浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2354-2363.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240939
温州海域水产品的重金属分布特征与健康风险评价
陈星星1,2,3( ), 虞雯煊4, 薛峰1,2,3, 吴越1,2,3,*(
), 虞雯煊4, 薛峰1,2,3, 吴越1,2,3,*( )
)
- 1.浙江省海洋水产养殖研究所,浙江 温州 325005
2.全省近岸生物种质资源保护与利用重点实验室,浙江 温州 325005
3.温州市海洋生物遗传育种重点实验室,浙江 温州 325005
4.福建农林大学 海洋学院,福建 福州 350002
-
收稿日期:2024-11-04出版日期:2025-11-25发布日期:2025-12-08 -
作者简介:陈星星(1988—),男,浙江三门人,硕士,工程师,研究方向为水产品质检与营养分析。E-mail:363316091@qq.com -
通讯作者:*吴越,E-mail:476281577@qq.com -
基金资助:浙江省科技厅项目(LGN19C030001);温州市基础性公益科研项目(S2023042)
Characteristics of heavy metals distribution and health risk evaluation of marine products in the sea areas of Wenzhou, China
CHEN Xingxing1,2,3( ), YU Wenxuan4, XUE Feng1,2,3, WU Yue1,2,3,*(
), YU Wenxuan4, XUE Feng1,2,3, WU Yue1,2,3,*( )
)
- 1. Zhejiang Mariculture Research Institute, Wenzhou 325005, Zhejiang, China
2. Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Coastal Biological Germplasm Resources Conservation and Utilization, Wenzhou 325005, Zhejiang, China
3. Wenzhou Key Laboratory of Marine Biological Genetics and Breeding, Wenzhou 325005, Zhejiang, China
4. College of Marine Sciences, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
摘要: 为探明温州海域水产品中铬(Cr)、铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、砷(As)、镉(Cd)、汞(Hg)、铅(Pb)7种重金属元素的分布特征,利用高效液相色谱电感耦合等离子体质谱法和电感耦合等离子体质谱技术对从温州海域采集的11种海洋生物样品中的重金属含量进行测定,综合采用单因子污染指数法、综合污染指数和食用安全性评估等方法全面评价样品的重金属污染程度及其健康风险。结果表明:样品中Hg、As(以无机砷计)、Cd、Pb、Cr、Cu、Zn含量的平均值分别为0.015、0.035、0.17、0.14、0.23、4.38、12.13 mg·kg-1。对照GB 2762—2022《食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量》,样品中Cr、Cd、Hg、As、Pb含量的平均值均未超标。单因子污染指数评价的结果显示,三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)的重金属污染情况相对严重,Cu、Cd、Pb为轻度污染,Zn为中度污染。此外,三疣梭子蟹的综合污染指数值也最高,为0.46。食用安全性评估结果显示,供试样品的健康风险较低。供试样品的目标危险系数(THQ)和危害指数(HI)值均低于1,表明其食用安全性较高。总体来看,本次检测的温州海域水产品的重金属安全风险较低,但三疣梭子蟹和厚壳贻贝(Mytilus coruscus)的HI值分别达到0.680和0.526,须对其加强风险监测。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈星星, 虞雯煊, 薛峰, 吴越. 温州海域水产品的重金属分布特征与健康风险评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2354-2363.
CHEN Xingxing, YU Wenxuan, XUE Feng, WU Yue. Characteristics of heavy metals distribution and health risk evaluation of marine products in the sea areas of Wenzhou, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2354-2363.
| 元素 Element | 限量值Limit value/(mg·kg-1) | PTWI/(mg·kg-1) | RfD/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物Molluscs | 鱼类Fishes | 甲壳类Crustaceans | |||
| Cr | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.006 7 | 1.5 |
| Cu | 50.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 3.5 | 0.04 |
| Zn | 40.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 7.0 | 0.3 |
| As | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.015 | 0.000 3 |
| Cd | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.5/3.0 | 0.007 | 0.001 |
| Hg | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.000 7 | 0.000 5 |
| Pb | 1.0/1.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.025 | 0.003 5 |
表1 水产品中重金属的限量值、暂定每周耐受摄入量(PTWI)和参考剂量(RfD)
Table 1 Limit values, provisional tolerable weekly intake (PTWI) and reference dose (RfD) of heavy metals in aquatic products
| 元素 Element | 限量值Limit value/(mg·kg-1) | PTWI/(mg·kg-1) | RfD/(mg·kg-1·d-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物Molluscs | 鱼类Fishes | 甲壳类Crustaceans | |||
| Cr | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.006 7 | 1.5 |
| Cu | 50.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 3.5 | 0.04 |
| Zn | 40.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 7.0 | 0.3 |
| As | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.015 | 0.000 3 |
| Cd | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.5/3.0 | 0.007 | 0.001 |
| Hg | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.000 7 | 0.000 5 |
| Pb | 1.0/1.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.025 | 0.003 5 |
| 类别 Category | 物种 Species | Cr含量 Cr content | Cu含量 Cu content | Zn含量 Zn content | As含量 As content | Cd含量 Cd content | Hg含量 Hg content | Pb含量 Pb content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物 Molluscs | 曼氏无针乌贼 Sepiella maindroni | 0.12~0.12 (0.12) | 2.42~2.45 (2.44) | 15.46~15.55 (15.49) | 7.70~7.74 (7.72) | 0.049~0.050 (0.050) | 0.015~0.018 (0.016) | 0.16~0.17 (0.16) |
| de Rochebrune | ||||||||
| 长蛸 Octopus minor | 0.10~0.12 (0.11) | 9.08~9.95 (9.51) | 17.38~18.97 (18.14) | 7.83~8.56 (8.18) | 0.046~0.050 (0.048) | 0.006 2~0.007 2 (0.006 6) | 0.17~0.19 (0.18) | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.21~0.23 (0.22) | 0.59~0.64 (0.62) | 6.56~7.01 (6.83) | 0.68~0.73 (0.71) | 0.77~0.81 (0.79) | 0.004 3~0.004 4 (0.004 4) | 0.18~0.19 (0.19) | |
| 管角螺 Hemifusus tuba | 0.070~0.076 (0.072) | 7.93~8.55 (8.15) | 20.68~22.31 (21.29) | 21.51~23.15 (22.19) | 0.076~0.082 (0.078) | 0.016~0.018 (0.017) | 0.067~0.074 (0.070) | |
| 鱼类 Fishes | 棘头梅童鱼 Collichthys lucidus | 0.076~2.900 (1.460) | 0.21~0.26 (0.24) | 4.13~4.86 (4.39) | 1.00~1.92 (1.42) | 0.004 8~0.023 0 (0.014 0) | 0.011~0.021 (0.016) | 0.058~0.140 (0.100) |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼 Odontamblyopus | 0.072~0.094 (0.083) | 0.35~0.69 (0.51) | 3.35~6.80 (5.02) | 0.71~1.12 (0.91) | 0.008 0~0.029 0 (0.018 0) | 0.007 4~0.013 0 (0.010 0) | 0.11~0.21 (0.16) | |
| lacepedii | ||||||||
| 凤鲚 Coilia mystus | 0.081~0.140 (0.110) | 0.20~0.39 (0.29) | 4.57~6.65 (5.51) | 1.17~1.64 (1.42) | 0.006 1~0.012 0 (0.009 2) | 0.015~0.016 (0.016) | 0.049~0.090 (0.068) | |
| 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus | 0.082~0.083 (0.082) | 0.14~0.15 (0.15) | 2.82~2.91 (2.88) | 0.47~0.49 (0.48) | 0.013~0.014 (0.014) | 0.004 1~0.004 7 (0.004 4) | 0.21~0.22 (0.22) | |
| 鳓 Ilisha elongata | 0.077~0.078 (0.078) | 0.22~0.22 (0.22) | 5.19~5.23 (5.21) | 0.71~0.72 (0.71) | 0.009 4~0.010 0 (0.010 0) | 0.026~0.027 (0.027) | 0.085~0.087 (0.086) | |
| 甲壳类 Crustaceans | 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus | 0.093~0.110 (0.098) | 15.95~17.67 (16.53) | 30.44~33.59 (31.55) | 8.08~8.96 (8.38) | 0.69~0.76 (0.71) | 0.041~0.045 (0.043) | 0.15~0.18 (0.16) |
| trituberculatus | ||||||||
| 脊尾白虾 Exopalaemon | 0.091~0.11 (0.10) | 8.82~10.19 (9.48) | 16.06~18.37 (17.13) | 5.93~6.78 (6.33) | 0.084~0.096 (0.090) | 0.007 9~0.009 2 (0.008 5) | 0.16~0.19 (0.18) | |
| carinicauda |
表2 供测水产品的重金属含量
Table 2 Heavy metals contents in tested aquatic products mg·kg-1
| 类别 Category | 物种 Species | Cr含量 Cr content | Cu含量 Cu content | Zn含量 Zn content | As含量 As content | Cd含量 Cd content | Hg含量 Hg content | Pb含量 Pb content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 软体动物 Molluscs | 曼氏无针乌贼 Sepiella maindroni | 0.12~0.12 (0.12) | 2.42~2.45 (2.44) | 15.46~15.55 (15.49) | 7.70~7.74 (7.72) | 0.049~0.050 (0.050) | 0.015~0.018 (0.016) | 0.16~0.17 (0.16) |
| de Rochebrune | ||||||||
| 长蛸 Octopus minor | 0.10~0.12 (0.11) | 9.08~9.95 (9.51) | 17.38~18.97 (18.14) | 7.83~8.56 (8.18) | 0.046~0.050 (0.048) | 0.006 2~0.007 2 (0.006 6) | 0.17~0.19 (0.18) | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.21~0.23 (0.22) | 0.59~0.64 (0.62) | 6.56~7.01 (6.83) | 0.68~0.73 (0.71) | 0.77~0.81 (0.79) | 0.004 3~0.004 4 (0.004 4) | 0.18~0.19 (0.19) | |
| 管角螺 Hemifusus tuba | 0.070~0.076 (0.072) | 7.93~8.55 (8.15) | 20.68~22.31 (21.29) | 21.51~23.15 (22.19) | 0.076~0.082 (0.078) | 0.016~0.018 (0.017) | 0.067~0.074 (0.070) | |
| 鱼类 Fishes | 棘头梅童鱼 Collichthys lucidus | 0.076~2.900 (1.460) | 0.21~0.26 (0.24) | 4.13~4.86 (4.39) | 1.00~1.92 (1.42) | 0.004 8~0.023 0 (0.014 0) | 0.011~0.021 (0.016) | 0.058~0.140 (0.100) |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼 Odontamblyopus | 0.072~0.094 (0.083) | 0.35~0.69 (0.51) | 3.35~6.80 (5.02) | 0.71~1.12 (0.91) | 0.008 0~0.029 0 (0.018 0) | 0.007 4~0.013 0 (0.010 0) | 0.11~0.21 (0.16) | |
| lacepedii | ||||||||
| 凤鲚 Coilia mystus | 0.081~0.140 (0.110) | 0.20~0.39 (0.29) | 4.57~6.65 (5.51) | 1.17~1.64 (1.42) | 0.006 1~0.012 0 (0.009 2) | 0.015~0.016 (0.016) | 0.049~0.090 (0.068) | |
| 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus | 0.082~0.083 (0.082) | 0.14~0.15 (0.15) | 2.82~2.91 (2.88) | 0.47~0.49 (0.48) | 0.013~0.014 (0.014) | 0.004 1~0.004 7 (0.004 4) | 0.21~0.22 (0.22) | |
| 鳓 Ilisha elongata | 0.077~0.078 (0.078) | 0.22~0.22 (0.22) | 5.19~5.23 (5.21) | 0.71~0.72 (0.71) | 0.009 4~0.010 0 (0.010 0) | 0.026~0.027 (0.027) | 0.085~0.087 (0.086) | |
| 甲壳类 Crustaceans | 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus | 0.093~0.110 (0.098) | 15.95~17.67 (16.53) | 30.44~33.59 (31.55) | 8.08~8.96 (8.38) | 0.69~0.76 (0.71) | 0.041~0.045 (0.043) | 0.15~0.18 (0.16) |
| trituberculatus | ||||||||
| 脊尾白虾 Exopalaemon | 0.091~0.11 (0.10) | 8.82~10.19 (9.48) | 16.06~18.37 (17.13) | 5.93~6.78 (6.33) | 0.084~0.096 (0.090) | 0.007 9~0.009 2 (0.008 5) | 0.16~0.19 (0.18) | |
| carinicauda |
| 物种 Species | 各形态砷的平均含量Mean contents of As in various species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AsC | AsB | AsⅢ | AsⅤ | DMA | MMA | |
| 曼氏无针乌贼 Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | ND | 10.74 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 长蛸 Octopus minor | ND | 8.41 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.006 9 (1.40%) | 0.41 (83.01%) | ND | 0.061 (12.35%) | 0.016 (3.24%) | ND |
| 管角螺 Hemifusus tuba | ND | 19.02 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 棘头梅童鱼 Collichthys lucidus | 0.012 (0.88%) | 1.29 (94.57%) | 0.017 (1.25%) | 0.045 (3.30%) | ND | ND |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼 Odontamblyopus lacepedii | 0.017 (1.77%) | 0.89 (92.62%) | 0.007 9 (0.82%) | 0.046 (4.79%) | ND | ND |
| 凤鲚 Coilia mystus | 0.012 (0.79%) | 1.43 (94.48%) | ND | 0.065 (4.29%) | 0.006 6 (0.44%) | ND |
| 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus | 0.027 (6.40%) | 0.37 (87.64%) | ND | 0.012 (2.84%) | 0.007 1 (1.68%) | 0.006 1 (1.44%) |
| 鳓 Ilisha elongata | 0.021 (2.94%) | 0.64 (89.57%) | ND | 0.040 (5.60%) | 0.007 2 (1.01%) | 0.006 3 (0.88%) |
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | ND | 8.15 (99.79%) | ND | 0.017 (0.21%) | ND | ND |
| 脊尾白虾 Exopalaemon carinicauda | 0.26 (3.46%) | 7.26 (96.54%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
表3 供测水产品各形态砷的含量分布
Table 3 Arsenic speciation analysis in tested aquatic products mg·kg-1
| 物种 Species | 各形态砷的平均含量Mean contents of As in various species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AsC | AsB | AsⅢ | AsⅤ | DMA | MMA | |
| 曼氏无针乌贼 Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | ND | 10.74 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 长蛸 Octopus minor | ND | 8.41 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.006 9 (1.40%) | 0.41 (83.01%) | ND | 0.061 (12.35%) | 0.016 (3.24%) | ND |
| 管角螺 Hemifusus tuba | ND | 19.02 (100%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 棘头梅童鱼 Collichthys lucidus | 0.012 (0.88%) | 1.29 (94.57%) | 0.017 (1.25%) | 0.045 (3.30%) | ND | ND |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼 Odontamblyopus lacepedii | 0.017 (1.77%) | 0.89 (92.62%) | 0.007 9 (0.82%) | 0.046 (4.79%) | ND | ND |
| 凤鲚 Coilia mystus | 0.012 (0.79%) | 1.43 (94.48%) | ND | 0.065 (4.29%) | 0.006 6 (0.44%) | ND |
| 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus | 0.027 (6.40%) | 0.37 (87.64%) | ND | 0.012 (2.84%) | 0.007 1 (1.68%) | 0.006 1 (1.44%) |
| 鳓 Ilisha elongata | 0.021 (2.94%) | 0.64 (89.57%) | ND | 0.040 (5.60%) | 0.007 2 (1.01%) | 0.006 3 (0.88%) |
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | ND | 8.15 (99.79%) | ND | 0.017 (0.21%) | ND | ND |
| 脊尾白虾 Exopalaemon carinicauda | 0.26 (3.46%) | 7.26 (96.54%) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 物种 Species | 重金属元素的单因子污染指数Single factor pollution index of heavy metals (Pi) | P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | ||
| 曼氏无针乌贼Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0 |
| 长蛸Octopus minor | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0 |
| 厚壳贻贝Mytilus coruscus | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| 管角螺Hemifusus tuba | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.53 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0 |
| 棘头梅童鱼Collichthys lucidus | 0 . 73 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0 . 62 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼Odontamblyopus lacepedii | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.54 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.12 |
| 凤鲚Coilia mystus | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0 . 65 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.11 |
| 龙头鱼Harpadon nehereus | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.07 |
| 鳓Ilisha elongata | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| 三疣梭子蟹Portunus trituberculatus | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0 . 79 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 0.46 |
| 脊尾白虾Exopalaemon carinicauda | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0 |
表4 供测水产品的重金属污染指数情况评价
Table 4 Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in tested aquatic products
| 物种 Species | 重金属元素的单因子污染指数Single factor pollution index of heavy metals (Pi) | P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | ||
| 曼氏无针乌贼Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0 |
| 长蛸Octopus minor | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0 |
| 厚壳贻贝Mytilus coruscus | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| 管角螺Hemifusus tuba | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.53 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0 |
| 棘头梅童鱼Collichthys lucidus | 0 . 73 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0 . 62 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼Odontamblyopus lacepedii | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.54 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.12 |
| 凤鲚Coilia mystus | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0 . 65 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.11 |
| 龙头鱼Harpadon nehereus | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.07 |
| 鳓Ilisha elongata | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| 三疣梭子蟹Portunus trituberculatus | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0 . 79 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 0.46 |
| 脊尾白虾Exopalaemon carinicauda | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0 |
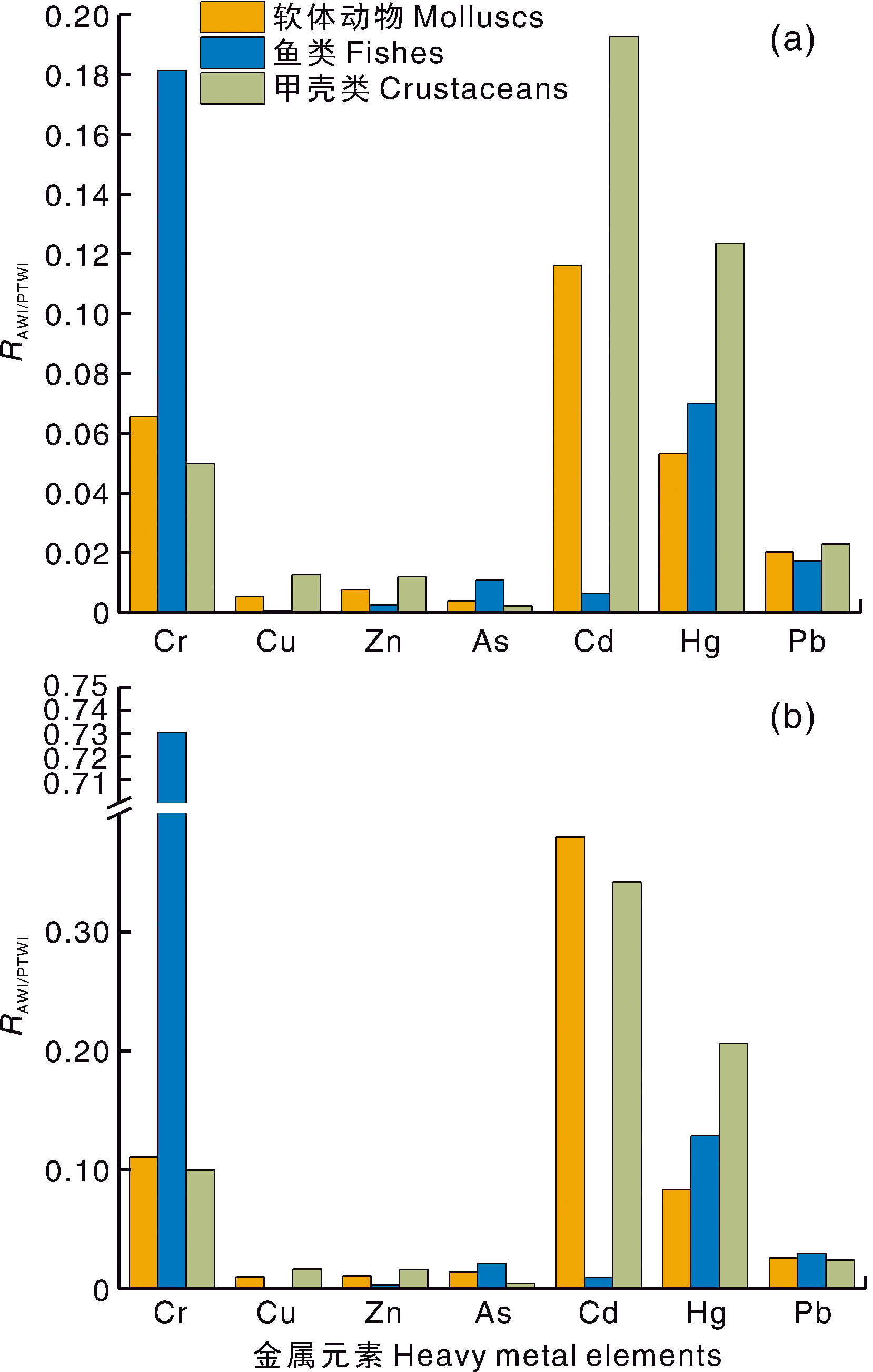
图1 供测水产品的食用安全性 a,以水产品中重金属的平均含量计;b,以水产品中重金属的最大含量计。RAWI/PTWI为本地区居民的每周实际重金属摄入量(AWI)与暂定每周耐受摄入量(PTWI)之比。
Fig.1 Food safety assessment of tested aquatic products a, Evaluation result based on the mean concentration of heavy metals in aquatic products; b, Evaluation result based on the maximum concentration of heavy metals in aquatic products. RAWI/PTWI, Ratio of the local adult weekly intake (AWI) of heavy metals to the provisionally tolerable weekly intake (PTWI).
| 物种 Species | 重金属元素的目标危险系数(THQ) Target hazard quotient of heavy metals (THQ) | 危害指数(HI) Hazard index (HI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | ||
| 曼氏无针乌贼Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | <0.001 | 0.029 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.015 | 0.022 | 0.115 |
| 长蛸Octopus minor | <0.001 | 0.110 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0.024 | 0.192 |
| 厚壳贻贝Mytilus coruscus | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.097 | 0.380 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.526 |
| 管角螺Hemifusus tuba | <0.001 | 0.098 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.037 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.196 |
| 棘头梅童鱼Collichthys lucidus | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.099 | 0.007 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.146 |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼Odontamblyopus lacepedii | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.085 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.140 |
| 凤鲚Coilia mystus | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.100 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.141 |
| 龙头鱼Harpadon nehereus | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.029 | 0.065 |
| 鳓Ilisha elongata | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.064 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0.118 |
| 三疣梭子蟹Portunus trituberculatus | <0.001 | 0.200 | 0.050 | 0.027 | 0.340 | 0.041 | 0.022 | 0.680 |
| 脊尾白虾Exopalaemon carinicauda | <0.001 | 0.110 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.212 |
表5 样品的非致癌健康风险
Table 5 Evaluation of non-carcinogenic health risk in samples
| 物种 Species | 重金属元素的目标危险系数(THQ) Target hazard quotient of heavy metals (THQ) | 危害指数(HI) Hazard index (HI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | ||
| 曼氏无针乌贼Sepiella maindroni de Rochebrune | <0.001 | 0.029 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.015 | 0.022 | 0.115 |
| 长蛸Octopus minor | <0.001 | 0.110 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.006 | 0.024 | 0.192 |
| 厚壳贻贝Mytilus coruscus | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.097 | 0.380 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.526 |
| 管角螺Hemifusus tuba | <0.001 | 0.098 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.037 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.196 |
| 棘头梅童鱼Collichthys lucidus | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.099 | 0.007 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.146 |
| 拉氏狼牙虾虎鱼Odontamblyopus lacepedii | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.085 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.140 |
| 凤鲚Coilia mystus | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.100 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.141 |
| 龙头鱼Harpadon nehereus | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.029 | 0.065 |
| 鳓Ilisha elongata | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.064 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0.118 |
| 三疣梭子蟹Portunus trituberculatus | <0.001 | 0.200 | 0.050 | 0.027 | 0.340 | 0.041 | 0.022 | 0.680 |
| 脊尾白虾Exopalaemon carinicauda | <0.001 | 0.110 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.212 |
| [1] | GOLDEN C D, ZACHARY KOEHN J, SHEPON A, et al. Aquatic foods to nourish nations[J]. Nature, 2021, 598(7880): 315-320. |
| [2] | MARTINEZ E C, SAJI S Z, ORE J V S, et al. The effects of omega-3, DHA, EPA, souvenaid in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology Reports, 2024, 44(3): 545-556. |
| [3] | HE Y T, DING M J, ZHANG J K, et al. Astaxanthin alleviates autoimmune hepatitis by modulating CD8+ T cells: insights from mass cytometry and single-cell RNA sequencing analyses[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(30): 2403148. |
| [4] | LIBRIZZI M, MARTINO C, MAURO M, et al. Natural anticancer peptides from marine animal species: evidence from in vitro cell model systems[J]. Cancers, 2023, 16(1): 36. |
| [5] | XIE H J, SHI Y H, WANG L, et al. Source and risk assessment of heavy metals in mining-affected areas in Jiangxi Province, China, based on Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2024, 31(14): 21765-21780. |
| [6] | NEETHU K V, PRAVED P H, XAVIER N, et al. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in seafood resources from the southwest coast of India: human health risk assessment and importance of seafood security[J]. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences, 2024, 16(2): 217-231. |
| [7] | GANI A, PATHAK S, HUSSAIN A. Comprehensive analysis of modified heavy metal pollution index and health risk assessment in the Yamuna River of Delhi, India: crucial study for environmental health management[J]. Journal of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste, 2024, 28(4): 04024021. |
| [8] | DEY S, RAJAK P, SEN K. Bioaccumulation of metals and metalloids in seafood: a comprehensive overview of mobilization, interactive effects in eutrophic environments, and implications for public health risks[J]. Journal of Trace Elements and Minerals, 2024, 8: 100141. |
| [9] | 冉茂霞, 莫晓, 史永富, 等. 东海三门湾主要海产品中典型重金属累积状况[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2024, 19(2): 349-358. |
| RAN M X, MO X, SHI Y F, et al. Typical heavy metals accumulation in main seafood of Sanmen Bay, the East China Sea[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2024, 19(2): 349-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 魏天飞. 杭州湾海域常见生物体内有机物及重金属含量研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2023, 40(4): 53-60. |
| WEI T F. The contents of organic matter and heavy metals in common organisms in Hangzhou Bay[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2023, 40(4): 53-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 陆昱养, 周伦敏, 何云亚. 象山县养殖水产品重金属污染与环境相关性研究[J]. 农村科学实验, 2024(10): 193-195. |
| LU Y Y, ZHOU L M, HE Y Y. Study on the correlation between heavy metal pollution and environment of aquatic products in Xiangshan County[J]. Rural Scientific Experiment, 2024(10): 193-195. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 徐菲菲, 胡红美, 郭远明, 等. 温州苍南海域表层沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(6): 577-582. |
| XU F F, HU H M, GUO Y M, et al. Heavy metals pollution characteristics and their potential ecological risk assessment in surface sediments from Cangnan Sea area, Wenzhou[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2020, 39(6): 577-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | HASEEB-UR-REHMAN M, MUNSHI A B, ATIQUE U, et al. Metal pollution and potential human health risk assessment in major seafood items (fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 188: 114581. |
| [14] | PANDION K, ARUNACHALAM K D, RAJAGOPAL R, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in the seafood at Kalpakkam coast, Southeast Bay of Bengal[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 189: 114766. |
| [15] | 吴昊, 张乐蒙, 黄智伟, 等. 厦门湾常见海洋经济生物重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2022, 41(3): 395-406. |
| WU H, ZHANG L M, HUANG Z W, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metal pollution of common marine commercial organisms in Xiamen Bay[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 395-406. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 李航, 蔡砚芳, 王奥, 等. 遵义市鱼腥草中汞·硒和锌的含量分布特征及其健康风险[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2024, 52(2): 187-189. |
| LI H, CAI Y F, WANG A, et al. Distribution characteristics of Hg, Se and Zn contents in Houttuynia cordata and its health risks in Zunyi City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(2): 187-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 刘冰, 王怡, 朱艳杰, 等. 膳食摄入水产品中重金属的风险评估[J]. 中国食品学报, 2021, 21(7): 267-275. |
| LIU B, WANG Y, ZHU Y J, et al. Risk assessment about the dietary intake of heavy metals in aquatic products[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(7): 267-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 叶海湄, 吴永宁. 鱼及加工产品中重金属指标的比较[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2009, 21(3): 273-276. |
| YE H M, WU Y N. Comparison of lead arsenic cadmium and mercury contamination on fish and fish products[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2009, 21(3): 273-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 侯彦琳, 郝青, 孙秀梅, 等. 苍南近岸海域水产品重金属分布特征及风险评估[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2024, 14(9): 1255-1263. |
| HOU Y L, HAO Q, SUN X M, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in aquatic products from the coastal area of Cangnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 14(9): 1255-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | ACEVES-MEDINA G, JIMÉNEZ-ROSENBERG S P A, DURAZO R, et al. Fish larvae as indicator species of interannual environmental variability in a subtropical transition area off the Baja California peninsula[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2019, 169/170: 104631. |
| [21] | MTHEMBU P P, ELUMALAI V, LI P Y, et al. Integration of heavy metal pollution indices and health risk assessment of groundwater in semi-arid coastal aquifers, South Africa[J]. Exposure and Health, 2022, 14(2): 487-502. |
| [22] | 熊怡然, 崔芮菲, 彭菲, 等. 东海近海及远洋捕捞水产品中重金属污染特征及膳食风险[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2022, 50(5): 147-151. |
| XIONG Y R, CUI R F, PENG F, et al. Concentrations and dietary risk of heavy metals in the seafood from the coastal area of the East China Sea and remote ocean areas[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(5): 147-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | DJEDJIBEGOVIC J, MARJANOVIC A, TAHIROVIC D, et al. Heavy metals in commercial fish and seafood products and risk assessment in adult population in Bosnia and Herzegovina[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 13238. |
| [24] | ARISEKAR U, SHAKILA R J, SHALINI R, et al. Accumulation potential of heavy metals at different growth stages of Pacific white leg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei farmed along the Southeast coast of Peninsular India: a report on ecotoxicology and human health risk assessment[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 212: 113105. |
| [25] | CHEN H J, HUANG X, TAYYAB M, et al. Copper homeostasis and its impact on innate immunity in crustaceans[J]. Reviews in Aquaculture, 2025, 17(1): e12963. |
| [26] | DAWOOD M A O, ALAGAWANY M, SEWILAM H. The role of zinc microelement in aquaculture: a review[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2022, 200(8): 3841-3853. |
| [27] | 刘香丽, 汪倩, 宋超, 等. 安徽养殖中华绒螯蟹体内砷形态的分布特征及膳食风险评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 2020, 16(6): 105-114. |
| LIU X L, WANG Q, SONG C, et al. Distribution characteristics and dietary risk assessment of arsenic speciations in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in Anhui Province[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2020, 16(6): 105-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | RAN M X, SHI Y F, WU D, et al. Characteristics of arsenic speciation in mainly cultured shellfish from Sanmen Bay, Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2023, 197: 115793. |
| [29] | BYEON E, JEONG H, KIM M S, et al. Toxicity and speciation of inorganic arsenics and their adverse effects on in vivo endpoints and oxidative stress in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 473: 134641. |
| [30] | DE CAMPOS F V, DE OLIVEIRA J A, DA SILVA A A, et al. Involvement of glutathione and glutathione metabolizing enzymes in Pistia stratiotes tolerance to arsenite[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2020, 22(4): 404-411. |
| [31] | 王雨璇, 陈冠虹, 喻敏, 等. 淡水硅藻的砷甲基化和砷氧化代谢机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(5): 1620-1630. |
| WANG Y X, CHEN G H, YU M, et al. Metabolic mechanisms of arsenic methylation and oxidation in freshwater diatoms[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2023, 17(5): 1620-1630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 陈星星, 虞雯煊, 徐健炜, 张鹏. 裙带菜不同部位重金属含量特征分析及健康风险评估[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1794-1804. |
| [2] | 徐汇镔, 朱洁, 周朝生, 胡园, 陆荣茂. 基于响应面分析的养殖水产品中高风险喹诺酮类抗生素残留及其基质效应研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(3): 689-700. |
| [3] | 王芸, 俞朝, 沈泓, 曹米娜, 周其耀, 胡智鹏, 金崇伟, 冯英. 硅锌叶面肥对芹菜镉积累和营养品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(1): 61-66. |
| [4] | 朱仁超, 原樱其, 杨宇, 杨琦玥, 余爱华. 公路沿线农田重金属污染研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(8): 1887-1897. |
| [5] | 肖银润, 马吉平, 王赟萍, 王素贞, 钟国祥, 熊小文, 张诚. 三种钝化剂对土壤重金属和羊肚菌子实体重金属含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1646-1656. |
| [6] | 王晓梅, 骆玉琴, 赵学平, 陆兰菲, 方楠, 王祥云, 蒋金花, 何红梅, 张昌朋, 王强. 氟吡菌酰胺在铁皮石斛中的残留与膳食风险[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1666-1676. |
| [7] | 褚田芬, 雷玲, 李勤锋, 吴平, 洪文杰, 郑蔚然. 浙江省西瓜中农药残留风险评估[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(5): 1153-1160. |
| [8] | 鲁子正钢, 朱立新, 季宏兵, 汪康. 鞘氨醇单胞菌修复土壤重金属污染研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(5): 1208-1216. |
| [9] | 俞朝, 王音予, 刘奇珍, 王芸, 沈泓, 冯英. 不同原料生物炭与无机钝化剂配施对小白菜地上部镉积累和土壤镉钝化的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(3): 613-621. |
| [10] | 刘玉红, 金检生, 陈丽萍, 孙彩霞. 黄桃中4种农药残留动态与风险评估[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 432-440. |
| [11] | 孙玖明, 张大乐, 宋纪斌, 赵守强, 李晓彤, 李中阳, 宋伟平, 刘源. 低积累作物品种筛选技术在保障重金属污染农田安全生产中的研究进展与应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(12): 2895-2908. |
| [12] | 吴雨珂, 王峰, 王依凡, 吴雪萍, 朱维琴. 牛粪蚯蚓堆肥条件优化与堆制物的性状变化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2308-2315. |
| [13] | 梁秀美, 张维一, 陈官菊, 夏海涛, 郭秀珠, 何如意, 蒋佳铭, 林定鹏. 温州市杨梅农药残留与重金属污染特征及膳食摄入风险评估[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2347-2357. |
| [14] | 杨西帆, 郭彬, 裘高扬, 刘俊丽, 童文彬, 杨海峻, 祝伟东, 毛聪妍. 不同钝化产品对水稻生产中镉、铅、砷的钝化效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 1-8. |
| [15] | 鲁帅, 罗晓刚, 刘全伟, 张屹, 孟洋昊, 李洁, 张景来. 有机无机复混肥对小麦生长、土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(4): 922-930. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

