Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2441-2448.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250214
• Review • Previous Articles
Progress in the synthesis and biological functions of peptidoglycans in plant plastids
- College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
-
Received:2025-03-20Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHI Yi, LI Dongdong. Progress in the synthesis and biological functions of peptidoglycans in plant plastids[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2441-2448.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250214
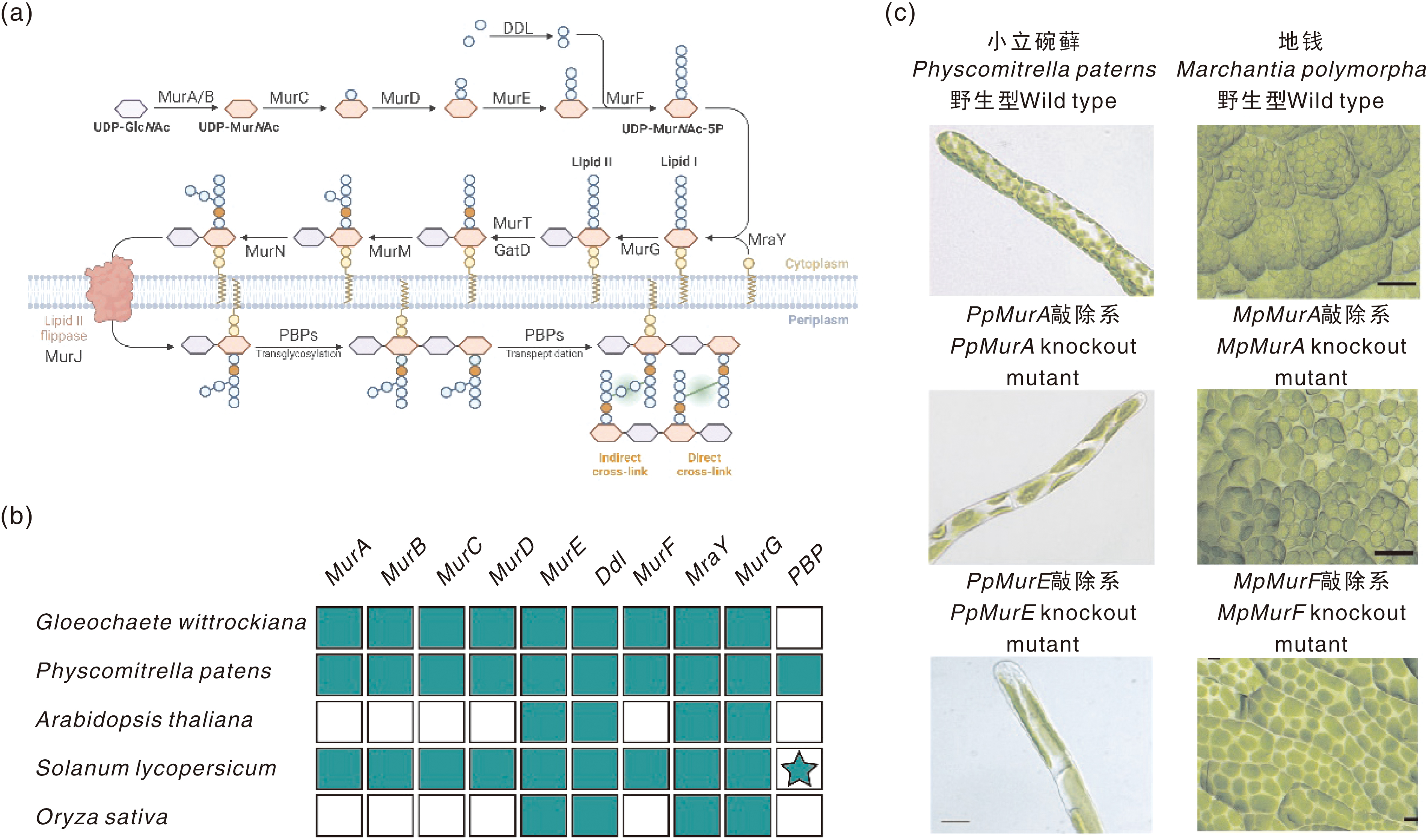
Fig.1 The peptidoglycan biosynthesis pathway, conservation of peptidoglycan synthesis genes, and representative phenotype of peptidoglycan synthesis gene knockout lines a, Bacterial peptidoglycan biosynthesis pathway (modified from literature [15]); b, Homologous genes for bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis retained in plants such as Physcomitrium patens and Arabidopsis thaliana(based on literature [16]), green boxes or blanks indicate the presence or absence of homologous genes, respectively, asterisks denote potential penicillin-binding protein (PBP); c, Knockout mutants of peptidoglycan synthesis pathway genes in P. patens and Marchantia polymorpha both show giant chloroplast phenotypes (modified from literatures [5,17-18]).
| 物种 Species | 基因 Gene | 表型 Phenotype | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小立碗藓Physcomitrella patens | PpMurA | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体、细胞质Chloroplast, cytoplasm | [ |
| PpMurE | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpDDL | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpMraY | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpMurJ | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ | |
| PpPBP | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| 地钱Marchantia polymorpha | MpMurA | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ |
| MpMurF | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ | |
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana | AtMurE | 白化幼苗表型Albino seedlings | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ |
| AtDDL | 无明显表型No obvious phenotype | ? | [ |
Table 1 Research progress on peptidoglycans in plants
| 物种 Species | 基因 Gene | 表型 Phenotype | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小立碗藓Physcomitrella patens | PpMurA | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体、细胞质Chloroplast, cytoplasm | [ |
| PpMurE | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpDDL | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpMraY | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| PpMurJ | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ | |
| PpPBP | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ | |
| 地钱Marchantia polymorpha | MpMurA | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ |
| MpMurF | 巨型叶绿体Giant chloroplast | ? | [ | |
| 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana | AtMurE | 白化幼苗表型Albino seedlings | 叶绿体Chloroplast | [ |
| AtDDL | 无明显表型No obvious phenotype | ? | [ |
| [1] | VOLLMER W, JORIS B, CHARLIER P, et al. Bacterial peptidoglycan (murein) hydrolases[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2008, 32(2): 259-286. |
| [2] | KOHANSKI M A, DWYER D J, COLLINS J J. How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(6): 423-435. |
| [3] | TAKANO H, TAKECHI K. Plastid peptidoglycan[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta(BBA)-General Subjects, 2010, 1800(2): 144-151. |
| [4] | VOLLMER W, BLANOT D, DE PEDRO M A. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2008, 32(2): 149-167. |
| [5] | MACHIDA M, TAKECHI K, SATO H, et al. Genes for the peptidoglycan synthesis pathway are essential for chloroplast division in moss[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(17): 6753-6758. |
| [6] | DOWSON A J, LLOYD A J, CUMING A C, et al. Plant peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis: conservation between moss chloroplasts and Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 190(1): 165-179. |
| [7] | MERESCHKOWSKY K. On the nature and origin of chromatophores in the plant kingdom[J]. Biologisches Centralblatt, 1905(25): 593-604. |
| [8] | ROTEN C A H, KARAMATA D. Endogenous synthesis of peptidoglycan in eukaryotic cells; a novel concept involving its essential role in cell division, tumor formation and the biological clock[J]. Experientia, 1992, 48(10): 921-931. |
| [9] | PRICE D C, CHAN C X, YOON H S, et al. Cyanophora paradoxa genome elucidates origin of photosynthesis in algae and plants[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6070): 843-847. |
| [10] | VAN BAREN M J, BACHY C, REISTETTER E N, et al. Evidence-based green algal genomics reveals marine diversity and ancestral characteristics of land plants[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 267. |
| [11] | DE VRIES J, GOULD S B. The monoplastidic bottleneck in algae and plant evolution[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2018, 131(2): jcs203414. |
| [12] | KASTEN B, RESKI R. β-Lactam antibiotics inhibit chloroplast division in a moss (Physcomitrella patens) but not in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum)[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1997, 150(1/2): 137-140. |
| [13] | TOUNOU E, TAKIO S, SAKAI A, et al. Ampicillin inhibits chloroplast division in cultured cells of the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha[J]. Cytologia, 2002, 67(4): 429-434. |
| [14] | RAVEN J A. Carboxysomes and peptidoglycan walls of cyanelles: possible physiological functions[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 2003, 38(1): 47-53. |
| [15] | HIRANO T, TANIDOKORO K, SHIMIZU Y, et al. Moss chloroplasts are surrounded by a peptidoglycan wall containing D-amino acids[J]. The Plant Cell, 2016, 28(7): 1521-1532. |
| [16] | DOWSON A J. A snapshot of the tree of chloroplast evolution[J]. New Phytologist, 2024, 241(3): 958-961. |
| [17] | HOMI S, TAKECHI K, TANIDOKORO K, et al. The peptidoglycan biosynthesis genes MurA and MraY are related to chloroplast division in the moss Physcomitrella patens[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(12): 2047-2056. |
| [18] | CAYGILL S, KÖCHER T, DOLAN L. MurA-catalyzed synthesis of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate confers glyphosate tolerance in bryophytes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2024, 121(47): e2412997121. |
| [19] | UTSUNOMIYA H, SAIKI N, KADOGUCHI H, et al. Genes encoding lipid Ⅱ flippase MurJ and peptidoglycan hydrolases are required for chloroplast division in the moss Physcomitrella patens[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2021, 107(4): 405-415. |
| [20] | GARCIA M, MYOUGA F, TAKECHI K, et al. An Arabidopsis homolog of the bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis enzyme MurE has an essential role in chloroplast development[J]. The Plant Journal, 2008, 53(6): 924-934. |
| [21] | LIN X F, LI N N, KUDO H, et al. Genes sufficient for synthesizing peptidoglycan are retained in gymnosperm genomes, and MurE from Larix gmelinii can rescue the albino phenotype of Arabidopsis MurE mutation[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2017, 58(3): 587-597. |
| [22] | TRAN X, KESKIN E, WINKLER P, et al. The chloroplast envelope of angiosperms contains a peptidoglycan layer[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(4): 563. |
| [23] | NANNINGA N. Morphogenesis of Escherichia coli[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 1998, 62(1): 110-129. |
| [24] | HÖLTJE J V. Growth of the stress-bearing and shape-maintaining murein sacculus of Escherichia coli[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 1998, 62(1): 181-203. |
| [25] | GUST A A. Peptidoglycan perception in plants[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2015, 11(12): e1005275. |
| [26] | GUST A A, BISWAS R, LENZ H D, et al. Bacteria-derived peptidoglycans constitute pathogen-associated molecular patterns triggering innate immunity in Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(44): 32338-32348. |
| [27] | ZIPFEL C. Plant pattern-recognition receptors[J]. Trends in Immunology, 2014, 35(7): 345-351. |
| [28] | CHANG Y, TANG N, ZHANG M. The peptidoglycan synthase PBP interacts with PLASTID DIVISION2 to promote chloroplast division in Physcomitrium patens[J]. New Phytologist, 2024, 241(3): 1115-1129. |
| [29] | TAKANO Y, CHIKARAISHI Y, OHKOUCHI N. Enantiomer-specific isotope analysis of D- and L-alanine: nitrogen isotopic hetero- and homogeneity in microbial and chemical processes[J]. Earth, Life, and Isotopes, 2010: 387-402. |
| [30] | HIRNER A, LADWIG F, STRANSKY H, et al. Arabidopsis LHT1 is a high-affinity transporter for cellular amino acid uptake in both root epidermis and leaf mesophyll[J]. The Plant Cell, 2006, 18(8): 1931-1946. |
| [31] | 宋奇超, 曹凤秋, 巩元勇, 等. 高等植物氨基酸吸收与转运及生物学功能的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(6): 1507-1517. |
| SONG Q C, CAO F Q, GONG Y Y, et al. Current research progresses of amino acids uptake, transport and their biological roles in higher plants[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2012, 18(6): 1507-1517. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [32] | 郭宁, 曲红岩, 高飞, 等. 氨基酸转运蛋白在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(12): 2360-2370. |
| GUO N, QU H Y, GAO F, et al. The roles of amino acid transporters in plant immunity[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(12): 2360-2370. | |
| [33] | LIU L, YU X C, YAN Y, et al. Amino acid transporters on amino acid absorption, transport and distribution in crops[J]. Horticulturae, 2024, 10(9): 999. |
| [34] | TAKANO H, HIGUCHI H, SATO N, et al. Visualization of plastid peptidoglycan in the charophyte alga Klebsormidium nitens using a metabolic labeling method[J]. Cytologia, 2018, 83(4): 375-380. |
| [35] | HIGUCHI H, TAKECHI K, TAKANO H. Visualization of cyanelle peptidoglycan in Cyanophora paradoxa using a metabolic labeling method with click chemistry[J]. Cytologia, 2016, 81(4): 357-358. |
| [36] | SATO N, TOYOSHIMA M, TAJIMA N, et al. Single-pixel densitometry revealed the presence of peptidoglycan in the intermembrane space of the moss chloroplast envelope in conventional electron micrographs[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 2017, 58(10): 1743-1751. |
| [1] | YANG Chun, LIANG Sihui, WANG Anran, CHEN Juan, LI Yan, LIN Kaiqin, MI Xiaozeng, QIAO Dahe, CHEN Zhengwu, GUO Yan. Characteristic metabolite content and cold resistance of 54 tea germplasms [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(9): 1860-1871. |
| [2] | HU Yingjie, DU Chenqi, WANG Liufan, SHOU Jianxin, WANG Chao, XU Mei, YAN Xu. Research progress of vesicle trafficking in plant response to salt stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(9): 2003-2011. |
| [3] | SHI Yangyang, LYU Lixia, TUO Dengfeng. Effects of AMF and PGPR on growth and nutrient absorption of Matthiola incana under low temperature and weak light stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1694-1705. |
| [4] | CHEN Min, ZHANG Qiaoyan, WANG Xiajun, WANG Shunli, ZHENG Weiran. Determination of arbutin in plant-derived products by solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1776-1784. |
| [5] | ZHAO Hongyu, ZHOU Yujie, LI Jianzhong, ZHENG Han, BI Ji’an, YU Chulang, ZHOU Yuhang, HOU Fan, DAI Binfeng, ZHONG Liequan, YAN Chengqi, ZHANG Haipeng, YANG Yong, CHEN Jianping, WANG Chengyu. Current research status and future perspectives on the effects of microplastics on plants and the molecular biological mechanisms of plant hormones in resistance to microplastics [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(7): 1595-1604. |
| [6] | XIE Changyan, JIN Yumeng, ZHANG Miao, DONG Qingjun, LI Qing, JI Li, ZHONG Ping, CHEN Chuan, ZHANG Ankang. Application effect of nutrient soil made from river sludge for machine-transplanted rice seedling [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(3): 538-547. |
| [7] | XIA Si, FANG Xiangjun, WU Weijie, LIU Ruiling, CHEN Huizhi, NIU Ben, GAO Haiyan. Preparation of fermented Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) pulp and its functional activity and flavor quality [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(3): 667-678. |
| [8] | ZHENG Hang, FENG Haodong, XUE Xianglei, YE Yunxiang, YU Jianlin, YU Guohong. Study on navigation line extraction algorithm for leaf vegetable ridges based on instance segmentations [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(3): 701-711. |
| [9] | WAN Shaoyuan, LIU Xianbo, CAI Shuo, SHI Hong, CHENG Jie. Effect of irrigation and planting methods on the yield and quality of double-cropping rice [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 257-268. |
| [10] | TANG Aoran, JIN Xiu, WANG Tan, RAO Yuan, LI Jiajia, ZHANG Wu. Physiological plant height measurement method based on the reconstruction of the main stem skeleton for curved soybean plants [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 466-479. |
| [11] | QIU Yan, YE Ziran, TAN Xiangfeng, DAI Mengdi, GE Shihao, RUAN Yunjie, ZHAO Xianliang, KONG Dedong. Design and experiment of strawberry picking and grading robot based on YOLOv5-7.0 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2364-2375. |
| [12] | LIU Yuexuan, CHEN Yanling, ZHANG Peiqiang, YAN Peng. Research progress on soil acidification and its regulation in tea plantations [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(1): 245-254. |
| [13] | BAI Jian, LUO Laicong, LI Aixin, LAI Xiaoqin, SHEN Zhan, LIU Liangying, GUO Shengmao, ZHANG Ling. Response of carbon emissions from invasive plant alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides) to nitrogen and phosphorus input in different habitats [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(9): 2070-2078. |
| [14] | ZHAN Mengqi, SU Aoxue, HOU Qian, ZHANG Haoyu, JIANG Xinrui, XU Yan. Uptake and accumulation of lindane in rice and its metabolomics [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(9): 2110-2121. |
| [15] | WANG Jianlin, TIAN Xingmiao, WANG Jingsong, DAI Shasha, GUO Yanan, HE Shenghu, LI Jidong. Establishment of a visual recombinase polymerase amplification assays for Mycoplasma bovis [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(8): 1811-1819. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


