浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 24-34.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250087
基于SSR标记的浙江省地方玉米种质遗传关系分析
何苏悦1( ), 李燕2, 丁云倩1, 李欣泽1, 韩庆辉1, 陈小央2,*(
), 李燕2, 丁云倩1, 李欣泽1, 韩庆辉1, 陈小央2,*( )
)
- 1.浙江农林大学 现代农学院,浙江 杭州 311300
2.浙江省种子管理总站,浙江 杭州 310020
-
收稿日期:2025-02-05出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:陈小央,E-mail: caroline1201@163.com
何苏悦,研究方向为玉米遗传育种。E-mail:2758494789@qq.com -
通讯作者:陈小央 -
基金资助:浙江省玉米种质资源精准鉴定项目(2022-2024);浙江省旱粮新品种选育重大科技专项(2021C02064-4-3);国家自然科学基金(32301833);浙江省自然科学基金(LTGN24C130001)
Phylogenetic analysis of maize landraces in Zhejiang Province of China based on SSR markers
HE Suyue1( ), LI Yan2, DING Yunqian1, LI Xinze1, HAN Qinghui1, CHEN Xiaoyang2,*(
), LI Yan2, DING Yunqian1, LI Xinze1, HAN Qinghui1, CHEN Xiaoyang2,*( )
)
- 1. College of Advanced Agricultural Sciences, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou 311300, China
2. Zhejiang Provincial Seed Management Station, Hangzhou 310020, China
-
Received:2025-02-05Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:CHEN Xiaoyang
摘要:
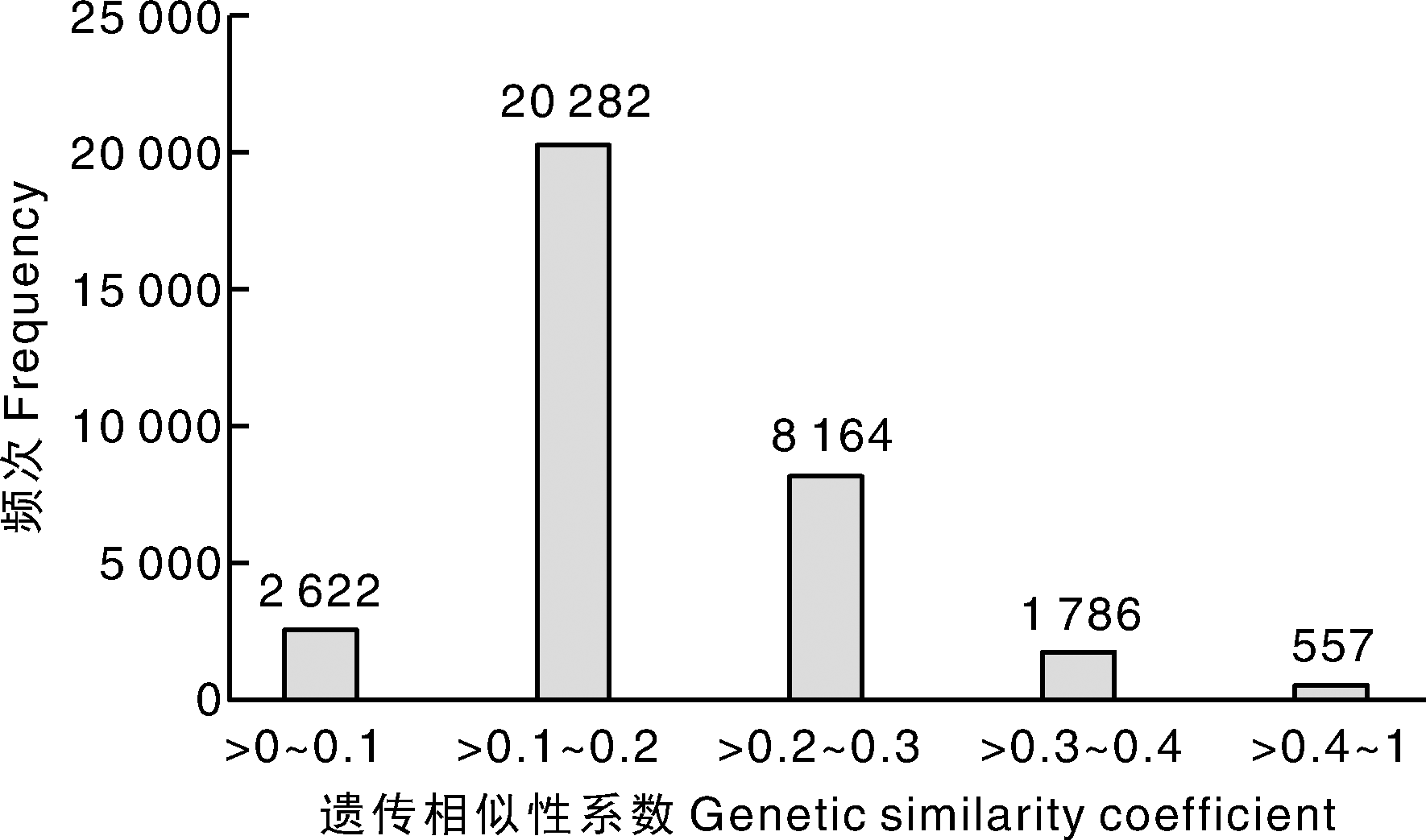
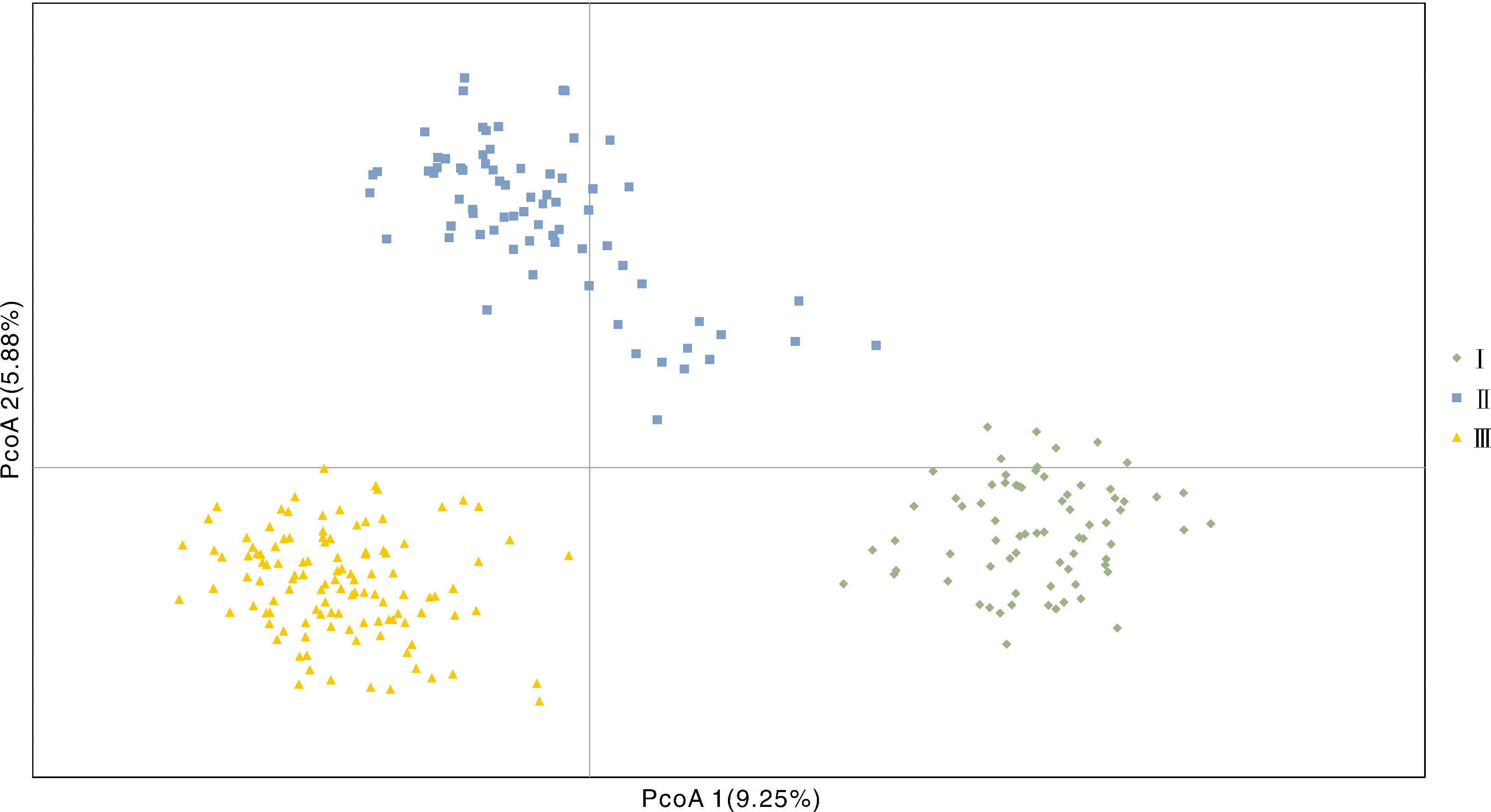
为探究浙江省地方玉米种质的遗传基础与亲缘关系,本研究利用40对简单重复序列(simple sequence repeat, SSR)标记对来自浙江省的259份地方玉米种质进行了遗传多样性分析。 结果表明,40对SSR标记引物共检测出399个等位变异,每对引物检测到的等位基因变异数为4~22个,平均为9.975个;有效等位基因数范围为0.818 5~1.000 0,平均为0.982 2;基因多样性指数范围为0.303 6~0.903 3,平均为0.717 1;多态信息含量范围为0.289 0~0.895 4,平均为0.686 8;Shannon指数范围为0.655~2.527,平均值为1.615。通过UPGMA聚类分析,将259份地方玉米种质划分为3个类群,第Ⅰ类群包含72份种质,占27.8%;第Ⅱ类群包含72份种质,占27.8%;第Ⅲ类群包含115份种质,占44.4%。主坐标分析表明,类群内个体距离较近,类群间距离大且无重叠,进一步证实聚类分析结果的可靠性。综上所述,浙江省地方玉米种质在育种实践过程中形成了相对独立的优势类群,遗传多样性丰富,可为玉米优异基因挖掘、优异种质创制和新品种培育奠定基础。
中图分类号:
引用本文
何苏悦, 李燕, 丁云倩, 李欣泽, 韩庆辉, 陈小央. 基于SSR标记的浙江省地方玉米种质遗传关系分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 24-34.
HE Suyue, LI Yan, DING Yunqian, LI Xinze, HAN Qinghui, CHEN Xiaoyang. Phylogenetic analysis of maize landraces in Zhejiang Province of China based on SSR markers[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 24-34.
| 编号 Code | 标记名称 Marker name | 等位基因数 Number of alleles | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index | 有效等位基因数 Number of effective alleles | 多态信息含量 Polymorphism information content | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01 | bnlg439w1 | 16 | 0.857 9 | 0.996 1 | 0.843 8 | 2.216 |
| P02 | umc1335y5 | 10 | 0.418 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.392 9 | 0.886 |
| P03 | umc2007y4 | 11 | 0.810 7 | 0.992 3 | 0.787 5 | 1.916 |
| P04 | bnlg1940k7 | 12 | 0.771 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.745 1 | 1.748 |
| P05 | umc2105k3 | 22 | 0.887 8 | 0.976 8 | 0.878 4 | 2.473 |
| P06 | phi053k2 | 19 | 0.903 3 | 0.996 1 | 0.895 4 | 2.527 |
| P07 | phi072k4 | 7 | 0.738 3 | 0.996 1 | 0.697 6 | 1.533 |
| P08 | bnlg2291k4 | 12 | 0.864 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.849 7 | 2.146 |
| P09 | umc1705w1 | 13 | 0.778 9 | 0.996 1 | 0.748 6 | 1.782 |
| P10 | bnlg2305k4 | 10 | 0.835 7 | 1.000 0 | 0.817 8 | 2.006 |
| P11 | bnlg161k8 | 18 | 0.897 4 | 0.988 4 | 0.888 4 | 2.424 |
| P12 | bnlg1702k1 | 13 | 0.770 6 | 0.996 1 | 0.737 1 | 1.723 |
| P13 | umc1545y2 | 17 | 0.869 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.856 2 | 2.251 |
| P14 | umc1125y3 | 7 | 0.590 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.552 9 | 1.205 |
| P15 | bnlg240k1 | 8 | 0.780 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.750 3 | 1.691 |
| P16 | phi080k15 | 11 | 0.830 4 | 0.992 3 | 0.808 6 | 1.938 |
| P17 | phi065k9 | 6 | 0.594 5 | 0.992 3 | 0.557 3 | 1.230 |
| P18 | umc1492y13 | 4 | 0.614 4 | 0.953 7 | 0.558 8 | 1.116 |
| P19 | umc1432y6 | 10 | 0.750 9 | 0.992 3 | 0.713 7 | 1.551 |
| P20 | umc1506k12 | 8 | 0.803 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.774 3 | 1.723 |
| P21 | umc1147y4 | 5 | 0.510 5 | 0.969 1 | 0.449 2 | 0.933 |
| P22 | bnlg1671y17 | 12 | 0.823 4 | 0.992 3 | 0.800 3 | 1.908 |
| P23 | phi96100y1 | 9 | 0.738 3 | 0.988 4 | 0.712 1 | 1.656 |
| P24 | umc1536k9 | 6 | 0.696 4 | 0.996 1 | 0.656 0 | 1.414 |
| P25 | bnlg1520k1 | 8 | 0.762 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.725 5 | 1.604 |
| P26 | umc1489y3 | 12 | 0.790 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.761 7 | 1.747 |
| P27 | bnlg490y4 | 13 | 0.794 1 | 0.818 5 | 0.775 1 | 1.962 |
| P28 | umc1999y3 | 5 | 0.303 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.289 0 | 0.655 |
| P29 | umc2115k3 | 5 | 0.636 9 | 0.988 4 | 0.600 7 | 1.274 |
| P30 | umc1429y7 | 8 | 0.724 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.682 6 | 1.467 |
| P31 | bnlg249k2 | 7 | 0.606 0 | 1.000 0 | 0.537 2 | 1.139 |
| P32 | phi299852y2 | 9 | 0.811 3 | 0.965 3 | 0.787 4 | 1.860 |
| P33 | umc2160k3 | 11 | 0.409 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.396 2 | 0.987 |
| P34 | umc1936k4 | 4 | 0.382 4 | 0.861 0 | 0.351 0 | 0.711 |
| P35 | bnlg2235y5 | 6 | 0.765 6 | 0.973 0 | 0.730 7 | 1.596 |
| P36 | phi233376y1 | 9 | 0.738 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.697 6 | 1.576 |
| P37 | umc2084w2 | 11 | 0.812 4 | 1.000 0 | 0.788 6 | 1.843 |
| P38 | umc123lk4 | 6 | 0.620 5 | 0.915 1 | 0.568 8 | 1.196 |
| P39 | phi041y6 | 10 | 0.655 4 | 0.996 1 | 0.616 9 | 1.430 |
| P40 | umc2163w3 | 9 | 0.732 5 | 0.957 5 | 0.692 0 | 1.539 |
| 平均值Average | 9.975 | 0.717 1 | 0.982 2 | 0.686 8 | 1.615 | |
表1 40对SSR标记在259份地方玉米种质之间遗传多样性统计结果
Table 1 Genetic diversity among 259 maize landraces based on 40 pairs of SSR markers
| 编号 Code | 标记名称 Marker name | 等位基因数 Number of alleles | 基因多样性指数 Gene diversity index | 有效等位基因数 Number of effective alleles | 多态信息含量 Polymorphism information content | Shannon指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01 | bnlg439w1 | 16 | 0.857 9 | 0.996 1 | 0.843 8 | 2.216 |
| P02 | umc1335y5 | 10 | 0.418 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.392 9 | 0.886 |
| P03 | umc2007y4 | 11 | 0.810 7 | 0.992 3 | 0.787 5 | 1.916 |
| P04 | bnlg1940k7 | 12 | 0.771 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.745 1 | 1.748 |
| P05 | umc2105k3 | 22 | 0.887 8 | 0.976 8 | 0.878 4 | 2.473 |
| P06 | phi053k2 | 19 | 0.903 3 | 0.996 1 | 0.895 4 | 2.527 |
| P07 | phi072k4 | 7 | 0.738 3 | 0.996 1 | 0.697 6 | 1.533 |
| P08 | bnlg2291k4 | 12 | 0.864 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.849 7 | 2.146 |
| P09 | umc1705w1 | 13 | 0.778 9 | 0.996 1 | 0.748 6 | 1.782 |
| P10 | bnlg2305k4 | 10 | 0.835 7 | 1.000 0 | 0.817 8 | 2.006 |
| P11 | bnlg161k8 | 18 | 0.897 4 | 0.988 4 | 0.888 4 | 2.424 |
| P12 | bnlg1702k1 | 13 | 0.770 6 | 0.996 1 | 0.737 1 | 1.723 |
| P13 | umc1545y2 | 17 | 0.869 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.856 2 | 2.251 |
| P14 | umc1125y3 | 7 | 0.590 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.552 9 | 1.205 |
| P15 | bnlg240k1 | 8 | 0.780 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.750 3 | 1.691 |
| P16 | phi080k15 | 11 | 0.830 4 | 0.992 3 | 0.808 6 | 1.938 |
| P17 | phi065k9 | 6 | 0.594 5 | 0.992 3 | 0.557 3 | 1.230 |
| P18 | umc1492y13 | 4 | 0.614 4 | 0.953 7 | 0.558 8 | 1.116 |
| P19 | umc1432y6 | 10 | 0.750 9 | 0.992 3 | 0.713 7 | 1.551 |
| P20 | umc1506k12 | 8 | 0.803 5 | 1.000 0 | 0.774 3 | 1.723 |
| P21 | umc1147y4 | 5 | 0.510 5 | 0.969 1 | 0.449 2 | 0.933 |
| P22 | bnlg1671y17 | 12 | 0.823 4 | 0.992 3 | 0.800 3 | 1.908 |
| P23 | phi96100y1 | 9 | 0.738 3 | 0.988 4 | 0.712 1 | 1.656 |
| P24 | umc1536k9 | 6 | 0.696 4 | 0.996 1 | 0.656 0 | 1.414 |
| P25 | bnlg1520k1 | 8 | 0.762 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.725 5 | 1.604 |
| P26 | umc1489y3 | 12 | 0.790 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.761 7 | 1.747 |
| P27 | bnlg490y4 | 13 | 0.794 1 | 0.818 5 | 0.775 1 | 1.962 |
| P28 | umc1999y3 | 5 | 0.303 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.289 0 | 0.655 |
| P29 | umc2115k3 | 5 | 0.636 9 | 0.988 4 | 0.600 7 | 1.274 |
| P30 | umc1429y7 | 8 | 0.724 6 | 1.000 0 | 0.682 6 | 1.467 |
| P31 | bnlg249k2 | 7 | 0.606 0 | 1.000 0 | 0.537 2 | 1.139 |
| P32 | phi299852y2 | 9 | 0.811 3 | 0.965 3 | 0.787 4 | 1.860 |
| P33 | umc2160k3 | 11 | 0.409 8 | 1.000 0 | 0.396 2 | 0.987 |
| P34 | umc1936k4 | 4 | 0.382 4 | 0.861 0 | 0.351 0 | 0.711 |
| P35 | bnlg2235y5 | 6 | 0.765 6 | 0.973 0 | 0.730 7 | 1.596 |
| P36 | phi233376y1 | 9 | 0.738 2 | 1.000 0 | 0.697 6 | 1.576 |
| P37 | umc2084w2 | 11 | 0.812 4 | 1.000 0 | 0.788 6 | 1.843 |
| P38 | umc123lk4 | 6 | 0.620 5 | 0.915 1 | 0.568 8 | 1.196 |
| P39 | phi041y6 | 10 | 0.655 4 | 0.996 1 | 0.616 9 | 1.430 |
| P40 | umc2163w3 | 9 | 0.732 5 | 0.957 5 | 0.692 0 | 1.539 |
| 平均值Average | 9.975 | 0.717 1 | 0.982 2 | 0.686 8 | 1.615 | |
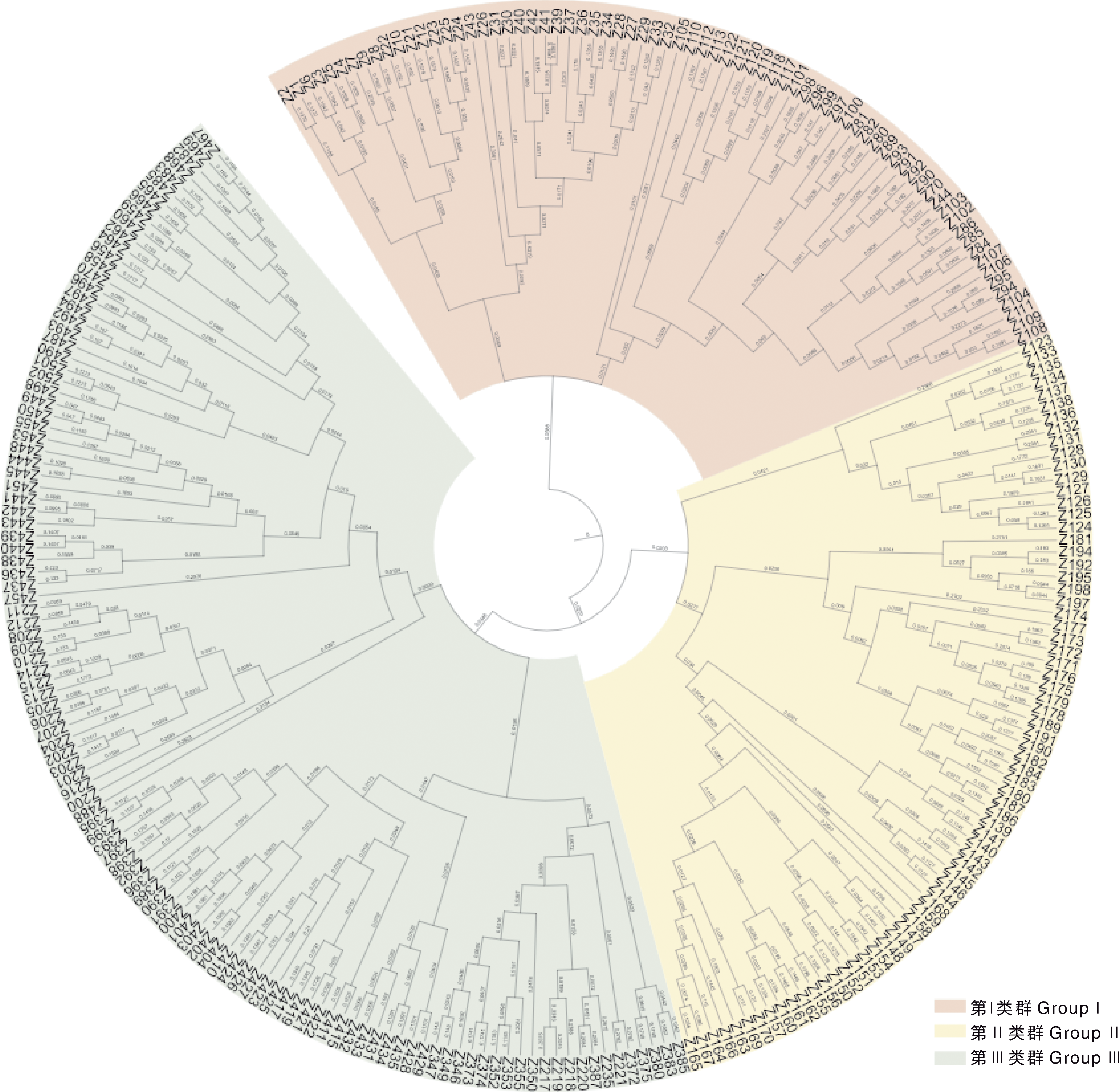
图2 259份地方玉米种质的UPGMA聚类图 编号对应的玉米种质见附表1。
Fig.2 UPGMA clustering of 259 maize landraces The corresponding maize landraces for each number are provided in Supplementary Table 1.
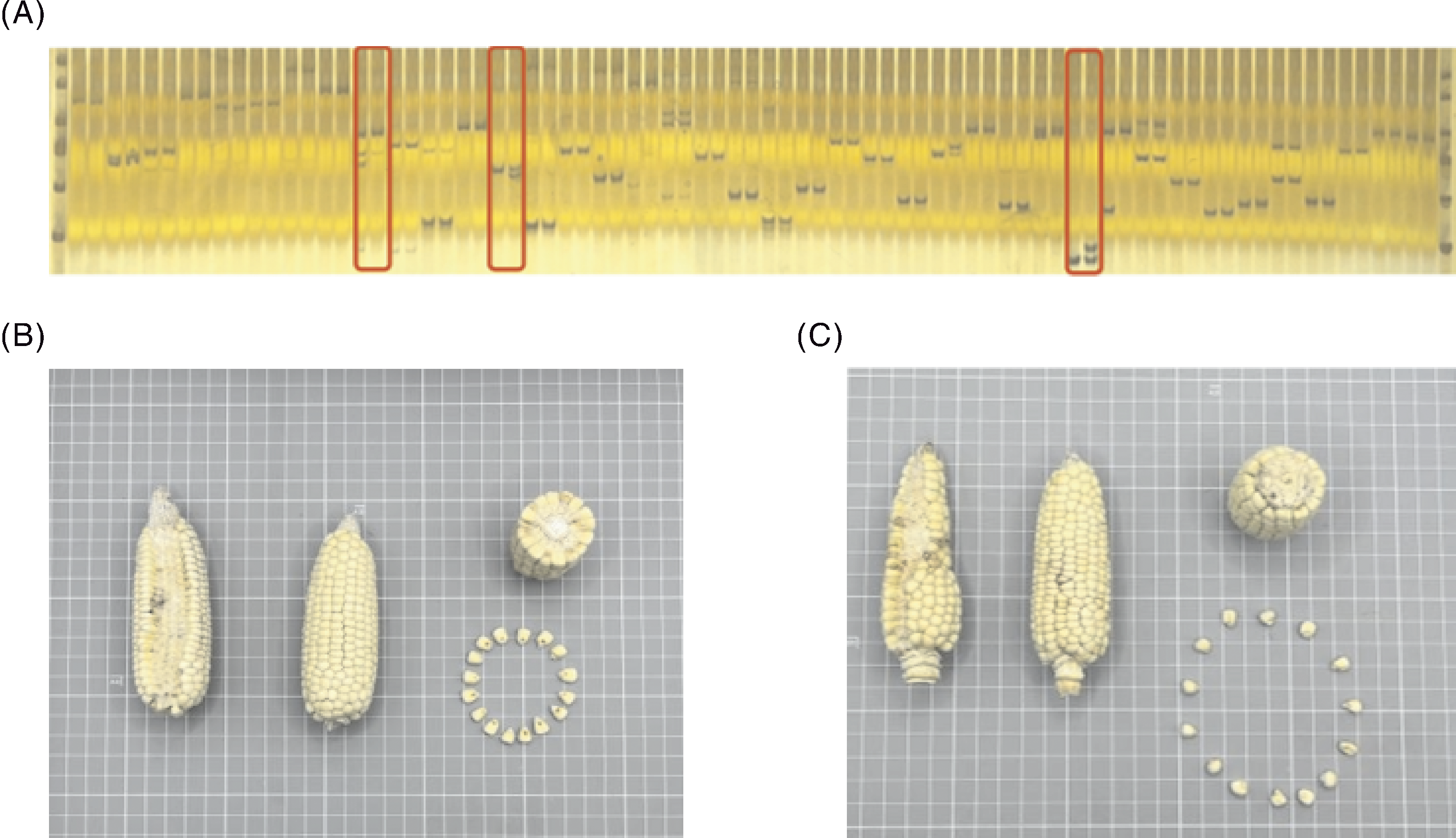
图3 慈溪糯玉米(大粒)和慈溪糯玉米(小粒)种质比较 A,2份种质SSR标记对比;B,慈溪糯玉米(大粒)籽粒性状;C,慈溪糯玉米(小粒)籽粒性状。
Fig.3 Comparison of Cixi Waxy Corn (large kernel) and Cixi Waxy Corn (small kernel) A, SSR markers of the two germplasms; B, Seed traits of Cixi Waxy Corn (large kernel); C, Seed traits of Cixi Waxy Corn (small kernel).
| 种质 Germplasm | 株高/cm Plant height/cm | 穗位高/cm Ear height/cm | 播种至抽雄时间/d Time for sowing to tasseling /d | 播种至散粉时间/d Time for sowing to anthesis/d | 播种至吐丝时间/d Time for sowing to silking/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 慈溪糯玉米(大粒)Cixi Waxy Corn (large kernel) | 173.3 | 88.2 | 70 | 74 | 75 |
| 慈溪糯玉米(小粒)Cixi Waxy Corn (small kernel) | 167.3 | 79.1 | 73 | 77 | 78 |
| 炬秋玉米Juqiu Corn | 190.6 | 62.5 | 65 | 68 | 69 |
| 开化地玉米Kaihua Di Corn | 170.6 | 81.3 | 62 | 64 | 65 |
| 紫包早Zi Bao Zao | 259.3 | 105.7 | 66 | 70 | 71 |
| 余杭八十日Yuhang 80 Days | 239.4 | 110.1 | 70 | 73 | 74 |
| 临海黄玉米Linhai Yellow Corn | 165.6 | 75.7 | 62 | 65 | 66 |
| 黄包萝(110175)Yellow Baoluo (110175) | 195.6 | 74.1 | 61 | 64 | 65 |
| 山玉米(2018331072) | 277.1 | 147.6 | 75 | 79 | 80 |
| Mountain Corn (2018331072) | |||||
| 山玉米2(新收集) | 300.5 | 146.0 | 75 | 79 | 80 |
| Mountain Corn 2 (new collection) |
表2 不同玉米种质的农艺性状
Table 2 Agronomic traits of different maize landraces
| 种质 Germplasm | 株高/cm Plant height/cm | 穗位高/cm Ear height/cm | 播种至抽雄时间/d Time for sowing to tasseling /d | 播种至散粉时间/d Time for sowing to anthesis/d | 播种至吐丝时间/d Time for sowing to silking/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 慈溪糯玉米(大粒)Cixi Waxy Corn (large kernel) | 173.3 | 88.2 | 70 | 74 | 75 |
| 慈溪糯玉米(小粒)Cixi Waxy Corn (small kernel) | 167.3 | 79.1 | 73 | 77 | 78 |
| 炬秋玉米Juqiu Corn | 190.6 | 62.5 | 65 | 68 | 69 |
| 开化地玉米Kaihua Di Corn | 170.6 | 81.3 | 62 | 64 | 65 |
| 紫包早Zi Bao Zao | 259.3 | 105.7 | 66 | 70 | 71 |
| 余杭八十日Yuhang 80 Days | 239.4 | 110.1 | 70 | 73 | 74 |
| 临海黄玉米Linhai Yellow Corn | 165.6 | 75.7 | 62 | 65 | 66 |
| 黄包萝(110175)Yellow Baoluo (110175) | 195.6 | 74.1 | 61 | 64 | 65 |
| 山玉米(2018331072) | 277.1 | 147.6 | 75 | 79 | 80 |
| Mountain Corn (2018331072) | |||||
| 山玉米2(新收集) | 300.5 | 146.0 | 75 | 79 | 80 |
| Mountain Corn 2 (new collection) |
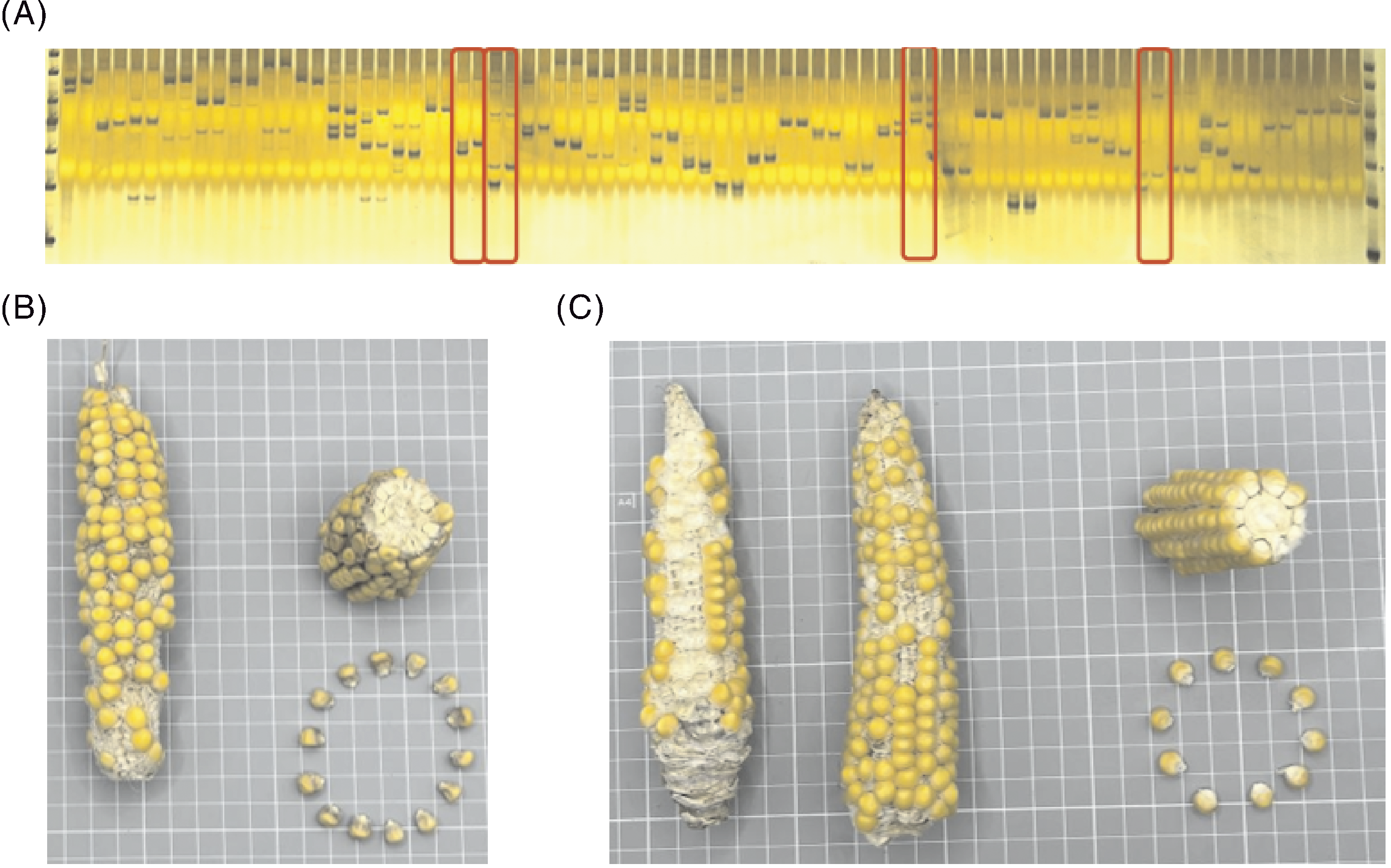
图4 炬秋玉米和开化地玉米种质比较 A,2份种质SSR标记;B,炬秋玉米(110027)籽粒性状;C,开化地玉米(110013)籽粒性状。
Fig.4 Comparison of Juqiu Corn and Kaihua Di Corn A, SSR markers of the two germplasms; B, Seed traits of Juqiu Corn ; C, Seed traits of Kaihua Di Corn.
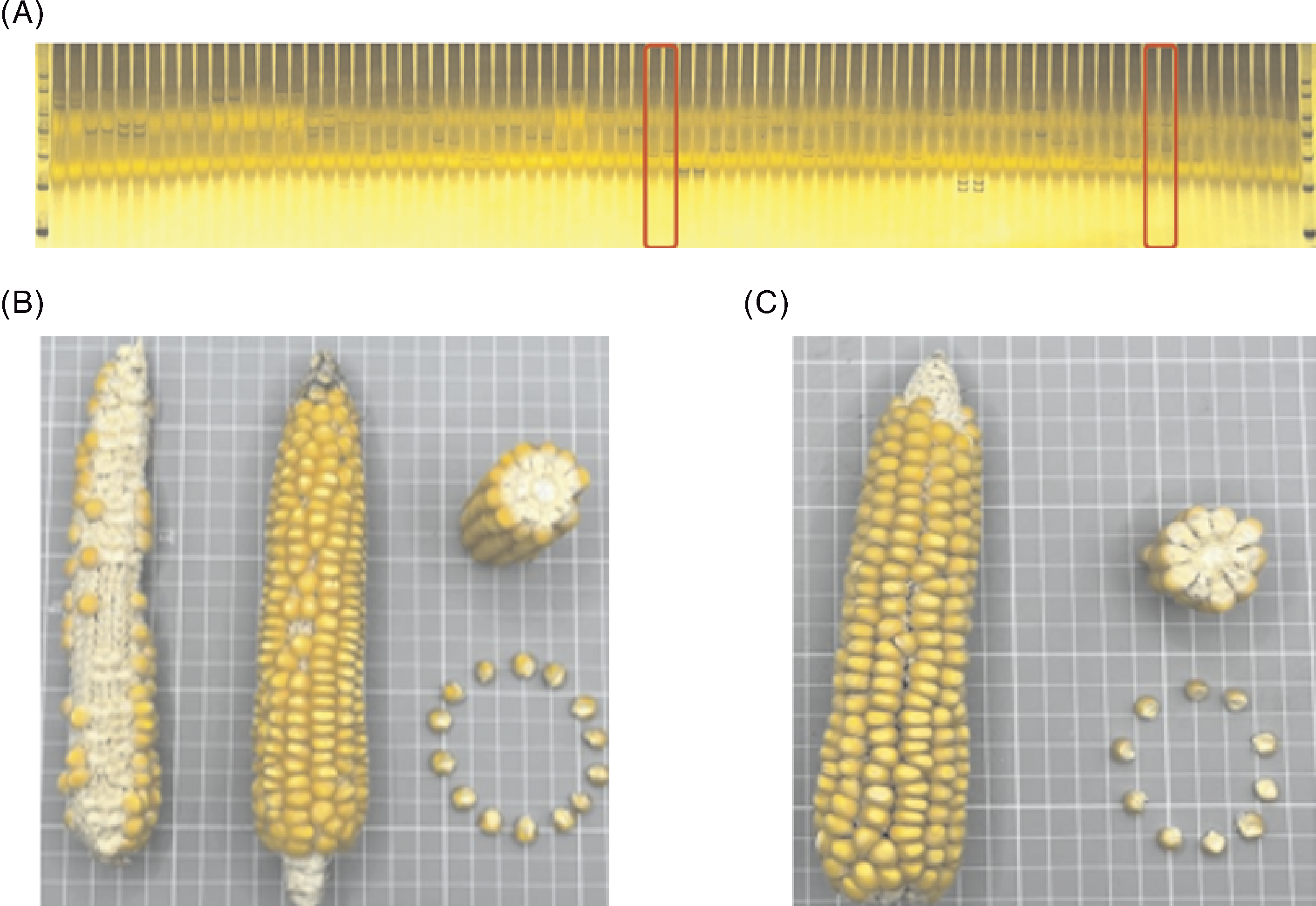
图5 紫包早和余杭八十日种质比较 A,2份种质SSR标记;B,紫包早籽粒性状;C,余杭八十日籽粒性状。
Fig.5 Comparison of Zi Bao Zao and Yuhang 80 Days A, SSR markers of the two germplasms; B, Seed traits of Zi Bao Zao; C, Seed traits of Yuhang 80 Days.
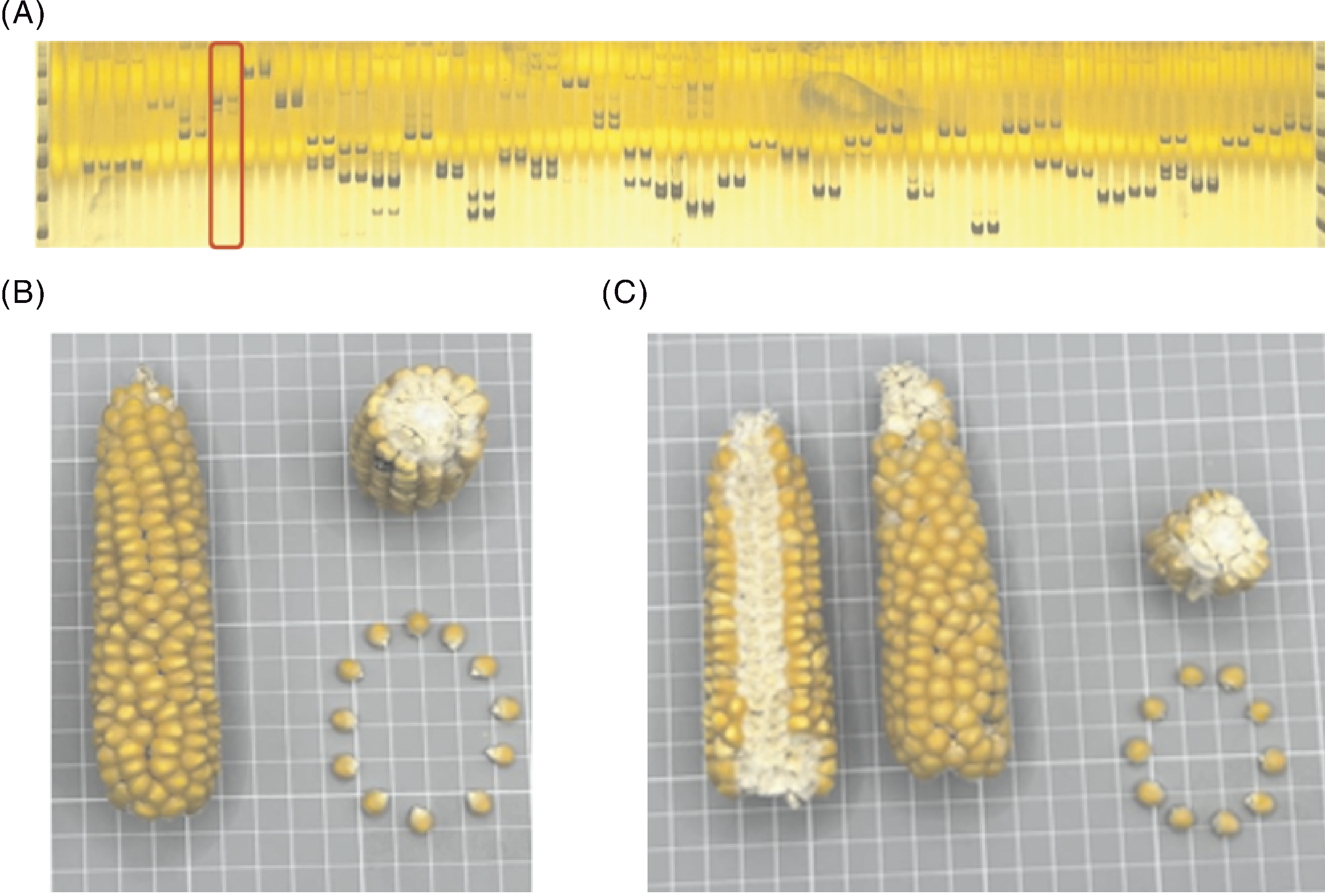
图6 临海黄玉米和黄包萝种质比较 A,2份种质SSR标记;B,临海黄玉米籽粒性状;C,黄包萝(110175)。
Fig.6 Comparison of Linhai Yellow Corn and Yellow Baoluo (110175) A, SSR markers of the two germplasms; B, Seed traits of Linhai Yellow Corn; C, Seed traits of Yellow Baoluo (110175).
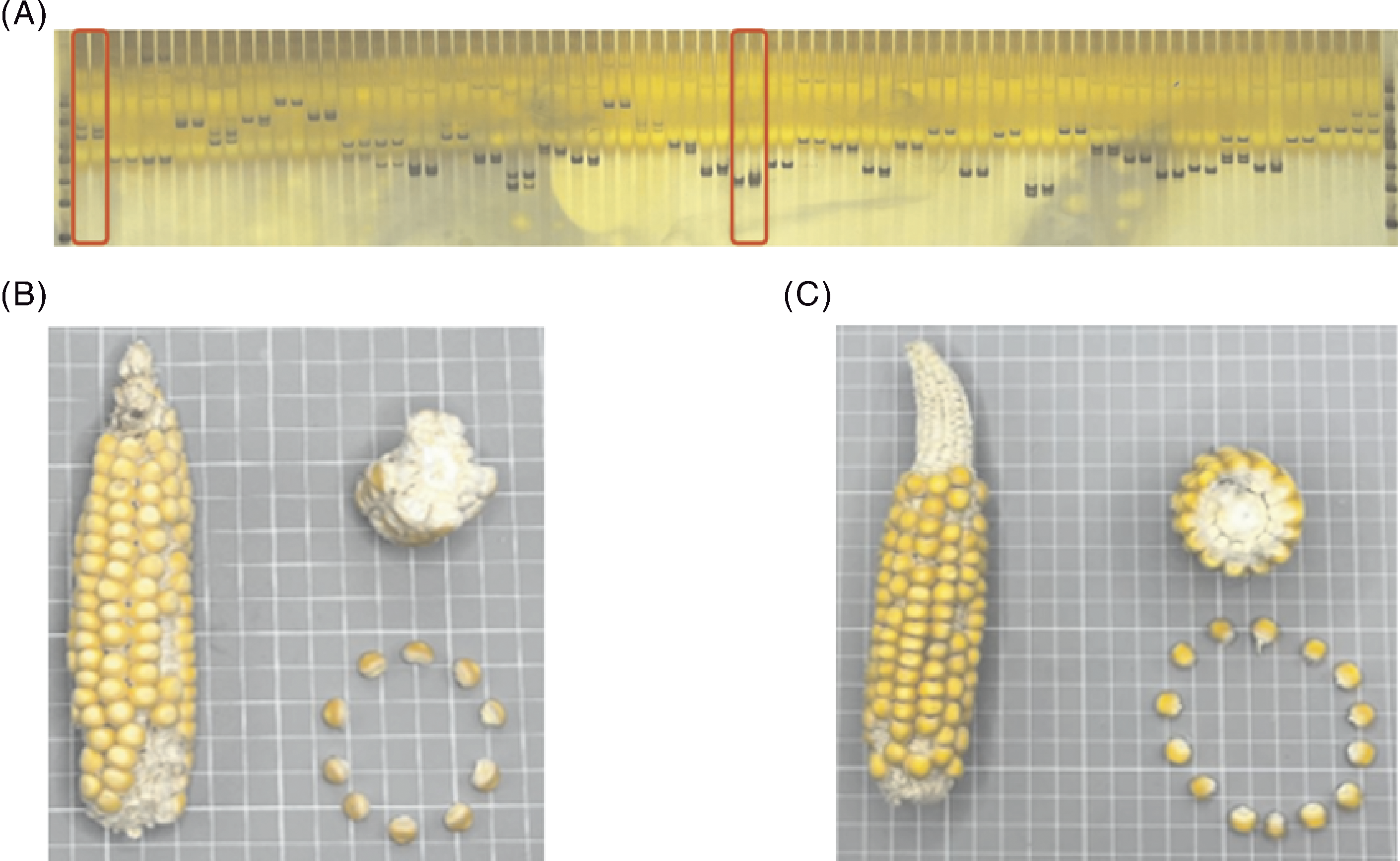
图7 山玉米(2018331072)和山玉米2(新收集)种质比较 A,2份种质SSR标记;B,山玉米(2018331072)籽粒性状;C,山玉米2(新收集)。
Fig.7 Comparison of Mountain Corn (2018331072) and Mountain Corn 2 (new collection) A, SSR markers of the two germplasms; B, Seed traits of Mountain Corn (2018331072); C, Seed traits of Mountain Corn 2 (new collection).
| [1] | SHIFERAW B, PRASANNA B M, HELLIN J, et al. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security[J]. Food Security, 2011, 3(3): 307-327. |
| [2] | 孙敬华. 浅谈玉米育种的途径及方法[J]. 中国农业信息, 2006, 18(4): 33-34. |
| SUN J H. Talking about the ways and methods of maize breeding[J]. China Agricultural Information, 2006, 18(4): 33-34. | |
| [3] | 常宏兵, 王晨, 何美敬, 等. 60份玉米种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(4): 1162-1168. |
| CHANG H B, WANG C, HE M J, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of 60 maize germplasm resources[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(4): 1162-1168. | |
| [4] | 杨前勇. 地方品种遗传多样性和群体结构的分析与统计方法[J]. 江西畜牧兽医杂志, 2017(5): 1-4. |
| YANG Q Y. Analysis and statistical methods of genetic diversity and population structure of local varieties[J]. Jiangxi Journal of Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017(5): 1-4. | |
| [5] | 王成树, 李增智. 分子数据的遗传多样性分析方法[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2002, 29(1): 90-94. |
| WANG C S, LI Z Z. Genetic diversity analysis methods of molecular data (review)[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2002, 29(1): 90-94. | |
| [6] | 何琳, 王群. 基于PCR的SSR标记分离方法综述[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2010, 29(4): 775-782. |
| HE L, WANG Q. Review on the PCR-based SSR markers isolation methods[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2010, 29(4): 775-782. | |
| [7] | GAUTHIER P, GOUESNARD B, DALLARD J, et al. RFLP diversity and relationships among traditional European maize populations[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 105(1): 91-99. |
| [8] | BELALIA N, LUPINI A, DJEMEL A, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure in Saharan maize (Zea mays L.) populations using phenotypic traits and SSR markers[J]. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 2019, 66(1): 243-257. |
| [9] | 景建洲, 张勇, 李东亮, 等. 利用RAPD分子标记分析玉米种质遗传多样性[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(12): 405-408. |
| JING J Z, ZHANG Y, LI D L, et al. Assessment of genetic diversity of maize detected by RAPD molecular markers[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(12): 405-408. | |
| [10] | 高山, 闫晓翠, 王楠, 等. 基于10K SNP芯片分析255份玉米种质资源的遗传多样性[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2024, 26(8): 20-33. |
| GAO S, YAN X C, WANG N, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of 255 maize germplasm resources based on 10K SNP chip[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2024, 26(8): 20-33. | |
| [11] | SENIOR M L, HEUN M. Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CT primer[J]. Genome, 1993, 36(5): 884-889. |
| [12] | SMITH J S C, CHIN E C L, SHU H, et al. An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPS and pedigree[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 95(1): 163-173. |
| [13] | ENOKI H, SATO H, KOINUMA K. SSR analysis of genetic diversity among maize inbred lines adapted to cold regions of Japan[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104(8): 1270-1277. |
| [14] | 刘志斋, 吴迅, 刘海利, 等. 基于40个核心SSR标记揭示的820份中国玉米重要自交系的遗传多样性与群体结构[J]. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(11): 2107-2138. |
| LIU Z Z, WU X, LIU H L, et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of important Chinese maize inbred lines revealed by 40 core simple sequence repeats (SSRs)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(11): 2107-2138. | |
| [15] | 陈晓龙, 应多, 包斐, 等. 浙江省50份甜玉米核心种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(10): 2258-2262. |
| CHEN X L, YING D, BAO F, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of 50 sweet maize germplasm resources in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 63(10): 2258-2262. | |
| [16] | 石建尧. 浙江省玉米种质资源现状与利用[J]. 种子世界, 2008(3): 1-2. |
| SHI J Y. Status and utilization of maize germplasm resources in Zhejiang Province[J]. Seed World, 2008(3): 1-2. | |
| [17] | 朱正歌, 贾继增, 孙宗修. 水稻AFLP指纹银染法显带研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2002, 16(1): 71-73. |
| ZHU Z G, JIA J Z, SUN Z X. Improvement of AFLP protocol for silver-staining in rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2002, 16(1): 71-73. | |
| [18] | 樊文强, 盖红梅, 孙鑫, 等. SSR数据格式转换软件DataFormater[J]. 分子植物育种, 2016, 14(1): 265-270. |
| FAN W Q, GAI H M, SUN X, et al. Data formater, a software for SSR data formatting to develop population genetics analysis[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(1): 265-270. | |
| [19] | MATHIANG E A, SA K J, PARK H, et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of normal maize germplasm collected in south Sudan revealed by SSR markers[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(20): 2787. |
| [20] | 王凤格, 田红丽, 赵久然, 等. 中国328个玉米品种(组合)SSR标记遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(5): 856-864. |
| WANG F G, TIAN H L, ZHAO J R, et al. Genetic diversity analysis of 328 maize varieties (hybridized combinations) using SSR markers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(5): 856-864. | |
| [21] | 李庆锋, 任雪娇, 许赢, 等. 基于SSR标记的148份玉米自交系亲缘关系分析[J]. 玉米科学, 2024, 32(2): 54-61. |
| LI Q F, REN X J, XU Y, et al. Genetic relationship analysis of 148 maize inbred lines based on SSR molecular markers[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2024, 32(2): 54-61. | |
| [22] | YUAN Y B, CAIRNS J E, BABU R, et al. Genome-wide association mapping and genomic prediction analyses reveal the genetic architecture of grain yield and flowering time under drought and heat stress conditions in maize[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 9: 1919. |
| [23] | 张建国. 玉米萌发至出苗期耐低温性全基因组关联分析及候选基因挖掘[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG J G. Association analysis and candidate gene mining of low temprature tolerance in maize from the germination stage to seedling stage[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [24] | 杨雪, 丁小兰, 何增磊, 等. 玉米南方锈病发生温度范围测定[J]. 植物保护, 2015, 41(5): 145-147. |
| YANG X, DING X L, HE Z L, et al. Determination of temperature required by southern corn rust[J]. Plant Protection, 2015, 41(5): 145-147. | |
| [25] | 章慧玉, 张香粉, 张留声, 等. 46份黄淮海玉米新品种南方锈病抗性剖析[J]. 种子, 2024, 43(9): 109-115. |
| ZHANG H Y, ZHANG X F, ZHANG L S, et al. Analysis of resistance to southern rust of 46 new maize varieties from the Huang-Huai-Hai Region[J]. Seed, 2024, 43(9): 109-115. | |
| [26] | GAO J, ZHANG N, LIU G H, et al. Regulation of maize growth and immunity by ZmSKI3-mediated RNA decay and post-transcriptional gene silencing[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2024, 66(11): 2561-2577. |
| [27] | ZHU M, ZHONG T, XU L, et al. The ZmCPK39-ZmDi19-ZmPR10 immune module regulates quantitative resistance to multiple foliar diseases in maize[J]. Nature Genetics, 2024, 56(12): 2815-2826. |
| [1] | 许卫猛, 徐妍, 陈国立. 基于多种分析方法的糯玉米品质综合评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1840-1848. |
| [2] | 闫沛中, 陈亮, 张生银, 刘斌. 水肥耦合对景电灌区膜下滴灌玉米产量及水肥利用效率的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1849-1859. |
| [3] | 关秀生, 刘铁山, 王娟, 张茂林, 刘春晓, 董瑞, 关海英, 刘强, 徐扬, 何春梅. 玉米NF-YA家族基因的生物信息学分析与克隆[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1605-1614. |
| [4] | 咸若彤, 缪青梅, 彭城, 陈笑芸, 杨蕾, 徐晓丽, 魏巍, 徐俊锋, 李玥莹, 汪小福. 转基因玉米WYN17132转化体特异性实时荧光PCR检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(7): 1397-1406. |
| [5] | 王闻琦, 王盼盼, 张严玲, 刘青青, 洪双双, 赵高鹏, 刘泓畅, 王翠玲. 玉米生物钟基因ZmPRR1-2互作蛋白质的筛选[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(5): 977-986. |
| [6] | 刘思彤, 侯宇, 潘家荃, 周桦楠, 崔亮, 万博, 于涛. 甘薯对低温胁迫的生理响应及耐寒性评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 767-778. |
| [7] | 郭赛赛, 聂智星, 傅鸿妃, 王同林, 邵志勇, 王宏, 郑积荣. 37份辣椒种质资源的表型性状及SRAP遗传多样性分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(2): 300-310. |
| [8] | 王晓阳, 李强, 赵武云, 戴飞, 严兆荣, 王久鑫. 铲式青贮玉米起茬及残膜回收联合作业机设计与试验[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(9): 2132-2145. |
| [9] | 董莉莉, 徐志浩, 严灿龙, 范小平, 金泽兰, 王忠华. 基于表型与分子标记对浙贝母不同育种群体的分子鉴定与亲缘关系研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(8): 1719-1730. |
| [10] | 李清超, 杨珊, 张登峰, 刘建新, 孙开利, 吴迅. 四百八十七份玉米地方种质资源穗部性状的表型多样性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1481-1491. |
| [11] | 李亚东, 罗小波, 彭潇, 杨光乾, 金月月, 祖贵东, 田欢, 张万萍. 萝卜SNP和InDel分子标记开发及与表型性状关联分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(5): 1055-1066. |
| [12] | 薛贤滨, 贾琼, 陈峥峰, 黎瑞源, 陈庆富, 石桃雄. 基于主成分分析的苦荞麦重组自交系农艺性状综合评价[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(4): 748-759. |
| [13] | 周丽丽, 冯海宽, 聂臣巍, 许晓斌, 刘媛, 孟麟, 薛贝贝, 明博, 梁齐云, 苏涛, 金秀良. 无人机观测时间对玉米冠层叶绿素密度估算的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 18-31. |
| [14] | 冷益丰, 罗樊, 陈从顺, 丁鑫, 蔡光泽. 基于GBS测序的全基因组SNP揭示大凉山玉米地方品种资源的亲缘关系与遗传分化[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(1): 32-47. |
| [15] | 马启良, 杨小明, 胡水星, 黄子鸿, 祁亨年. 基于Mask RCNN和视觉技术的玉米种子发芽自动检测方法[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(8): 1927-1936. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||