magnaporthe grisea derive from indica and japonica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2006, 33(4): 337-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | HAO Z N, ZHANG Z, QIU H P, et al. Differences in pathogenicity and physiologic races between Pyricularia oryzae isolates from indica and japonica rice varieties[J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2021, 103: 1141-1146. |
| [18] | 孙漱沅. 水稻稻瘟病及其防治[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1986. |
| [19] | 林建荣, 宋昕蔚, 吴明国, 等. 籼粳超级杂交稻育种技术创新与品种培育[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(2): 207-218. |
| LIN J R, SONG X W, WU M G, et al. Breeding technology innovation of indica-japonica super hybrid rice and varietal breeding[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(2): 207-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 阮晓亮, 石建尧, 陆永法, 等. 浙江省籼粳杂交晚稻品种发展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2016, 22(4): 8-12. |
| RUAN X L, SHI J Y, LU Y F, et al. Development and prospect of indica-japonica hybrid late rice cultivar in Zhejiang Province[J]. China Rice, 2016, 22(4): 8-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | LIU Guomin, ZHENG Xu, LIAO Yujiao, QIN Yexin, QIN Weizhi. Effect of grafting on cold resistance of potato seedlings under low temperature stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1615-1623. |
| [2] | WANG Yidi, WANG Jinglei, HU Tianhua, XU Yunmin, BAO Chonglai. Development of molecular markers for clubroot resistance and their application in Brassicaceae breeding [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1272-1284. |
| [3] | YI Ming, SUN Hong, SHEN Qi, TANG Jiangwu. Research progress on ectopic fermentation system in treatment of fecal residue and waste water of livestock and poultry [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1390-1396. |
| [4] | WANG Chao, LI Yanjie, NIU Yun, WEN Lianhao, CHEN Jingjing, WU Hongzhi, YANG Yuyong, WU Yandi. Biological characterization of black spot pathogens in Rosa chinensis and evaluation of varietal resistance [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(5): 1087-1096. |
| [5] | HU Xinrou, WANG Mei, ZHANG Yafen, CAI Weiming, JIN Qunli. Effect of abiotic stress on growth development and response mechanism of Ganoderma [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(5): 1182-1190. |
| [6] | ZHAO Jiahao, XU Xing, ZHOU Weidong, YANG Hua, ZHAO Xihong, WANG Wen. Characteristics of bacteria community and antibiotic resistance genes in piggery wastewater and surrounding water environment [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(3): 621-632. |
| [7] | WU Jiaqi, ZHU Xueming, BAO Jiandong, WANG Caoyi, ZHOU Xiaoyu, LI Lin, LIN Fucheng. Research progress on biological control of rice blast [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(3): 736-744. |
| [8] | GU Xingguo, FANG Qiaokun. Distribution characteristics and value assessment of agricultural heritage systems in Zhejiang Province, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 493-506. |
| [9] | YANG Zhijian, RUAN Miaohong, LIN Shanshan, LIN Shiqiang, LIAO Sufeng, CHEN Xuanyang. Breeding and growth characteristics of purple sweet potato cultivar Jinshu 20 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2249-2257. |
| [10] | XU Wenwu, WANG Zhenzhen, LU Lizhi. Analysis on egg-laying performance and stress resistance of four egg duck breeds [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(8): 1773-1778. |
| [11] | HAN Qingyu, CHENG Linrun, LI Yuehong, QIU Zhiling, HOU Meng, LOU Binggan. Evaluation of resistance to foot rot and analysis of disease resistance related indexes of 60 sweet potato germplasm resources [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(7): 1616-1625. |
| [12] | CHU Tianfen, LEI Ling, LI Qinfeng, WU Ping, HONG Wenjie, ZHENG Weiran. Quality safety risk assessment of watermelon industry in Zhejiang Province, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(5): 1153-1160. |
| [13] | LI Jingjing, LI Chuang, LU Yanan, ZHENG Wenming. Identification and expression analysis of Thionin-like gene family in wheat [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(4): 729-737. |
| [14] | SONG Peng, LI Lixiang, JIANG Houlong, WANG Ru, LI Hui, ZHAO Pengyu, ZHANG Jun, QIN Pingwei, REN Jiangbo, CHEN Qingming. Effect of application of Brevibacillus laterosporus on potassium content of cured tobacco leaves and physiological characteristics of tobacco plants [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(3): 494-502. |
| [15] | CHAI Rongyao, YOU Yuxin, QIU Haiping, GUO Junning, ZHANG Zhen, LI Bin, SHEN Shengfa, WANG Yanli. Establishment of sweet potato stem rot resistance identification technology and analysis of germplasm resource resistance [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(3): 569-578. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||