浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2283-2292.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240960
2个绣线菊品种对镉的积累特性与耐性机制
- 北京林业大学 国家花卉工程技术研究中心,城乡生态环境北京实验室,北京 100083
-
收稿日期:2024-11-09出版日期:2025-11-25发布日期:2025-12-08 -
作者简介:谭欣蕊(1999—),女,重庆丰都人,硕士研究生,研究方向为园林植物应用与园林生态。E-mail: 644729687@qq.com -
通讯作者:*王美仙,E-mail: wangmx@bjfu.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31600574);北京市共建项目专项;北京林业大学建设世界一流学科和特色发展引导专项资金(2019XKJS0322);北京市教委科学研究与研究生培养共建科研项目(2019GJ-03)
Cadmium accumulation characteristics and tolerance mechanism of 2 meadowsweet varieties
TAN Xinrui( ), TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian(
), TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian( )
)
- Beijing Laboratory of Urban and Rural Ecological Environment, National Engineering Research Center for Floriculture, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing 100083, China
-
Received:2024-11-09Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
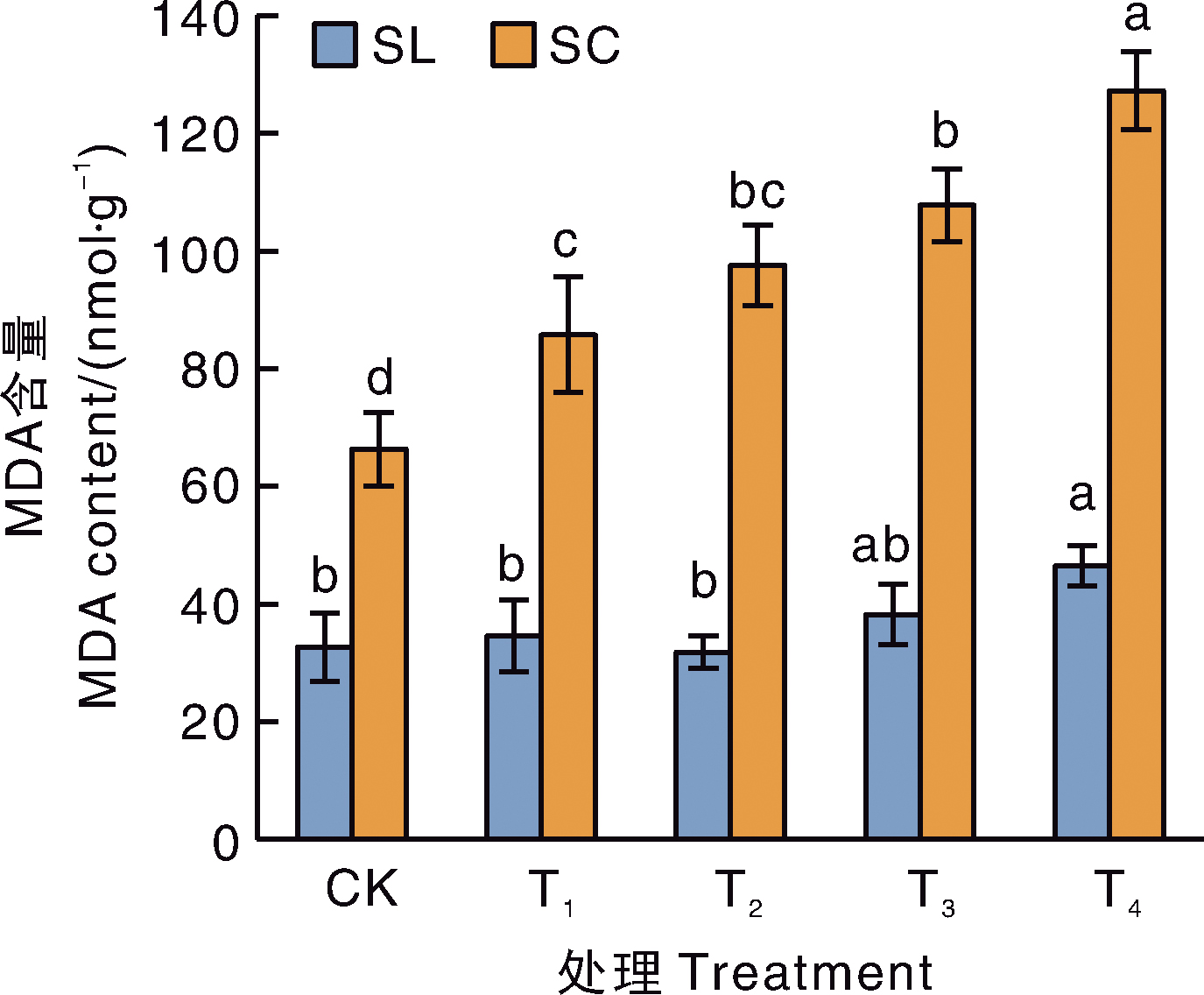
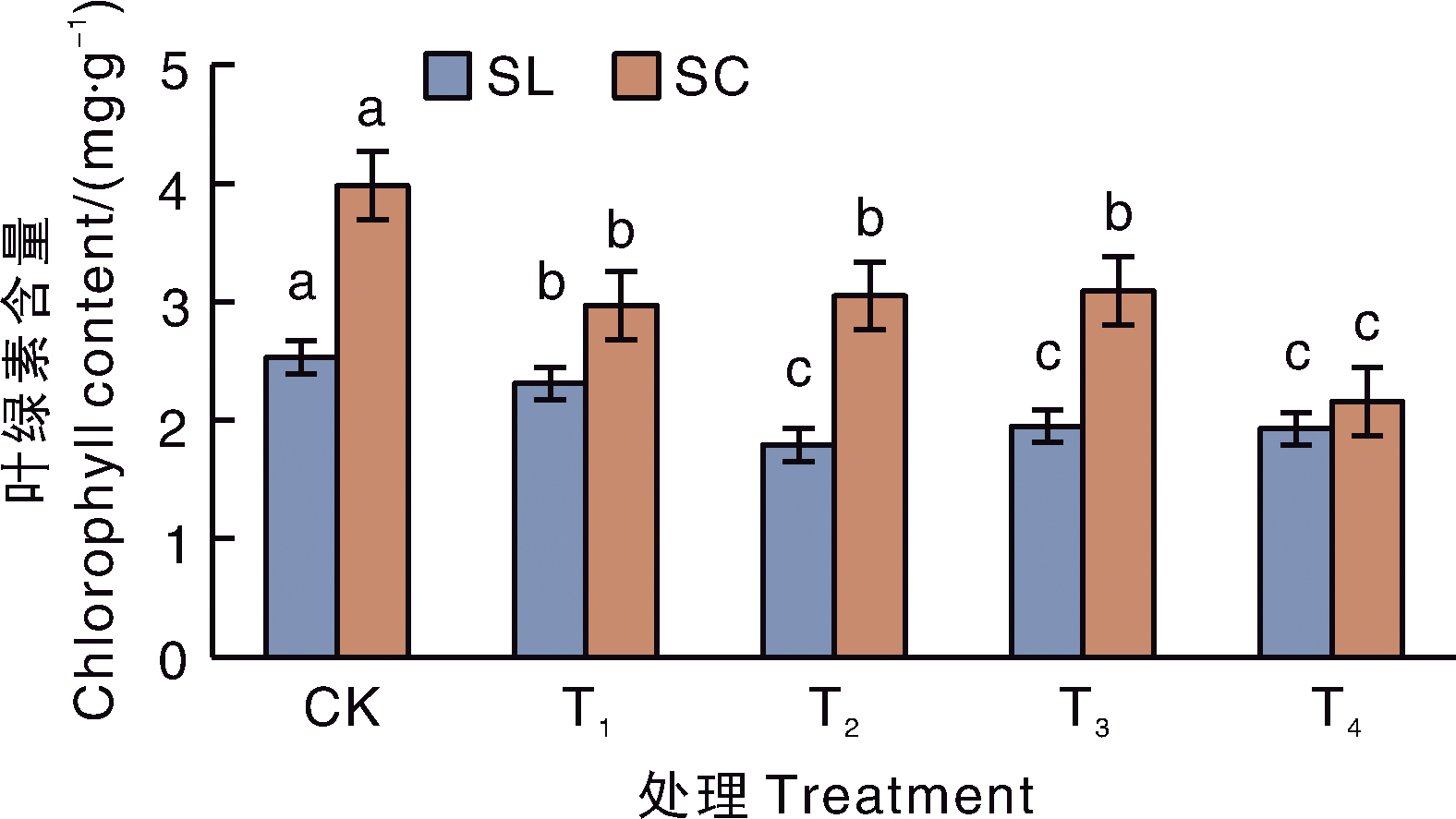
摘要: 为了探明小公主绣线菊(Spiraea japonica Little Princess,简记为SL)和鲜红绣线菊(Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea,简记为SC)对Cd的积累特性和耐性机制,采用盆栽污染模拟试验,研究了不同Cd含量(25、50、100、200 mg·kg-1,依次记为T1~T4处理)胁迫下2个绣线菊品种的生长、生理指标,及Cd的积累、分布和转运特点。结果表明:与不加镉的CK相比,T2~T4处理显著(p<0.05)降低SC的整株生物量,降幅为22.4%~53.0%,且各加Cd处理均显著降低2种绣线菊叶片的叶绿素含量。T4处理下,SL和SC叶片的相对电导率分别是CK的1.17倍和1.38倍,MDA含量分别是CK的1.42、1.92倍。两个品种相比,SC的镉耐受系数和富集能力均低于SL。Cd在这2种绣线菊上的分布比例均表现为根>茎>叶,在亚细胞水平上均主要积累在细胞壁(T1~T4处理下,在SC和SL上的占比分别为59.12%~71.10%和57.05%~62.47%),主要以NaCl提取态存在(T1~T4处理下,在SC和SL上的占比分别为46.61%~57.86%和60.51%~67.65%)。
中图分类号:
引用本文
谭欣蕊, 唐敏, 刘燕, 王美仙. 2个绣线菊品种对镉的积累特性与耐性机制[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2283-2292.
TAN Xinrui, TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian. Cadmium accumulation characteristics and tolerance mechanism of 2 meadowsweet varieties[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2283-2292.
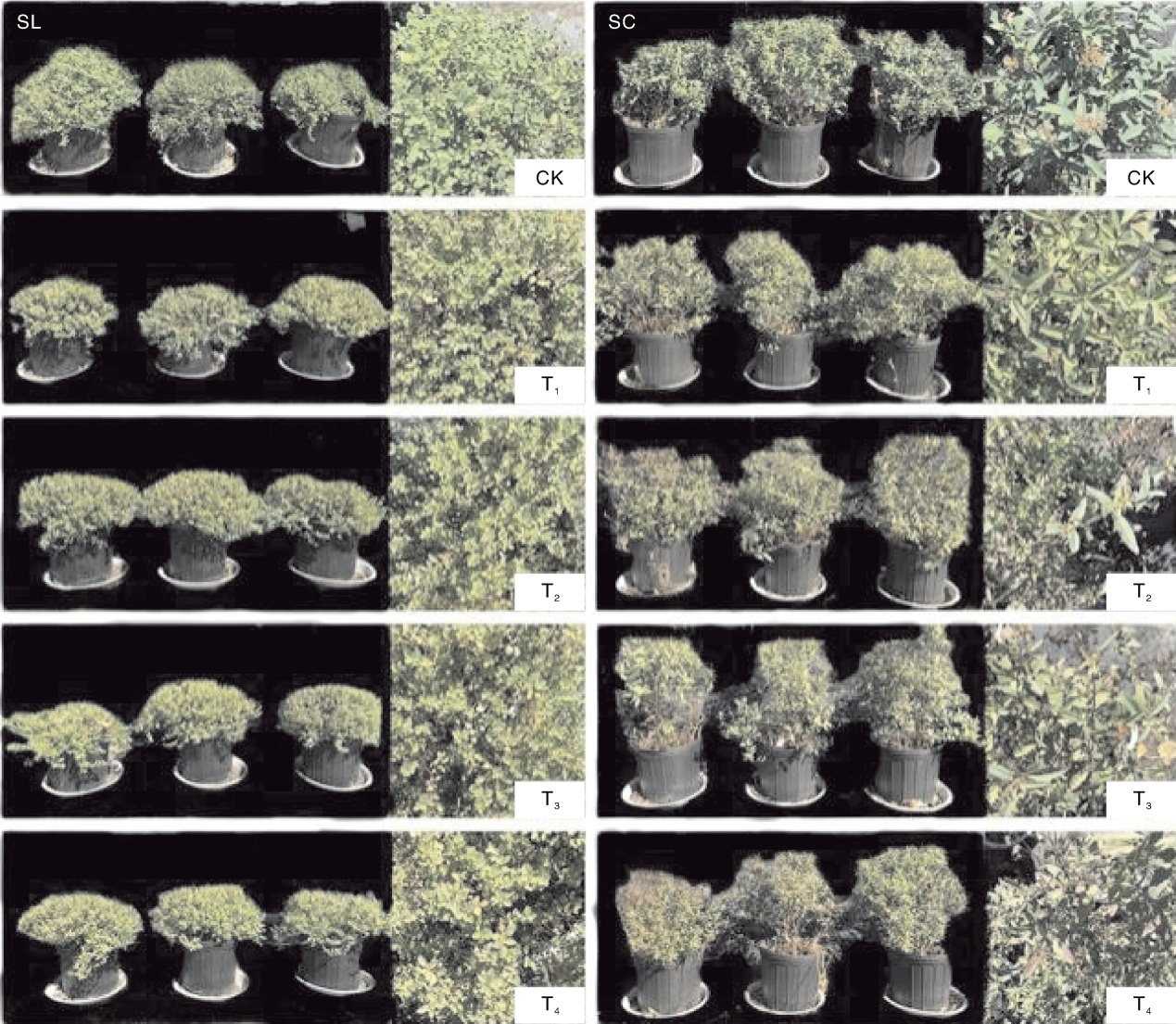
图1 不同处理下小公主绣线菊(左)、鲜红绣线菊(右)的生长状况
Fig.1 Growth status of Spiraea japonica Little Princess (left) and Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea under different treatments
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小公主 | CK | 32.87±3.31 a | 27.56±3.04 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 31.03±2.65 a | 25.80±1.86 a |
| T2 | 24.07±1.16 b | 24.49±2.61 a | |
| T3 | 25.53±2.55 b | 22.40±3.09 a | |
| T4 | 25.83±2.46 b | 22.18±2.76 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 49.50±0.79 ab | 31.90±4.16 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 48.70±2.26 ab | 25.53±2.78 ab |
| T2 | 49.00±3.11 ab | 25.38±3.67 ab | |
| T3 | 50.53±2.08 a | 20.66±2.93 b | |
| T4 | 44.67±4.48 b | 14.19±3.57 c |
表1 不同处理下两个绣线菊品种的形态学指标
Table 1 Morphological indexes of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments cm
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小公主 | CK | 32.87±3.31 a | 27.56±3.04 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 31.03±2.65 a | 25.80±1.86 a |
| T2 | 24.07±1.16 b | 24.49±2.61 a | |
| T3 | 25.53±2.55 b | 22.40±3.09 a | |
| T4 | 25.83±2.46 b | 22.18±2.76 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 49.50±0.79 ab | 31.90±4.16 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 48.70±2.26 ab | 25.53±2.78 ab |
| T2 | 49.00±3.11 ab | 25.38±3.67 ab | |
| T3 | 50.53±2.08 a | 20.66±2.93 b | |
| T4 | 44.67±4.48 b | 14.19±3.57 c |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的单株生物量Biomass of different parts per plant | 整株生物量 Biomass of whole plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | |||
| 小公主 | CK | 205.30±33.61 a | 141.35±24.49 a | 95.92±6.26 a | 442.57±62.14 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 202.95±9.33 a | 139.60±2.61 a | 92.05±0.73 ab | 434.60±7.73 a |
| T2 | 179.68±10.66 a | 124.09±6.19 a | 78.94±7.43 b | 382.71±22.51 a | |
| T3 | 180.66±15.81 a | 126.56±11.58 a | 78.64±9.08 b | 385.85±35.77 a | |
| T4 | 168.76±17.14 a | 121.41±11.96 a | 76.15±5.76 b | 366.32±33.61 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 290.69±57.88 a | 244.54±39.60 a | 146.11±7.05 a | 681.34±104.15 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 248.52±40.36 ab | 234.13±14.83 ab | 127.56±13.29 ab | 610.21±48.82 ab |
| T2 | 223.37±2.15 ab | 190.26±11.05 bc | 114.70±8.20 bc | 528.33±15.78 b | |
| T3 | 208.29±20.36 b | 181.08±16.52 cd | 95.54±16.32 c | 484.91±22.42 b | |
| T4 | 125.89±50.45 c | 129.99±44.37 d | 63.99±12.15 d | 319.87±105.86 c | |
表2 不同处理下两个绣线菊品种的生物量
Table 2 Biomass of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments g
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的单株生物量Biomass of different parts per plant | 整株生物量 Biomass of whole plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | |||
| 小公主 | CK | 205.30±33.61 a | 141.35±24.49 a | 95.92±6.26 a | 442.57±62.14 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 202.95±9.33 a | 139.60±2.61 a | 92.05±0.73 ab | 434.60±7.73 a |
| T2 | 179.68±10.66 a | 124.09±6.19 a | 78.94±7.43 b | 382.71±22.51 a | |
| T3 | 180.66±15.81 a | 126.56±11.58 a | 78.64±9.08 b | 385.85±35.77 a | |
| T4 | 168.76±17.14 a | 121.41±11.96 a | 76.15±5.76 b | 366.32±33.61 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 290.69±57.88 a | 244.54±39.60 a | 146.11±7.05 a | 681.34±104.15 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 248.52±40.36 ab | 234.13±14.83 ab | 127.56±13.29 ab | 610.21±48.82 ab |
| T2 | 223.37±2.15 ab | 190.26±11.05 bc | 114.70±8.20 bc | 528.33±15.78 b | |
| T3 | 208.29±20.36 b | 181.08±16.52 cd | 95.54±16.32 c | 484.91±22.42 b | |
| T4 | 125.89±50.45 c | 129.99±44.37 d | 63.99±12.15 d | 319.87±105.86 c | |
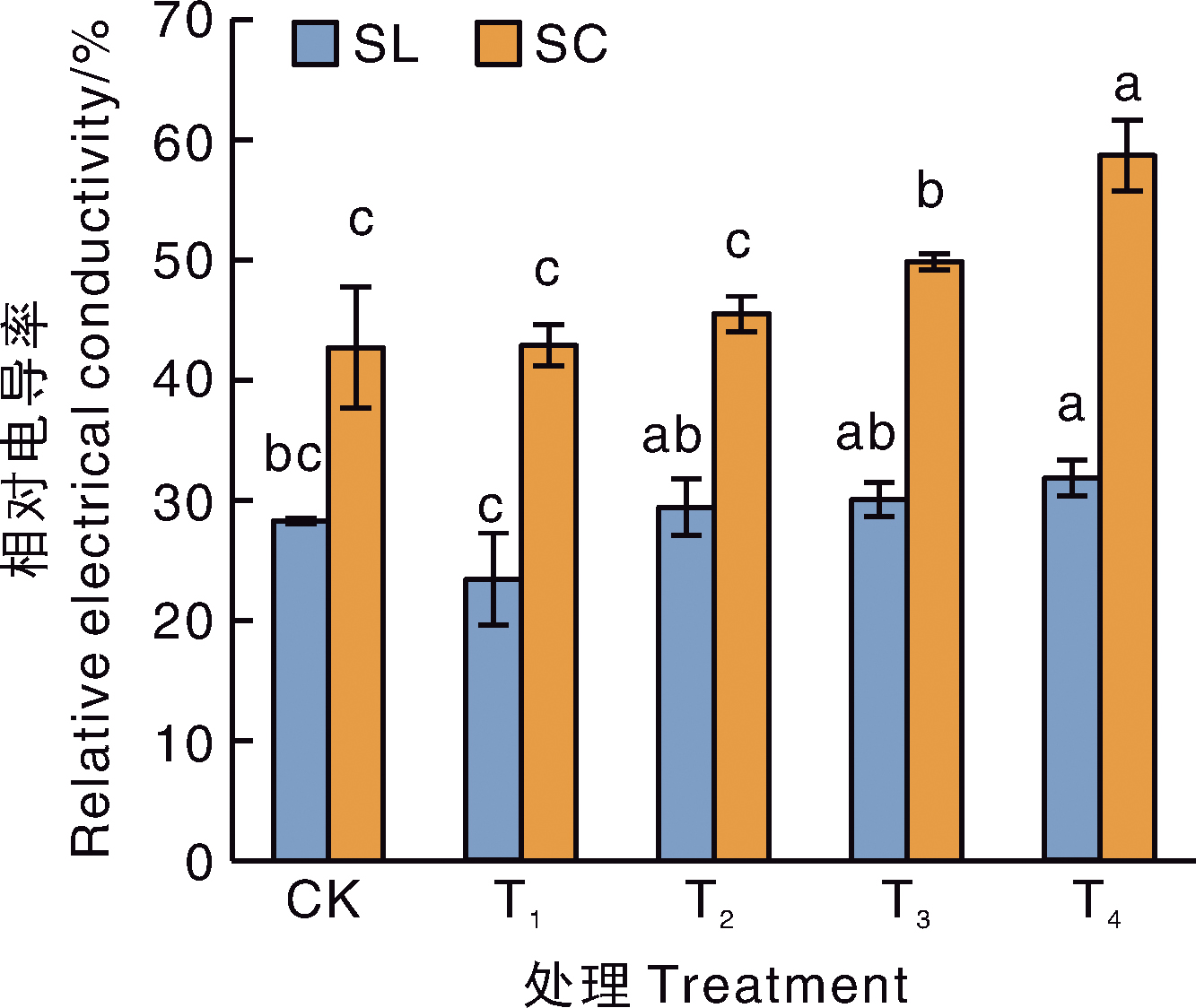
图2 不同处理下两个绣线菊品种的相对电导率 SL,小公主绣线菊;SC,鲜红绣线菊。同一品种柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.2 Relative electric conductivity of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments SL, Spiraea japonica Little Princess; SL, Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea. Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference within treatments at p<0.05 for the same variety. The same as below.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的镉含量Cd conten in different parts of plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||
| 小公主Little Princess | CK | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.13±0.01 e | 0.51±0.13 e |
| T1 | 6.85±0.44 c | 14.99±1.40 d | 63.97±3.04 d | |
| T2 | 15.66±1.68 b | 27.89±5.71 c | 78.61±4.03 c | |
| T3 | 17.66±0.64 b | 40.62±6.33 b | 89.28±4.48 b | |
| T4 | 26.55±2.54 a | 55.51±7.16 a | 99.23±6.03 a | |
| 鲜红Coccimea | CK | 0.10±0.02 d | 0.60±0.04 d | 0.76±0.16 d |
| T1 | 6.71±0.51 c | 16.24±3.45 c | 16.94±1.04 c | |
| T2 | 8.53±0.26 c | 16.20±3.15 c | 17.89±1.47 c | |
| T3 | 11.64±1.03 b | 23.81±0.96 b | 41.44±7.04 b | |
| T4 | 20.26±3.46 a | 41.60±6.13 a | 59.36±8.14 a | |
表3 两个绣线菊品种的镉含量
Table 3 Cd content in two meadowsweet varieties mg·kg-1
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的镉含量Cd conten in different parts of plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||
| 小公主Little Princess | CK | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.13±0.01 e | 0.51±0.13 e |
| T1 | 6.85±0.44 c | 14.99±1.40 d | 63.97±3.04 d | |
| T2 | 15.66±1.68 b | 27.89±5.71 c | 78.61±4.03 c | |
| T3 | 17.66±0.64 b | 40.62±6.33 b | 89.28±4.48 b | |
| T4 | 26.55±2.54 a | 55.51±7.16 a | 99.23±6.03 a | |
| 鲜红Coccimea | CK | 0.10±0.02 d | 0.60±0.04 d | 0.76±0.16 d |
| T1 | 6.71±0.51 c | 16.24±3.45 c | 16.94±1.04 c | |
| T2 | 8.53±0.26 c | 16.20±3.15 c | 17.89±1.47 c | |
| T3 | 11.64±1.03 b | 23.81±0.96 b | 41.44±7.04 b | |
| T4 | 20.26±3.46 a | 41.60±6.13 a | 59.36±8.14 a | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的生物富集系数Bioconcentration factor of different parts of plant | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 耐受系数 Tolerance index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||||
| 小公主 | CK | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.56±0.05 a | 2.22±0.56 a | 0.72±0.05 a | — |
| Little Princess | T1 | 0.14±0.01 ab | 0.30±0.03 b | 1.28±0.06 b | 0.44±0.02 b | 0.98±0.02 a |
| T2 | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.79±0.04 bc | 0.36±0.19 b | 0.86±0.05 ab | |
| T3 | 0.12±0.00 b | 0.27±0.04 b | 0.60±0.03 c | 0.39±0.04 b | 0.87±0.08 ab | |
| T4 | 0.13±0.01 ab | 0.28±0.04 b | 0.50±0.03 c | 0.41±0.05 b | 0.83±0.08 b | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 0.49±0.07 a | 2.60±0.19 a | 3.30±0.69 a | 3.08±0.27 a | — |
| Coccimea | T1 | 0.13±0.01 b | 0.32±0.07 b | 0.34±0.02 b | 0.46±0.07 b | 0.90±0.07 a |
| T2 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.17±0.03 bc | 0.18±0.01 b | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.78±0.02 ab | |
| T3 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.28±0.05 b | 0.24±0.01 b | 0.71±0.03 b | |
| T4 | 0.11±0.02 b | 0.21±0.03 bc | 0.30±0.04 b | 0.31±0.05 b | 0.47±0.16 c | |
表4 两个绣线菊品种的镉富集系数、转移系数和耐受系数
Table 4 Cd bioconcentration factor, translocation factor and tolerance index of two meadowsweet varieties
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的生物富集系数Bioconcentration factor of different parts of plant | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 耐受系数 Tolerance index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||||
| 小公主 | CK | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.56±0.05 a | 2.22±0.56 a | 0.72±0.05 a | — |
| Little Princess | T1 | 0.14±0.01 ab | 0.30±0.03 b | 1.28±0.06 b | 0.44±0.02 b | 0.98±0.02 a |
| T2 | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.79±0.04 bc | 0.36±0.19 b | 0.86±0.05 ab | |
| T3 | 0.12±0.00 b | 0.27±0.04 b | 0.60±0.03 c | 0.39±0.04 b | 0.87±0.08 ab | |
| T4 | 0.13±0.01 ab | 0.28±0.04 b | 0.50±0.03 c | 0.41±0.05 b | 0.83±0.08 b | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 0.49±0.07 a | 2.60±0.19 a | 3.30±0.69 a | 3.08±0.27 a | — |
| Coccimea | T1 | 0.13±0.01 b | 0.32±0.07 b | 0.34±0.02 b | 0.46±0.07 b | 0.90±0.07 a |
| T2 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.17±0.03 bc | 0.18±0.01 b | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.78±0.02 ab | |
| T3 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.28±0.05 b | 0.24±0.01 b | 0.71±0.03 b | |
| T4 | 0.11±0.02 b | 0.21±0.03 bc | 0.30±0.04 b | 0.31±0.05 b | 0.47±0.16 c | |
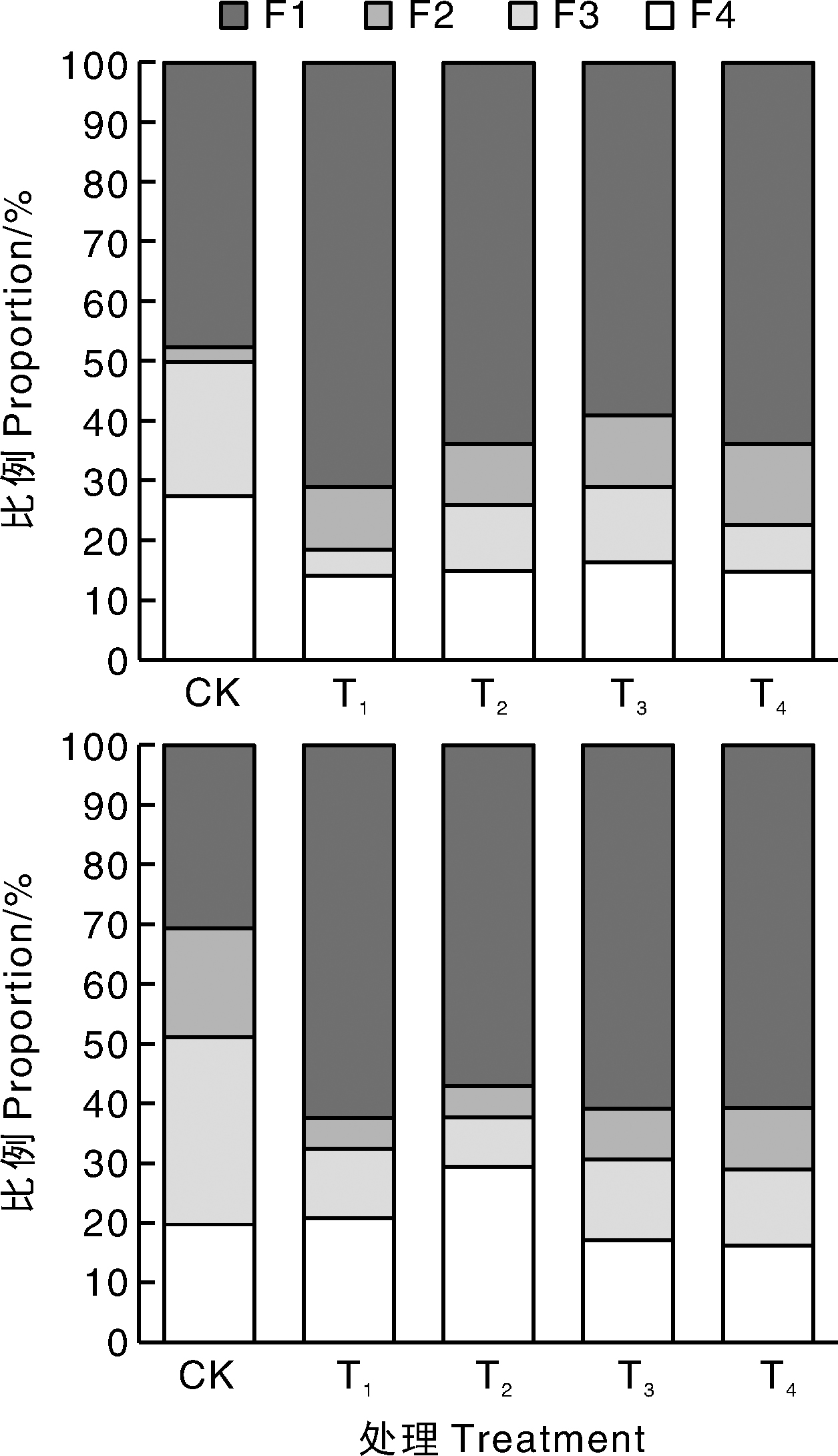
图5 不同处理下小公主绣线菊(上)、鲜红绣线菊(下)各亚细胞组分中的镉分布 F1,细胞壁;F2,细胞核;F3,线粒体和叶绿体;F4,核糖核蛋白和可溶性成分。
Fig.5 Cd distribution in subcellular components of leaves of Spiraea japonica Little Princess (up) and Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea (down) under different treatments F1, Cell walls; F2, Cell nucleus; F3, Mitochondria and chloroplast; F4, Ribonucleoprotein and soluble composition.
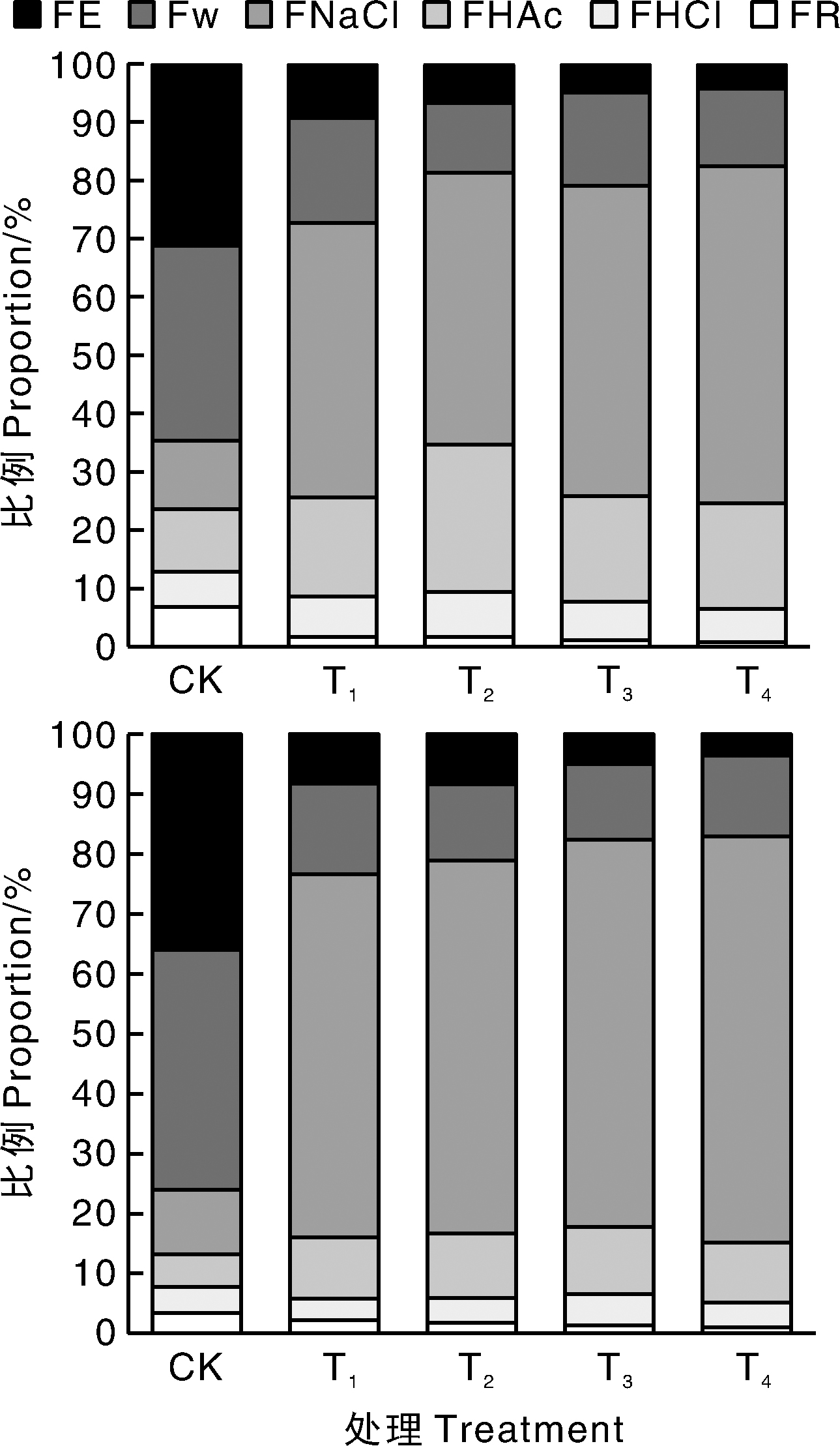
图6 不同处理下小公主绣线菊(上)、鲜红绣线菊(下)叶片中不同化学形态镉的分布 FE、FW、FNaCl、FHAc、FHCl和FR分别代表用80%乙醇、去离子水、1 mol·L-1 NaCl、2%乙酸、0.6 mol·L-1 HCl提取的Cd和残留态Cd。
Fig.6 Distribution of different Cd chemical forms in leaves of Spiraea japonica Little Princess (up) and Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea (down) under different treatments FE, FW, FNaCl, FHAc, FHCl and FR represented the fractions extracted by 80% ethanol, deionized water, 1 mol·L-1 NaCl, 2% HAC, 0.6 mol·L-1 HCl and residue, respectively.
| [1] | GRAMLICH A, TANDY S, ANDRES C, et al. Cadmium uptake by cocoa trees in agroforestry and monoculture systems under conventional and organic management[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 580: 677-686. |
| [2] | PELFRÊNE A, WATERLOT C, MAZZUCA M, et al. Assessing Cd, Pb, Zn human bioaccessibility in smelter-contaminated agricultural topsoils (northern France)[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(5): 477-493. |
| [3] | ŠMUC N R, DOLENEC T, SERAFIMOVSKI T, et al. Heavy metal characteristics in Kočani Field plant system (Republic of Macedonia)[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2012 34(4): 513-526. |
| [4] | WAISBERG M, JOSEPH P, HALE B, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis[J]. Toxicology, 2003, 192(2/3): 95-117. |
| [5] | 徐永梅, 字润祥, 卞世闻. 云龙水库周边土壤中重金属的危害评价[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2019, 38(1): 88-91. |
| XU Y M, ZI R X, BIAN S W. Hazard assessment of heavy metal in the soil around Yunlong Reservoir[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2019, 38(1): 88-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 张雁鸿. 镉污染土壤修复治理技术研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2023(24): 56-58. |
| ZHANG Y H. Research on remediation technology for cadmium contaminated soil[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2023(24): 56-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | CAO D, ZHANG H Z, WANG Y D, et al. Accumulation and distribution characteristics of zinc and cadmium in the hyperaccumulator plant Sedum plumbizincicola[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2014, 93(2): 171-176. |
| [8] | 韩飞, 邹光得, 晋方学, 等. 龙葵修复不同浓度土壤镉污染研究[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43(1): 74-78. |
| HAN F, ZOU G D, JIN F X, et al. Remediation of cadmium pollution in different concentrations of soil by Solanum nigrum L[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2023, 43(1): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 徐晓寒. 不同品种柳树幼苗对重金属镉、铅富集能力与耐性机理研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2019. |
| XU X H. Accumulation capacity and tolerance mechanism of four Salix genotypes exposed to cadmium and lead[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 代惠萍. 灰杨幼苗对镉的耐性及解毒生理机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. |
| DAI H P. Unraveling the mechanisms of cadmium tolerance and detoxification in Populus×canescens[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 庞璐. 柳属(Salix)植物对镉和锌重金属胁迫的耐受差异及机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021. |
| PANG L. Difference and mechanism for Cd and Zn tolerance in Salix species[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李香君. 铜、镉、铅胁迫对玫瑰生理及吸收积累特性的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2017. |
| LI X J. Study on physiological and accumulation characteristics of Rosa rugosa-cv. to copper, cadmium and lead stress[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 卢圣凡. 忍冬镉富集特性及对叶片有机酸类有效成分积累影响研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2023. |
| LU S F. Research on cadmium enrichment in Lonicera japonica Thunb. and its impact on organic acid accumulation in leaf[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 崔仕杰. 山苍子幼苗对重金属镉和铅的富集特征与胁迫响应研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2023. |
| CUI S J. Enrichment characteristics and stress response of Litsea cubeba seedlings to heavy metals cadmium and lead[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 吴梦媛. 杉木镉积累特性与镉胁迫响应机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2022. |
| WU M Y. Characterization of cadmium accumulation and response mechanisms to cadmium stress in Cunninghamia lanceolata[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 顾翠花, 王懿祥, 白尚斌, 等. 四种园林植物对土壤镉污染的耐受性[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(8): 2536-2544. |
| GU C H, WANG Y X, BAI S B, et al. Tolerance and accumulation of four ornamental species seedlings to soil cadmium contamination[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(8): 2536-2544. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | LI X D, MA H, LI L L, et al. Subcellular distribution, chemical forms and physiological responses involved in cadmium tolerance and detoxification in Agrocybe aegerita[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 66-74. |
| [18] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| [19] | 林龙勇, 阎秀兰, 廖晓勇, 等. 三七对土壤中镉、铬、铜、铅的累积特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(11): 2868-2875. |
| LIN L Y, YAN X L, LIAO X Y, et al. Accumulation of soil Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb by Panax notoginseng and its associated health risk[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(11): 2868-2875. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 周守标, 徐礼生, 吴龙华, 等. 镉和锌在皖景天细胞内的分布及化学形态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(11): 2515-2520. |
| ZHOU S B, XU L S, WU L H, et al. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Cd and Zn in Sedum jinianum[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(11): 2515-2520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | LU H P, LI Z A, WU J T, et al. Influences of calcium silicate on chemical forms and subcellular distribution of cadmium in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40583. |
| [22] | 周晓声, 娄厦, RADNAEVA L, 等. 植物对土壤重金属富集特性研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(3): 400-410. |
| ZHOU X S, LOU S, RADNAEVA L, et al. Advances in heavy metal accumulation characteristics of plants in soil[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(3): 400-410. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | METWALLY A, SAFRONOVA V I, BELIMOV A A, et al. Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(409): 167-178. |
| [24] | 朱润华, 贺忠群, 王海霞, 等. 镉胁迫处理对水培苦苣幼苗生理响应及叶片超微结构的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(6): 1302-1308. |
| ZHU R H, HE Z Q, WANG H X, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on physiological response and leaf ultrastructure of hydroponic Cichorium endivia L. seedling[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(6): 1302-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 郑逢中, 林鹏, 郑文教. 红树植物秋茄幼苗对镉耐性的研究[J]. 生态学报, 1994, 14(4): 408-414. |
| ZHENG F Z, LIN P, ZHENG W J. Study on the tolerance of Kandelia candel mangrove seedlings to cadmium[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1994, 14(4): 408-414. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 谢倚慧, 张明华, 熊瑞, 等. 马缨丹在镉、铅、锌复合胁迫下的耐性和解毒机制[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(9): 1209-1217. |
| XIE Y H, ZHANG M H, XIONG R, et al. Study on the tolerance and detoxification mechanisms of Lantana camara under the combined stress of cadmium, lead and zinc[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(9): 1209-1217. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 肖才升, 谢心, 李锋, 等. 锰处理下棉花幼苗根部对镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 华北农学报, 2023, 38(6): 55-61. |
| XIAO C S, XIE X, LI F, et al. Physiological response of two cotton seedlings to cadmium stress treated with different concentrations of manganese[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2023, 38(6): 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 唐星林, 刘斌, 刘光正, 等. 氮肥对镉胁迫下龙葵叶绿素含量和叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(6): 39-46. |
| TANG X L, LIU B, LIU G Z, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Solanum nigrum under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 41(6): 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 自海云, 李琬婷, 程小毛, 等. 镉胁迫对洋常春藤叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 38(5): 7-12. |
| ZI H Y, LI W T, CHENG X M, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Hedera helix[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences), 2018, 38(5): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | AMAN M S, JAFARI M, REIHAN M K, et al. Assessing some shrub species for phytoremediation of soils contaminated with lead and zinc[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(3): 82. |
| [31] | BROOKS R R, LEE J, REEVES R D, et al. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1977, 7: 49-57. |
| [32] | 李欣, 孙文, 金政, 等. 燃煤火电厂周边土壤重金属污染状况及绿化树种对重金属的积累特性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2016, 34(4): 21-29. |
| LI X, SUN W, JIN Z, et al. Heavy metal contamination of soil and accumulation in greening trees surrounding coal-fired power plant[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University(Agricultural Science), 2016, 34(4): 21-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 王广林, 张金池, 庄家尧, 等. 31种园林植物对重金属的富集研究[J]. 皖西学院学报, 2011, 27(5): 83-87. |
| WANG G L, ZHANG J C, ZHUANG J Y, et al. Accumulation research of 31 species of ornamental plants on heavy metal[J]. Journal of West Anhui University, 2011, 27(5): 83-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 李萧萧, 冯丽涵, 李凌. 复合胁迫下复羽叶栾树对Cd和Pb的吸收富集研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 45(5): 103-108. |
| LI X X, FENG L H, LI L. On absorption and accumulation characteristics of Koelreuteria bipinnata Franch. under combined pollution of Cd2+ and Pb2+[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 45(5): 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 刘金秀, 张松彦, 周建. 镉胁迫对刺槐幼苗生长与光合生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2023, 36(3): 168-178. |
| LIU J X, ZHANG S Y, ZHOU J. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Forest Research, 2023, 36(3): 168-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | GALLEGO S M, PENA L B, BARCIA R A, et al. Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2012, 83: 33-46. |
| [37] | 唐敏, 张欣, 刘燕, 等. 镉在3种乔木中的积累及其亚细胞分布和化学形态研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(6): 2440-2447. |
| TANG M, ZHANG X, LIU Y, et al. Accumulation, subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in three tree species[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(6): 2440-2447. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 秦宏, 张宝锋, 陈俊乔, 等. 镉污染土壤伴矿景天的萃取强化螯合剂和植物激素的叶面调控[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(4): 363-369. |
| QIN H, ZHANG B F, CHEN J Q, et al. An enhanced phytoextraction of Sedum plumbizicola in Cd contaminated soil-the foliar application of chelating agent and phytohormones[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(4): 363-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | FU X P, DOU C M, CHEN Y X, et al. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Phytolacca americana L[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 103-107. |
| [40] | PERRONNET K, SCHWARTZ C, MOREL J L. Distribution of cadmium and zinc in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens grown on multicontaminated soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 249(1): 19-25. |
| [41] | 张欣. 北京道路绿地18种乔木重金属富集能力评价和积累特征差异研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG X. A study on the evaluation and accumulation of heavy metal enrichment ability of 18 trees in Beijing greenbelt[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 董名扬, 孙瑶, 冯晓晖, 等. 两种生态型香根草对镉的耐受和积累特性比较[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(8): 1330-1338. |
| DONG M Y, SUN Y, FENG X H, et al. Comparative tolerance and accumulation characteristics of cadmium in two vetiver grass ecotypes[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 1330-1338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 裴惠民, 巫明明, 翟荣荣, 叶靖, 金月, 朱仪, 侯建军, 朱国富, 叶胜海. 低镉水稻基因功能与新品种培育研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 2012-2020. |
| [2] | 董爱琴, 陈院华, 杨涛, 徐昌旭, 程丽群, 谢杰. 紫云英和石灰配施对水稻镉吸收的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(3): 600-612. |
| [3] | 彭佳诚, 吴越, 徐洁皓, 夏美文, 齐天鹏, 徐海圣. 日本沼虾桩蛋白基因的克隆与镉胁迫对其表达的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 247-253. |
| [4] | 李秋铷, 蔡晶晶, 李华, 俞海平, 裘高扬, 刘俊丽, 郭彬. 几种无机与有机材料对镉的吸附和钝化效果比较[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(12): 2774-2783. |
| [5] | 林小兵, 张鸿燕, 张秋梅, 周利军, 徐德胜, 郭乃嘉, 邱祥凤, 黄海平. 基于多指标的镉低积累水稻品种筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(11): 2507-2515. |
| [6] | 宋盼盼, 常会庆, 李岚坤, 王启震. 叶面阻控剂在轻度镉污染石灰性麦田上的降镉效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(11): 2655-2663. |
| [7] | 王建兵, 王金涛, 颜可昕, 郭小兰, 王盾, 戴洪文. 豆瓣菜在镉铅复合污染条件下的镉铅积累特性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(11): 2664-2672. |
| [8] | 范丽莹, 范婷婷, 仝宗军, 梁立韵, 赵志勇, 陈辉, 周昌艳, 赵晓燕. 镉胁迫对不同品种羊肚菌镉富集规律与抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(10): 2321-2331. |
| [9] | 姜昊梁, 黄允, 梁绍芳, 谢梦晨, 徐天成, 宋芷婷, 向文文, 陈青春, 万小荣, 孙伟. 镉胁迫对不同甜玉米自交系幼苗生长的影响及其相关简单重复序列分子标记初筛[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1582-1590. |
| [10] | 黄锋, 邢建平, 符少怀, 潘攀, 吴琳, 刘贝贝, 陈淼. 不同安全利用技术对琼北地区稻菜轮作系统镉削减的效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1725-1733. |
| [11] | 邰粤鹰, 何腾兵, 陈小然, 张旺, 黄啸云, 刘鸿雁, 高珍冉. 叶面喷施阻控剂对常淹水稻田水稻吸收转运镉的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(6): 1248-1257. |
| [12] | 杜红, 李玉鹏, 程文, 肖荣英, 胡鹏. 丛枝菌根真菌改善镉胁迫下植物根系和土壤微环境的效应[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(5): 1039-1048. |
| [13] | 王灿, 付天岭, 龚思同, 娄飞, 周凯, 代良羽, 刘静, 林大松, 何腾兵. 叶面阻控剂对黔中喀斯特地区水稻Cd富集特征的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(9): 1710-1719. |
| [14] | 刘如, 董畅茹, 张祎雯, 屈铭慧, 张伟, 洒海洋, 陈海燕, 叶文玲, 樊霆. 镉胁迫下黑曲霉TL-F2的促生特征及其对黑麦草种子萌发、幼苗生长和镉含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(2): 326-334. |
| [15] | 董爱琴, 李建国, 杨涛, 陈院华, 徐昌旭, 万辉, 彭志平, 谢杰. 金属硫酸盐浸种对水稻种子萌发和秧苗镉吸收的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(12): 2213-2223. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||