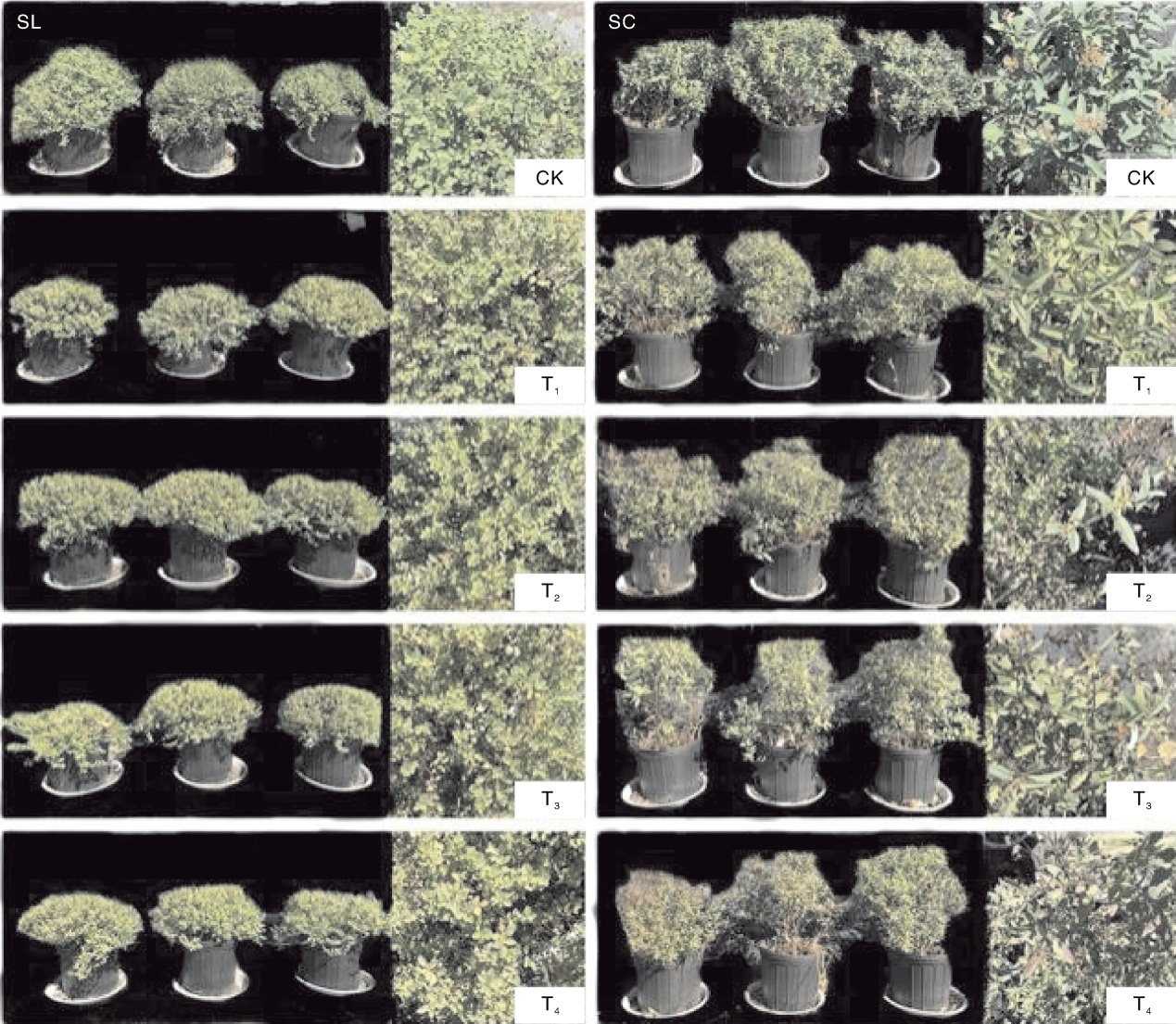
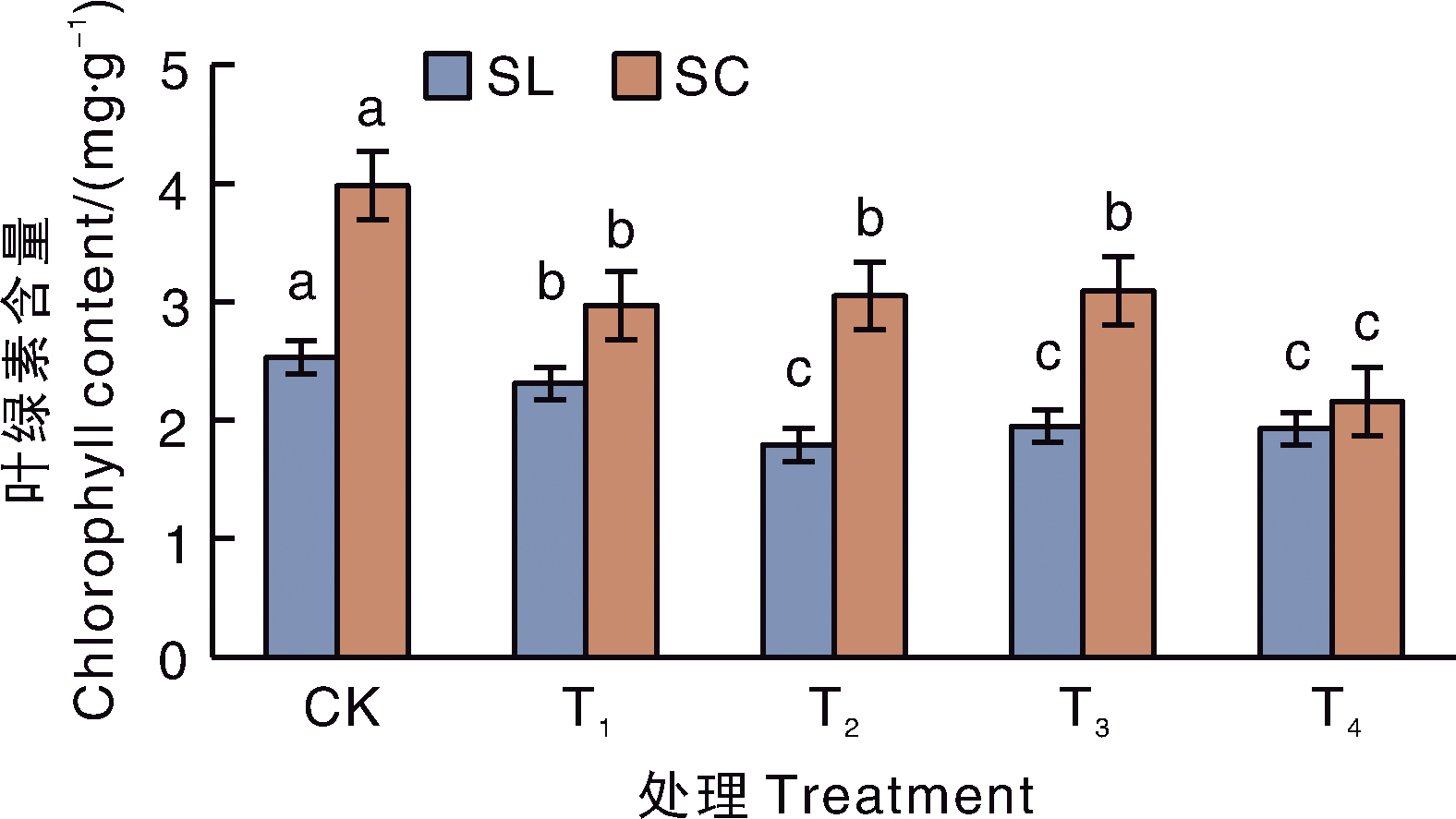
Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2283-2292.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240960
• Horticultural Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cadmium accumulation characteristics and tolerance mechanism of 2 meadowsweet varieties
TAN Xinrui( ), TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian(
), TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian( )
)
- Beijing Laboratory of Urban and Rural Ecological Environment, National Engineering Research Center for Floriculture, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing 100083, China
-
Received:2024-11-09Online:2025-11-25Published:2025-12-08
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TAN Xinrui, TANG Min, LIU Yan, WANG Meixian. Cadmium accumulation characteristics and tolerance mechanism of 2 meadowsweet varieties[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2283-2292.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240960
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小公主 | CK | 32.87±3.31 a | 27.56±3.04 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 31.03±2.65 a | 25.80±1.86 a |
| T2 | 24.07±1.16 b | 24.49±2.61 a | |
| T3 | 25.53±2.55 b | 22.40±3.09 a | |
| T4 | 25.83±2.46 b | 22.18±2.76 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 49.50±0.79 ab | 31.90±4.16 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 48.70±2.26 ab | 25.53±2.78 ab |
| T2 | 49.00±3.11 ab | 25.38±3.67 ab | |
| T3 | 50.53±2.08 a | 20.66±2.93 b | |
| T4 | 44.67±4.48 b | 14.19±3.57 c |
Table 1 Morphological indexes of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments cm
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 小公主 | CK | 32.87±3.31 a | 27.56±3.04 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 31.03±2.65 a | 25.80±1.86 a |
| T2 | 24.07±1.16 b | 24.49±2.61 a | |
| T3 | 25.53±2.55 b | 22.40±3.09 a | |
| T4 | 25.83±2.46 b | 22.18±2.76 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 49.50±0.79 ab | 31.90±4.16 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 48.70±2.26 ab | 25.53±2.78 ab |
| T2 | 49.00±3.11 ab | 25.38±3.67 ab | |
| T3 | 50.53±2.08 a | 20.66±2.93 b | |
| T4 | 44.67±4.48 b | 14.19±3.57 c |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的单株生物量Biomass of different parts per plant | 整株生物量 Biomass of whole plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | |||
| 小公主 | CK | 205.30±33.61 a | 141.35±24.49 a | 95.92±6.26 a | 442.57±62.14 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 202.95±9.33 a | 139.60±2.61 a | 92.05±0.73 ab | 434.60±7.73 a |
| T2 | 179.68±10.66 a | 124.09±6.19 a | 78.94±7.43 b | 382.71±22.51 a | |
| T3 | 180.66±15.81 a | 126.56±11.58 a | 78.64±9.08 b | 385.85±35.77 a | |
| T4 | 168.76±17.14 a | 121.41±11.96 a | 76.15±5.76 b | 366.32±33.61 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 290.69±57.88 a | 244.54±39.60 a | 146.11±7.05 a | 681.34±104.15 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 248.52±40.36 ab | 234.13±14.83 ab | 127.56±13.29 ab | 610.21±48.82 ab |
| T2 | 223.37±2.15 ab | 190.26±11.05 bc | 114.70±8.20 bc | 528.33±15.78 b | |
| T3 | 208.29±20.36 b | 181.08±16.52 cd | 95.54±16.32 c | 484.91±22.42 b | |
| T4 | 125.89±50.45 c | 129.99±44.37 d | 63.99±12.15 d | 319.87±105.86 c | |
Table 2 Biomass of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments g
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的单株生物量Biomass of different parts per plant | 整株生物量 Biomass of whole plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | |||
| 小公主 | CK | 205.30±33.61 a | 141.35±24.49 a | 95.92±6.26 a | 442.57±62.14 a |
| Little Princess | T1 | 202.95±9.33 a | 139.60±2.61 a | 92.05±0.73 ab | 434.60±7.73 a |
| T2 | 179.68±10.66 a | 124.09±6.19 a | 78.94±7.43 b | 382.71±22.51 a | |
| T3 | 180.66±15.81 a | 126.56±11.58 a | 78.64±9.08 b | 385.85±35.77 a | |
| T4 | 168.76±17.14 a | 121.41±11.96 a | 76.15±5.76 b | 366.32±33.61 a | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 290.69±57.88 a | 244.54±39.60 a | 146.11±7.05 a | 681.34±104.15 a |
| Coccimea | T1 | 248.52±40.36 ab | 234.13±14.83 ab | 127.56±13.29 ab | 610.21±48.82 ab |
| T2 | 223.37±2.15 ab | 190.26±11.05 bc | 114.70±8.20 bc | 528.33±15.78 b | |
| T3 | 208.29±20.36 b | 181.08±16.52 cd | 95.54±16.32 c | 484.91±22.42 b | |
| T4 | 125.89±50.45 c | 129.99±44.37 d | 63.99±12.15 d | 319.87±105.86 c | |
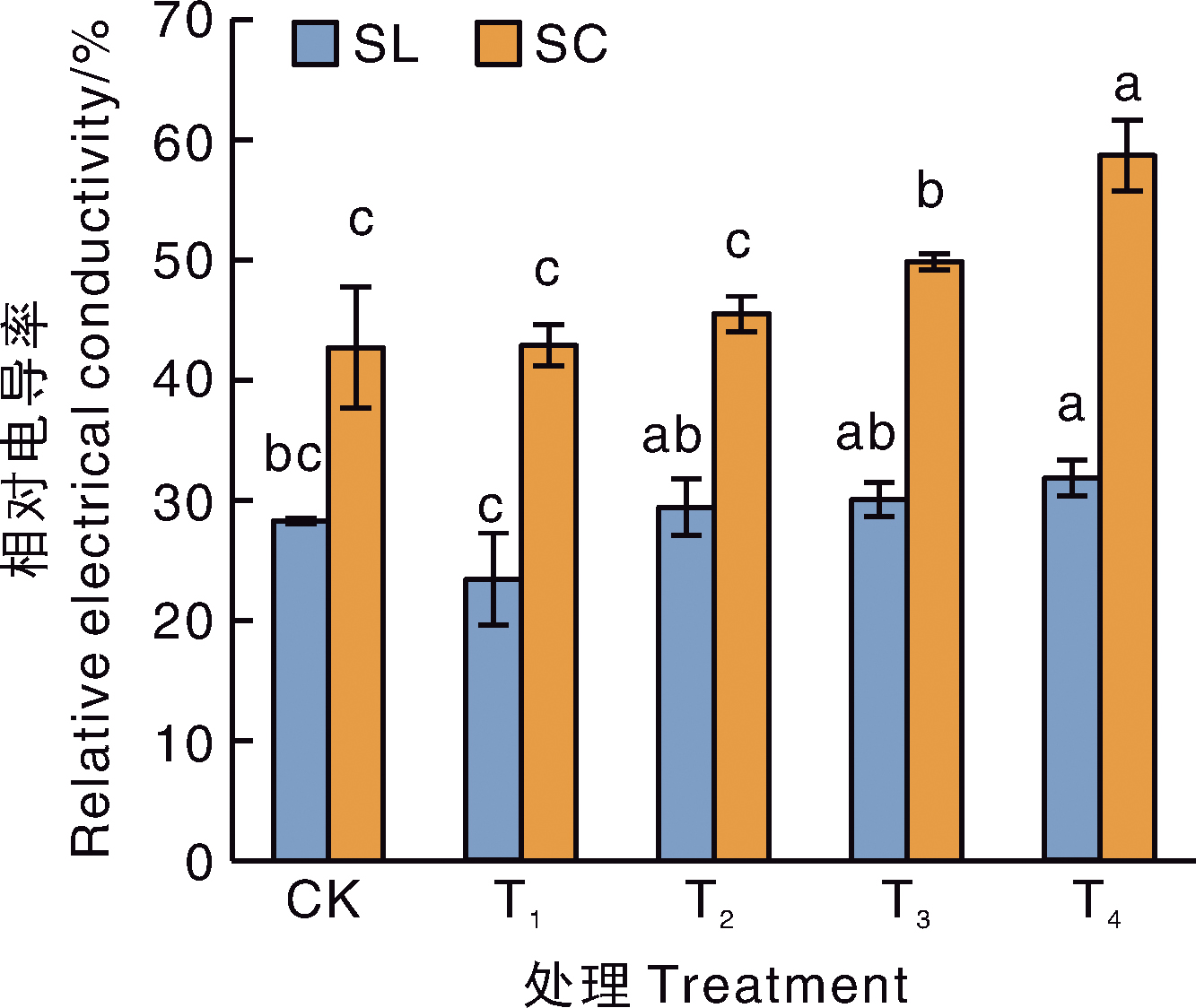
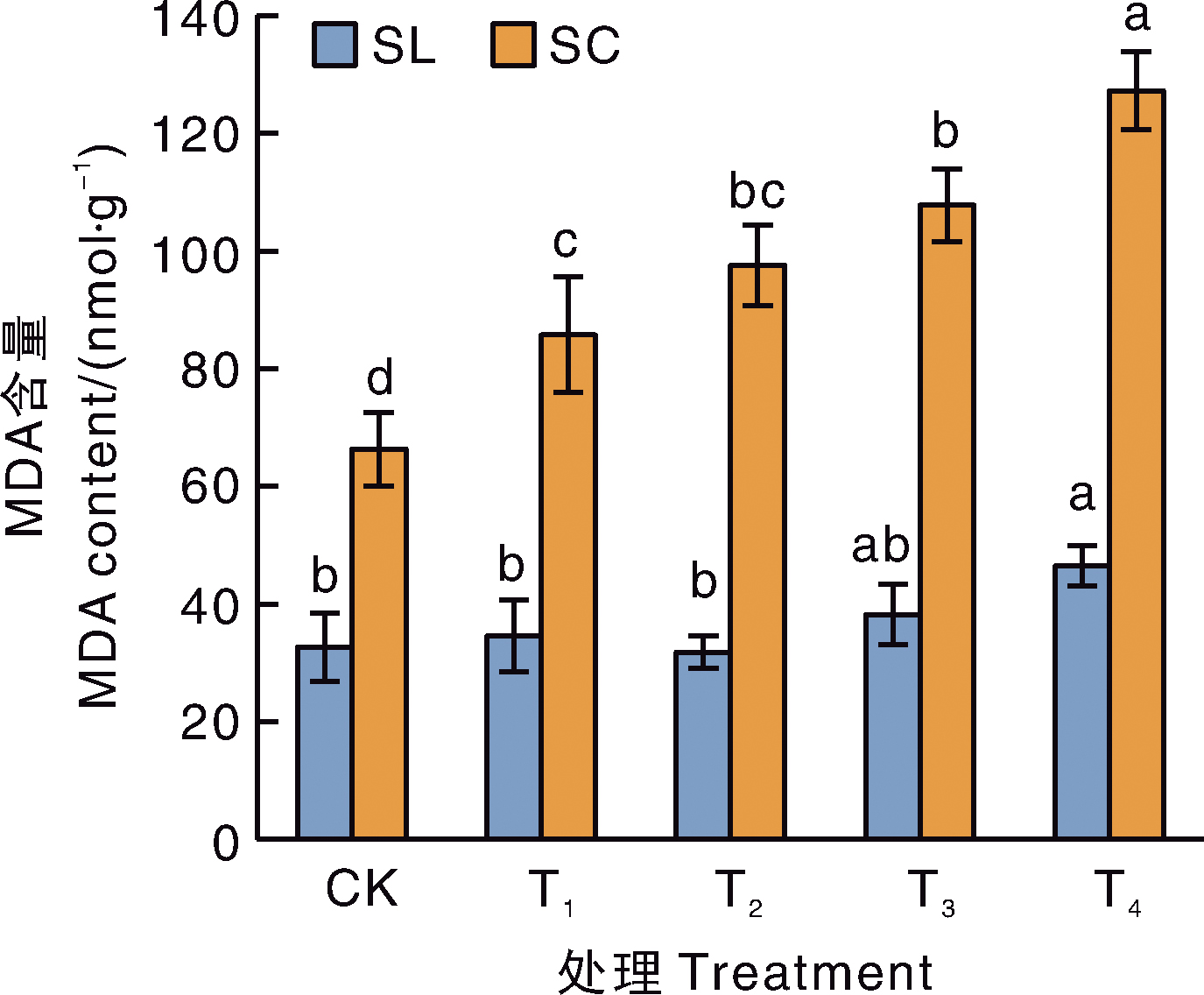
Fig.2 Relative electric conductivity of two meadowsweet varieties under different treatments SL, Spiraea japonica Little Princess; SL, Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea. Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference within treatments at p<0.05 for the same variety. The same as below.
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的镉含量Cd conten in different parts of plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||
| 小公主Little Princess | CK | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.13±0.01 e | 0.51±0.13 e |
| T1 | 6.85±0.44 c | 14.99±1.40 d | 63.97±3.04 d | |
| T2 | 15.66±1.68 b | 27.89±5.71 c | 78.61±4.03 c | |
| T3 | 17.66±0.64 b | 40.62±6.33 b | 89.28±4.48 b | |
| T4 | 26.55±2.54 a | 55.51±7.16 a | 99.23±6.03 a | |
| 鲜红Coccimea | CK | 0.10±0.02 d | 0.60±0.04 d | 0.76±0.16 d |
| T1 | 6.71±0.51 c | 16.24±3.45 c | 16.94±1.04 c | |
| T2 | 8.53±0.26 c | 16.20±3.15 c | 17.89±1.47 c | |
| T3 | 11.64±1.03 b | 23.81±0.96 b | 41.44±7.04 b | |
| T4 | 20.26±3.46 a | 41.60±6.13 a | 59.36±8.14 a | |
Table 3 Cd content in two meadowsweet varieties mg·kg-1
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的镉含量Cd conten in different parts of plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||
| 小公主Little Princess | CK | 0.04±0.01 d | 0.13±0.01 e | 0.51±0.13 e |
| T1 | 6.85±0.44 c | 14.99±1.40 d | 63.97±3.04 d | |
| T2 | 15.66±1.68 b | 27.89±5.71 c | 78.61±4.03 c | |
| T3 | 17.66±0.64 b | 40.62±6.33 b | 89.28±4.48 b | |
| T4 | 26.55±2.54 a | 55.51±7.16 a | 99.23±6.03 a | |
| 鲜红Coccimea | CK | 0.10±0.02 d | 0.60±0.04 d | 0.76±0.16 d |
| T1 | 6.71±0.51 c | 16.24±3.45 c | 16.94±1.04 c | |
| T2 | 8.53±0.26 c | 16.20±3.15 c | 17.89±1.47 c | |
| T3 | 11.64±1.03 b | 23.81±0.96 b | 41.44±7.04 b | |
| T4 | 20.26±3.46 a | 41.60±6.13 a | 59.36±8.14 a | |
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的生物富集系数Bioconcentration factor of different parts of plant | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 耐受系数 Tolerance index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||||
| 小公主 | CK | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.56±0.05 a | 2.22±0.56 a | 0.72±0.05 a | — |
| Little Princess | T1 | 0.14±0.01 ab | 0.30±0.03 b | 1.28±0.06 b | 0.44±0.02 b | 0.98±0.02 a |
| T2 | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.79±0.04 bc | 0.36±0.19 b | 0.86±0.05 ab | |
| T3 | 0.12±0.00 b | 0.27±0.04 b | 0.60±0.03 c | 0.39±0.04 b | 0.87±0.08 ab | |
| T4 | 0.13±0.01 ab | 0.28±0.04 b | 0.50±0.03 c | 0.41±0.05 b | 0.83±0.08 b | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 0.49±0.07 a | 2.60±0.19 a | 3.30±0.69 a | 3.08±0.27 a | — |
| Coccimea | T1 | 0.13±0.01 b | 0.32±0.07 b | 0.34±0.02 b | 0.46±0.07 b | 0.90±0.07 a |
| T2 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.17±0.03 bc | 0.18±0.01 b | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.78±0.02 ab | |
| T3 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.28±0.05 b | 0.24±0.01 b | 0.71±0.03 b | |
| T4 | 0.11±0.02 b | 0.21±0.03 bc | 0.30±0.04 b | 0.31±0.05 b | 0.47±0.16 c | |
Table 4 Cd bioconcentration factor, translocation factor and tolerance index of two meadowsweet varieties
| 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 不同部位的生物富集系数Bioconcentration factor of different parts of plant | 转移系数 Translocation factor | 耐受系数 Tolerance index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶Leaf | 茎Stem | 根Root | ||||
| 小公主 | CK | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.56±0.05 a | 2.22±0.56 a | 0.72±0.05 a | — |
| Little Princess | T1 | 0.14±0.01 ab | 0.30±0.03 b | 1.28±0.06 b | 0.44±0.02 b | 0.98±0.02 a |
| T2 | 0.16±0.02 a | 0.28±0.06 b | 0.79±0.04 bc | 0.36±0.19 b | 0.86±0.05 ab | |
| T3 | 0.12±0.00 b | 0.27±0.04 b | 0.60±0.03 c | 0.39±0.04 b | 0.87±0.08 ab | |
| T4 | 0.13±0.01 ab | 0.28±0.04 b | 0.50±0.03 c | 0.41±0.05 b | 0.83±0.08 b | |
| 鲜红 | CK | 0.49±0.07 a | 2.60±0.19 a | 3.30±0.69 a | 3.08±0.27 a | — |
| Coccimea | T1 | 0.13±0.01 b | 0.32±0.07 b | 0.34±0.02 b | 0.46±0.07 b | 0.90±0.07 a |
| T2 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.17±0.03 bc | 0.18±0.01 b | 0.25±0.03 b | 0.78±0.02 ab | |
| T3 | 0.08±0.01 b | 0.16±0.01 c | 0.28±0.05 b | 0.24±0.01 b | 0.71±0.03 b | |
| T4 | 0.11±0.02 b | 0.21±0.03 bc | 0.30±0.04 b | 0.31±0.05 b | 0.47±0.16 c | |
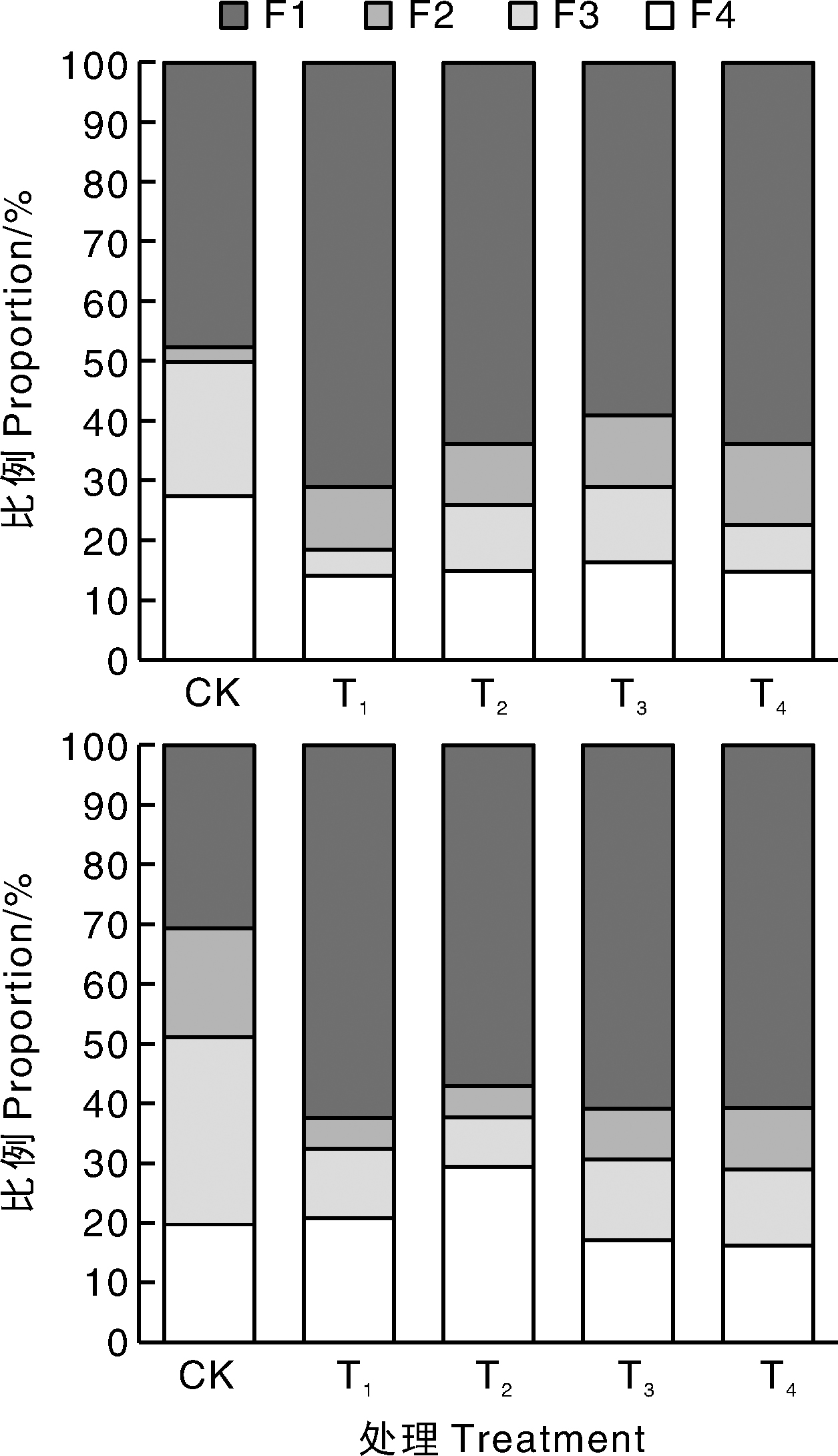
Fig.5 Cd distribution in subcellular components of leaves of Spiraea japonica Little Princess (up) and Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea (down) under different treatments F1, Cell walls; F2, Cell nucleus; F3, Mitochondria and chloroplast; F4, Ribonucleoprotein and soluble composition.
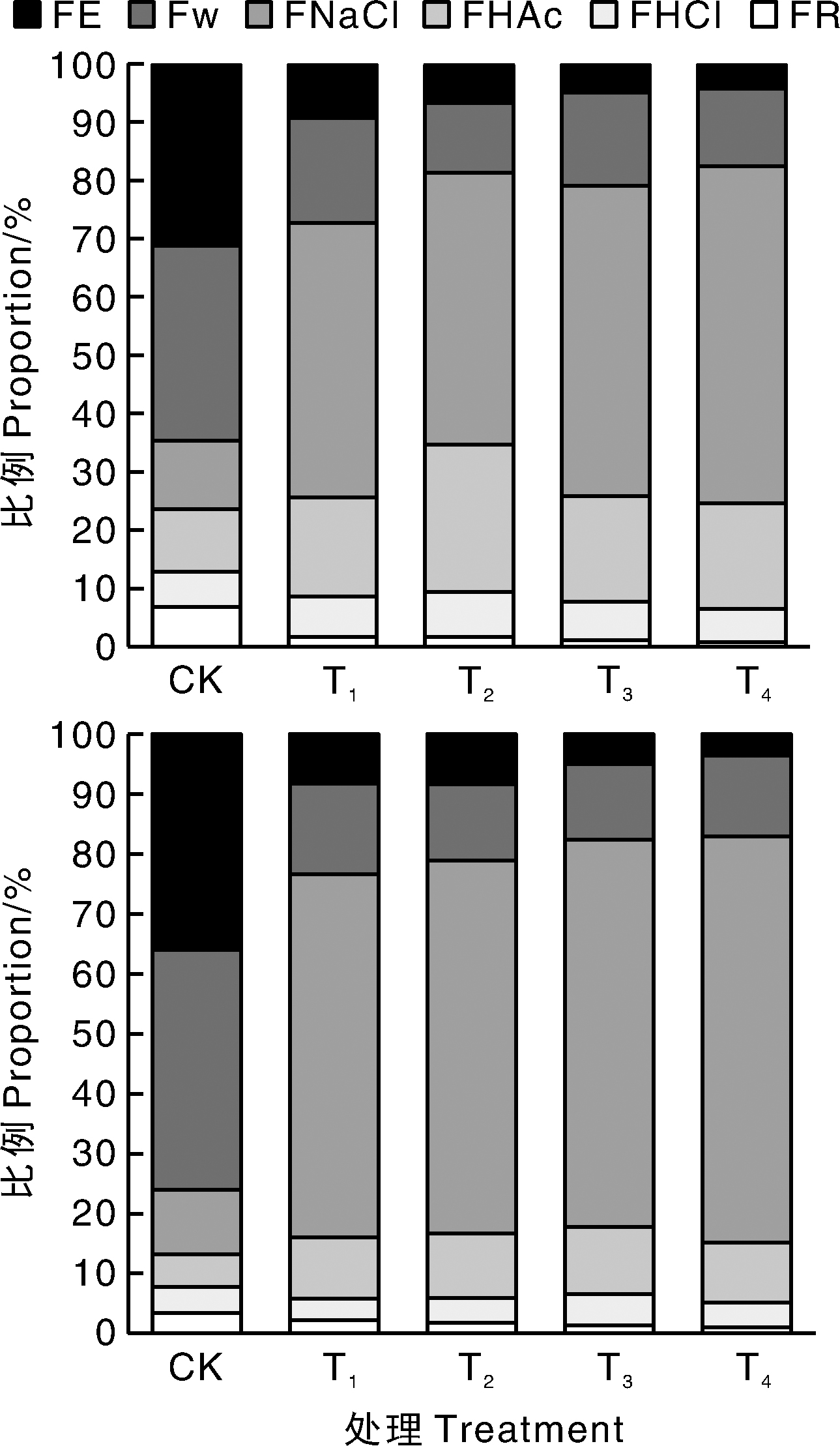
Fig.6 Distribution of different Cd chemical forms in leaves of Spiraea japonica Little Princess (up) and Spiraea×bumalda Coccimea (down) under different treatments FE, FW, FNaCl, FHAc, FHCl and FR represented the fractions extracted by 80% ethanol, deionized water, 1 mol·L-1 NaCl, 2% HAC, 0.6 mol·L-1 HCl and residue, respectively.
| [1] | GRAMLICH A, TANDY S, ANDRES C, et al. Cadmium uptake by cocoa trees in agroforestry and monoculture systems under conventional and organic management[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 580: 677-686. |
| [2] | PELFRÊNE A, WATERLOT C, MAZZUCA M, et al. Assessing Cd, Pb, Zn human bioaccessibility in smelter-contaminated agricultural topsoils (northern France)[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(5): 477-493. |
| [3] | ŠMUC N R, DOLENEC T, SERAFIMOVSKI T, et al. Heavy metal characteristics in Kočani Field plant system (Republic of Macedonia)[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2012 34(4): 513-526. |
| [4] | WAISBERG M, JOSEPH P, HALE B, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis[J]. Toxicology, 2003, 192(2/3): 95-117. |
| [5] | 徐永梅, 字润祥, 卞世闻. 云龙水库周边土壤中重金属的危害评价[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2019, 38(1): 88-91. |
| XU Y M, ZI R X, BIAN S W. Hazard assessment of heavy metal in the soil around Yunlong Reservoir[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2019, 38(1): 88-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 张雁鸿. 镉污染土壤修复治理技术研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2023(24): 56-58. |
| ZHANG Y H. Research on remediation technology for cadmium contaminated soil[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2023(24): 56-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | CAO D, ZHANG H Z, WANG Y D, et al. Accumulation and distribution characteristics of zinc and cadmium in the hyperaccumulator plant Sedum plumbizincicola[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2014, 93(2): 171-176. |
| [8] | 韩飞, 邹光得, 晋方学, 等. 龙葵修复不同浓度土壤镉污染研究[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43(1): 74-78. |
| HAN F, ZOU G D, JIN F X, et al. Remediation of cadmium pollution in different concentrations of soil by Solanum nigrum L[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2023, 43(1): 74-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 徐晓寒. 不同品种柳树幼苗对重金属镉、铅富集能力与耐性机理研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2019. |
| XU X H. Accumulation capacity and tolerance mechanism of four Salix genotypes exposed to cadmium and lead[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 代惠萍. 灰杨幼苗对镉的耐性及解毒生理机制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. |
| DAI H P. Unraveling the mechanisms of cadmium tolerance and detoxification in Populus×canescens[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 庞璐. 柳属(Salix)植物对镉和锌重金属胁迫的耐受差异及机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2021. |
| PANG L. Difference and mechanism for Cd and Zn tolerance in Salix species[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 李香君. 铜、镉、铅胁迫对玫瑰生理及吸收积累特性的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2017. |
| LI X J. Study on physiological and accumulation characteristics of Rosa rugosa-cv. to copper, cadmium and lead stress[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 卢圣凡. 忍冬镉富集特性及对叶片有机酸类有效成分积累影响研究[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2023. |
| LU S F. Research on cadmium enrichment in Lonicera japonica Thunb. and its impact on organic acid accumulation in leaf[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 崔仕杰. 山苍子幼苗对重金属镉和铅的富集特征与胁迫响应研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2023. |
| CUI S J. Enrichment characteristics and stress response of Litsea cubeba seedlings to heavy metals cadmium and lead[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 吴梦媛. 杉木镉积累特性与镉胁迫响应机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2022. |
| WU M Y. Characterization of cadmium accumulation and response mechanisms to cadmium stress in Cunninghamia lanceolata[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A & F University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 顾翠花, 王懿祥, 白尚斌, 等. 四种园林植物对土壤镉污染的耐受性[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(8): 2536-2544. |
| GU C H, WANG Y X, BAI S B, et al. Tolerance and accumulation of four ornamental species seedlings to soil cadmium contamination[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(8): 2536-2544. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | LI X D, MA H, LI L L, et al. Subcellular distribution, chemical forms and physiological responses involved in cadmium tolerance and detoxification in Agrocybe aegerita[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 66-74. |
| [18] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| [19] | 林龙勇, 阎秀兰, 廖晓勇, 等. 三七对土壤中镉、铬、铜、铅的累积特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(11): 2868-2875. |
| LIN L Y, YAN X L, LIAO X Y, et al. Accumulation of soil Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb by Panax notoginseng and its associated health risk[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(11): 2868-2875. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 周守标, 徐礼生, 吴龙华, 等. 镉和锌在皖景天细胞内的分布及化学形态[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(11): 2515-2520. |
| ZHOU S B, XU L S, WU L H, et al. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Cd and Zn in Sedum jinianum[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(11): 2515-2520. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | LU H P, LI Z A, WU J T, et al. Influences of calcium silicate on chemical forms and subcellular distribution of cadmium in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40583. |
| [22] | 周晓声, 娄厦, RADNAEVA L, 等. 植物对土壤重金属富集特性研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(3): 400-410. |
| ZHOU X S, LOU S, RADNAEVA L, et al. Advances in heavy metal accumulation characteristics of plants in soil[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(3): 400-410. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | METWALLY A, SAFRONOVA V I, BELIMOV A A, et al. Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(409): 167-178. |
| [24] | 朱润华, 贺忠群, 王海霞, 等. 镉胁迫处理对水培苦苣幼苗生理响应及叶片超微结构的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(6): 1302-1308. |
| ZHU R H, HE Z Q, WANG H X, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on physiological response and leaf ultrastructure of hydroponic Cichorium endivia L. seedling[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(6): 1302-1308. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 郑逢中, 林鹏, 郑文教. 红树植物秋茄幼苗对镉耐性的研究[J]. 生态学报, 1994, 14(4): 408-414. |
| ZHENG F Z, LIN P, ZHENG W J. Study on the tolerance of Kandelia candel mangrove seedlings to cadmium[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1994, 14(4): 408-414. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 谢倚慧, 张明华, 熊瑞, 等. 马缨丹在镉、铅、锌复合胁迫下的耐性和解毒机制[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(9): 1209-1217. |
| XIE Y H, ZHANG M H, XIONG R, et al. Study on the tolerance and detoxification mechanisms of Lantana camara under the combined stress of cadmium, lead and zinc[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(9): 1209-1217. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 肖才升, 谢心, 李锋, 等. 锰处理下棉花幼苗根部对镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 华北农学报, 2023, 38(6): 55-61. |
| XIAO C S, XIE X, LI F, et al. Physiological response of two cotton seedlings to cadmium stress treated with different concentrations of manganese[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2023, 38(6): 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] | 唐星林, 刘斌, 刘光正, 等. 氮肥对镉胁迫下龙葵叶绿素含量和叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 41(6): 39-46. |
| TANG X L, LIU B, LIU G Z, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on chlorophyll content and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Solanum nigrum under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 41(6): 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [29] | 自海云, 李琬婷, 程小毛, 等. 镉胁迫对洋常春藤叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 38(5): 7-12. |
| ZI H Y, LI W T, CHENG X M, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Hedera helix[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences), 2018, 38(5): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [30] | AMAN M S, JAFARI M, REIHAN M K, et al. Assessing some shrub species for phytoremediation of soils contaminated with lead and zinc[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(3): 82. |
| [31] | BROOKS R R, LEE J, REEVES R D, et al. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1977, 7: 49-57. |
| [32] | 李欣, 孙文, 金政, 等. 燃煤火电厂周边土壤重金属污染状况及绿化树种对重金属的积累特性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2016, 34(4): 21-29. |
| LI X, SUN W, JIN Z, et al. Heavy metal contamination of soil and accumulation in greening trees surrounding coal-fired power plant[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University(Agricultural Science), 2016, 34(4): 21-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 王广林, 张金池, 庄家尧, 等. 31种园林植物对重金属的富集研究[J]. 皖西学院学报, 2011, 27(5): 83-87. |
| WANG G L, ZHANG J C, ZHUANG J Y, et al. Accumulation research of 31 species of ornamental plants on heavy metal[J]. Journal of West Anhui University, 2011, 27(5): 83-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | 李萧萧, 冯丽涵, 李凌. 复合胁迫下复羽叶栾树对Cd和Pb的吸收富集研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 45(5): 103-108. |
| LI X X, FENG L H, LI L. On absorption and accumulation characteristics of Koelreuteria bipinnata Franch. under combined pollution of Cd2+ and Pb2+[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 45(5): 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [35] | 刘金秀, 张松彦, 周建. 镉胁迫对刺槐幼苗生长与光合生理特性的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2023, 36(3): 168-178. |
| LIU J X, ZHANG S Y, ZHOU J. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Forest Research, 2023, 36(3): 168-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [36] | GALLEGO S M, PENA L B, BARCIA R A, et al. Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2012, 83: 33-46. |
| [37] | 唐敏, 张欣, 刘燕, 等. 镉在3种乔木中的积累及其亚细胞分布和化学形态研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(6): 2440-2447. |
| TANG M, ZHANG X, LIU Y, et al. Accumulation, subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in three tree species[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(6): 2440-2447. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [38] | 秦宏, 张宝锋, 陈俊乔, 等. 镉污染土壤伴矿景天的萃取强化螯合剂和植物激素的叶面调控[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(4): 363-369. |
| QIN H, ZHANG B F, CHEN J Q, et al. An enhanced phytoextraction of Sedum plumbizicola in Cd contaminated soil-the foliar application of chelating agent and phytohormones[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(4): 363-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [39] | FU X P, DOU C M, CHEN Y X, et al. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Phytolacca americana L[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 103-107. |
| [40] | PERRONNET K, SCHWARTZ C, MOREL J L. Distribution of cadmium and zinc in the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens grown on multicontaminated soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 249(1): 19-25. |
| [41] | 张欣. 北京道路绿地18种乔木重金属富集能力评价和积累特征差异研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG X. A study on the evaluation and accumulation of heavy metal enrichment ability of 18 trees in Beijing greenbelt[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [42] | 董名扬, 孙瑶, 冯晓晖, 等. 两种生态型香根草对镉的耐受和积累特性比较[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(8): 1330-1338. |
| DONG M Y, SUN Y, FENG X H, et al. Comparative tolerance and accumulation characteristics of cadmium in two vetiver grass ecotypes[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 1330-1338. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | PEI Huimin, WU Mingming, ZHAI Rongrong, YE Jing, JIN Yue, ZHU Yi, HOU Jianjun, ZHU Guofu, YE Shenghai. Research progress on gene function and breeding of low-cadmium rice cultivars [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(9): 2012-2020. |
| [2] | DONG Aiqin, CHEN Yuanhua, YANG Tao, XU Changxu, CHENG Liqun, XIE Jie. Effect of application of lime with Chinese milk vetch on the cadmium uptake in rice [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(3): 600-612. |
| [3] | PENG Jiacheng, WU Yue, XU Jiehao, XIA Meiwen, QI Tianpeng, XU Haisheng. Cloning of paxillin gene from Macrobrachium nipponense and effect of cadmium stress on its expression [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(2): 247-253. |
| [4] | LI Qiuru, CAI Jingjing, LI Hua, YU Haiping, QIU Gaoyang, LIU Junli, GUO Bin. Comparison of adsorption and passivation effects of inorganic and organic materials on cadmium [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(12): 2774-2783. |
| [5] | LI Chunlei, XU Hongmei, LIU Jie, ZHANG Rujun, MA Xingyun, ZHANG Hua. Aluminum subcellular distribution and its combining characreristics with cell wall in tea leaves [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(3): 509-514. |
| [6] | LIN Xiaobing, ZHANG Hongyan, ZHANG Qiumei, ZHOU Lijun, XU Desheng, GUO Naijia, QIU Xiangfeng, HUANG Haiping. Screening of rice varieties with low cadmium accumulation based on multiple indicators [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(11): 2507-2515. |
| [7] | SONG Panpan, CHANG Huiqing, LI Lankun, WANG Qizhen. Effects of foliar spraying inhibitor on reducing cadmium content of wheat under calcareous soil with slight cadmium pollution [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(11): 2655-2663. |
| [8] | WANG Jianbing, WANG Jintao, YAN Kexin, GUO Xiaolan, WANG Dun, DAI Hongwen. Cadmium and lead accumulation characteristics of watercress under cadmium-lead combined pollution [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(11): 2664-2672. |
| [9] | FAN Liying, FAN Tingting, TONG Zongjun, LIANG Liyun, ZHAO Zhiyong, CHEN Hui, ZHOU Changyan, ZHAO Xiaoyan. Effects on accumulation of cadmium and antioxidant system of different Morchella spp. under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(10): 2321-2331. |
| [10] | JIANG Haoliang, HUANG Yun, LIANG Shaofang, XIE Mengchen, XU Tiancheng, SONG Zhiting, XIANG Wenwen, CHEN Qingchun, WAN Xiaorong, SUN Wei. Influences of cadmium stress on seedling growth of different sweet corn inbred lines and screening of associated molecular markers via simple sequence repeats [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(8): 1582-1590. |
| [11] | HUANG Feng, XING Jianping, FU Shaohuai, PAN Pan, WU Lin, LIU Beibei, CHEN Miao. Effects of different safe utilization technologies on cadmium reduction in rice-vegetable rotation system in northern Hainan, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(8): 1725-1733. |
| [12] | LOU Fei, FU Tianling, DAI Liangyu, ZHOU Kai, LIN Dasong, HE Tengbing. Effects of soil conditioners on Cd translocation and accumulation and yield of rice in central Guizhou Province, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(7): 1493-1501. |
| [13] | TAI Yueying, HE Tengbing, CHEN Xiaoran, ZHANG Wang, HUANG Xiaoyun, LIU Hongyan, GAO Zhenran. Effects of foliar spraying inhibitor on uptake and translocation of cadmium in rice under flooded paddy field [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(6): 1248-1257. |
| [14] | DU Hong, LI Yupeng, CHENG Wen, XIAO Rongying, HU Peng. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant roots and soil microenvironment under cadmium stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(5): 1039-1048. |
| [15] | WANG Can, FU Tianling, GONG Sitong, LOU Fei, ZHOU Kai, DAI Liangyu, LIU Jing, LIN Dasong, HE Tengbing. Effects of foliar control agents on cadmium enrichment characteristics of rice in karst area in central Guizhou [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(9): 1710-1719. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||