浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 136-147.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240955
新型肥料对典型黄河故道区土壤养分、微生物群落及稻麦产量的影响
李传哲1( ), 董青君1, 纪力1, 汪吉东2, 陈川1, 章安康1, 张永春2, 邵文奇1,*(
), 董青君1, 纪力1, 汪吉东2, 陈川1, 章安康1, 张永春2, 邵文奇1,*( )
)
- 1.江苏徐淮地区淮阴农业科学研究所,江苏 淮安 223001
2.江苏省农业科学院 农业资源与环境研究所,江苏 南京 210014
-
收稿日期:2024-11-07出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:邵文奇, E-mail:wqshao1103@sina.com
李传哲,主要从事农业资源利用研究。E-mail:lichuanzhe66@163.com -
通讯作者:邵文奇 -
基金资助:江苏省重点研发计划(BE2021378);淮安市级基础研究计划项目(联合专项)(HABL2023053);淮安市级基础研究计划项目(联合专项)(3070)
Effects of new-type fertilizers on soil nutrients, microbial community, and yield of rice and wheat in the typical ancient course area of Yellow River, China
LI Chuanzhe1( ), DONG Qingjun1, JI Li1, WANG Jidong2, CHEN Chuan1, ZHANG Ankang1, ZHANG Yongchun2, SHAO Wenqi1,*(
), DONG Qingjun1, JI Li1, WANG Jidong2, CHEN Chuan1, ZHANG Ankang1, ZHANG Yongchun2, SHAO Wenqi1,*( )
)
- 1. Huaiyin Institute of Agricultural Sciences of Xuhuai Area in Jiangsu, Huai’an 223001, Jiangsu, China
2. Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanjing 210014, China
-
Received:2024-11-07Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:SHAO Wenqi
摘要:
为探究不同新型肥料对典型黄河故道区土壤养分、土壤微生物群落及作物产量的影响,本研究开展田间定位试验,设置CK(常规施肥)、NM(增施氮肥187.5 kg·hm-2与微生物菌剂30 kg·hm-2)、F(施用生物有机肥6 000 kg·hm-2)、FE(施用生物有机肥6 000 kg·hm-2+土壤酶制剂15 kg·hm-2)共4个处理,待作物收获后测定土壤理化性质、土壤酶活性及作物产量等指标,并采用16S rRNA高通量测序技术对土壤细菌群落的组成进行分析。 结果表明,与CK相比: F和FE处理的土壤有机质和有效磷含量显著(p<0.05)升高,增幅分别为16.90%~22.17%、78.39%~207.70%,而NM处理的土壤有机质和有效磷含量分别显著降低22.64%和24.91%;NM、F、FE处理的土壤pH值均显著降低,降幅在1.55%~2.46%;NM处理的土壤β-葡萄糖苷酶、纤维二糖水解酶活性显著增强,增幅分别为56.42%、139.26%,而F、FE处理的α-葡萄糖苷酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶、酸性磷酸酶活性显著减弱,降幅分别为73.50%~78.42%、33.15%~36.72%、23.72%~28.64%。在土壤细菌群落丰富度上,NM处理较CK显著下降,而F处理较CK显著增加。在门水平上,与CK相比:F处理变形菌门的相对丰度从33.3%下降至27.8%,绿弯菌门的相对丰度从19.3%上升至22.3%,拟杆菌门的相对丰度从7.3%上升至9.2%;FE处理拟杆菌门的相对丰度从7.3%上升至8.4%。与CK相比,各处理均能提高稻、麦产量,其中,FE处理的增幅最大,并在改善千粒重等产量结构方面具有明显优势。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李传哲, 董青君, 纪力, 汪吉东, 陈川, 章安康, 张永春, 邵文奇. 新型肥料对典型黄河故道区土壤养分、微生物群落及稻麦产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 136-147.
LI Chuanzhe, DONG Qingjun, JI Li, WANG Jidong, CHEN Chuan, ZHANG Ankang, ZHANG Yongchun, SHAO Wenqi. Effects of new-type fertilizers on soil nutrients, microbial community, and yield of rice and wheat in the typical ancient course area of Yellow River, China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 136-147.
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质含量/(g·kg-1) Organic matter content/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量/(g·kg-1) Total nitrogen content/ (g·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/(mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/(mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.45±0.28 b | 0.60±0.01 b | 2.73±0.06 c | 46.53±1.09 b | 7.73±0.01 a |
| NM | 4.99±0.13 c | 0.37±0.01 c | 2.05±0.04 d | 40.37±1.06 d | 7.54±0.05 c |
| F | 7.54±0.37 a | 0.61±0.01 b | 8.40±0.13 a | 50.50±0.39 a | 7.61±0.01 b |
| FE | 7.88±0.08 a | 0.68±0.01 a | 4.87±0.12 b | 43.06±0.12 c | 7.60±0.02 b |
表1 不同处理下的土壤理化性状
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质含量/(g·kg-1) Organic matter content/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量/(g·kg-1) Total nitrogen content/ (g·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/(mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/(mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) | pH值 pH value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.45±0.28 b | 0.60±0.01 b | 2.73±0.06 c | 46.53±1.09 b | 7.73±0.01 a |
| NM | 4.99±0.13 c | 0.37±0.01 c | 2.05±0.04 d | 40.37±1.06 d | 7.54±0.05 c |
| F | 7.54±0.37 a | 0.61±0.01 b | 8.40±0.13 a | 50.50±0.39 a | 7.61±0.01 b |
| FE | 7.88±0.08 a | 0.68±0.01 a | 4.87±0.12 b | 43.06±0.12 c | 7.60±0.02 b |
| 处理 Treatment | AG | BG | CB | XYL | NAG | LAP | PHOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 55.92±9.52 a | 70.65±3.99 b | 2.98±1.70 b | 33.70±15.40 ab | 0.97±0.71 a | 15.87±4.38 bc | 465.40±20.84 a |
| NM | 67.04±10.97 a | 110.51±10.51 a | 7.13±0.53 a | 43.67±3.79 a | 2.35±0.58 a | 19.84±3.08 ab | 492.73±28.09 a |
| F | 12.07±1.44 b | 44.71±5.51 c | 4.00±0.46 b | 25.63±5.99 bc | 2.47±2.48 a | 22.49±0.46 a | 355.01±30.81 b |
| FE | 14.82±0.90 b | 47.23±6.36 c | 2.52±0.13 b | 14.15±2.89 c | 2.05±0.50 a | 13.13±2.95 c | 332.10±9.98 b |
表2 不同处理下的土壤酶活性
Table 2 Soil enzymes activity under different treatments nmol·g-1·h-1
| 处理 Treatment | AG | BG | CB | XYL | NAG | LAP | PHOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 55.92±9.52 a | 70.65±3.99 b | 2.98±1.70 b | 33.70±15.40 ab | 0.97±0.71 a | 15.87±4.38 bc | 465.40±20.84 a |
| NM | 67.04±10.97 a | 110.51±10.51 a | 7.13±0.53 a | 43.67±3.79 a | 2.35±0.58 a | 19.84±3.08 ab | 492.73±28.09 a |
| F | 12.07±1.44 b | 44.71±5.51 c | 4.00±0.46 b | 25.63±5.99 bc | 2.47±2.48 a | 22.49±0.46 a | 355.01±30.81 b |
| FE | 14.82±0.90 b | 47.23±6.36 c | 2.52±0.13 b | 14.15±2.89 c | 2.05±0.50 a | 13.13±2.95 c | 332.10±9.98 b |
| 处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | 覆盖率/% Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6 556.47±47.23 b | 7.42±0.12 a | 0.997 6±0.000 1 a | 98.17±0.12 a |
| NM | 6 442.17±50.72 c | 7.49±0.04 a | 0.998 5±0.000 1 a | 98.29±0.18 a |
| F | 6 763.60±82.97 a | 7.54±0.10 a | 0.998 4±0.000 1 a | 98.17±0.15 a |
| FE | 6 634.20±101.09 ab | 7.53±0.07 a | 0.998 6±0.000 1 a | 98.14±0.16 a |
表3 不同处理的土壤细菌α多样性
Table 3 Alpha diversity of soil bacteria under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | 覆盖率/% Coverage/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6 556.47±47.23 b | 7.42±0.12 a | 0.997 6±0.000 1 a | 98.17±0.12 a |
| NM | 6 442.17±50.72 c | 7.49±0.04 a | 0.998 5±0.000 1 a | 98.29±0.18 a |
| F | 6 763.60±82.97 a | 7.54±0.10 a | 0.998 4±0.000 1 a | 98.17±0.15 a |
| FE | 6 634.20±101.09 ab | 7.53±0.07 a | 0.998 6±0.000 1 a | 98.14±0.16 a |
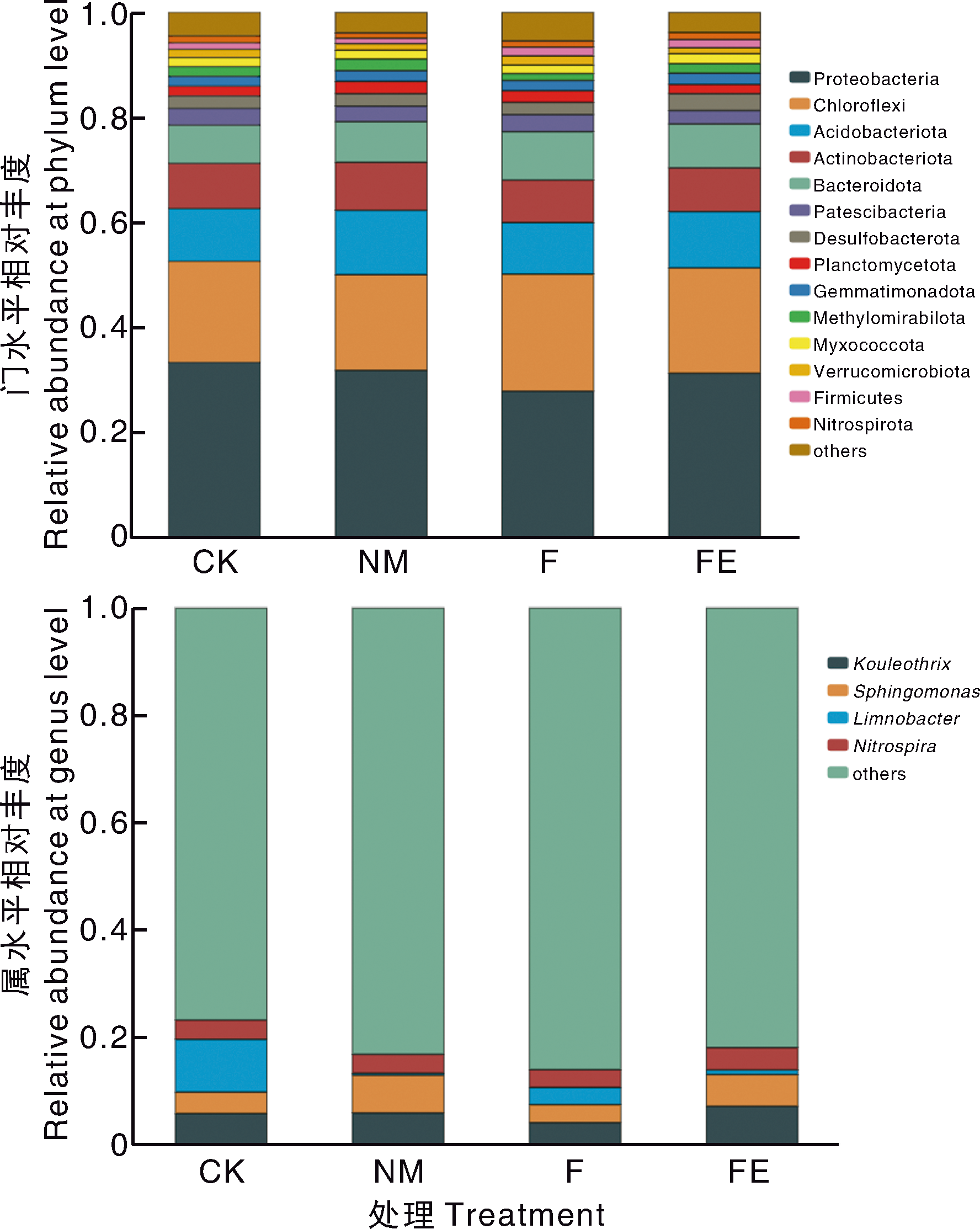
图1 不同处理门水平和属水平的土壤细菌群落组成 Proteobacteria,变形菌门;Chloroflexi,绿弯菌门;Acidobacteriota,酸杆菌门;Actinobacteriota,放线菌门;Bacteroidota,拟杆菌门;Patescibacteria,髌骨细菌门;Desulfobacterota,脱硫杆菌门;Planctomycetota,浮霉菌门;Gemmatimonadota,芽单胞菌门;Myxococcota,黏细菌门;Verrucomicrobiota,疣微菌门;Firmicutes,厚壁菌门;Nitrospirota,硝化螺菌门;others,其他。Sphingomonas,鞘氨醇单胞菌属;Limnobacter,湖沉积杆菌属;Nitrospira,硝化螺菌属。下同。在属水平上,图中仅给出相对丰度超过1%的菌属,其他菌属均归为“其他(others)”类别。At genus level, only those with relative abundance over 1% are listed, all the others go to the category of “others”.
Fig.1 Soil bacterial community composition at phylum and genus level under different treatments
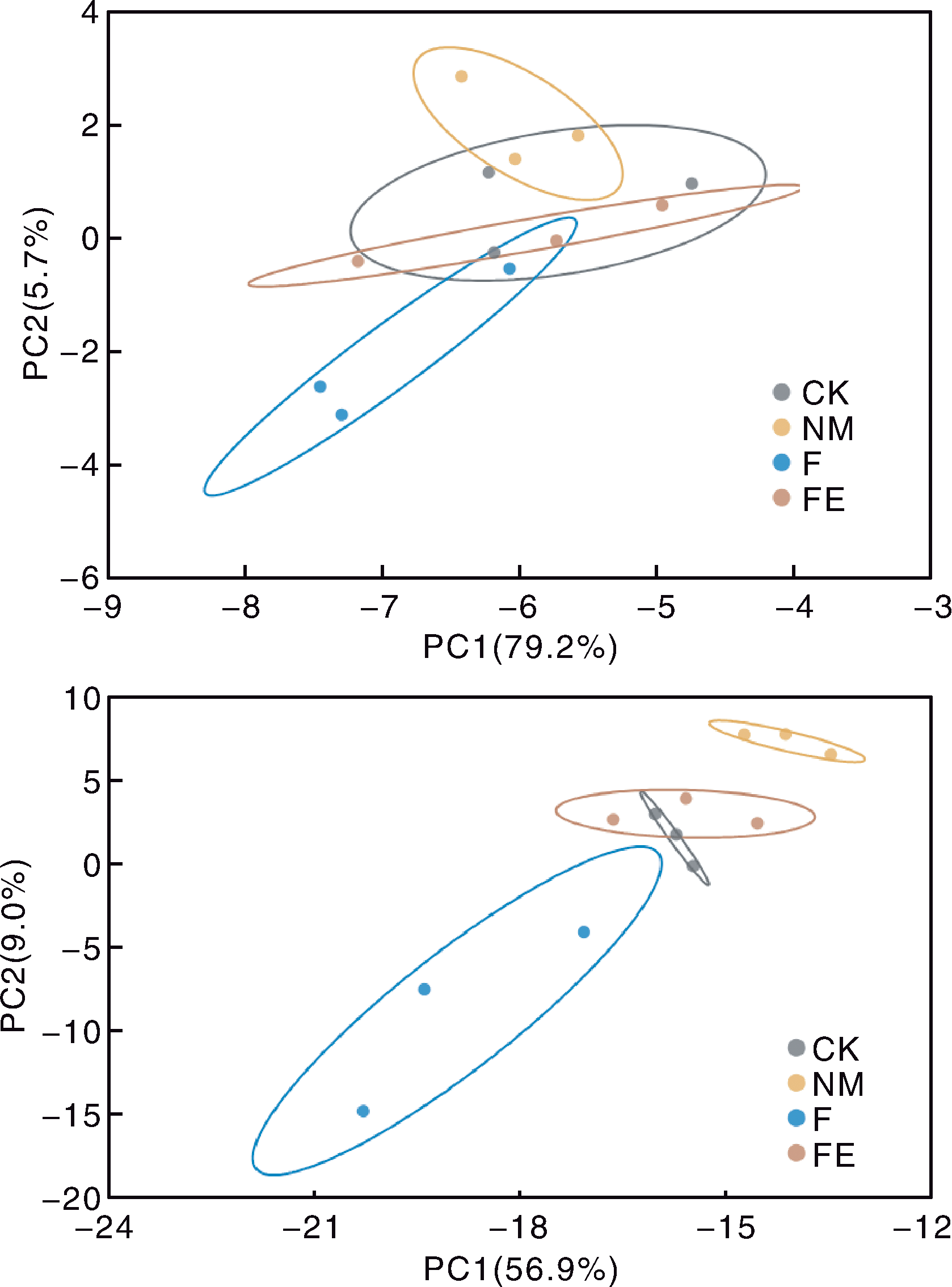
图2 不同处理土壤细菌群落组成在门水平(上)和属水平(下)的主成分分析
Fig.2 Principal component analysis of soil bacterial community composition at phylum (top) and genus (bottom) level
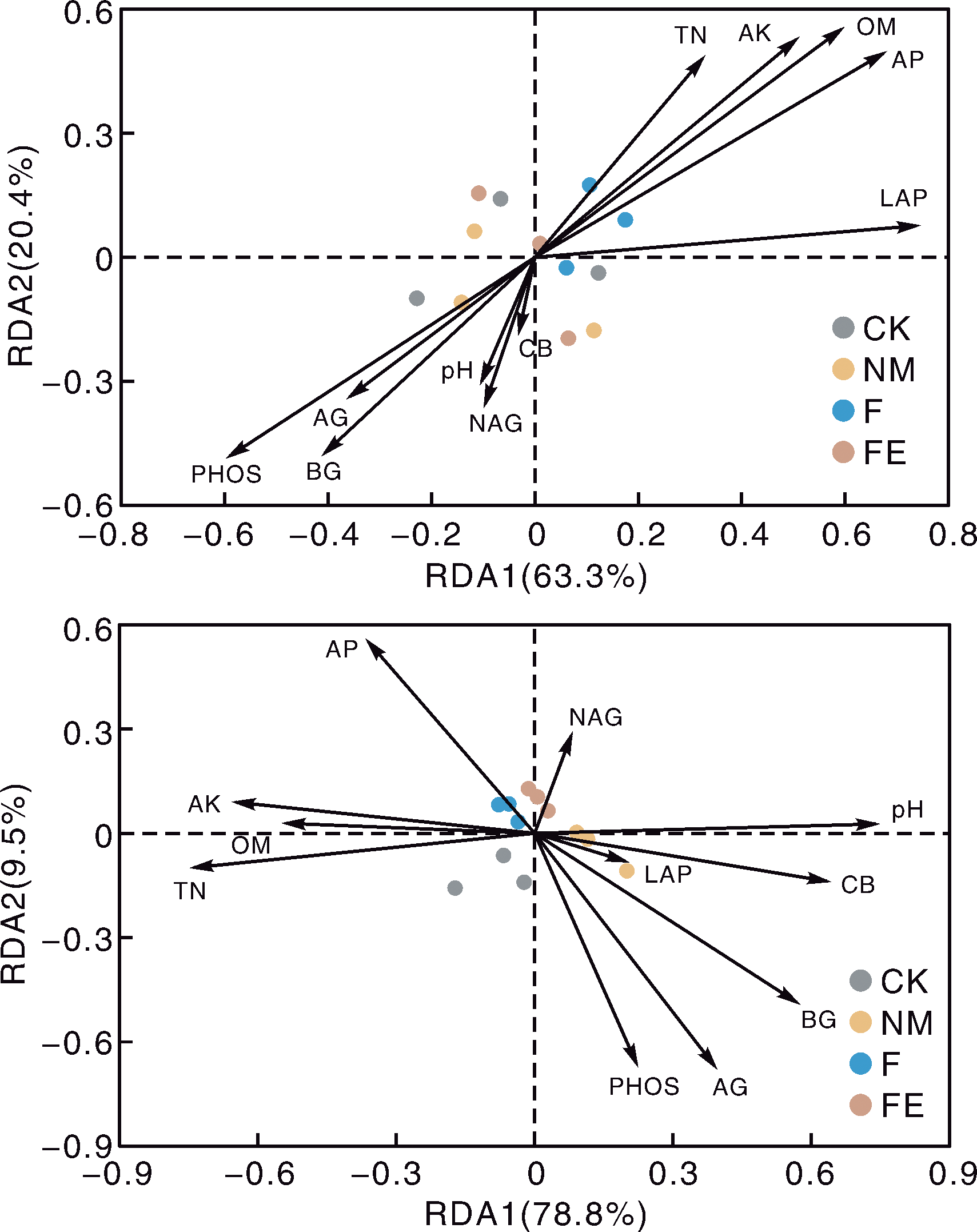
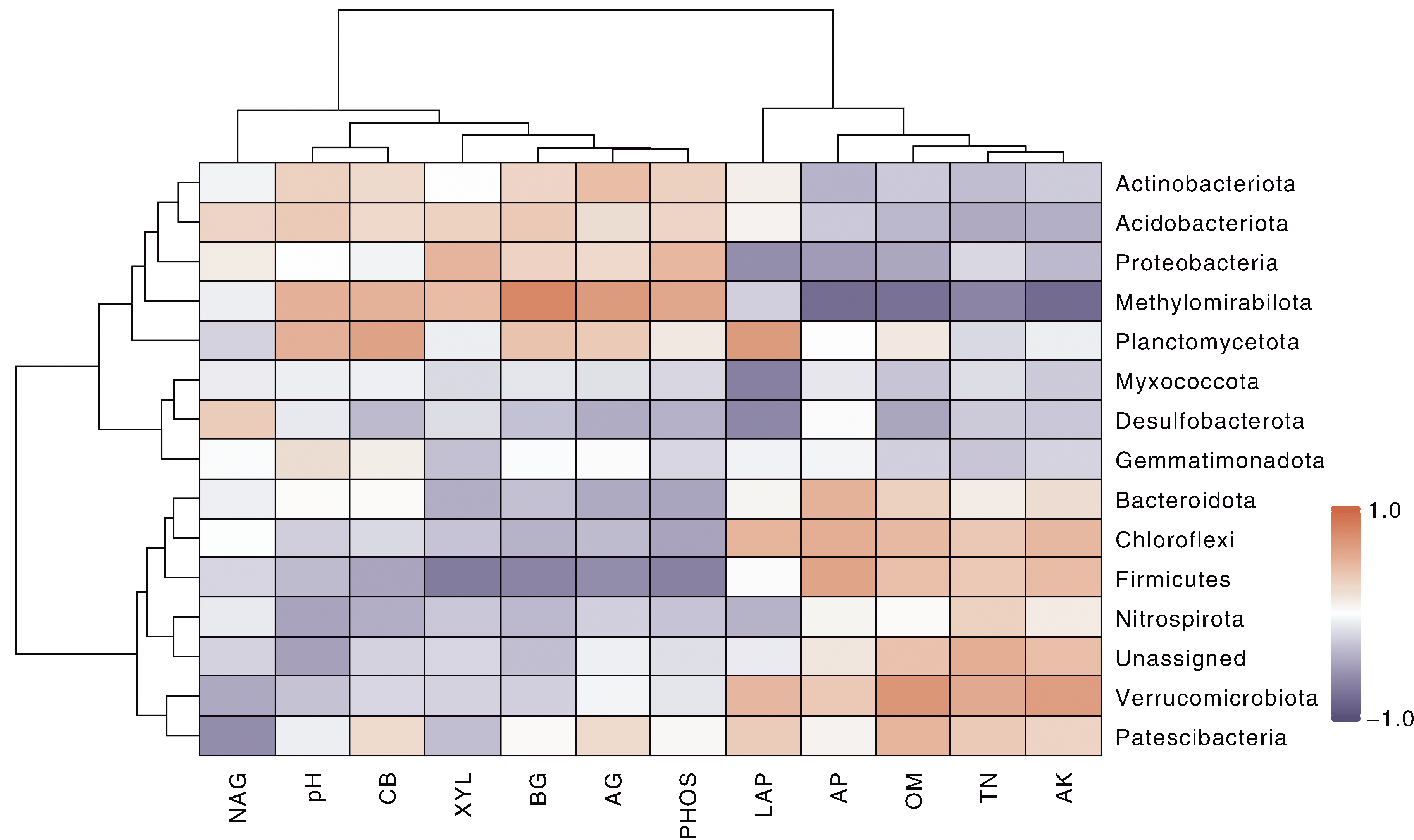
图3 土壤因子与门水平(上)、属水平(下)细菌群落组成的冗余分析(RDA) pH,pH值;OM,有机质含量;TN,全氮含量;AP,有效磷含量;AK,速效钾含量;AG,α-葡萄糖苷酶活性;BG,β-葡萄糖苷酶活性;CB,纤维二糖水解酶活性;XYL,木糖苷酶活性;NAG,N-乙酰-β-氨基葡萄糖苷酶活性;LAP,亮氨酸氨基肽酶活性;PHOS,酸性磷酸酶活性。下同。
Fig.3 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil bacterial community composition at phylum (top) and genus (bottom) level and soil factors pH, pH value; OM, Organic matter content; TN, Total nitrogen content; AP, Available phosphorus content; AK, Available potassium content; AG, α-Glucosidase activity; BG, β-Glucosidase activity; CB, β-D-Cellobiohydrolase activity; XYL, Xylosidase activity; NAG, β-1,4-N-Acetyl-glucosaminidase activity; LAP, Leucine aminopeptidase activity; PHOS, Acid phosphatase activity. The same as below.
| 作物 Crop | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数/(104 hm-2) Effective panicle number/(104 hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grain number per spike | 千粒重/g 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量(kg·hm-2) Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻Rice | CK | 270.27±5.44 b | 98.96±0.94 a | 26.73±0.14 b | 7 148.6±122.9 c |
| NM | 277.47±4.10 ab | 101.09±5.03 a | 26.81±0.48 b | 7 513.6±133.6 b | |
| F | 283.21±3.84 a | 100.74±0.44 a | 26.88±0.06 b | 7 669.3±86.4 b | |
| FE | 282.81±1.22 a | 100.74±1.82 a | 27.64±0.42 a | 7 873.2±72.2 a | |
| 小麦Wheat | CK | 340.97±2.74 c | 29.68±1.17 a | 48.87±0.96 b | 4 944.4±191.8 c |
| NM | 375.79±8.37 b | 28.13±1.01 b | 48.60±0.37 b | 5 135.2±132.7 bc | |
| F | 435.82±8.24 a | 26.97±0.54 c | 45.72±1.33 c | 5 371.4±85.7 ab | |
| FE | 372.19±4.54 b | 28.11±0.26 b | 52.22±0.06 a | 5 463.4±107.9 a |
表4 不同处理的稻麦产量及其组成因素
Table 4 Rice and wheat yield and their components under different treatments
| 作物 Crop | 处理 Treatment | 有效穗数/(104 hm-2) Effective panicle number/(104 hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grain number per spike | 千粒重/g 1 000-grain weight/g | 产量(kg·hm-2) Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水稻Rice | CK | 270.27±5.44 b | 98.96±0.94 a | 26.73±0.14 b | 7 148.6±122.9 c |
| NM | 277.47±4.10 ab | 101.09±5.03 a | 26.81±0.48 b | 7 513.6±133.6 b | |
| F | 283.21±3.84 a | 100.74±0.44 a | 26.88±0.06 b | 7 669.3±86.4 b | |
| FE | 282.81±1.22 a | 100.74±1.82 a | 27.64±0.42 a | 7 873.2±72.2 a | |
| 小麦Wheat | CK | 340.97±2.74 c | 29.68±1.17 a | 48.87±0.96 b | 4 944.4±191.8 c |
| NM | 375.79±8.37 b | 28.13±1.01 b | 48.60±0.37 b | 5 135.2±132.7 bc | |
| F | 435.82±8.24 a | 26.97±0.54 c | 45.72±1.33 c | 5 371.4±85.7 ab | |
| FE | 372.19±4.54 b | 28.11±0.26 b | 52.22±0.06 a | 5 463.4±107.9 a |
| [1] | 李传哲, 章欢, 姚文静, 等. 生物炭配施氮肥对典型黄河故道区土壤理化性质和冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(10): 3424-3432. |
| LI C Z, ZHANG H, YAO W J, et al. Effects of biochar application combined with nitrogen fertilizer on soil physicochemical properties and winter wheat yield in the typical ancient region of Yellow River, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(10): 3424-3432. | |
| [2] | YAHAYA S M, AHMAD MAHMUD A, ABDULLAHI M, et al. Recent advances in the chemistry of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium as fertilizers in soil: a review[J]. Pedosphere, 2023, 33(3): 385-406. |
| [3] | 郝胜磊, 蔡廷瑶, 冯小杰, 等. 新型肥料对全球三大粮食作物产量和土壤生物学活性影响的Meta分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(9): 1496-1505. |
| HAO S L, CAI T Y, FENG X J, et al. Effects of new fertilizers on the yield and soil biological activity of three major food crops: a global meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(9): 1496-1505. | |
| [4] | 丁文成, 何萍, 周卫. 我国新型肥料产业发展战略研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(2): 201-221. |
| DING W C, HE P, ZHOU W. Development strategies of the new-type fertilizer industry in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(2): 201-221. | |
| [5] | 鲁凯珩, 金杰人, 肖明. 微生物肥料在盐碱土壤中的应用展望[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(7): 1695-1705. |
| LU K H, JIN J R, XIAO M. Prospect of microbial fertilizer in saline soil[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(7): 1695-1705. | |
| [6] | 伍少福, 韩科峰, 吴良欢. 生物有机肥加专用肥对葡萄园土壤养分、微生物和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1099-1112. |
| WU S F, HAN K F, WU L H. Effects of biological-organic fertilizer combined with specialized fertilizer on soil nutrients, microbial diversity and yield in vineyards[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1099-1112. | |
| [7] | WANG L, ZHANG H, XU C, et al. Long-term nitrogen fertilization and sweetpotato cultivation in the wheat-sweetpotato rotation system decrease alkaline phosphomonoesterase activity by regulating soil phoD-harboring bacteria communities[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 900: 165916. |
| [8] | RASHID M I, MUJAWAR L H, SHAHZAD T, et al. Bacteria and fungi can contribute to nutrients bioavailability and aggregate formation in degraded soils[J]. Microbiological Research, 2016, 183: 26-41. |
| [9] | JURASINSKI G, RETZER V, BEIERKUHNLEIN C. Inventory, differentiation, and proportional diversity: a consistent terminology for quantifying species diversity[J]. Oecologia, 2009, 159(1): 15-26. |
| [10] | ABDELKRIM S, JEBARA S H, JEBARA M. Antioxidant systems responses and the compatible solutes as contributing factors to lead accumulation and tolerance in Lathyrus sativus inoculated by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 166: 427-436. |
| [11] | 刘希港, 李楠, 季托, 等. 微生物菌剂和玉米蛋白酵素对番茄叶片生理特性和产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(11): 3039-3044. |
| LIU X G, LI N, JI T, et al. Effects of microbial agents and corn protein ferment on physiological characteristics in leaves and yield of tomato[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(11): 3039-3044. | |
| [12] | 许芳. 辅酶Q10提取方法研究和高产光合菌的选育[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2008. |
| XU F. Methods of extracting of CoQ10 and selection of high yield PSB[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2008. | |
| [13] | 索全义, 徐鲁明, 张建平, 等. 辅酶Q10污泥施用对作物和土壤效应的研究[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2015, 43(2): 12-15. |
| SUO Q Y, XU L M, ZHANG J P, et al. Research on the effects of coenzyme Q10 sludge applied on the soil and crop[J]. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 43(2): 12-15. | |
| [14] | PUISSANT J, JONES B, GOODALL T, et al. The pH optimum of soil exoenzymes adapt to long term changes in soil pH[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 138: 107601. |
| [15] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999: 25-96. |
| [16] | 李东, 田秋香, 赵小祥, 等. 贡嘎山树线过渡带土壤胞外酶活性及其化学计量比特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2): 232-242. |
| LI D, TIAN Q X, ZHAO X X, et al. Soil extracellular enzyme activities and their stoichiometric ratio in the alpine treeline ecotones in Gongga Mountain, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(2): 232-242. | |
| [17] | YANG J S, ZHAO S S, ZHI W B, et al. Improvement of silage characteristics of Lactobacillus salivarius HMC4 and improvement of silage quality of king grass[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2024, 15: 1468577. |
| [18] | EDGAR R C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 996-998. |
| [19] | FINN D R. A metagenomic alpha-diversity index for microbial functional biodiversity[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2024, 100(3): fiae019. |
| [20] | LI W X, ZHANG F Y, CUI G H, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, microbial community composition, and potato growth[J]. ScienceAsia, 2021, 47(3): 347. |
| [21] | 臧小平, 周兆禧, 林兴娥, 等. 不同用量有机肥对芒果果实品质及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(1): 98-101. |
| ZANG X P, ZHOU Z X, LIN X E, et al. Effects of different organic manure application rate on mango fruit quality and soil fertility[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(1): 98-101. | |
| [22] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 等. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| ZHANG X L, WANG G L, CHANG F D, et al. Effects of microbial agents on physicochemical properties and microbial flora of rhizosphere saline-alkali soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. | |
| [23] | GRZYB A, WOLNA-MARUWKA A, NIEWIADOMSKA A. The significance of microbial transformation of nitrogen compounds in the light of integrated crop management[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(7): 1415. |
| [24] | 虞轶俊, 徐青山, 张均华, 等. 土壤培肥技术对土壤健康的影响途径与作用机制[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024(2): 220-227. |
| YU Y J, XU Q S, ZHANG J H, et al. The influence and mechanism of soil fertilization technology on soil health[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2024(2): 220-227. | |
| [25] | MÜHLBACHOVÁ G, RŬŽEK P, KUSÁ H, et al. Winter wheat straw decomposition under different nitrogen fertilizers[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(2): 83. |
| [26] | WONG J W C, KARTHIKEYAN O P, SELVAM A. Biological nutrient transformation during composting of pig manure and paper waste[J]. Environmental Technology, 2017, 38(6): 754-761. |
| [27] | 梁天, 张晓东, 张玉, 等. 不同C/N条件下菌酶制剂对牛粪堆肥进程的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(31): 77-82. |
| LIANG T, ZHANG X D, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of bacterial enzyme preparation on composting of cow manure under different C/N conditions[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(31): 77-82. | |
| [28] | YAN P, WU L Q, WANG D H, et al. Soil acidification in Chinese tea plantations[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 715: 136963. |
| [29] | 刘聪, 万翠翠, 宋旭, 等. 复合菌剂对新疆辣椒的促生效果和根际真核生物群落结构的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(6): 1599-1607. |
| LIU C, WAN C C, SONG X, et al. Effects of effective microorganisms on growth promotion and the rhizosphere eukaryotic community structure of pepper in Xinjiang, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(6): 1599-1607. | |
| [30] | VEPSÄLÄINEN M, KUKKONEN S, VESTBERG M, et al. Application of soil enzyme activity test kit in a field experiment[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2001, 33(12/13): 1665-1672. |
| [31] | 许立阳, 王亚男, 曾希柏, 等. 微生物菌肥对瘠薄稻田土壤养分及水稻生长的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(10): 2350-2362. |
| XU L Y, WANG Y N, ZENG X B, et al. Microbial fertilizer effects on soil nutrients and rice growth in barren paddy fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(10): 2350-2362. | |
| [32] | 曲成闯, 陈效民, 张志龙, 等. 生物有机肥提高设施土壤生产力减缓黄瓜连作障碍的机制[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(5): 814-823. |
| QU C C, CHEN X M, ZHANG Z L, et al. Mechanism of bio-organic fertilizer on improving soil productivity for continuous cucumber in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(5): 814-823. | |
| [33] | LIU X, CHEN Q, ZHANG H C, et al. Effects of exogenous organic matter addition on agricultural soil microbial communities and relevant enzyme activities in Southern China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 8045. |
| [34] | 黄阔, 江其鹏, 姚晓远, 等. 微生物菌剂对烟草根结线虫及根际微生物群落多样性的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2019, 40(5): 36-43. |
| HUANG K, JIANG Q P, YAO X Y, et al. Effects of microbial agents on tobacco root-knot nematode and diversity of rhizosphere microbial communities[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2019, 40(5): 36-43. | |
| [35] | BURNS K N, KLUEPFEL D A, STRAUSS S L, et al. Vineyard soil bacterial diversity and composition revealed by 16S rRNA genes: differentiation by geographic features[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 91: 232-247. |
| [36] | LIU X Z, MA Y Y, MANEVSKI K, et al. Biochar and alternate wetting-drying cycles improving rhizosphere soil nutrients availability and tobacco growth by altering root growth strategy in Ferralsol and Anthrosol[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150513. |
| [37] | JANUSZ G, PAWLIK A, ŚWIDERSKA-BUREK U, et al. Laccase properties, physiological functions, and evolution[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 966. |
| [38] | 邢亚薇, 李春越, 刘津, 等. 长期施肥对黄土旱塬农田土壤微生物丰度的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(4): 1351-1358. |
| XING Y W, LI C Y, LIU J, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial abundance in farmland of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(4): 1351-1358. | |
| [39] | 王娟娟, 朱紫娟, 钱晓晴, 等. 全年稻麦秸秆还田对稻田土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(4): 57-65. |
| WANG J J, ZHU Z J, QIAN X Q, et al. Effects of year-round rice-wheat straw return on soil bacterial community structure in paddy fields[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(4): 57-65. | |
| [40] | SHA M H, XU J, ZHENG Z C, et al. Enhanced atmospheric nitrogen deposition triggered little change in soil microbial diversity and structure in a desert ecosystem[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2021, 31: e01879. |
| [41] | 赵阳安, 芦光新, 邓晔, 等. 根瘤菌拌种对两种苜蓿生长及根际微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(2): 370-378. |
| ZHAO Y A, LU G X, DENG Y, et al. Effect of Rhizobium seed dressing on growth of two alfalfa and rhizosphere microbial diversity[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(2): 370-378. | |
| [42] | SUN L, XUN W B, HUANG T, et al. Alteration of the soil bacterial community during parent material maturation driven by different fertilization treatments[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 96: 207-215. |
| [43] | AHSAN T, TIAN P C, GAO J, et al. Effects of microbial agent and microbial fertilizer input on soil microbial community structure and diversity in a peanut continuous cropping system[J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2024, 64: 1-13. |
| [44] | 谢亚军, 陈晓萍, 倪亮, 等. 基于辅酶Q10发酵液的有机液肥对小白菜生长和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2011, 37(5): 545-550. |
| XIE Y J, CHEN X P, NI L, et al. Effects of organic liquid fertilizer made by coenzyme Q10 fermentation broth on pakchoi (Brassica campestris) growth and soil enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2011, 37(5): 545-550. |
| [1] | 张智, 何豪豪, 郁妙, 许剑锋. 化肥减量配施土壤改良剂对土壤酸度、土壤养分和水稻产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1301-1308. |
| [2] | 韦新航, 周铨, 李亚妮, 陈卫良, 毛碧增. 生物有机肥对温郁金根际微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 892-900. |
| [3] | 胡铁军. 化肥减量配施微生物肥对西蓝花产量品质与土壤性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1657-1665. |
| [4] | 岳宗伟, 李嘉骁, 孙向阳, 刘国梁, 李素艳, 王晨晨, 查贵超, 魏宁娴. 化肥有机肥配施对土壤性质、樱桃果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(9): 2192-2201. |
| [5] | 吴传美, 何季, 吴文珊, 蔡俊, 向仰州. 间作对刺梨园土壤团聚体化学计量特征和养分贡献率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(5): 1132-1143. |
| [6] | 鲁帅, 罗晓刚, 刘全伟, 张屹, 孟洋昊, 李洁, 张景来. 有机无机复混肥对小麦生长、土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(4): 922-930. |
| [7] | 冯林, 周铨, 陈卫良, 毛碧增. 防控温郁金细菌性枯萎病的生物有机肥研制与应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(3): 630-638. |
| [8] | 高风, 文仕知, 韦铄星, 欧汉彪, 王智慧. 桂西北石漠化区不同植被恢复类型对土壤理化性质、酶活与真菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(10): 2425-2435. |
| [9] | 杨胜竹, 李响, 李朝文, 陈海念, 刘丽, 陆引罡, 曹卓洋. 贵州省烟草青枯病害区根际土壤养分及酶活性特征分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(1): 146-155. |
| [10] | 茹朝, 郁继华, 武玥, 冯致, 缑兆辉, 金宁, 王舒亚, 刘泽慈, 吕剑. 化肥减量配施生物有机肥对露地大白菜产量及品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1626-1637. |
| [11] | 孙文艳, 刘小刚, 张文慧, 李慧永, 吴朗, 杨启良, 熊国美. 基于根区土壤质量指数优化小粒种咖啡滴灌施肥方案[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(3): 566-573. |
| [12] | 张鑫鹏, 王信, 孙健, 伊国云, 李松龄. 一株假单胞菌的分离鉴定及其在青海地区堆肥中的应用潜力[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(2): 343-351. |
| [13] | 张健利, 王振华, 陈睿, 王东旺, 梁永辉, 刘茹华. 水肥互作对滴灌红枣产量、品质与土壤养分的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(11): 2428-2437. |
| [14] | 高志远, 杨淑娜, 王朝丽, 王智豪, 奚昕琰, 何娟, 贾惠娟. 不同熏蒸方式对连作桃园土壤的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(10): 2251-2258. |
| [15] | 李菊, 颉博杰, 魏守辉, 张国斌, 武玥, 唐中祺, 肖雪梅, 郁继华. 有机肥与化肥配施对松花菜花球营养品质和挥发性物质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(7): 1199-1211. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||