Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2408-2425.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240992
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress on the mechanisms of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in stabilizing soil aggregates and organic carbon
LIAO Yanfeng1,2( ), ZHOU Jiahao1,*(
), ZHOU Jiahao1,*( ), YAN Xinyu1, LIU Junyao1, LI Tao1, ZHU Hai1,3, YANG Jun1,3,*(
), YAN Xinyu1, LIU Junyao1, LI Tao1, ZHU Hai1,3, YANG Jun1,3,*( )
)
- 1. College of Agriculture, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434025, Hubei, China
2. Key Laboratory of Agro-Ecological Processes in Subtropical Regions, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha 410125, China
3. Engineering Research Center of Ecology and Agricultural Use of Wetland, Ministry of Education, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434025, Hubei, China
-
Received:2024-11-15Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIAO Yanfeng, ZHOU Jiahao, YAN Xinyu, LIU Junyao, LI Tao, ZHU Hai, YANG Jun. Research progress on the mechanisms of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in stabilizing soil aggregates and organic carbon[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2408-2425.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240992
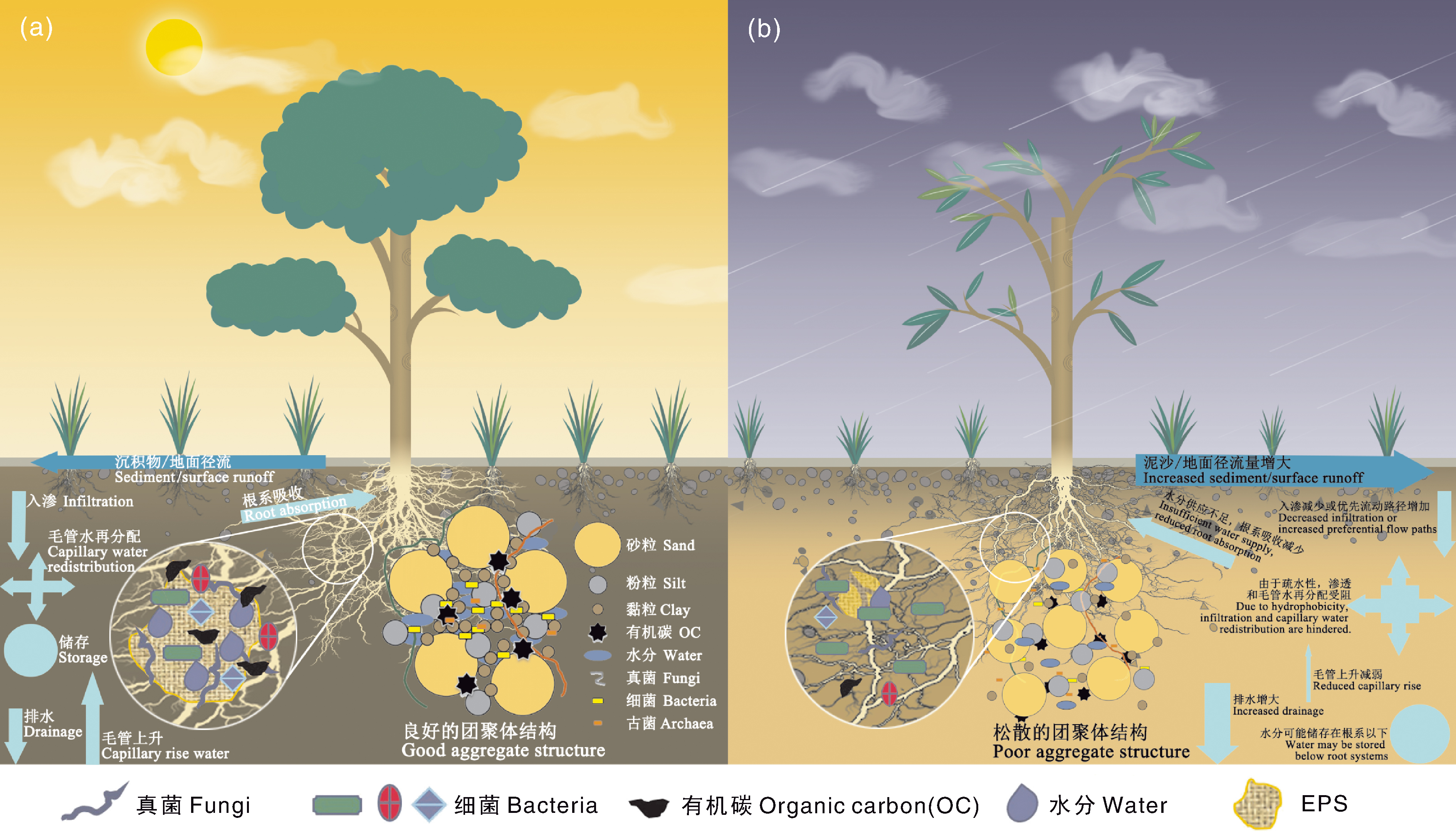
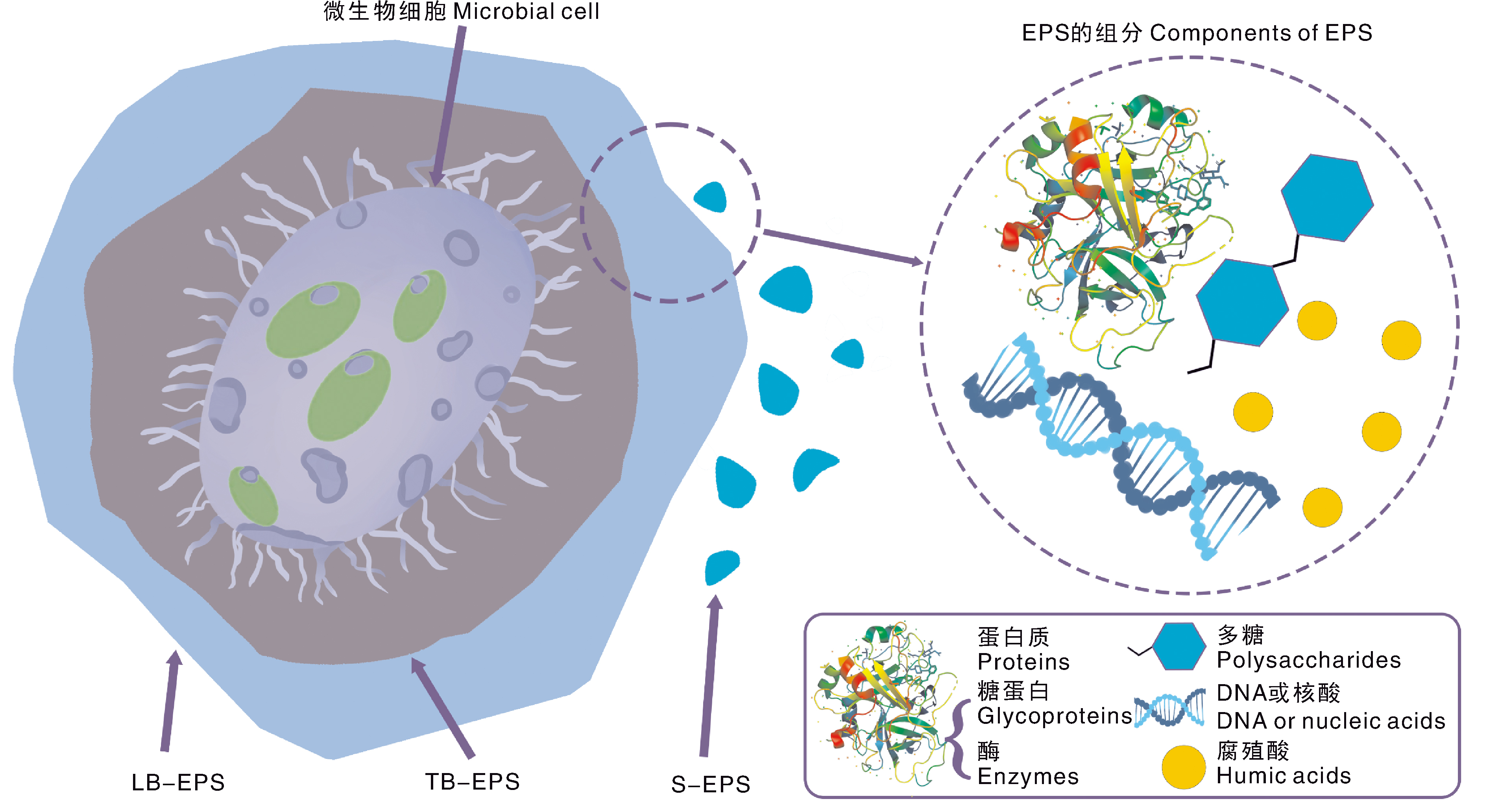
Fig.1 Key roles of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in aggregate and organic carbon distribution in healthy (a) and degraded (b) soils This figure illustrates the distinct roles of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in healthy versus degraded soils, emphasizing the critical importance of aggregate structure and organic carbon distribution for soil health. In healthy soil [panel (a)], EPS functions as a biological binding agent that firmly binds soil particles into stable aggregates, effectively preserving organic carbon storage within the soil matrix. Through its cohesive properties, EPS immobilizes microorganisms, fungi, and organic carbon within the aggregate core, while facilitating optimal water distribution through capillary action. This creates a stable reservoir of moisture and nutrients accessible to plant roots. In contrast, panel (b) demonstrates degraded soil conditions where diminished EPS content leads to structural disintegration. The weakened binding capacity results in loose aggregate formation, rapid water loss, and inefficient organic carbon sequestration. The absence of EPS-mediated protection accelerates organic carbon loss through leaching while reducing microbial activity. Consequently, the degraded soil exhibits compromised aggregate architecture, diminished water and nutrient retention capacities, and restricted plant growth potential. This comparative analysis underscores EPS’s indispensable role in maintaining soil structural integrity, stabilizing carbon reservoirs, and enhancing hydrological regulation. The schematic representation was developed based on methodologies described by Coban et al.[19].
| 功能类别 Functional category | EPS功能 EPS function | 参与EPS功能表达的组分 Components involved in the expression of EPS function | 对土壤团聚体形成与有机碳稳定的潜在作用 Potential role for soil aggregates formation and organic carbon stabilization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构与附着功能 Structure and attachment functions | 黏附作用 Adhesion | 多糖、蛋白质(如菌毛)、环境DNA(eDNA) Polysaccharides, proteins (e.g., pili), environmental DNA (eDNA) | 增强微生物与土壤颗粒间的黏结力,形成稳定的团聚体 Enhancing adhesion between microorganisms and soil particles, forming stable aggregates | |
| 细菌细胞聚集 Bacterial cell aggregation | 多糖、蛋白质、DNA Polysaccharides, proteins, DNA | 支持微生物群体的聚集,促进团聚体内的微环境稳定 Supporting microbial community aggregation, stabilizing the microenvironment within aggregates | ||
| 生物膜的内聚性 Biofilm cohesion | 中性和带电多糖、蛋白质(如淀粉样 蛋白、凝集素)、DNA Neutral and charged polysaccharides, proteins (e.g., amyloid proteins, lectins), DNA | 提高团聚体的机械稳定性和持水性,增强结构完整性 Enhancing mechanical stability and water retention of aggregates, improving structural integrity | ||
| 水分保持 Water retention | 亲水性多糖和蛋白质,形成保护膜的 疏水性蛋白 Hydrophilic polysaccharides and proteins, hydrophobic proteins forming protective films | 在土壤微环境中保水,增强抗干旱能力,有助于有机碳的保护与固定 Retaining water in the soil microenvironment, enhancing drought resistance, aiding organic carbon protection and stabilization | ||
| 保护与存储功能 Protective and storage functions | 抗菌保护屏障 Antimicrobial protective barrier | 多糖、蛋白质 Polysaccharides, proteins | 减少微生物捕食和侵害,支持有机碳的稳定性 Reducing microbial predation and damage, supporting organic carbon stability | |
| 吸附极性有机化 合物 Adsorption of polar organic compounds | 带电或疏水性的多糖和蛋白质 Charged or hydrophobic polysaccharides and proteins | 捕获土壤中的营养,支持微生物活性,提升碳的固定与利用 Capturing nutrients in the soil, supporting microbial activity, enhancing carbon sequestration and utilization | ||
| 吸附无机离子 Adsorption of inorganic ions | 带电多糖和蛋白质(含无机成分, 如磷酸盐和硫酸盐) Charged polysaccharides and proteins (including inorganic components, such as phosphates and sulfates) | 增强土壤团聚体的稳定性,减少有害金属移动性,保护土壤碳库 Enhancing soil aggregate stability, reducing mobility of harmful metals, protecting soil carbon pools | ||
| 遗传信息 Genetic information | DNA | 提供基因交换的基础,维护微生物多样性,稳定土壤生态系统功能 Providing basis for gene exchange, maintaining microbial diversity, stabilizing soil ecosystem functions | ||
| 多余能量的存储 Excess energy storage | 多糖 Polysaccharides | 碳氮失衡时的碳储存,有助于土壤有机碳的积累与稳定 Serving as a carbon reserve under carbon-nitrogen imbalances, contributing to soil organic carbon accumulation and stabilization | ||
| 资源获取与代谢功能 Resource acquisition and metabolic functions | 吸附非极性 有机物 Adsorption of non- polar organic matter | 蛋白质,疏水性区域 Proteins, hydrophobic regions | 捕获有机资源,促进土壤有机碳的积累 Capturing organic resources, promoting the accumulation of soil organic carbon | |
| 吸附颗粒 Particle adsorption | 黏性基质成分 Adhesive matrix components | 提高团聚体的形成和稳定性,保护有机碳 Enhancing the formation and stability of soil aggregates, protecting organic carbon | ||
| 增强对基质中 捕获资源的获 取能力 Enhancement of resource acquisition from the matrix | 膜小泡(含核酸、酶、蛋白质、脂多糖等) Membrane vesicles (including nucleic acids, enzymes, proteins, lipopolysaccharides) | 支持微生物的营养获取,增强团聚体内有机碳的利用和稳定性 Supporting microbial nutrient acquisition, stabilizing and enhancing organic carbon within aggregates | ||
| 酶促活性 Enzymatic activity | 蛋白质 Proteins | 增强有机质分解与利用,提升土壤有机碳的周转和存储 Promoting the decomposition and utilization of organic matter, improving soil organic carbon turnover and storage | ||
| 营养来源 Nutrient source | 几乎所有的EPS成分 Potentially all EPS components | 为土壤微生物提供碳、氮和磷,有助于团聚体中的碳稳定和土壤肥力 Providing carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus for soil microorganisms, aiding carbon stabilization in aggregates, improving soil fertility | ||
| 细胞间信息 Intercellular signaling | 多糖 Polysaccharides | 调控土壤微生物群体动态,优化有机碳的周转效率 Regulating microbial community dynamics, optimizing organic carbon turnover efficiency | ||
| 电子供体或受体 Electron donor or acceptor | 蛋白质(如菌毛、纳米导线)、腐殖质 Proteins (e.g., pili, nanowires), humic substances | 增强氧化还原活性,促进代谢,支持团聚体结构与碳的稳定 Enhancing redox activity, supporting metabolic processes, stabilizing aggregate structure and carbon | ||
| 通过酶向基质的 输出捕获资源 Resource capture through enzymatic output to the matrix | 外膜小泡(含核酸、酶蛋白、脂多糖、磷脂) Outer membrane vesicles (including nucleic acids, enzymes, proteins, lipopolysaccharides, phospholipids) | 提高有机质分解能力,增加碳的有效性,促进团聚体碳周转 Enhancing organic matter decomposition, increasing carbon availability, promoting carbon turnover of aggregates | ||
| 酶的结合 Enzyme binding | 多糖、酶蛋白 Polysaccharides, enzyme proteins | 稳定酶活性,支持团聚体内有机碳的有效性与稳定性 Stabilizing enzymatic activity, supporting the effectiveness and stability of organic carbon within aggregates | ||
Table 1 Functions of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) components and their potential roles in soil aggregate formation and organic carbon stabilization (adapted from Flemming et al. [20])
| 功能类别 Functional category | EPS功能 EPS function | 参与EPS功能表达的组分 Components involved in the expression of EPS function | 对土壤团聚体形成与有机碳稳定的潜在作用 Potential role for soil aggregates formation and organic carbon stabilization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 结构与附着功能 Structure and attachment functions | 黏附作用 Adhesion | 多糖、蛋白质(如菌毛)、环境DNA(eDNA) Polysaccharides, proteins (e.g., pili), environmental DNA (eDNA) | 增强微生物与土壤颗粒间的黏结力,形成稳定的团聚体 Enhancing adhesion between microorganisms and soil particles, forming stable aggregates | |
| 细菌细胞聚集 Bacterial cell aggregation | 多糖、蛋白质、DNA Polysaccharides, proteins, DNA | 支持微生物群体的聚集,促进团聚体内的微环境稳定 Supporting microbial community aggregation, stabilizing the microenvironment within aggregates | ||
| 生物膜的内聚性 Biofilm cohesion | 中性和带电多糖、蛋白质(如淀粉样 蛋白、凝集素)、DNA Neutral and charged polysaccharides, proteins (e.g., amyloid proteins, lectins), DNA | 提高团聚体的机械稳定性和持水性,增强结构完整性 Enhancing mechanical stability and water retention of aggregates, improving structural integrity | ||
| 水分保持 Water retention | 亲水性多糖和蛋白质,形成保护膜的 疏水性蛋白 Hydrophilic polysaccharides and proteins, hydrophobic proteins forming protective films | 在土壤微环境中保水,增强抗干旱能力,有助于有机碳的保护与固定 Retaining water in the soil microenvironment, enhancing drought resistance, aiding organic carbon protection and stabilization | ||
| 保护与存储功能 Protective and storage functions | 抗菌保护屏障 Antimicrobial protective barrier | 多糖、蛋白质 Polysaccharides, proteins | 减少微生物捕食和侵害,支持有机碳的稳定性 Reducing microbial predation and damage, supporting organic carbon stability | |
| 吸附极性有机化 合物 Adsorption of polar organic compounds | 带电或疏水性的多糖和蛋白质 Charged or hydrophobic polysaccharides and proteins | 捕获土壤中的营养,支持微生物活性,提升碳的固定与利用 Capturing nutrients in the soil, supporting microbial activity, enhancing carbon sequestration and utilization | ||
| 吸附无机离子 Adsorption of inorganic ions | 带电多糖和蛋白质(含无机成分, 如磷酸盐和硫酸盐) Charged polysaccharides and proteins (including inorganic components, such as phosphates and sulfates) | 增强土壤团聚体的稳定性,减少有害金属移动性,保护土壤碳库 Enhancing soil aggregate stability, reducing mobility of harmful metals, protecting soil carbon pools | ||
| 遗传信息 Genetic information | DNA | 提供基因交换的基础,维护微生物多样性,稳定土壤生态系统功能 Providing basis for gene exchange, maintaining microbial diversity, stabilizing soil ecosystem functions | ||
| 多余能量的存储 Excess energy storage | 多糖 Polysaccharides | 碳氮失衡时的碳储存,有助于土壤有机碳的积累与稳定 Serving as a carbon reserve under carbon-nitrogen imbalances, contributing to soil organic carbon accumulation and stabilization | ||
| 资源获取与代谢功能 Resource acquisition and metabolic functions | 吸附非极性 有机物 Adsorption of non- polar organic matter | 蛋白质,疏水性区域 Proteins, hydrophobic regions | 捕获有机资源,促进土壤有机碳的积累 Capturing organic resources, promoting the accumulation of soil organic carbon | |
| 吸附颗粒 Particle adsorption | 黏性基质成分 Adhesive matrix components | 提高团聚体的形成和稳定性,保护有机碳 Enhancing the formation and stability of soil aggregates, protecting organic carbon | ||
| 增强对基质中 捕获资源的获 取能力 Enhancement of resource acquisition from the matrix | 膜小泡(含核酸、酶、蛋白质、脂多糖等) Membrane vesicles (including nucleic acids, enzymes, proteins, lipopolysaccharides) | 支持微生物的营养获取,增强团聚体内有机碳的利用和稳定性 Supporting microbial nutrient acquisition, stabilizing and enhancing organic carbon within aggregates | ||
| 酶促活性 Enzymatic activity | 蛋白质 Proteins | 增强有机质分解与利用,提升土壤有机碳的周转和存储 Promoting the decomposition and utilization of organic matter, improving soil organic carbon turnover and storage | ||
| 营养来源 Nutrient source | 几乎所有的EPS成分 Potentially all EPS components | 为土壤微生物提供碳、氮和磷,有助于团聚体中的碳稳定和土壤肥力 Providing carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus for soil microorganisms, aiding carbon stabilization in aggregates, improving soil fertility | ||
| 细胞间信息 Intercellular signaling | 多糖 Polysaccharides | 调控土壤微生物群体动态,优化有机碳的周转效率 Regulating microbial community dynamics, optimizing organic carbon turnover efficiency | ||
| 电子供体或受体 Electron donor or acceptor | 蛋白质(如菌毛、纳米导线)、腐殖质 Proteins (e.g., pili, nanowires), humic substances | 增强氧化还原活性,促进代谢,支持团聚体结构与碳的稳定 Enhancing redox activity, supporting metabolic processes, stabilizing aggregate structure and carbon | ||
| 通过酶向基质的 输出捕获资源 Resource capture through enzymatic output to the matrix | 外膜小泡(含核酸、酶蛋白、脂多糖、磷脂) Outer membrane vesicles (including nucleic acids, enzymes, proteins, lipopolysaccharides, phospholipids) | 提高有机质分解能力,增加碳的有效性,促进团聚体碳周转 Enhancing organic matter decomposition, increasing carbon availability, promoting carbon turnover of aggregates | ||
| 酶的结合 Enzyme binding | 多糖、酶蛋白 Polysaccharides, enzyme proteins | 稳定酶活性,支持团聚体内有机碳的有效性与稳定性 Stabilizing enzymatic activity, supporting the effectiveness and stability of organic carbon within aggregates | ||
| 类别 Category | 影响因素 Influencing factors | 影响机制 Mechanisms | 潜在功能响应 Potential functional responses | 参考文献 References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境条件 Environmental conditions | 温度 Temperature | 温度直接影响微生物代谢活动和生长速率,在适宜温度下(如25~35 ℃),微生物代谢加快,EPS分泌量增加;低温下,代谢活动减缓,EPS生成量减少 Temperature directly affects microbial metabolism and growth rates. At optimal temperatures (e.g., 25-35 ℃), microbial activity increases EPS secretion, while low temperatures reduce EPS production | 适宜温度下,EPS含量增加,促进土壤团聚体形成,增强土壤的稳定性和保水性;极端温度下,EPS生成量减少,土壤团聚体稳定性减弱 Increased EPS content at optimal temperatures promotes soil aggregate formation, enhancing soil stability and water retention. Extreme temperatures reduce EPS production, weakening aggregate stability | [ | ||||
| 湿度 Moisture | 适宜湿度下,EPS生成量增加,增强土壤颗粒的黏结力和水分保持能力;干旱条件下,EPS生成量下降,但生物膜有助于维持微生物生存 Under optimal moisture conditions, EPS production increases, enhancing soil particle adhesion and water retention. In drought conditions, EPS production decreases, but biofilms help sustain microbial survival | 湿润环境下,土壤中EPS含量增加,提升团聚体稳定性和抗侵蚀性;干旱条件下,EPS的保水特性帮助植物和微生物生存 In moist environments, increased EPS content improves aggregate stability and erosion resistance. Under drought, the water retention properties of EPS support plant and microbial survival | [ | |||||
| pH值 pH value | pH值影响微生物的生长环境:在中性到弱碱性条件下(6.5~7.5),大多数细菌会生成更多EPS;在酸性或碱性条件下,EPS生成量减少 pH value influences microbial growth conditions. Most bacteria produce more EPS under neutral to slightly alkaline conditions (6.5-7.5). Acidic or highly alkaline conditions reduce EPS production | 中性或微酸性条件下,EPS功能增强,促进土壤团聚体稳定和碳固定;极端pH值下,EPS结构不稳定,保护功能减弱 Neutral or slightly acidic conditions enhance EPS function, stabilizing aggregates and sequestering carbon. Extreme pH value destabilizes EPS structure, reducing its protective function | [ | |||||
| 盐分/重金属 Salinity/heavy metals | 高盐度增加重金属的移动性,对微生物产生金属毒性,刺激微生物生成EPS以缓解毒性并增强对重金属的吸附 High salinity increases heavy metal mobility and toxicity to microbes, stimulates EPS production to mitigate toxicity and enhance heavy metal adsorption | EPS能有效固定重金属,减少污染物迁移,促进土壤修复和健康 EPS effectively immobilizes heavy metals, reducing pollutant migration and promoting soil remediation and health | [ | |||||
| 营养物质 Nutrients | 碳源 Carbon source | 碳源是EPS合成的主要原料,在碳源(如葡萄糖和蔗糖)充足条件下,EPS生成量增加3~5倍,形成保护性EPS基质 Carbon is the primary raw material for EPS synthesis. Under sufficient carbon (e.g., glucose or sucrose) availability, EPS production increases by 3-5 times, forming protective EPS matrices | 充足碳源提升EPS生成量,增强土壤团聚体的稳定性,提高土壤碳固定和水分保持能力 Adequate carbon sources enhance EPS production, improving soil aggregate stability, carbon sequestration, and water retention | [ | ||||
| 氮源 Nitrogen source | 氮源是EPS合成所需的重要成分,适量氮源促进EPS生成,但氮源过量时,微生物优先分解氮而非生成EPS Nitrogen is essential for EPS synthesis. Moderate nitrogen levels increase EPS production, but excessive nitrogen leads microbes to prioritize nitrogen metabolism over EPS synthesis | 适量氮源提升微生物活性和EPS生成,增强土壤团聚体和碳固定能力;过量氮源抑制EPS生成,影响土壤平衡 Moderate nitrogen enhances microbial activity and EPS production, stabilizing soil aggregates and carbon sequestration. Excessive nitrogen suppresses EPS production, disrupting soil balance | [ | |||||
| 碳氮比 C/N ratio | 碳氮比适宜(如8∶1)时,EPS生成量最多;当碳源丰富但氮源不足时,微生物优先用于能量代谢而非EPS生成 Optimal C/N ratio (e.g., 8∶1) maximizes EPS production. When carbon is abundant but nitrogen is insufficient, microbes prioritize energy metabolism over EPS synthesis | 适宜的碳氮比促进EPS合成,增强土壤团聚体的稳定性和养分保持能力;不平衡的碳氮比会导致微生物生态失衡 Optimal C/N ratio boosts EPS synthesis, enhancing soil aggregate stability and nutrient retention. Imbalanced C/N ratios disrupt microbial ecology | [ | |||||
| 生物因素 Biological factors | 种群结构 Population structure | 微生物群落的多样性提高EPS生成量,多样性较高的群落中,EPS生成量增加50%。特定微生物(如假单胞菌和蓝藻)共同作用更高效生成EPS Microbial diversity increases EPS production. Diverse microbial communities produce 50% more EPS. Specific microbes (e.g., Pseudomonas and Cyanobacteria) collaborate to enhance EPS production | 丰富的微生物种群多样性增强EPS数量和质量,形成稳定的土壤团聚体,促进土壤团聚体稳定和碳固定 Rich microbial diversity improves EPS quantity and quality, forming stable soil aggregates and promoting aggregate stability and carbon sequestration | [ | ||||
| 微生物活性 Microbial activity | 较高的微生物活性提高EPS生成速率,在温暖湿润条件下,活跃微生物群落生成的EPS量显著增加 Increased microbial activity accelerates EPS production. In warm and moist conditions, active microbial communities significantly boost EPS secretion | 活跃的微生物活动提升EPS生成量,增加土壤团聚体数量和稳定性,提高抗侵蚀和保水能力 Active microbial activity increases EPS production, enhancing aggregate quantity and stability, as well as erosion resistance and water retention | [ | |||||
| 交互作用 Interactions | 微生物之间的共生、竞争和代谢互补能增加EPS多样性和稳定性;细菌与真菌的共生在根际促进EPS生成 Symbiosis, competition, and metabolic complementarity among microbes increase EPS diversity and stability. Bacteria-fungi symbiosis in the rhizosphere enhances EPS production | 微生物之间的互作关系使EPS更具多样性和功能性,形成强大土壤团聚体,促进碳固定和土壤稳定 Microbial interactions make EPS more diverse and functional, forming robust soil aggregates and promoting carbon sequestration and soil stability | [ | |||||
Table 2 Mechanism of different influencing factors on extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production and their potential functional responses
| 类别 Category | 影响因素 Influencing factors | 影响机制 Mechanisms | 潜在功能响应 Potential functional responses | 参考文献 References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境条件 Environmental conditions | 温度 Temperature | 温度直接影响微生物代谢活动和生长速率,在适宜温度下(如25~35 ℃),微生物代谢加快,EPS分泌量增加;低温下,代谢活动减缓,EPS生成量减少 Temperature directly affects microbial metabolism and growth rates. At optimal temperatures (e.g., 25-35 ℃), microbial activity increases EPS secretion, while low temperatures reduce EPS production | 适宜温度下,EPS含量增加,促进土壤团聚体形成,增强土壤的稳定性和保水性;极端温度下,EPS生成量减少,土壤团聚体稳定性减弱 Increased EPS content at optimal temperatures promotes soil aggregate formation, enhancing soil stability and water retention. Extreme temperatures reduce EPS production, weakening aggregate stability | [ | ||||
| 湿度 Moisture | 适宜湿度下,EPS生成量增加,增强土壤颗粒的黏结力和水分保持能力;干旱条件下,EPS生成量下降,但生物膜有助于维持微生物生存 Under optimal moisture conditions, EPS production increases, enhancing soil particle adhesion and water retention. In drought conditions, EPS production decreases, but biofilms help sustain microbial survival | 湿润环境下,土壤中EPS含量增加,提升团聚体稳定性和抗侵蚀性;干旱条件下,EPS的保水特性帮助植物和微生物生存 In moist environments, increased EPS content improves aggregate stability and erosion resistance. Under drought, the water retention properties of EPS support plant and microbial survival | [ | |||||
| pH值 pH value | pH值影响微生物的生长环境:在中性到弱碱性条件下(6.5~7.5),大多数细菌会生成更多EPS;在酸性或碱性条件下,EPS生成量减少 pH value influences microbial growth conditions. Most bacteria produce more EPS under neutral to slightly alkaline conditions (6.5-7.5). Acidic or highly alkaline conditions reduce EPS production | 中性或微酸性条件下,EPS功能增强,促进土壤团聚体稳定和碳固定;极端pH值下,EPS结构不稳定,保护功能减弱 Neutral or slightly acidic conditions enhance EPS function, stabilizing aggregates and sequestering carbon. Extreme pH value destabilizes EPS structure, reducing its protective function | [ | |||||
| 盐分/重金属 Salinity/heavy metals | 高盐度增加重金属的移动性,对微生物产生金属毒性,刺激微生物生成EPS以缓解毒性并增强对重金属的吸附 High salinity increases heavy metal mobility and toxicity to microbes, stimulates EPS production to mitigate toxicity and enhance heavy metal adsorption | EPS能有效固定重金属,减少污染物迁移,促进土壤修复和健康 EPS effectively immobilizes heavy metals, reducing pollutant migration and promoting soil remediation and health | [ | |||||
| 营养物质 Nutrients | 碳源 Carbon source | 碳源是EPS合成的主要原料,在碳源(如葡萄糖和蔗糖)充足条件下,EPS生成量增加3~5倍,形成保护性EPS基质 Carbon is the primary raw material for EPS synthesis. Under sufficient carbon (e.g., glucose or sucrose) availability, EPS production increases by 3-5 times, forming protective EPS matrices | 充足碳源提升EPS生成量,增强土壤团聚体的稳定性,提高土壤碳固定和水分保持能力 Adequate carbon sources enhance EPS production, improving soil aggregate stability, carbon sequestration, and water retention | [ | ||||
| 氮源 Nitrogen source | 氮源是EPS合成所需的重要成分,适量氮源促进EPS生成,但氮源过量时,微生物优先分解氮而非生成EPS Nitrogen is essential for EPS synthesis. Moderate nitrogen levels increase EPS production, but excessive nitrogen leads microbes to prioritize nitrogen metabolism over EPS synthesis | 适量氮源提升微生物活性和EPS生成,增强土壤团聚体和碳固定能力;过量氮源抑制EPS生成,影响土壤平衡 Moderate nitrogen enhances microbial activity and EPS production, stabilizing soil aggregates and carbon sequestration. Excessive nitrogen suppresses EPS production, disrupting soil balance | [ | |||||
| 碳氮比 C/N ratio | 碳氮比适宜(如8∶1)时,EPS生成量最多;当碳源丰富但氮源不足时,微生物优先用于能量代谢而非EPS生成 Optimal C/N ratio (e.g., 8∶1) maximizes EPS production. When carbon is abundant but nitrogen is insufficient, microbes prioritize energy metabolism over EPS synthesis | 适宜的碳氮比促进EPS合成,增强土壤团聚体的稳定性和养分保持能力;不平衡的碳氮比会导致微生物生态失衡 Optimal C/N ratio boosts EPS synthesis, enhancing soil aggregate stability and nutrient retention. Imbalanced C/N ratios disrupt microbial ecology | [ | |||||
| 生物因素 Biological factors | 种群结构 Population structure | 微生物群落的多样性提高EPS生成量,多样性较高的群落中,EPS生成量增加50%。特定微生物(如假单胞菌和蓝藻)共同作用更高效生成EPS Microbial diversity increases EPS production. Diverse microbial communities produce 50% more EPS. Specific microbes (e.g., Pseudomonas and Cyanobacteria) collaborate to enhance EPS production | 丰富的微生物种群多样性增强EPS数量和质量,形成稳定的土壤团聚体,促进土壤团聚体稳定和碳固定 Rich microbial diversity improves EPS quantity and quality, forming stable soil aggregates and promoting aggregate stability and carbon sequestration | [ | ||||
| 微生物活性 Microbial activity | 较高的微生物活性提高EPS生成速率,在温暖湿润条件下,活跃微生物群落生成的EPS量显著增加 Increased microbial activity accelerates EPS production. In warm and moist conditions, active microbial communities significantly boost EPS secretion | 活跃的微生物活动提升EPS生成量,增加土壤团聚体数量和稳定性,提高抗侵蚀和保水能力 Active microbial activity increases EPS production, enhancing aggregate quantity and stability, as well as erosion resistance and water retention | [ | |||||
| 交互作用 Interactions | 微生物之间的共生、竞争和代谢互补能增加EPS多样性和稳定性;细菌与真菌的共生在根际促进EPS生成 Symbiosis, competition, and metabolic complementarity among microbes increase EPS diversity and stability. Bacteria-fungi symbiosis in the rhizosphere enhances EPS production | 微生物之间的互作关系使EPS更具多样性和功能性,形成强大土壤团聚体,促进碳固定和土壤稳定 Microbial interactions make EPS more diverse and functional, forming robust soil aggregates and promoting carbon sequestration and soil stability | [ | |||||
| [1] | FONTAINE S, ABBADIE L, AUBERT M, et al. Plant-soil synchrony in nutrient cycles: learning from ecosystems to design sustainable agrosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 2024, 30(1): e17034. |
| [2] | HAO H J, LIANG Y J, PIAN D, et al. Macroaggregate is crucial in soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation under different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2024, 569: 122161. |
| [3] | SARKER T C, ZOTTI M, FANG Y N, et al. Soil aggregation in relation to organic amendment: a synthesis[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2022, 22(2): 2481-2502. |
| [4] | SIDDHARTH T, SRIDHAR P, VINILA V, et al. Environmental applications of microbial extracellular polymeric substance (EPS): a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 287: 112307. |
| [5] | FLEMMING H C, VAN HULLEBUSCH E D, LITTLE B J, et al. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in the environment, technology and medicine[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2025, 23(2): 87-105. |
| [6] | SONG B, SHANG S Y, CAI F M, et al. Microbial resistance in rhizosphere hotspots under biodegradable and conventional microplastic amendment: community and functional sensitivity[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2023, 180: 108989. |
| [7] | CAO T T, LUO Y C, SHI M, et al. Microbial interactions for nutrient acquisition in soil: miners, scavengers, and carriers[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2024, 188: 109215. |
| [8] | MASON-JONES K, ROBINSON S L, VEEN G F C, et al. Microbial storage and its implications for soil ecology[J]. The ISME Journal, 2022, 16(3): 617-629. |
| [9] | 陈君帅, 赵辉, 闫华晓, 等. 基于文献计量的微生物胞外聚合物研究可视化分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2024, 51(11): 4768-4786. |
| CHEN J S, ZHAO H, YAN H X, et al. Visual analysis of research on microbial extracellular polymeric substances based on bibliometrics[J]. Microbiology China, 2024, 51(11): 4768-4786. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | OLAGOKE F K, BETTERMANN A, NGUYEN P T B, et al. Importance of substrate quality and clay content on microbial extracellular polymeric substances production and aggregate stability in soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2022, 58(4): 435-457. |
| [11] | REDMILE-GORDON M, GREGORY A S, WHITE R P, et al. Soil organic carbon, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), and soil structural stability as affected by previous and current land-use[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 363: 114143. |
| [12] | COSTA O Y A, RAAIJMAKERS J M, KURAMAE E E. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: ecological function and impact on soil aggregation[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1636. |
| [13] | GUHRA T, STOLZE K, TOTSCHE K U. Pathways of biogenically excreted organic matter into soil aggregates[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2022, 164: 108483. |
| [14] | JUNAID M, WANG J. Interaction of nanoplastics with extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in the aquatic environment: a special reference to eco-corona formation and associated impacts[J]. Water Research, 2021, 201: 117319. |
| [15] | WANG L, HUANG Y, YANG Q S, et al. Biocrust reduces the soil erodibility of coral calcareous sand by regulating microbial community and extracellular polymeric substances on tropical coral island, South China Sea[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14: 1283073. |
| [16] | SHI K, LIAO J H, ZOU X M, et al. Forest development induces soil aggregate formation and stabilization: implications for sequestration of soil carbon and nitrogen[J]. CATENA, 2024, 246: 108363. |
| [17] | SHENG G P, YU H Q, LI X Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2010, 28(6): 882-894. |
| [18] | KUZYAKOV Y, HORWATH W R, DORODNIKOV M, et al. Review and synthesis of the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on soil processes: no changes in pools, but increased fluxes and accelerated cycles[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 128: 66-78. |
| [19] | COBAN O, DE DEYN G B, VAN DER PLOEG M. Soil microbiota as game-changers in restoration of degraded lands[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6584): abe0725. |
| [20] | FLEMMING H C. EPS: then and now[J]. Microorganisms, 2016, 4(4): 41. |
| [21] | SAHA I, DATTA S, BISWAS D. Exploring the role of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances for sustainable development in agriculture[J]. Current Microbiology, 2020, 77(11): 3224-3239. |
| [22] | HOMERO U, TORTELLA G, SANDOVAL E, et al. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) produced by Streptomyces sp. biofilms: chemical composition and anticancer properties[J]. Microbiological Research, 2021, 253: 126877. |
| [23] | NASEEM M, CHAUDHRY A N, JILANI G, et al. Biosynthesis and characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from divergent microbial and ecological bioresources[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2024, 49(7): 9043-9052. |
| [24] | 王小姣, 李梦雅, 王文丽, 等. 接种单细胞微生物对土壤团聚体形成及其稳定性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2021, 52(2): 355-360. |
| WANG X J, LI M Y, WANG W L, et al. Effect of single cell and filamentous microorganisms on formation of soil aggregates[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2021, 52(2): 355-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | ABU HASAN H, RAHIM N F M, ALIAS J, et al. A review on the roles of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in wastewater treatment: source, mechanism study, bioproducts, limitations, and future challenges[J]. Water, 2024, 16(19): 2812. |
| [26] | YANG Y R, HE C J, HUANG L, et al. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on glomalin-related soil protein distribution, aggregate stability and their relationships with soil properties at different soil depths in lead-zinc contaminated area[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(8): e0182264. |
| [27] | KOHLER J, ROLDÁN A, CAMPOY M, et al. Unraveling the role of hyphal networks from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in aggregate stabilization of semiarid soils with different textures and carbonate contents[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 410(1): 273-281. |
| [28] | LIN H R, CHEN G C, LONG D Y, et al. Responses of unsaturated Pseudomonas putida CZ1 biofilms to environmental stresses in relation to the EPS composition and surface morphology[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2014, 30(12): 3081-3090. |
| [29] | 张铭, 蔡鹏, 吴一超, 等. 细菌胞外聚合物: 基于土壤生态功能的视角[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(2): 308-323. |
| ZHANG M, CAI P, WU Y C, et al. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances: from the perspective of soil ecological functions[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(2): 308-323. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | WEI Z, NIU S, WEI Y, et al. The role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in chemical-degradation of persistent organic pollutants in soil: a review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 912: 168877. |
| [31] | ZHANG M, XU Y, XIAO K Q, et al. Characterising soil extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by application of spectral-chemometrics and deconstruction of the extraction process[J]. Chemical Geology, 2023, 618: 121271. |
| [32] | LUO Y J, LOPEZ J B G, VAN VEELEN H P J, et al. Effects of different soil organic amendments (OAs) on extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2024, 121: 103624. |
| [33] | HARIMAWAN A, TING Y P. Investigation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties of P. aeruginosa and B. subtilis and their role in bacterial adhesion[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2016, 146: 459-467. |
| [34] | ZIMMERMAN A E, GRAHAM E B, MCDERMOTT J, et al. Estimating the importance of viral contributions to soil carbon dynamics[J]. Global Change Biology, 2024, 30(10): e17524. |
| [35] | YU J L, XIAO K, XU H, et al. Spectroscopic fingerprints profiling the polysaccharide/protein/humic architecture of stratified extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2023, 235: 119866. |
| [36] | REHMAN Z U, VROUWENVELDER J S, SAIKALY P E. Physicochemical properties of extracellular polymeric substances produced by three bacterial isolates from biofouled reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 668761. |
| [37] | JUNG J H, CHOI N Y, LEE S Y. Biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide (EPS) production by Cronobacter sakazakii depending on environmental conditions[J]. Food Microbiology, 2013, 34(1): 70-80. |
| [38] | BENGOA A A, LLAMAS M G, IRAPORDA C, et al. Impact of growth temperature on exopolysaccharide production and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus paracasei strains isolated from kefir grains[J]. Food Microbiology, 2018, 69: 212-218. |
| [39] | HE R, MA R C, YAO X Z, et al. Response of methanotrophic activity to extracellular polymeric substance production and its influencing factors[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 69: 289-297. |
| [40] | LOOIJESTEIJN P J, HUGENHOLTZ J. Uncoupling of growth and exopolysaccharide production by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris NIZO B40 and optimization of its synthesis[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 1999, 88(2): 178-182. |
| [41] | LUPI F M, FERNANDES H M L, SÁ-CORREIA I, et al. Temperature profiles of cellular growth and exopolysaccharide synthesis by Botryococus braunii Kütz. UC 58[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 1991, 3(1): 35-42. |
| [42] | VERA PINGITORE E, PESSIONE A, FONTANA C, et al. Comparative proteomic analyses for elucidating metabolic changes during EPS production under different fermentation temperatures by Lactobacillus plantarum Q823[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2016, 238: 96-102. |
| [43] | GUO Y S, FURRER J M, KADILAK A L, et al. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances amplify water content variability at the pore scale[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2018, 6: 93. |
| [44] | DENG J Z, ORNER E P, CHAU J F, et al. Synergistic effects of soil microstructure and bacterial EPS on drying rate in emulated soil micromodels[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 83: 116-124. |
| [45] | WANG L L, WANG L F, REN X M, et al. pH dependence of structure and surface properties of microbial EPS[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(2): 737-744. |
| [46] | SHI Y, LI Y T, YANG T, et al. Threshold effects of soil pH on microbial co-occurrence structure in acidic and alkaline arable lands[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 800: 149592. |
| [47] | MIKUTTA R, ZANG U, CHOROVER J, et al. Stabilization of extracellular polymeric substances (Bacillus subtilis) by adsorption to and coprecipitation with Al forms[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(11): 3135-3154. |
| [48] | RAIESI F, SADEGHI E. Interactive effect of salinity and cadmium toxicity on soil microbial properties and enzyme activities[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 221-229. |
| [49] | REDMILE-GORDON M, CHEN L. Zinc toxicity stimulates microbial production of extracellular polymers in a copiotrophic acid soil[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 119: 413-418. |
| [50] | PRABHAKARAN P, ASHRAF M A, AQMA W S. Microbial stress response to heavy metals in the environment[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(111): 109862-109877. |
| [51] | MIQUELETO A P, DOLOSIC C C, POZZI E, et al. Influence of carbon sources and C/N ratio on EPS production in anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactors for wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(4): 1324-1330. |
| [52] | KHANI M, BAHRAMI A, CHEGENI A, et al. Optimization of carbon and nitrogen sources for extracellular polymeric substances production by Chryseobacterium indologenes MUT.2[J]. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 14(2): 13-18. |
| [53] | ELISASHVILI V, TAN K K. Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources in the medium on Tremella mesenterica Retz. Fr. (Heterobasidiomycetes) growth and polysaccharide production[J]. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 2003, 5(1): 8. |
| [54] | ROBERSON E B, SHENNAN C, FIRESTONE M K, et al. Nutritional management of microbial polysaccharide production and aggregation in an agricultural soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1995, 59(6): 1587-1594. |
| [55] | WANG Y D, WANG Z L, ZHANG Q Z, et al. Long-term effects of nitrogen fertilization on aggregation and localization of carbon, nitrogen and microbial activities in soil[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 624: 1131-1139. |
| [56] | WANG X C, CHEN Z L, SHEN J M, et al. Impact of carbon to nitrogen ratio on the performance of aerobic granular reactor and microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 271: 258-265. |
| [57] | WU Y C, CAI P, JING X X, et al. Soil biofilm formation enhances microbial community diversity and metabolic activity[J]. Environment International, 2019, 132: 105116. |
| [58] | 谭文峰, 许运, 史志华, 等. 胶结物质驱动的土壤团聚体形成过程与稳定机制[J]. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(5): 1297-1308. |
| TAN W F, XU Y, SHI Z H, et al. The formation process and stabilization mechanism of soil aggregates driven by binding materials[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(5): 1297-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [59] | SHI Y H, HUANG J H, ZENG G M, et al. Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: an overview[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 180: 396-411. |
| [60] | HASSLER C S, ALASONATI E, MANCUSO NICHOLS C A, et al. Exopolysaccharides produced by bacteria isolated from the pelagic Southern Ocean: role in Fe binding, chemical reactivity, and bioavailability[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2011, 123(1/2/3/4): 88-98. |
| [61] | ZETHOF J, BETTERMANN A, VOGEL C, et al. The role of prokaryotes and their extracellular polymeric substances on soil aggregation in carbonate containing semiarid grasslands: EGU2020-13565[R/OL]. (2020-05-31) [2024-11-15].https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jeroen-Zethof/publication/339795470_The_role_of_prokaryotes_and_their_extracellular_polymeric_substances_on_soil_aggregation_in_carbonate_containing_semiarid_grasslands/links/5e663bdba6fdcc37dd11ea94/The-role-of-prokaryotes-and-their-extracellular-polymeric-substances-on-soil-aggregation-in-carbonate-containing-semiarid-grasslands.pdf. |
| [62] | TOLHURST T J, GUST G, PATERSON D M. The influence of an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) on cohesive sediment stability[J]. Proceedings in Marine Science, 2002, 5: 409-425. |
| [63] | ZHU C, WANG Q, HUANG X X, et al. Adsorption of amino acids at clay surfaces and implication for biochemical reactions: Role and impact of surface charges[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2019, 183: 110458. |
| [64] | CAI P, LIN D, PEACOCK C L, et al. EPS adsorption to goethite: molecular level adsorption mechanisms using 2D correlation spectroscopy[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 494: 127-135. |
| [65] | HONG Z N, CHEN W L, RONG X M, et al. The effect of extracellular polymeric substances on the adhesion of bacteria to clay minerals and goethite[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 360: 118-125. |
| [66] | SZEWCZUK-KARPISZ K, TOMCZYK A, KOMANIECKA I, et al. Impact of Sinorhizobium meliloti exopolysaccharide on adsorption and aggregation in the copper(II) ions/supporting electrolyte/kaolinite system[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(8): 1950. |
| [67] | LIN D, CAI P, PEACOCK C L, et al. Towards a better understanding of the aggregation mechanisms of iron (hydr)oxide nanoparticles interacting with extracellular polymeric substances: role of pH and electrolyte solution[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 645: 372-379. |
| [68] | DONTSOVA K M, BIGHAM J M. Anionic polysaccharide sorption by clay minerals[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2005, 69(4): 1026-1035. |
| [69] | AHMAD A, MARTSINOVICH N. Atomic-scale modelling of organic matter in soil: adsorption of organic molecules and biopolymers on the hydroxylated α-Al2O3 (0001) surface[J]. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2023, 381(2250): 20220254. |
| [70] | ZHAO H, QI N, LI Y. Interaction between polysaccharide monomer and SiO2/Al2O3/CaCO3 surfaces: a DFT theoretical study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 466: 607-614. |
| [71] | CHANDRASEKARAN N. Effect of topical magnesium application on epidermal integrity and barrier function[D]. Brisbane: The University of Queensland, 2016. |
| [72] | PFAFF N M, KLEIJN J M, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, et al. Formation and ripening of alginate-like exopolymer gel layers during and after membrane filtration[J]. Water Research, 2021, 195: 116959. |
| [73] | FALCHINI L, SPARVOLI E, TOMASELLI L. Effect of Nostoc(Cyanobacteria) inoculation on the structure and stability of clay soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1996, 23(3): 346-352. |
| [74] | NIKSERESHT F, LANDI A, SAYYAD G, et al. Sugarecane molasse and vinasse added as microbial growth substrates increase calcium carbonate content, surface stability and resistance against wind erosion of desert soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 268: 110639. |
| [75] | ZETHOF J H T, BETTERMANN A, VOGEL C, et al. Prokaryotic community composition and extracellular polymeric substances affect soil microaggregation in carbonate containing semiarid grasslands[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2020, 8: 51. |
| [76] | YANG C, LIU N, ZHANG Y J. Soil aggregates regulate the impact of soil bacterial and fungal communities on soil respiration[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 337: 444-452. |
| [77] | YANG J Q, ZHANG X N, BOURG I C, et al. 4D imaging reveals mechanisms of clay-carbon protection and release[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 622. |
| [78] | ALMAGRO M, RUIZ-NAVARRO A, DÍAZ-PEREIRA E, et al. Plant residue chemical quality modulates the soil microbial response related to decomposition and soil organic carbon and nitrogen stabilization in a rainfed Mediterranean agroecosystem[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 156: 108198. |
| [79] | CHENG C, SHANG-GUAN W L, HE L Y, et al. Effect of exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria on water-stable macro-aggregate formation in soil[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2020, 37(8): 738-745. |
| [80] | BIESGEN D, FRINDTE K, MAARASTAWI S, et al. Clay content modulates differences in bacterial community structure in soil aggregates of different size[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 376: 114544. |
| [81] | LEHMANN A, ZHENG W S, RILLIG M C. Soil biota contributions to soil aggregation[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2017, 1(12): 1828-1835. |
| [82] | PHILIPPOT L, CHENU C, KAPPLER A, et al. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024, 22(4): 226-239. |
| [83] | JAYATHILAKE P G, JANA S, RUSHTON S, et al. Extracellular polymeric substance production and aggregated bacteria colonization influence the competition of microbes in biofilms[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1865. |
| [84] | ANGELES-MARTINEZ L, HATZIMANIKATIS V. Spatio-temporal modeling of the crowding conditions and metabolic variability in microbial communities[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2021, 17(7): e1009140. |
| [85] | CHEN L Z, ROSSI F, DENG S Q, et al. Macromolecular and chemical features of the excreted extracellular polysaccharides in induced biological soil crusts of different ages[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 78: 1-9. |
| [86] | ADESSI A, CRUZ DE CARVALHO R, DE PHILIPPIS R, et al. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances improve water retention in dryland biological soil crusts[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 116: 67-69. |
| [87] | FLEMMING H C, WINGENDER J. The biofilm matrix[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(9): 623-633. |
| [88] | MAQBOOL T, CHO J, SHIN K H, et al. Using stable isotope labeling approach and two dimensional correlation spectroscopy to explore the turnover cycles of different carbon structures in extracellular polymeric substances[J]. Water Research, 2020, 170: 115355. |
| [89] | CHEN Y Q, WANG M L, ZHOU X W, et al. Sorption fractionation of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on mineral surfaces and associated effects on phenanthrene sorption to EPS-mineral complexes[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 263: 128264. |
| [90] | ZHANG M, PEACOCK C L, CAI P, et al. Selective retention of extracellular polymeric substances induced by adsorption to and coprecipitation with ferrihydrite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 299: 15-34. |
| [91] | SHER Y, BAKER N R, HERMAN D, et al. Microbial extracellular polysaccharide production and aggregate stability controlled by switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) root biomass and soil water potential[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 143: 107742. |
| [92] | HUANG L, JIN Y N, ZHOU D H, et al. A review of the role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in wastewater treatment systems[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(19): 12191. |
| [93] | BÜKS F, KAUPENJOHANN M. Enzymatic biofilm detachment causes a loss of aggregate stability in a sandy soil[J]. SOIL Discussions, 2016, 2016: 1-27. |
| [94] | LIU D X, MAI Z M, SUN C C, et al. Dynamics of extracellular polymeric substances and soil organic carbon with mangrove zonation along a continuous tidal gradient[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9: 967767. |
| [95] | SEPEHR A, HASSANZADEH M, RODRIGUEZ-CABALLERO E. The protective role of cyanobacteria on soil stability in two Aridisols in northeastern Iran[J]. Geoderma Regional, 2019, 16: e00201. |
| [96] | TANG C C, ZHANG X Y, HE Z W, et al. Role of extracellular polymeric substances on nutrients storage and transfer in algal-bacteria symbiosis sludge system treating wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 331: 125010. |
| [97] | BHATTACHARJEE A, THOMPSON A M, SCHWARZ K C, et al. Soil microbial EPS resiliency is influenced by carbon source accessibility[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2020, 151: 108037. |
| [98] | DOMEIGNOZ-HORTA L A, POLD G, LIU X A, et al. Microbial diversity drives carbon use efficiency in a model soil[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3684. |
| [99] | NKOH J N, XU R K, YAN J, et al. Mechanism of Cu(II) and Cd(II) immobilization by extracellular polymeric substances (Escherichia coli) on variable charge soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 136-145. |
| [100] | DO H, CHE C, ZHAO Z J, et al. Extracellular polymeric substance from Rahnella sp. LRP 3 converts available Cu into Cu5(PO4)2(OH)4 in soil through biomineralization process[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 260: 114051. |
| [1] | WANG Yunlong, JIA Shengqiang, CUI Lingyu, LYU Haohao, SHEN Alin, SU Yao. Interactions of soil carbon and nitrogen distribution with nitrogen fixing and denitrifying bacteria community under straw returning [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2150-2164. |
| [2] | XU Junyan, QIU Gaoyang, LIU Junli, GUO Bin, LI Hua, CHEN Xiaodong, WANG Yuan, FU Qinglin. Effects of montmorillonite, kaolinite and basalt on soil carbon sequestration [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(8): 1867-1877. |
| [3] | AI Ran, HE Jie, LIN Haizhong, WENG Liqing, CHEN Zhaoming, MA Junwei, WANG Qiang. Soil organic carbon content and structural characteristics in water bamboo fields with different cultivation time [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(11): 2558-2565. |
| [4] | ZHA Guichao, SUN Xiangyang, LI Suyan, YU Lei, YUE Zongwei, WANG Chenchen, WEI Ningxian, XU Xijie. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and its components in different green space types in Tongzhou District of Beijing, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(7): 1699-1708. |
| [5] | WU Chuanmei, HE Ji, WU Wenshan, CAI Jun, XIANG Yangzhou. Effects of intercropping on stoichiometric characteristics and nutrients contribution rate of soil aggregates in Rosa roxbunghii Tratt. orchard [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(5): 1132-1143. |
| [6] | HAO Liuliu, DAI Lili, PENG Liang, CHEN Siyuan, TAO Ling, LI Gu, ZHANG Hui. Active organic carbon, microbial community structure and their relationship in rice rhizosphere soil of rice-crayfish co-culture systems [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(12): 2901-2913. |
| [7] | DONG Jie, ZENG Mi. Research on compensation standard for carbon sequestration afforestation based on carbon sequestration income and loss of wood income [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(4): 790-800. |
| [8] | JIA Shengqiang, FAN Huishan, CHEN Xijing, YU Man, SHEN Alin, SU Yao. Driving mechanism of soil denitrifying bacterial community by soil organic carbon after long-term of straw return [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(9): 1686-1699. |
| [9] | ZHANG Qingqing, LIANG Jing, WU Haibing, ZHENG Sijun, HUANG Junhua. Effect of land use change on soil organic carbon pool in process of urbanization: a case study of Sanlin Green Wedge, Shanghai [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(6): 1062-1068. |
| [10] | CHEN Lirong, CHEN Lijuan, ZHU Zhenfeng, HAN Lijing, CAO Yukun. Development potential of forestry carbon sequestration projects in natural forest protection project area: taking Heilongjiang Natural Forest Protection Project area as an example [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(5): 944-954. |
| [11] | XIA Wenjian, QIN Wenjing, LIU Jia, CHEN Xiaofen, ZHANG Lifang, CAO Weidong, XU Changxu, CHEN Jingrui. Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in reddish paddy soil under long-term green manure utilization [J]. , 2020, 32(5): 878-885. |
| [12] | JIAN Xing, ZHAI Xiaoyu, WANG Yu, CAI Yangyang. Influence of land use changes on soil total organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in wetland [J]. , 2020, 32(3): 475-482. |
| [13] | LIAN Yuzhen, LIU Heman, CAO Lihua, HAN Xiaohao, MA Heping. Distribution of soil aggregate and organic carbon under different land use types in Linzhi, Tibet [J]. , 2019, 31(8): 1353-1360. |
| [14] | GUAN Qinzhuang, CHENG Yongxu, LI Cong, WANG Haifeng, CHEN Huangen, LI Jiayao. Changes of soil organic carbon and relationships with soil properties in rice-crayfish coculture system [J]. , 2019, 31(1): 113-120. |
| [15] | LI Yan, CHEN Yi, TANG Xu, WU Chunyan, JI Xiaojiang, TANG Liangliang. Balance characteristics of soil organic carbon under different long-term fertilization models in rice soil in South China [J]. , 2018, 30(12): 2094-2101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||