浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2458-2467.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20241082
两株新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及其致病性
丁莹莹1,2( ), 杨林平1, 杨庆1, 张子晨1, 蔡霖颖1, 杨康1, 李琛1, 刘惠文1, 鲍光彬1, 王晴1, 王桂军1,2,*(
), 杨林平1, 杨庆1, 张子晨1, 蔡霖颖1, 杨康1, 李琛1, 刘惠文1, 鲍光彬1, 王晴1, 王桂军1,2,*( )
)
- 1.安徽农业大学 动物科技学院,安徽 合肥 230036
2.兽医病理生物学与疫病防控安徽省重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230036
-
收稿日期:2024-12-12出版日期:2025-12-25发布日期:2026-01-09 -
作者简介:丁莹莹(2000—),女,安徽铜陵人,硕士研究生,主要从事畜禽传染病防治研究。E-mail:2548354778@qq.com -
通讯作者:*王桂军,E-mail:wgj@ahau.edu.cn -
基金资助:安徽省家禽产业技术体系项目(2023—2024);安徽省高校协同创新项目(GXXT-2022-057)
Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of two novel goose astrovirus strains
DING Yingying1,2( ), YANG Linping1, YANG Qing1, ZHANG Zichen1, CAI Linying1, YANG Kang1, LI Chen1, LIU Huiwen1, BAO Guangbin1, WANG Qing1, WANG Guijun1,2,*(
), YANG Linping1, YANG Qing1, ZHANG Zichen1, CAI Linying1, YANG Kang1, LI Chen1, LIU Huiwen1, BAO Guangbin1, WANG Qing1, WANG Guijun1,2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Animal Science and Technology, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei 230036, China
2. Anhui Provincial Key Laboratory of Veterinary Pathobiology and Disease Control, Hefei 230036, China
-
Received:2024-12-12Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
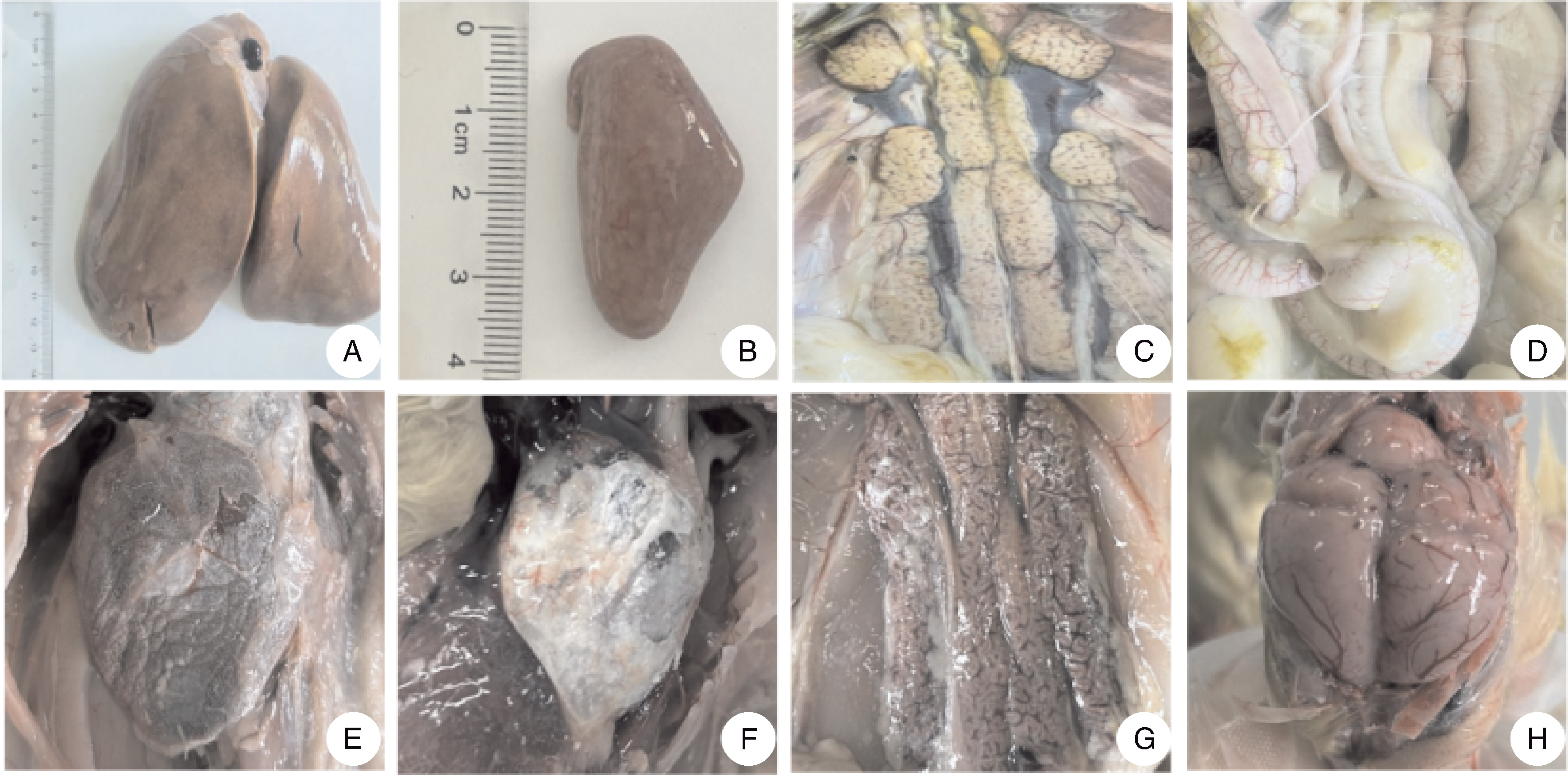
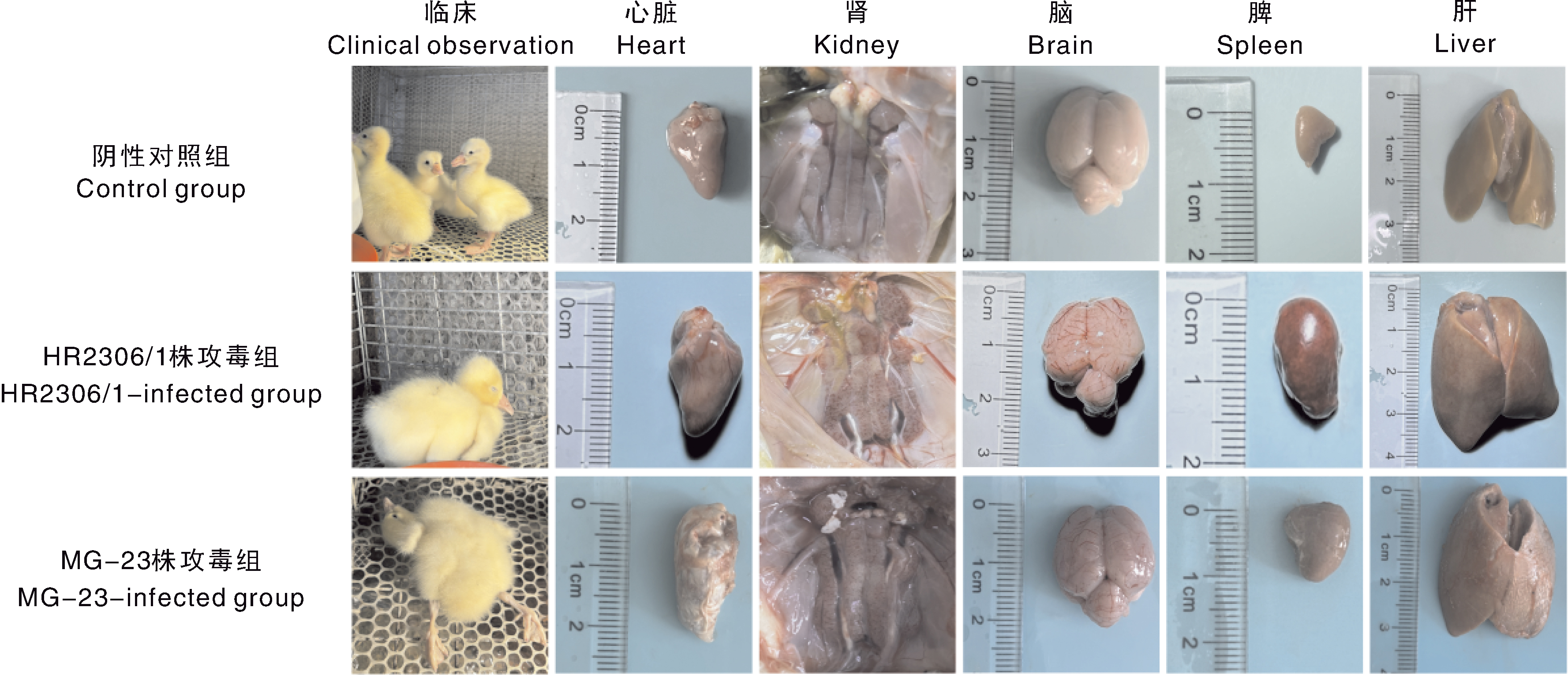
摘要: 为确定安徽省两处鹅场的鹅群发病原因,从2023年6—7月收集到的2份疑似新型鹅星状病毒(goose astrovirus, GAstV)感染病料(其中一例为70日龄育成鹅)中分离病毒,并进行全基因组测序和动物回归试验。结果表明:共分离鉴定出两株GAstV,分别将其命名为HR2306/1、MG-23株。这两株分离株的基因组全长均为7 175 nt,其开放阅读框2(ORF2)的核苷酸和氨基酸序列与2016—2023年其他分离株的同源性高于97%。ORF2编码的氨基酸序列的比对结果显示,这两个分离株与HR2110/1株(作者团队于2021年分离得到)含有共同的氨基酸变异位点,推测这两个分离株可能是由HR2110/1株演变而来的。动物回归试验结果显示,两株分离株对雏鹅有强致病性,与自然感染的雏鹅的临床表现一致,肾表面出现明显尿酸盐沉积。病理切片和免疫组织化学观察可见明显的病理学变化与星状病毒抗原,表明肾为GAstV的靶器官。上述结果说明,GAstV可以感染70日龄育成鹅,且该病毒对雏鹅仍具有较强的致病力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
丁莹莹, 杨林平, 杨庆, 张子晨, 蔡霖颖, 杨康, 李琛, 刘惠文, 鲍光彬, 王晴, 王桂军. 两株新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及其致病性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2458-2467.
DING Yingying, YANG Linping, YANG Qing, ZHANG Zichen, CAI Linying, YANG Kang, LI Chen, LIU Huiwen, BAO Guangbin, WANG Qing, WANG Guijun. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of two novel goose astrovirus strains[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2458-2467.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequences (5'→3') | 引物位置 Primer location |
|---|---|---|
| GASTV-1-F | AAACAGCGATATGGCGGC | 1~18 |
| GASTV-1-R | TGTACGACTTAGTCCAAGGAACG | 823~845 |
| GASTV-2-F | CACAGAGGCTACAATGCT | 378~395 |
| GASTV-2-R | CCTTCAACAACGACAATGG | 1 665~1 683 |
| GASTV-3-F | CAGTCCCTGTACAGATTTTA | 1 446~1 465 |
| GASTV-3-R | TCAACTTGTTCATCCTTTAC | 2 792~2 811 |
| GASTV-4-F | AGATTGATGAAGCCATTGAG | 2 604~2 623 |
| GASTV-4-R | CAGCCCGCCGTTCTGTCTGT | 3 939~3 958 |
| GASTV-5-F | AGGCTGTATCAGATATTGAT | 3 755~3 774 |
| GASTV-5-R | TCATTTTGTCATTAACGGG | 5 014~5 032 |
| GASTV-6-F | TCTGGTGAGTGGCGGACCGA | 4 799~4 818 |
| GASTV-6-R | TGTCATAACAGCCCACCAATTGTGT | 6 273~6 297 |
| GASTV-7-F | ACAACTGGACAAGGTACC | 6 028~6 045 |
| GASTV-7-R | TTTGCGGATTTTAAATGC | 7 131~7 148 |
表1 用于全基因组测序的引物的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of primers for whole genome sequencing
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'→3') Primer sequences (5'→3') | 引物位置 Primer location |
|---|---|---|
| GASTV-1-F | AAACAGCGATATGGCGGC | 1~18 |
| GASTV-1-R | TGTACGACTTAGTCCAAGGAACG | 823~845 |
| GASTV-2-F | CACAGAGGCTACAATGCT | 378~395 |
| GASTV-2-R | CCTTCAACAACGACAATGG | 1 665~1 683 |
| GASTV-3-F | CAGTCCCTGTACAGATTTTA | 1 446~1 465 |
| GASTV-3-R | TCAACTTGTTCATCCTTTAC | 2 792~2 811 |
| GASTV-4-F | AGATTGATGAAGCCATTGAG | 2 604~2 623 |
| GASTV-4-R | CAGCCCGCCGTTCTGTCTGT | 3 939~3 958 |
| GASTV-5-F | AGGCTGTATCAGATATTGAT | 3 755~3 774 |
| GASTV-5-R | TCATTTTGTCATTAACGGG | 5 014~5 032 |
| GASTV-6-F | TCTGGTGAGTGGCGGACCGA | 4 799~4 818 |
| GASTV-6-R | TGTCATAACAGCCCACCAATTGTGT | 6 273~6 297 |
| GASTV-7-F | ACAACTGGACAAGGTACC | 6 028~6 045 |
| GASTV-7-R | TTTGCGGATTTTAAATGC | 7 131~7 148 |
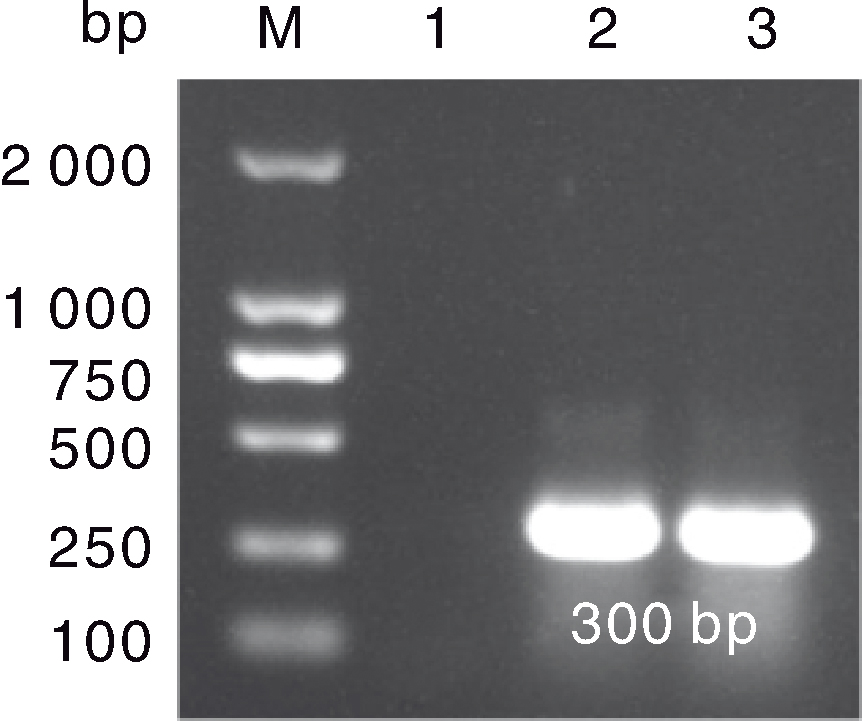
图2 鹅星状病毒(GAstV)的反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)检测结果 M,DL2000 marker;1,GAstV阴性对照;2,病例1样品;3,病例2样品。
Fig.2 Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) results of goose astrovirus (GAstV) M, DL2000 marker; 1, GAstV negative control; 2, Sample of case No.1;3: Sample of case No.2.
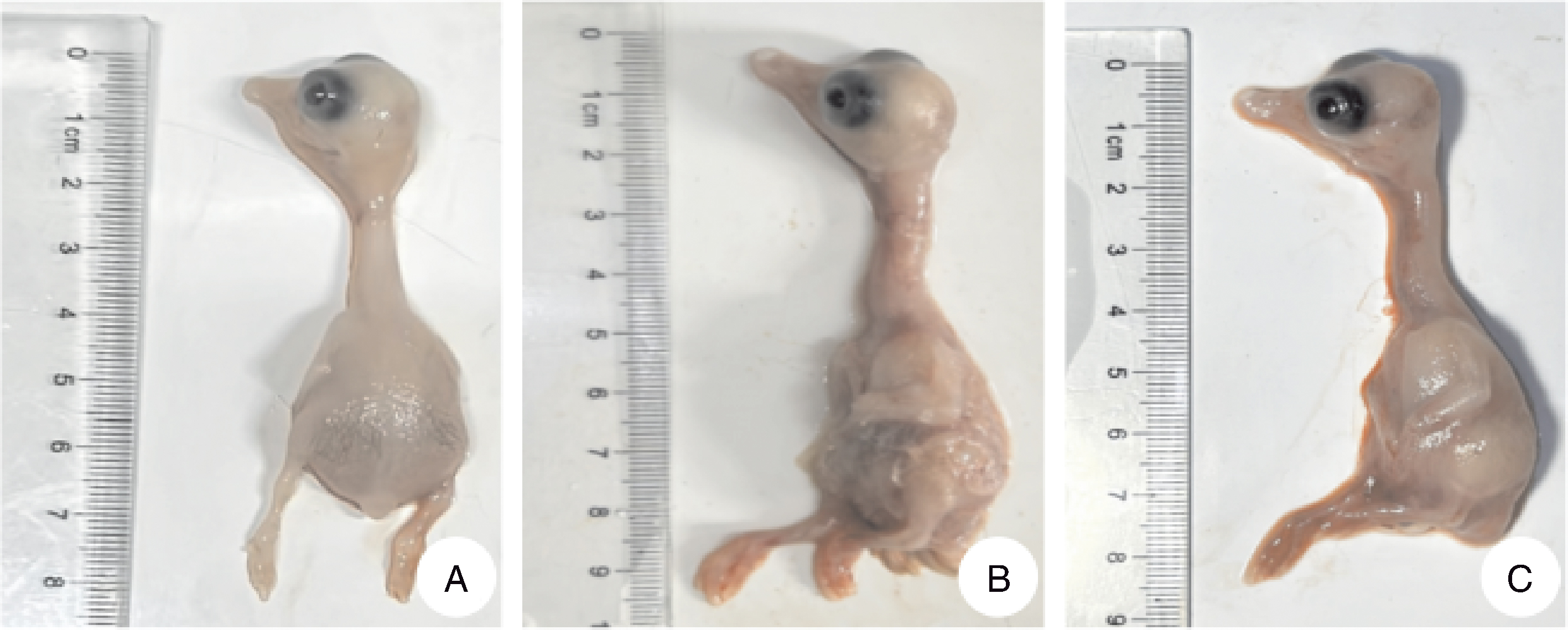
图3 HR2306/1、MG-23株接种3代的鹅胚病变图 A,对照组;B,接种HR2306/1株的鹅胚;C,接种MG-23株的鹅胚。
Fig.3 Pathological changes of goose embryo inoculated with HR2306/1 and MG-23 strains for 3 generations A, Goose embryo of control group; B, Goose embryo inoculated with HR2306/1 strain; C, Goose embryo inoculated with MG-23 strain.
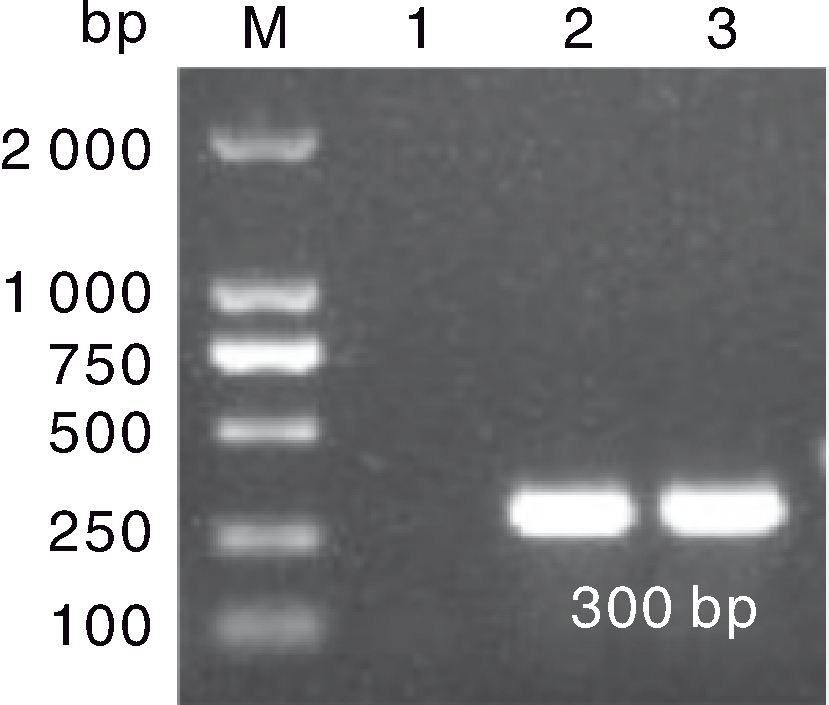
图4 F3代鹅胚的GAstV RT-PCR检测结果 M,DL2000 marker;1,阴性对照;2,接种HR2306/1株的F3代鹅胚尿囊液;3,接种MG-23株的F3代鹅胚尿囊液。
Fig.4 RT-PCR results of GAstV in F3 generation goose embryos M, DL2000 marker; 1, Negative control; 2, Allantoic fluid of F3 goose embryo inoculated with HR2306/1 strain ;3: Allantoic fluid of F3 goose embryo inoculated with MG-23 strain.
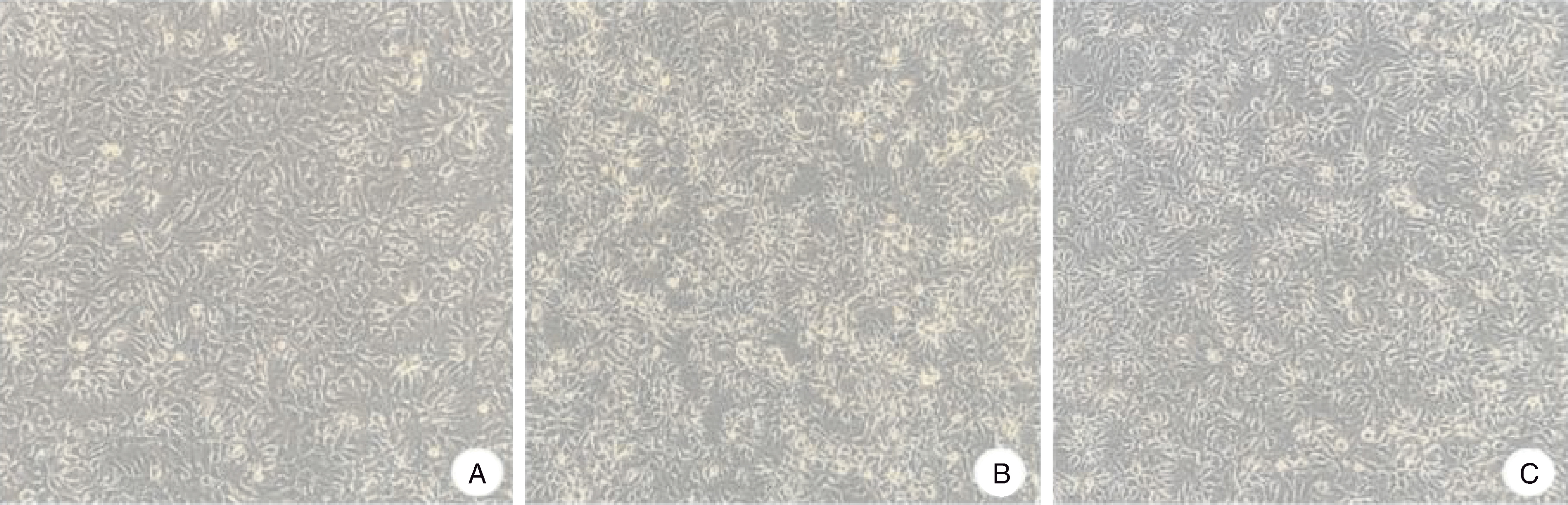
图5 LMH细胞接种鹅星状病毒后F3代的细胞病变情况(100×) A,对照组;B,HR2306/1株病毒液接种LMH细胞72 h;C,MG-23株病毒液接种LMH细胞72 h。
Fig.5 Cytopathic effect of F3 generation LMH cells inoculated with GAstV (100×) A, Control group; B, LMH cells inoculated with HR2306/1 viral fluids for 72 h; C, LMH cells inoculated with MG-23 viral fluids for 72 h.
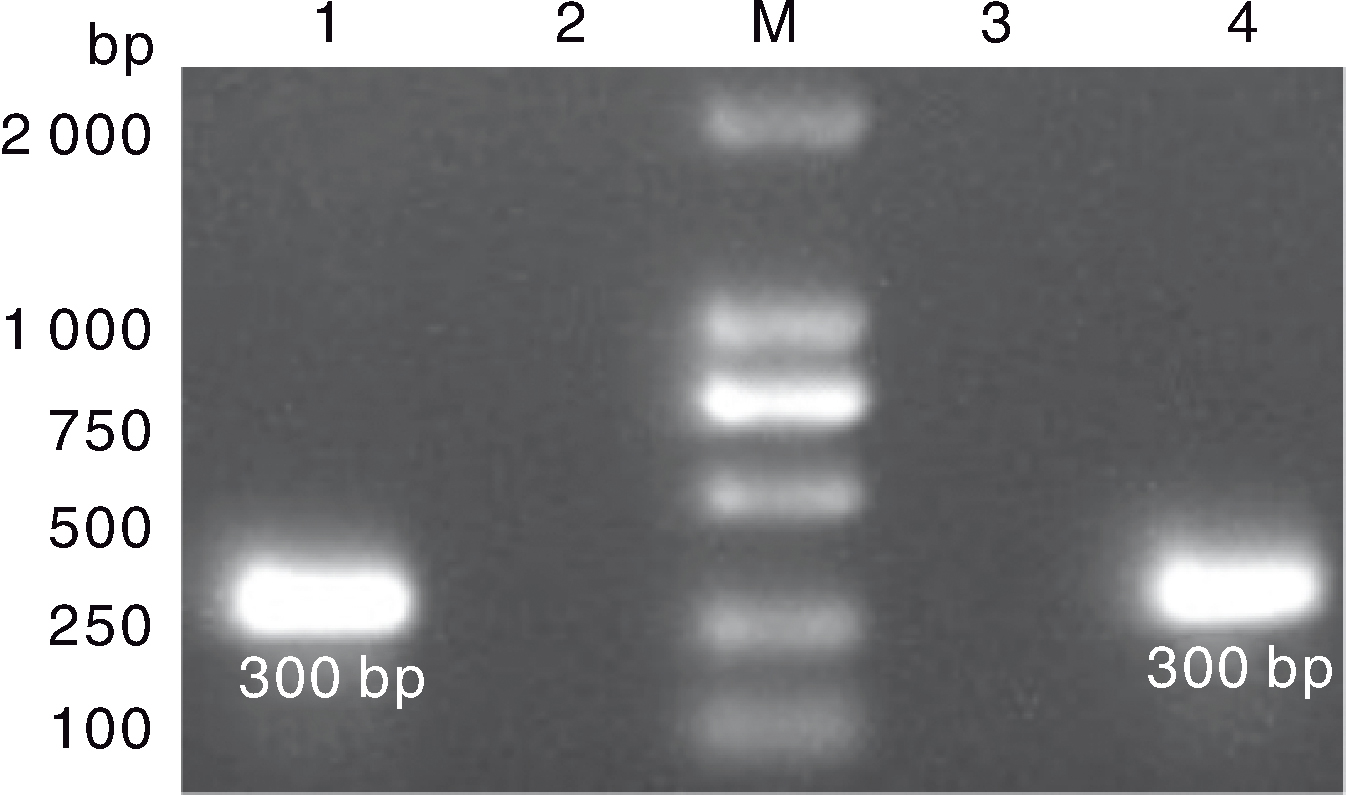
图6 LMH细胞GAstV的RT-PCR检测结果 M,DL2000 marker;1,MG-23株接种后的 F3代病毒液检测样;2、3:阴性对照;4,HR2306/1株接种后的F3代病毒液检测样。
Fig.6 RT-PCR result of GAstV on LMH cells M, DL2000 marker; 1, Fluid sample of F3 generation with inoculation of MG-23 strain; 2, 3, Negative control; 4, Fluid sample of F3 generation with inoculation of HR2306/1 strain.
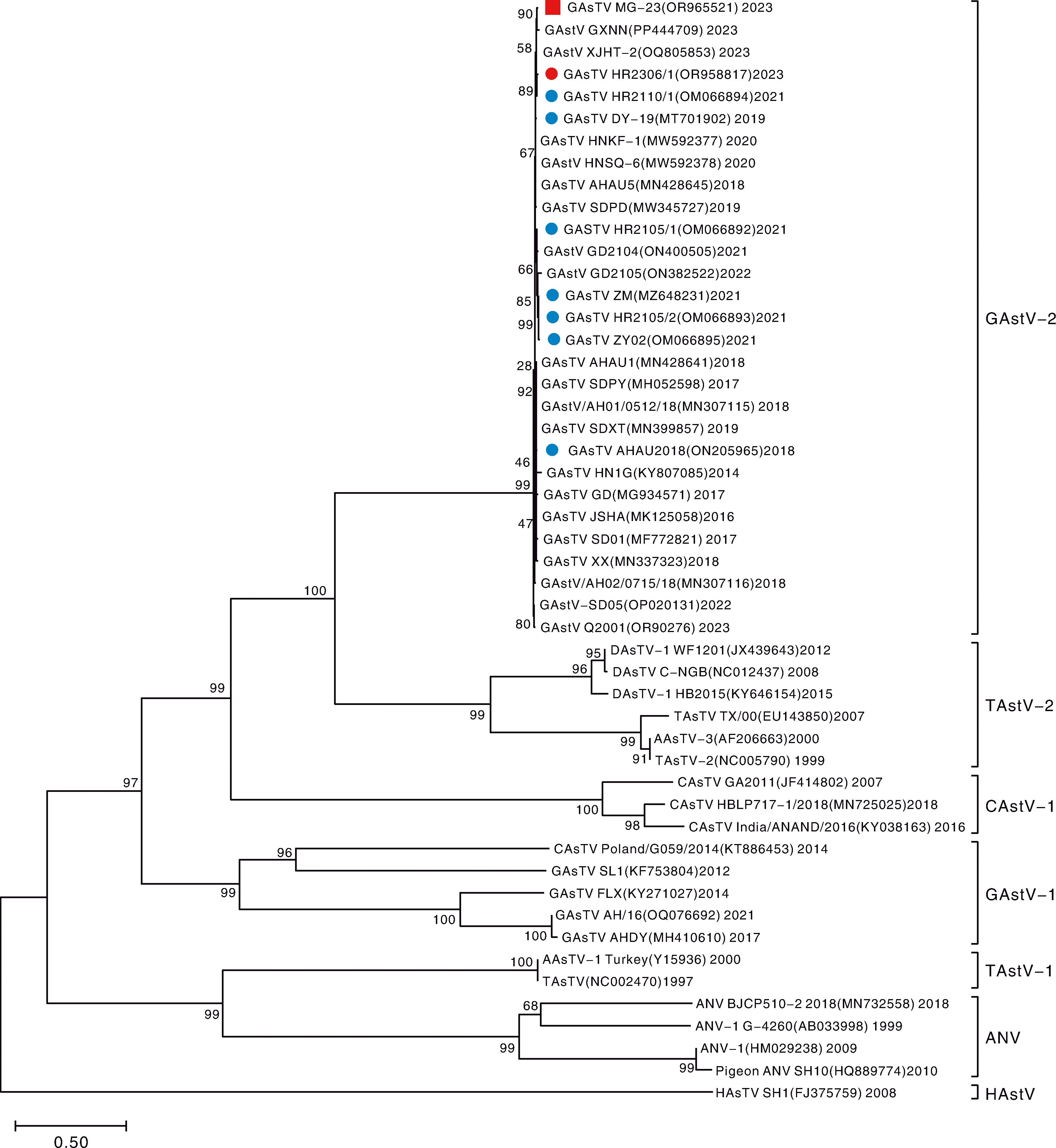
图7 基于星状病毒ORF2序列构建的系统发育树 “”标注序列为本研究分离毒株HR2306/1;“”标注序列为本研究分离毒株MG-23;“”标注序列为作者团队分离的其他毒株。GAstV-2,鹅星状病毒2型;TAstV-2,火鸡星状病毒2型;CAstV-1,鸡性状病毒1型;GAstV-1,鹅星状病毒1型;TAstV-1,火鸡星状病毒1型;ANV,禽肾炎病毒;HAstV,人星状病毒。
Fig.7 Phylogenetic tree based on the ORF2 sequence of astrovirus “ ” indicates the sequence of the isolated virus strain HR2306/1; “” indicates the sequence of the isolated virus strain MG-23; “” indicates the sequences of the other isolated virus strain by the authors’ team.GAstV-2,Goose astrovirus type 2; TAstV-2, Turkey astrovirus type 2; CAstV-1, Chicken astrovirus type 1; GAstV-1, Goose astrovirus type 1; TAstV-1, Turkey astrovirus type 1; ANV, Avian nephritis virus; HAstV, Human astrovirus.
| 年份 Year | 分离毒株 Virus strains | 核苷酸序列同源性 Nucleotide homology/% | 氨基酸序列同源性 Amino acid homology/% | 突变位点及其氨基酸 Mutation site and amino acid | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR2306/1 | MG-23 | HR2306/1 | MG-23 | HR2306/1 | MG-23 | ||||||||||||||
| ORF1a | ORF1b | ORF2 | ORF1a | ORF1b | ORF2 | 26 | 228 | 380 | 608 | 614 | 630 | 228 | 608 | 614 | 695 | ||||
| Q | T | S | T | T | A | S | T | T | T | ||||||||||
| 2023 | GXNN | 98.6 | 99.3 | 98.3 | 98.4 | 99.2 | 98.7 | 99.0 | 99.4 | H | S | N | T | T | T | S | T | T | A |
| Q2001 | 97.3 | 99.0 | 97.6 | 97.0 | 98.6 | 97.5 | 97.9 | 98.2 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| XJHT-2 | 98.3 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 97.8 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.7 | H | T | N | T | T | T | T | T | T | S | |
| 2022 | SD05 | 97.5 | 98.8 | 98.0 | 97.2 | 98.3 | 97.8 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| GD2105 | 96.9 | 98.7 | 97.3 | 96.3 | 98.2 | 97.2 | 97.4 | 97.9 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| 2021 | HR2105/1 | 99.2 | 99.5 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.9 | 98.4 | 99.0 | 99.0 | H | A | N | S | N | A | A | S | N | A |
| HR2105/2 | 98.6 | 98.5 | 98.2 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 97.9 | 98.4 | 98.9 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| HR2110/1 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 98.5 | 99.0 | 98.8 | 99.6 | 99.4 | Q | T | N | T | T | T | T | T | T | A | |
| ZY02 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 97.9 | 98.3 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| ZM | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.3 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.0 | 98.6 | 99.0 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| GD2104 | 98.8 | 99.3 | 98.5 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 98.7 | 98.9 | 99.3 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| 2020 | HNKF-1 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| HNSQ-6 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 98.5 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| 2019 | DY-19 | 99.0 | 99.5 | 98.8 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 98.6 | 98.4 | 98.7 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| SDXT | 96.3 | 98.2 | 98.2 | 96.0 | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| 2018 | AHAU2018 | 97.5 | 98.7 | 98.0 | 97.1 | 98.1 | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.2 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| CXZ | 96.7 | 98.5 | 98.3 | 96.3 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.2 | 98.4 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| AHAU1 | 97.4 | 98.5 | 98.1 | 96.6 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.6 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | T | |
| 2017 | SD01 | 97.8 | 98.5 | 97.8 | 97.3 | 98.1 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.7 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| GD | 97.5 | 98.5 | 97.6 | 96.9 | 98.0 | 97.4 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| SDPY | 97.1 | 98.6 | 98.2 | 96.7 | 98.2 | 98.1 | 98.4 | 99.0 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | T | |
| 2016 | JSHA | 97.2 | 98.6 | 98.0 | 96.9 | 98.0 | 97.7 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
表2 核苷酸和氨基酸序列的同源性与ORF2编码氨基酸的变异位点分析
Table 2 Analysis of nucleotide and amino acid sequences homology and variant sites of ORF2-encoded amino acids
| 年份 Year | 分离毒株 Virus strains | 核苷酸序列同源性 Nucleotide homology/% | 氨基酸序列同源性 Amino acid homology/% | 突变位点及其氨基酸 Mutation site and amino acid | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR2306/1 | MG-23 | HR2306/1 | MG-23 | HR2306/1 | MG-23 | ||||||||||||||
| ORF1a | ORF1b | ORF2 | ORF1a | ORF1b | ORF2 | 26 | 228 | 380 | 608 | 614 | 630 | 228 | 608 | 614 | 695 | ||||
| Q | T | S | T | T | A | S | T | T | T | ||||||||||
| 2023 | GXNN | 98.6 | 99.3 | 98.3 | 98.4 | 99.2 | 98.7 | 99.0 | 99.4 | H | S | N | T | T | T | S | T | T | A |
| Q2001 | 97.3 | 99.0 | 97.6 | 97.0 | 98.6 | 97.5 | 97.9 | 98.2 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| XJHT-2 | 98.3 | 99.2 | 99.1 | 97.8 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.7 | H | T | N | T | T | T | T | T | T | S | |
| 2022 | SD05 | 97.5 | 98.8 | 98.0 | 97.2 | 98.3 | 97.8 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| GD2105 | 96.9 | 98.7 | 97.3 | 96.3 | 98.2 | 97.2 | 97.4 | 97.9 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| 2021 | HR2105/1 | 99.2 | 99.5 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.9 | 98.4 | 99.0 | 99.0 | H | A | N | S | N | A | A | S | N | A |
| HR2105/2 | 98.6 | 98.5 | 98.2 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 97.9 | 98.4 | 98.9 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| HR2110/1 | 99.4 | 99.5 | 99.3 | 98.5 | 99.0 | 98.8 | 99.6 | 99.4 | Q | T | N | T | T | T | T | T | T | A | |
| ZY02 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.2 | 97.7 | 97.9 | 98.3 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| ZM | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.3 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.0 | 98.6 | 99.0 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| GD2104 | 98.8 | 99.3 | 98.5 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 98.7 | 98.9 | 99.3 | H | S | N | S | N | T | S | S | N | A | |
| 2020 | HNKF-1 | 99.0 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| HNSQ-6 | 98.9 | 99.4 | 99.1 | 98.5 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 99.0 | 99.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| 2019 | DY-19 | 99.0 | 99.5 | 98.8 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 98.6 | 98.4 | 98.7 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| SDXT | 96.3 | 98.2 | 98.2 | 96.0 | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| 2018 | AHAU2018 | 97.5 | 98.7 | 98.0 | 97.1 | 98.1 | 97.8 | 97.9 | 98.2 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| CXZ | 96.7 | 98.5 | 98.3 | 96.3 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.2 | 98.4 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| AHAU1 | 97.4 | 98.5 | 98.1 | 96.6 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.6 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | T | |
| 2017 | SD01 | 97.8 | 98.5 | 97.8 | 97.3 | 98.1 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.7 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
| GD | 97.5 | 98.5 | 97.6 | 96.9 | 98.0 | 97.4 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A | |
| SDPY | 97.1 | 98.6 | 98.2 | 96.7 | 98.2 | 98.1 | 98.4 | 99.0 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | T | |
| 2016 | JSHA | 97.2 | 98.6 | 98.0 | 96.9 | 98.0 | 97.7 | 98.0 | 98.3 | H | A | N | S | A | T | A | S | A | A |
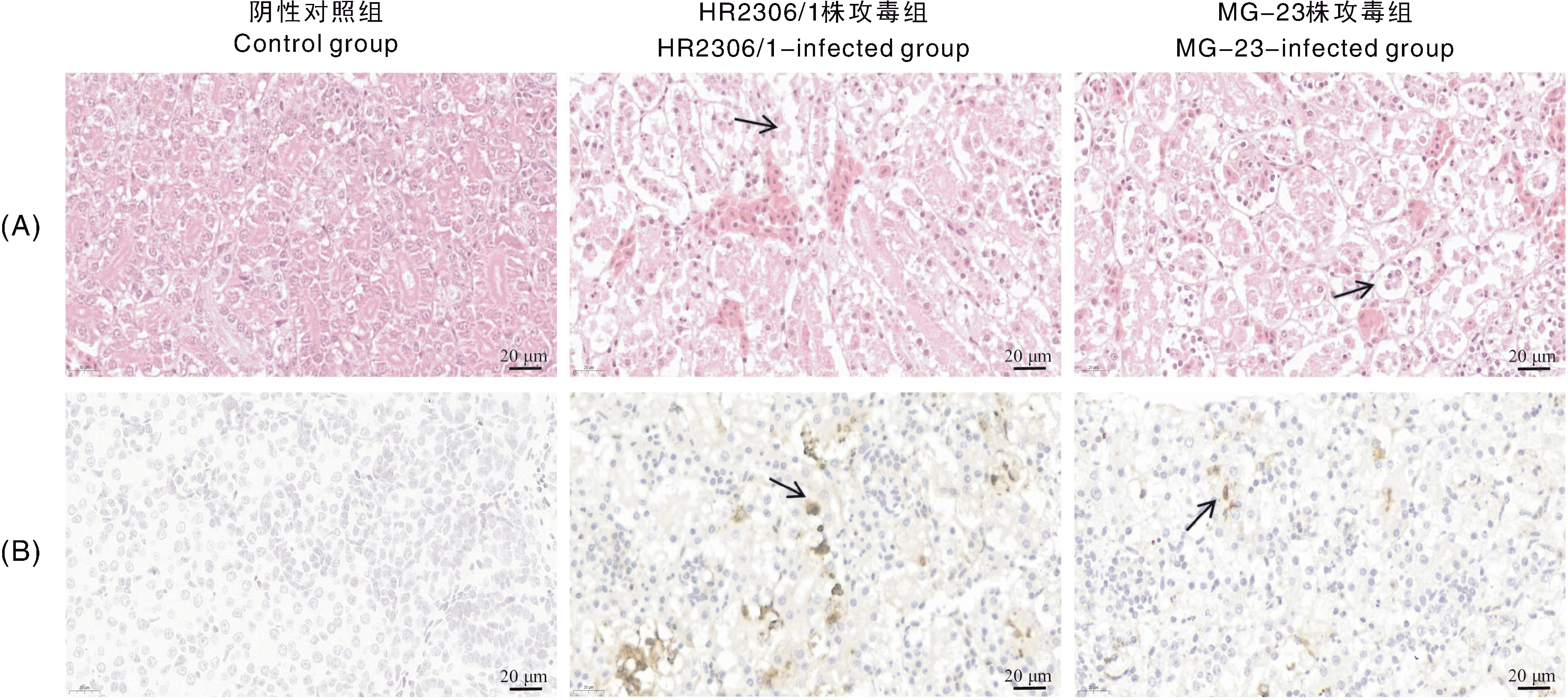
图9 雏鹅肾的苏木精-伊红(HE)染色(A)和免疫组织化学(IHC)染色(B)结果 图中黑色箭头指示病理变化与阳性信号。
Fig.9 Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining (A) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining (B) result of goslings kidney Black arrows point out pathological changes and positive signals.
| [1] | ZHANG Y X, WANG F M, LIU N, et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel avastrovirus in goose[J]. Archives of Virology, 2017, 162(7): 2135-2139. |
| [2] | ZHANG X Y, REN D, LI T F, et al. An emerging novel goose astrovirus associated with gosling gout disease, China[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 2018, 7(1): 1-8. |
| [3] | 孙舰. 新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及Cap蛋白多克隆抗体的制备[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2022. |
| SUN J. Isolation and identification of a novel goose astrovirus and preparation of polyclonal antibody against Cap protein[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | ZHU Y C, WANG H Y, HUA J G, et al. Isolation and pathogenicity of a novel goose astrovirus from overfed adult landaise geese in China[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(12): 2806. |
| [5] | BASS D M, QIU S. Proteolytic processing of the astrovirus capsid[J]. Journal of Virology, 2000, 74(4): 1810-1814. |
| [6] | SANDOVAL-JAIME C. Astrovirus reverse genetics systems, a story of success[J]. Current Opinion in Virology, 2020, 44: 57-65. |
| [7] | WANG Y, BAI C X, ZHANG D, et al. Genomic and phylogenetic characteristics of a novel goose astrovirus in Anhui Province, central-eastern China[J]. Gene, 2020, 756: 144898. |
| [8] | 张思远, 卢秀娴, 梁昭平, 等. 我国部分地区新型鹅星状病毒ORF2基因序列及遗传变异分析[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2021, 38(6): 1-5. |
| ZHANG S Y, LU X X, LIANG Z P, et al. ORF2 gene sequence of novel goose astroviruses isolated in China and genetic variation analysis[J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2021, 38(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | ZHU Q H, SUN D B. Goose astrovirus in China: a comprehensive review[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(8): 1759. |
| [10] | ARIAS C F, DUBOIS R M. The astrovirus capsid: a review[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9(1): 15. |
| [11] | 刘莉, 顾玲玲, 张硕, 等. 1型鹅星状病毒ORF2蛋白原核表达及其多克隆抗体的制备与鉴定[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2022, 49(1): 368-374. |
| LIU L, GU L L, ZHANG S, et al. Prokaryotic expression of ORF2 protein of goose astrovirus 1 and preparation and identification of its polyclonal antibody[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 49(1): 368-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | DE BENEDICTIS P, SCHULTZ-CHERRY S, BURNHAM A, et al. Astrovirus infections in humans and animals:molecular biology, genetic diversity, and interspecies transmissions[J]. Infection,Genetics and Evolution, 2011, 11(7): 1529-1544. |
| [13] | 张玉杰, 孙宁, 刘东, 等. 鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及全基因组序列分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2020, 51(11): 2765-2777. |
| ZHANG Y J, SUN N, LIU D, et al. Isolation, identification and complete genomic sequence analysis of goose astrovirus[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2020, 51(11): 2765-2777. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | YUAN X Y, MENG K, ZHANG Y X, et al. Genome analysis of newly emerging goose-origin nephrotic astrovirus in China reveals it belongs to a novel genetically distinct astrovirus[J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 2019, 67: 1-6. |
| [15] | CHEN Q X, YU Z L, XU X, et al. First report of a novel goose astrovirus outbreak in Muscovy ducklings in China[J]. Poultry Science, 2021, 100(10): 101407. |
| [16] | ZHANG X Z, DENG T W, SONG Y Z, et al. Identification and genomic characterization of emerging goose astrovirus in central China, 2020[J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2022, 69(3): 1046-1055. |
| [17] | 贾北平, 吕炫, 杨庆, 等. 安徽省5株新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定与遗传进化分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(5): 1048-1057. |
| JIA B P, LYU X, YANG Q, et al. Isolation, identification and genetic evolution analysis of novel goose astrovirus in Anhui Province, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(5): 1048-1057. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | ZHANG M, LV X, WANG B, et al. Development of a potential diagnostic monoclonal antibody against capsid spike protein VP27 of the novel goose astrovirus[J]. Poultry Science, 2022, 101(3): 101680. |
| [19] | 孙敏. 新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及其抗体竞争ELISA检测方法的建立[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021. |
| SUN M. Isolation and identification of new goose astrovirus and establishment of competitive ELISA for antigboy to goose astrovirus[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 邵骜骏, 李阁, 张思旺, 等. 一例鹅痛风病的诊断[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(6): 86-87, 171. |
| SHAO A J, LI G, ZHANG S W, et al. Diagnosis of a goose gout disease[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(6): 86-87, 171. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王晓冰, 施建鑫, 罗开健. 禽星状病毒感染的流行特点[J]. 养禽与禽病防治, 2018(10): 2-7. |
| WANG X B, SHI J X, LUO K J. Epidemiological features of avian astrovirus infection[J]. Poultry Husbandry and Disease Control, 2018(10): 2-7. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | LEE T W, KURTZ J B. Serial propagation of astrovirus in tissue culture with the aid of trypsin[J]. Journal of General Virology, 1981, 57(Pt 2): 421-424. |
| [23] | LIU N, JIANG M, WANG M H, et al. Isolation and detection of duck astrovirus CPH: implications for epidemiology and pathogenicity[J]. Avian Pathology, 2016, 45(2): 221-227. |
| [24] | WEI F, WANG Y M, WANG Q Q, et al. The isolation and characterization of duck astrovirus type-1 remerging in China[J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2022, 69(5): 2890-2897. |
| [25] | PENG Z F, GAO D S, SONG X H, et al. Isolation and genomic characterization of one novel goose astrovirus causing acute gosling gout in China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 10565. |
| [26] | 张清水. 新发肾致病型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及弱毒株选育[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2019. |
| ZHANG Q S. Characterizatin of a new nephropathogenic goose astrovirus and development of an attenuated vaccine candidate[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 金前跃, 郭永刚, 李俊朋, 等. 鹅星状病毒XX株的分离鉴定及遗传特征分析[J]. 河南农业科学, 2021, 50(6): 134-141. |
| JIN Q Y, GUO Y G, LI J P, et al. Isolation, identification and genetic characterization of goose astrovirus isolate XX[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 50(6): 134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 宋婷婷, 杨燚, 刘冠星, 等. 鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定及其在雏鹅体内的分布规律[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2020, 52(4): 72-79. |
| SONG T T, YANG Y, LIU G X, et al. In vivo isolation and identification of an astrovirus in goose and its dynamic distribution in goslings[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 52(4): 72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | YANG J, TIAN J J, TANG Y, et al. Isolation and genomic characterization of gosling gout caused by a novel goose astrovirus[J]. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 2018, 65(6): 1689-1696. |
| [30] | 侯展鹏, 梁宇, 王海悦, 等. 广东地区致雏鹅痛风鹅星状病毒的鉴定及遗传演化分析[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2023, 45(3): 310-314. |
| HOU Z P, LIANG Y, WANG H Y, et al. Identification and evolutionary analysis of goose astrovirus that causing gout in gosling in Guangdong province[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 45(3): 310-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 马献, 尤雨薇, 康娟, 王国琴, 郑蕊, 苏建宇, 岳思君. 枸杞采后致腐病原菌的分离鉴定与天然抑菌剂筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1327-1335. |
| [2] | 巩鑫鑫, 刘瑞玲, 韩延超, 孟祥红, 郜海燕, 陈杭君. 四种食用菌采后主要病原菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(2): 456-465. |
| [3] | 鲍梦楠, 李劲斌, 张宪, 闫佳会. 青海省海东市设施番茄根结线虫病原鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(12): 2545-2553. |
| [4] | 郭伟娜, 陶晶, 何梦婷, 王紫苇, 马佰贺, 赵磊. 鸡源鼠伤寒沙门菌的分离鉴定、药敏试验与毒力基因检测[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(2): 284-294. |
| [5] | 纪嵩岩, 邵长琪, 齐文康, 何煜晖, 张欣, 王翠平. 枸杞根腐病病原鉴定及拮抗菌筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2283-2297. |
| [6] | 贾北平, 吕炫, 杨庆, 王一楠, 李皖萧, 解新迪, 朱英奇, 王蓓, 殷冬冬, 张云凯, 王晴, 王桂军. 安徽省5株新型鹅星状病毒的分离鉴定与遗传进化分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(5): 1048-1057. |
| [7] | 张淑红, 张运峰, 武秋颖, 高凤菊, 李亚子, 纪景欣, 许可, 范永山. 玉米大斑病菌醇脱氢酶基因家族的鉴定和生物信息学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(5): 1108-1115. |
| [8] | 唐毅, 杨清麟, 王伟, 袁渊, 丁诗华, 孙翰昌, 吕浩. 宽体金线蛭水肿病病原的分离鉴定与病理学研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(12): 2844-2853. |
| [9] | 普梅英, 武自强, 张诗文, 李艳杰, 朱幼娇, 吴坤, 陈龙清, 王超. 华东山茶花腐病病原菌分离鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(1): 121-127. |
| [10] | 王志鹏, 赵剑, 黄盼, 崔雪梅, 南黎, 宋厚辉, 鲍国连, 刘燕. 兔源大肠埃希菌噬菌体分离鉴定与生物学特性研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1599-1608. |
| [11] | 詹佳飞, 徐魁, 张磊, 夏介英, 洪杨, 董涵, 刘洋露, 周静, 袁明铭, 王永金, 鄢良春. 毛蕊花糖苷抑制2型猪链球菌的溶血素蛋白活性而降低其小鼠致病性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1609-1616. |
| [12] | 李旭东, 刘永涛, 杨先乐, 杨移斌, 艾晓辉. 蛙类歪头、破头与白眼综合征病原分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1617-1625. |
| [13] | 王晓丽, 赵英伟, 孔晓娜, 曹子林. 蓝桉根际菌根真菌的分离鉴定及其对蓝桉生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(5): 1015-1023. |
| [14] | 朱寅初, 王宏宇, 云涛, 华炯钢, 叶伟成, 倪征, 陈柳, 张存. 浙江地区鹅星状病毒分离鉴定及其衣壳蛋白多克隆抗体的制备[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(10): 2149-2159. |
| [15] | 杨成年, 李芳, 朱成科, 唐征县, 易子琳, 韩璐璐, 阳龙江, 彭小倩, 贺蝶, 李杨, 任朝颖, 吕光俊. 杂交鲟出血病病原的分离鉴定与组织病理学观察[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(12): 2275-2285. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||