Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2525-2534.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240757
• Plant Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
Isolation, screening, and functional characteristics of endophytes from strawberry
XIE Yujia1( ), LI Zhenjiang1,2, SHA Feiyu1, ZHANG Lin3, TONG Yana4, QIAO Changsheng1,3, CAO Weifeng1,*(
), LI Zhenjiang1,2, SHA Feiyu1, ZHANG Lin3, TONG Yana4, QIAO Changsheng1,3, CAO Weifeng1,*( )
)
- 1. College of Biotechnology, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, Tianjin 300457, China
2. Sichuan Baichuan Jinkai Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., Chengdu 611130, China
3. Tianjin Huizhi Baichuan Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300456, China
4. The Research Institute of Forestry and Pomology, Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Tianjin 300384, China
-
Received:2024-08-23Online:2025-12-25Published:2026-01-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XIE Yujia, LI Zhenjiang, SHA Feiyu, ZHANG Lin, TONG Yana, QIAO Changsheng, CAO Weifeng. Isolation, screening, and functional characteristics of endophytes from strawberry[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2525-2534.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.zjnyxb.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20240757
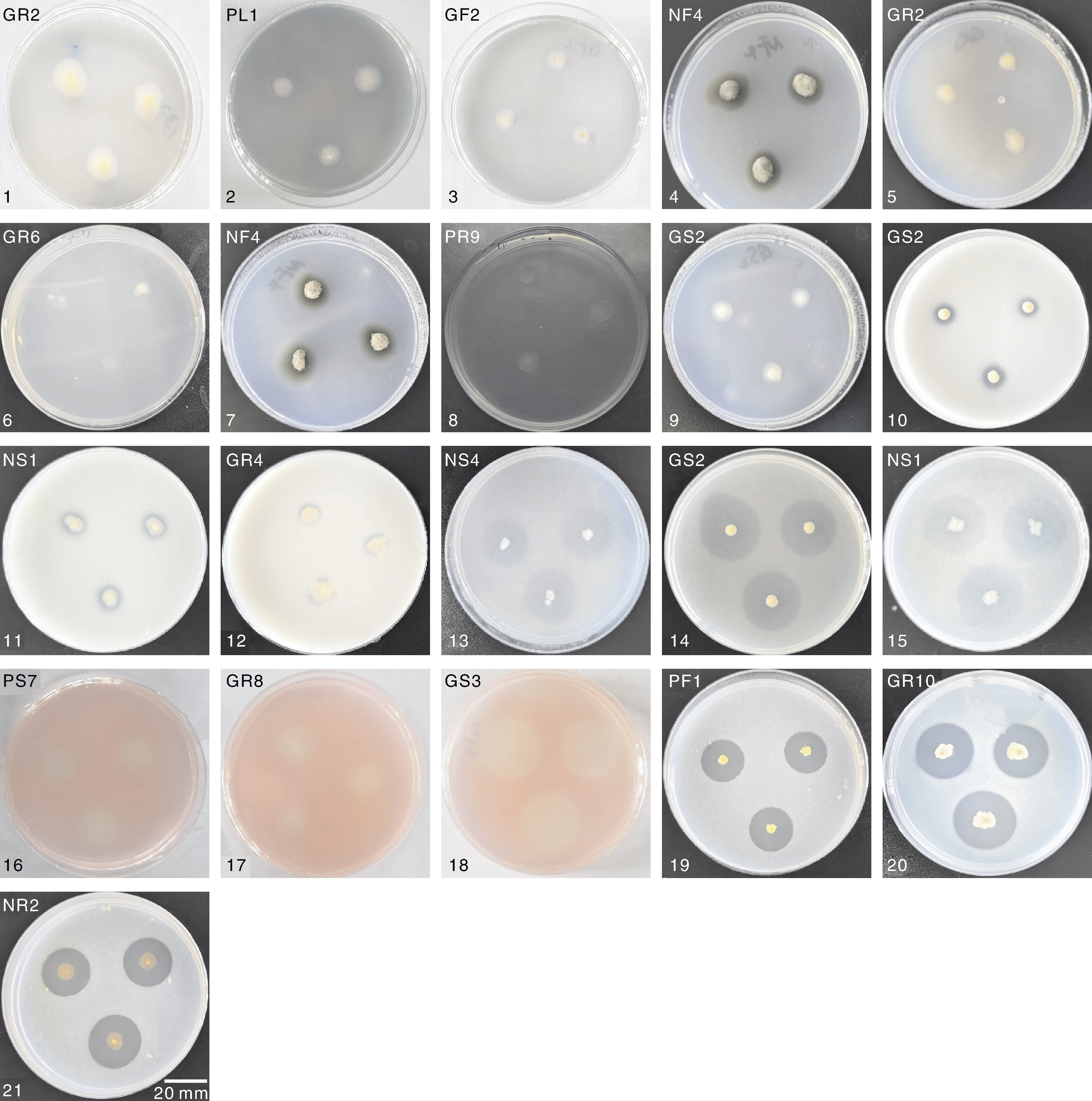
Fig.3 Photos showing the growth-promoting function of the isolated strains from strawberry 1-3 show the ability of test strains to produce iron carriers. 4-6 show the ability of test strains to fix nitrogen. 7-9 show the ability of strains to relases potassium. 10-12 show the ability of test strains to dissolve inorganic phosphorus. 13-15 show the ability of test strains to dissolve organic phosphorus. 16-18 show the ability of test strains to produce cellulase. 19-21 show the ability of test strains to produce protease.
| 编号 No. | YIAA/ (mg·L-1) | FN | RP | D/d | 编号 No. | YIAA/ (mg·L-1) | FN | RP | D/d | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC | IP | OP | CP | PP | IC | IP | OP | CP | PP | ||||||||
| NR1 | 9.79 | - | - | 1.77 | - | - | - | 1.13 | PS4 | - | + | + | 2.25 | - | - | - | - |
| NR2 | 19.31 | - | - | 1.38 | - | - | - | 3.14 | PS5 | - | + | + | - | - | - | 2.09 | 1.76 |
| NR3 | 5.31 | - | - | 2.08 | - | - | - | 2.85 | PS6 | 19.50 | - | + | - | - | 1.29 | - | - |
| NR4 | - | + | + | 2.33 | - | - | - | - | PS7 | - | + | + | 1.67 | - | 1.19 | 6.96 | - |
| NR5 | - | + | + | 1.41 | - | - | - | - | PL1 | - | - | - | 2.67 | - | - | 1.73 | 1.98 |
| NR6 | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | 1.88 | PL2 | - | + | + | 1.83 | - | - | - | 2.42 |
| NR7 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.11 | - | 3.14 | PL3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.26 | 1.50 |
| NR8 | - | + | + | 1.43 | - | 1.51 | 2.50 | 2.08 | PL4 | - | - | + | - | - | 1.16 | - | 1.54 |
| NR9 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.00 | - | 2.29 | PL5 | 17.50 | + | - | - | - | 1.47 | 1.43 | - |
| NR10 | - | + | + | 1.67 | - | - | 4.67 | 3.00 | PF1 | - | + | - | 2.10 | - | - | - | 4.38 |
| NR11 | - | + | + | - | - | 1.44 | 2.56 | 2.87 | PF2 | - | + | + | 1.64 | - | - | - | - |
| NS1 | 25.41 | - | + | 1.47 | 1.23 | 3.91 | - | - | GR1 | - | + | + | 2.21 | - | - | - | - |
| NS2 | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | 1.79 | GR2 | - | + | + | 4.09 | 1.32 | - | - | 1.14 |
| NS3 | 0.84 | + | + | 1.63 | - | - | 4.10 | 1.95 | GR3 | - | + | + | 1.91 | 1.18 | - | - | - |
| NS4 | 5.89 | + | + | 1.60 | 1.83 | 5.83 | - | 1.47 | GR4 | - | - | - | - | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.90 | - |
| NS5 | 8.36 | + | + | - | - | 1.20 | - | - | GR5 | 16.61 | + | + | 1.42 | - | - | - | - |
| NL1 | - | + | + | 1.25 | - | - | - | 2.56 | GR6 | 88.05 | + | + | 2.67 | - | - | - | - |
| NL2 | - | + | + | 1.56 | - | - | - | - | GR7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.50 | 2.83 |
| NF1 | 34.93 | + | + | 2.36 | - | - | - | - | GR8 | - | + | - | - | - | 1.46 | 5.79 | - |
| NF2 | 34.17 | + | - | 2.27 | - | - | - | - | GR9 | - | - | - | 1.89 | - | 1.54 | 1.67 | - |
| NF3 | - | + | + | 1.38 | - | - | 2.61 | - | GR10 | - | - | - | 1.60 | - | 1.48 | 1.62 | 3.52 |
| NF4 | - | + | + | 1.50 | - | - | 1.86 | 2.00 | GS1 | - | + | + | 1.20 | - | - | - | - |
| PR1 | - | - | + | 2.00 | - | - | - | 2.21 | GS2 | - | + | + | 1.75 | 1.93 | 5.07 | - | 1.17 |
| PR2 | - | + | + | 1.47 | - | - | 2.75 | - | GS3 | - | + | + | 1.35 | 1.32 | 3.63 | 5.07 | 1.39 |
| PR3 | - | - | + | 1.12 | - | - | 1.08 | - | GS4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.73 | 2.38 |
| PR4 | - | + | + | - | - | - | 1.06 | - | GS5 | 1.22 | - | - | - | - | 1.84 | 2.91 | - |
| PR5 | - | + | + | - | - | 1.88 | - | 2.36 | GS6 | - | + | + | 2.29 | - | - | 5.07 | - |
| PR6 | - | - | + | 1.75 | - | - | 2.59 | 2.66 | GS7 | - | - | + | 1.73 | - | - | - | - |
| PR7 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.19 | - | 1.91 | GS8 | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| PR8 | - | + | + | 1.46 | - | - | - | - | GL1 | - | + | + | 1.33 | 1.36 | 2.64 | 4.00 | - |
| PR9 | 16.08 | + | + | 1.78 | - | 1.27 | - | 2.48 | GL2 | - | + | + | 1.63 | - | 1.84 | - | 2.24 |
| PS1 | - | + | + | 1.38 | - | - | - | - | GF1 | - | + | - | 1.37 | - | - | - | - |
| PS2 | - | - | + | 1.67 | - | - | 2.75 | - | GF2 | - | + | + | 2.44 | - | - | - | - |
| PS3 | - | + | + | 1.60 | - | - | 1.80 | 1.79 | GF3 | - | - | - | 2.00 | - | - | 2.18 | - |
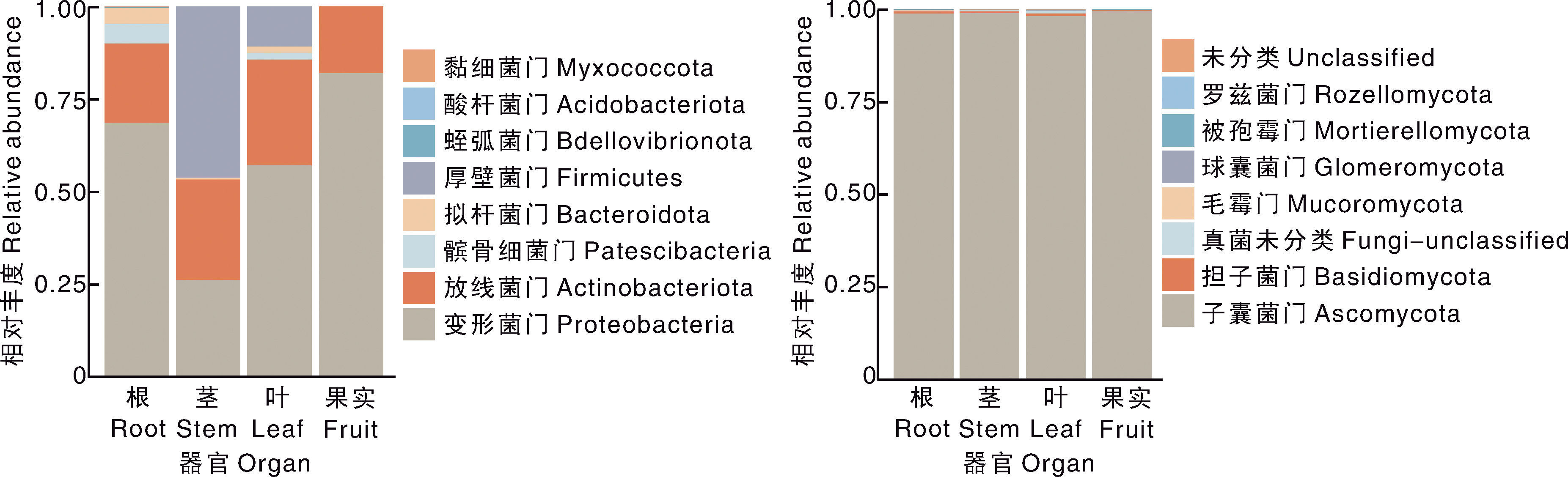
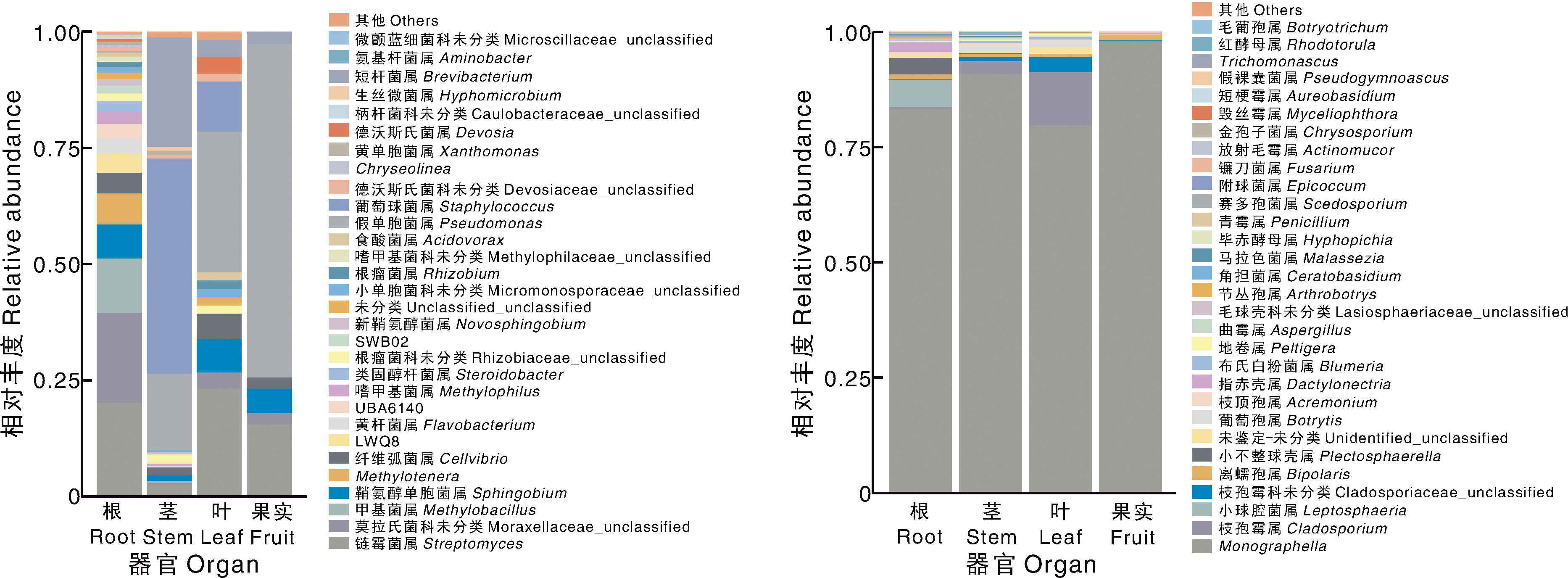
Table 1 Identification results of the growth-promoting ability of the isolated endophyte strains
| 编号 No. | YIAA/ (mg·L-1) | FN | RP | D/d | 编号 No. | YIAA/ (mg·L-1) | FN | RP | D/d | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC | IP | OP | CP | PP | IC | IP | OP | CP | PP | ||||||||
| NR1 | 9.79 | - | - | 1.77 | - | - | - | 1.13 | PS4 | - | + | + | 2.25 | - | - | - | - |
| NR2 | 19.31 | - | - | 1.38 | - | - | - | 3.14 | PS5 | - | + | + | - | - | - | 2.09 | 1.76 |
| NR3 | 5.31 | - | - | 2.08 | - | - | - | 2.85 | PS6 | 19.50 | - | + | - | - | 1.29 | - | - |
| NR4 | - | + | + | 2.33 | - | - | - | - | PS7 | - | + | + | 1.67 | - | 1.19 | 6.96 | - |
| NR5 | - | + | + | 1.41 | - | - | - | - | PL1 | - | - | - | 2.67 | - | - | 1.73 | 1.98 |
| NR6 | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | 1.88 | PL2 | - | + | + | 1.83 | - | - | - | 2.42 |
| NR7 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.11 | - | 3.14 | PL3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.26 | 1.50 |
| NR8 | - | + | + | 1.43 | - | 1.51 | 2.50 | 2.08 | PL4 | - | - | + | - | - | 1.16 | - | 1.54 |
| NR9 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.00 | - | 2.29 | PL5 | 17.50 | + | - | - | - | 1.47 | 1.43 | - |
| NR10 | - | + | + | 1.67 | - | - | 4.67 | 3.00 | PF1 | - | + | - | 2.10 | - | - | - | 4.38 |
| NR11 | - | + | + | - | - | 1.44 | 2.56 | 2.87 | PF2 | - | + | + | 1.64 | - | - | - | - |
| NS1 | 25.41 | - | + | 1.47 | 1.23 | 3.91 | - | - | GR1 | - | + | + | 2.21 | - | - | - | - |
| NS2 | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | 1.79 | GR2 | - | + | + | 4.09 | 1.32 | - | - | 1.14 |
| NS3 | 0.84 | + | + | 1.63 | - | - | 4.10 | 1.95 | GR3 | - | + | + | 1.91 | 1.18 | - | - | - |
| NS4 | 5.89 | + | + | 1.60 | 1.83 | 5.83 | - | 1.47 | GR4 | - | - | - | - | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.90 | - |
| NS5 | 8.36 | + | + | - | - | 1.20 | - | - | GR5 | 16.61 | + | + | 1.42 | - | - | - | - |
| NL1 | - | + | + | 1.25 | - | - | - | 2.56 | GR6 | 88.05 | + | + | 2.67 | - | - | - | - |
| NL2 | - | + | + | 1.56 | - | - | - | - | GR7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.50 | 2.83 |
| NF1 | 34.93 | + | + | 2.36 | - | - | - | - | GR8 | - | + | - | - | - | 1.46 | 5.79 | - |
| NF2 | 34.17 | + | - | 2.27 | - | - | - | - | GR9 | - | - | - | 1.89 | - | 1.54 | 1.67 | - |
| NF3 | - | + | + | 1.38 | - | - | 2.61 | - | GR10 | - | - | - | 1.60 | - | 1.48 | 1.62 | 3.52 |
| NF4 | - | + | + | 1.50 | - | - | 1.86 | 2.00 | GS1 | - | + | + | 1.20 | - | - | - | - |
| PR1 | - | - | + | 2.00 | - | - | - | 2.21 | GS2 | - | + | + | 1.75 | 1.93 | 5.07 | - | 1.17 |
| PR2 | - | + | + | 1.47 | - | - | 2.75 | - | GS3 | - | + | + | 1.35 | 1.32 | 3.63 | 5.07 | 1.39 |
| PR3 | - | - | + | 1.12 | - | - | 1.08 | - | GS4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.73 | 2.38 |
| PR4 | - | + | + | - | - | - | 1.06 | - | GS5 | 1.22 | - | - | - | - | 1.84 | 2.91 | - |
| PR5 | - | + | + | - | - | 1.88 | - | 2.36 | GS6 | - | + | + | 2.29 | - | - | 5.07 | - |
| PR6 | - | - | + | 1.75 | - | - | 2.59 | 2.66 | GS7 | - | - | + | 1.73 | - | - | - | - |
| PR7 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.19 | - | 1.91 | GS8 | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| PR8 | - | + | + | 1.46 | - | - | - | - | GL1 | - | + | + | 1.33 | 1.36 | 2.64 | 4.00 | - |
| PR9 | 16.08 | + | + | 1.78 | - | 1.27 | - | 2.48 | GL2 | - | + | + | 1.63 | - | 1.84 | - | 2.24 |
| PS1 | - | + | + | 1.38 | - | - | - | - | GF1 | - | + | - | 1.37 | - | - | - | - |
| PS2 | - | - | + | 1.67 | - | - | 2.75 | - | GF2 | - | + | + | 2.44 | - | - | - | - |
| PS3 | - | + | + | 1.60 | - | - | 1.80 | 1.79 | GF3 | - | - | - | 2.00 | - | - | 2.18 | - |
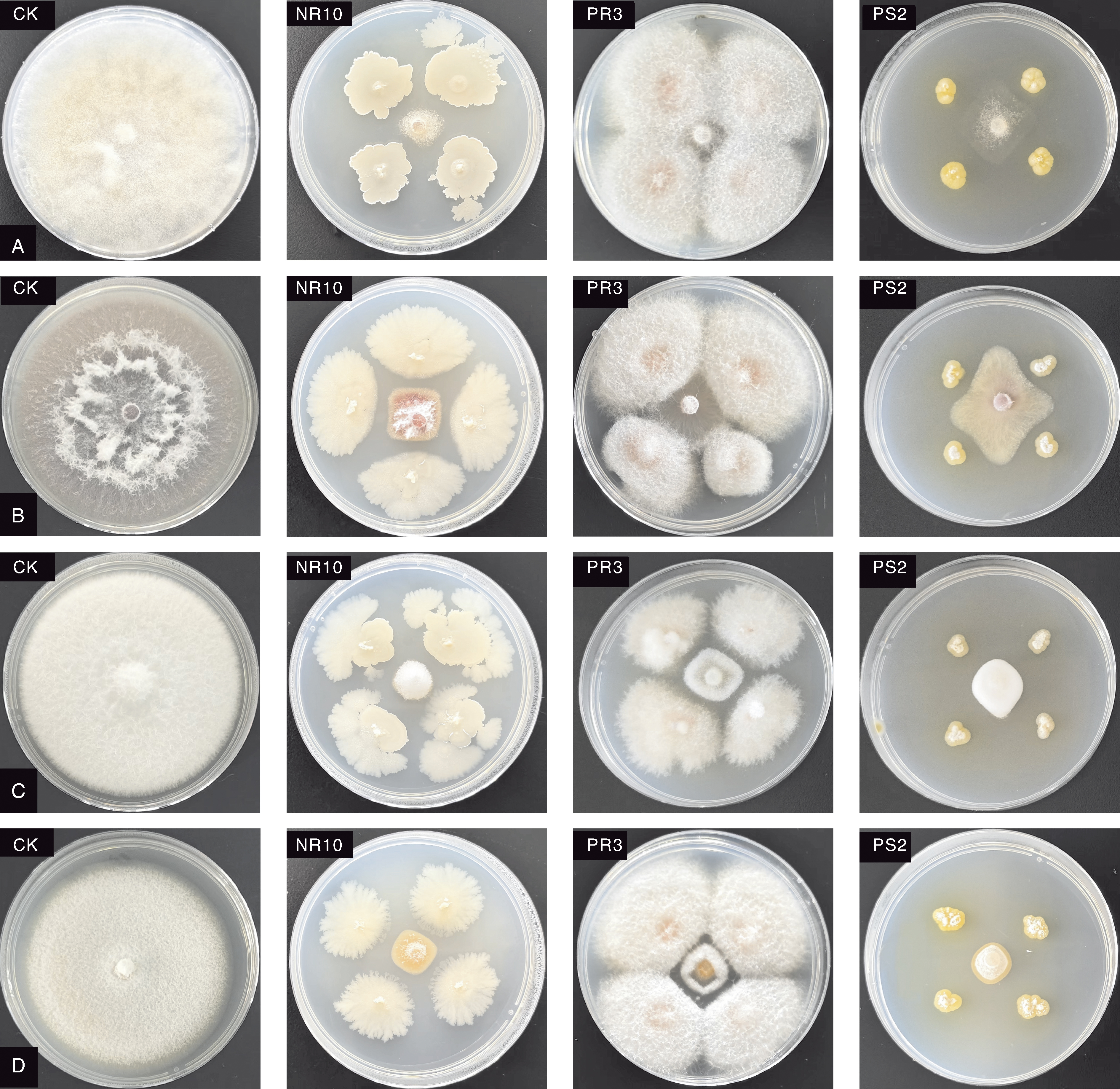
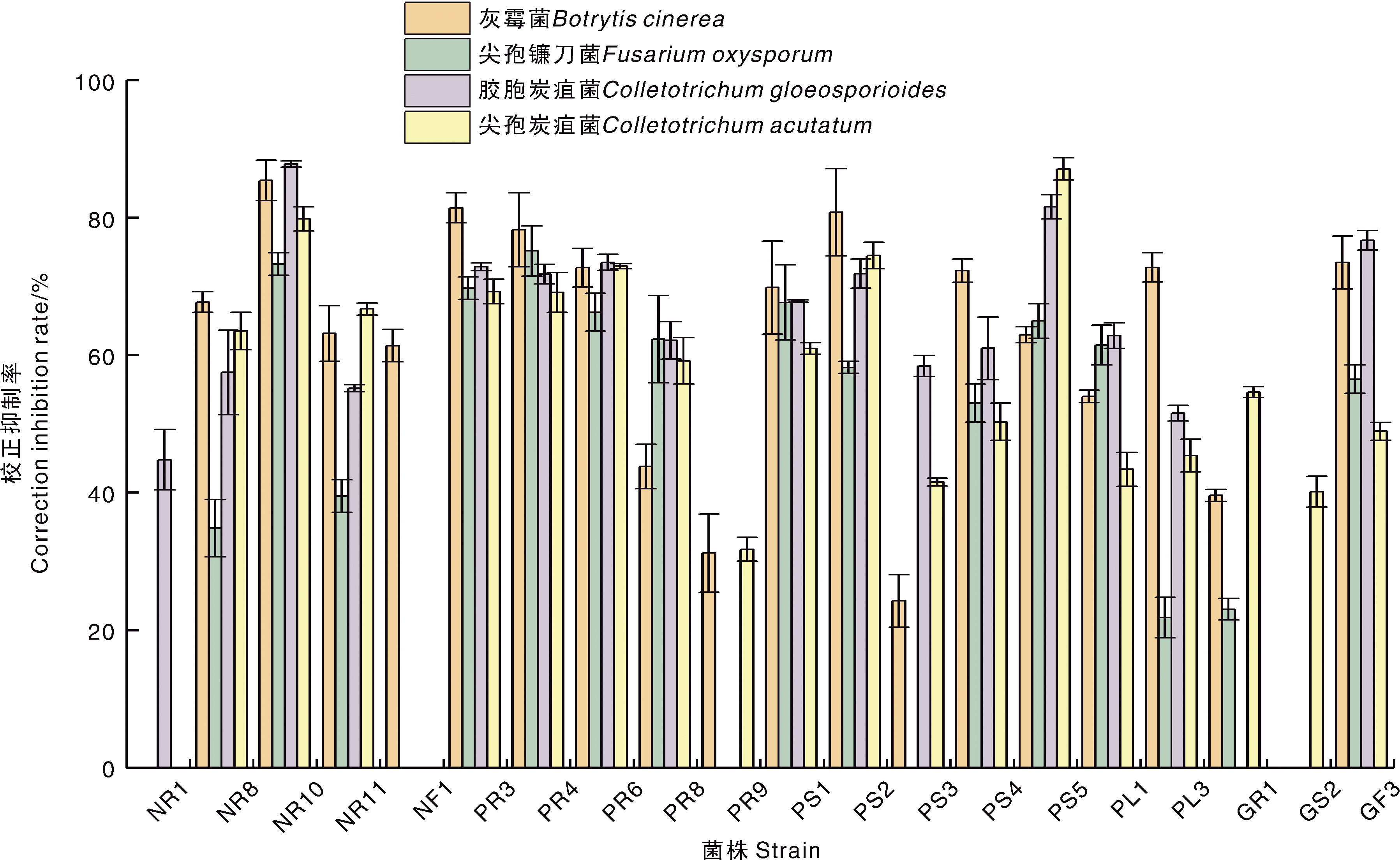
Fig.5 Five point confrontation effect of the isolated endophytes from strawberry against pathogens A, Botrytis cinerea; B, Fusarium oxysporum; C, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides; D,Colletotrichum acutatum.
| [1] | 刘畅, 王晓, 李宪松, 等. 我国草莓生产态势及国内外比较分析[J]. 中国果树, 2023(7): 136-140. |
| LIU C, WANG X, LI X S, et al. Strawberry production situation in China and comparative analysis at home and abroad[J]. China Fruits, 2023(7): 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | STURZ A V, CHRISTIE B R, NOWAK J. Bacterial endophytes: potential role in developing sustainable systems of crop production[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2000, 19(1): 1-30. |
| [3] | MARTINEZ-KLIMOVA E, RODRÍGUEZ-PEÑA K, SÁNCHEZ S. Endophytes as sources of antibiotics[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2017, 134: 1-17. |
| [4] | ZHANG Z Y, LI J, ZHANG Z Q, et al. Tomato endophytic bacteria composition and mechanism of suppressiveness of wilt disease (Fusarium oxysporum)[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 731764. |
| [5] | DE MOURA G G D, DE BARROS A V, MACHADO F, et al. The friend within: endophytic bacteria as a tool for sustainability in strawberry crops[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(12): 2341. |
| [6] | LIU J M, WANG S S, ZHENG X, et al. Antimicrobial activity against phytopathogens and inhibitory activity on solanine in potatoes of the endophytic bacteria isolated from potato tubers[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 570926. |
| [7] | GOODWIN P H. The endosphere microbiome of ginseng[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(3): 415. |
| [8] | 陈向东. 植物内生菌是有待深入开发的资源宝库[J]. 微生物学通报, 2012, 39(2): 282. |
| CHEN X D. Endophytic microorganisms are valuable resources worthy to be explored deeply[J]. Microbiology China, 2012, 39(2): 282. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 姜道宏. 植物内生真菌及其展望[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2015, 31(5): 742-749. |
| JIANG D H. Endophytic fungi and their prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2015, 31(5): 742-749. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 鲍敏, 康明浩. 植物内生菌研究发展现状[J]. 青海草业, 2011, 20(1): 21-25. |
| BAO M, KANG M H. The summarize on research of endogenous bacteria[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 2011, 20(1): 21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 康慧颖. 紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa)内生菌的分离纯化及鉴定[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2014. |
| KANG H Y. Isolation and identification of endophytic bacterial isolates from alfalfa[D]. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 肖蕾, 伍善东, 刘东华. 从油菜中分离到一株具多种生物学功能的优良内生细菌[J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(14): 5-8. |
| XIAO L, WU S D, LIU D H. An excellent endophytic bacterium with multiple biological functions was isolated from rape[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2021, 41(14): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 卢雨欣, 赵文娟, 白亚妮, 等. 耐盐碱番茄内生菌的筛选鉴定及功能研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(24): 50-58. |
| LU Y X, ZHAO W J, BAI Y N, et al. Saline-alkali tolerant endophytic bacteria in tomato: screening, identification and functional study[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(24): 50-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 张平, 李朝阳, 赵清泉, 等. 生防细菌对油茶炭疽病病原菌的抑制作用[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(10): 107-116. |
| ZHANG P, LI C Y, ZHAO Q Q, et al. Inhibition effects of biocontrol bacteria strains on the pathogen of Camellia oleifera anthracnose[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(10): 107-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 卜春亚, 孙晔, 张天蔚, 等. 一株草莓根腐尖孢镰刀菌拮抗内生细菌的分离鉴定及抑菌特性[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2014, 20(2): 300-304. |
| BU C Y, SUN Y, ZHANG T W, et al. Isolation and antagonistic character analysis of endophytic bacteria from the strawberry[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2014, 20(2): 300-304. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | GLICKMANN E, DESSAUX Y. A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(2): 793-796. |
| [17] | 雷平, 黄军, 黄彬彬, 等. 1株产铁载体辣椒内生细菌的分离鉴定及其促生长作用[J]. 激光生物学报, 2020, 29(4): 379-384. |
| LEI P, HUANG J, HUANG B B, et al. Isolation, identification and growth promoting effect of a siderophore-producing endophytic bacterium from capscium[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 379-384. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 张敏. 猕猴桃内生菌次生代谢产物抗菌活性及应用研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2019. |
| ZHANG M. Antimicrobial activity and application of secondary metabolites from Actinidia chinensis endophytic bacteria[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | ROSENBLUETH M, MARTÍNEZ-ROMERO E. Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19(8): 827-837. |
| [20] | 施宁雪, 张烨, 倪欢, 等. 健康草莓体内可分离培养微生物的多样性[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(7): 130-135. |
| SHI N X, ZHANG Y, NI H, et al. Diversity of isolatable and culturable endophytic microorganisms in healthy strawberry[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(7): 130-135. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 胡应平, 林冬梅, 胡弘正, 等. 一株旱稻联合固氮菌株的分离鉴定及促生作用[J]. 西南农业学报, 2024, 37(4): 780-788. |
| HU Y P, LIN D M, HU H Z, et al. Isolation, identification and growth-promoting characteristics of endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in upland rice roots[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 37(4): 780-788. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 任明霞, 李静, 艾加敏, 等. 白刺花根瘤中分离细菌的物种多样性及其促生效应[J]. 微生物学报, 2024, 64(8): 2940-2954. |
| REN M X, LI J, AI J M, et al. Species diversity and plant growth-promoting effects of bacteria isolated from the root nodules of Sophora davidii[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2024, 64(8): 2940-2954. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] | 李晴, 柴霜, 冯千禧, 等. 植物内生菌在农作物方面的应用探析[J]. 种子科技, 2021, 39(12): 8-9. |
| LI Q, CHAI S, FENG Q X, et al. Application of endophytic bacteria in crops[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2021, 39(12): 8-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | 赵杰, 田琼金, 聂蔓茹, 等. 红芸豆根腐病拮抗内生细菌的筛选和鉴定[J]. 山西农业科学, 2023, 51(10): 1226-1232. |
| ZHAO J, TIAN Q J, NIE M R, et al. Screening and identification of antagonistic endophytic bacteria against root rot of red kidney bean[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(10): 1226-1232. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 姜中宝, 黄宣雅, 唐振兴, 等. 具有抑菌和抗氧化活性紫金牛内生菌的筛选鉴定[J]. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 22(5): 497-504. |
| JIANG Z B, HUANG X Y, TANG Z X, et al. Screening and identification of endophytes with antibacterial and antioxidant activities from Ardisia japonica[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 22(5): 497-504. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 李方舟. 普洱茶树叶片内生细菌Bacillus velezensis FZ06的基因组测序及抗菌活性代谢产物研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. |
| LI F Z. Study on genome sequencing and antimicrobial metabolites produced by endophytic bacterium Bacillus velezensis FZ06 isolated from leaves of Camellia assamica[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | CHEN Wei, WANG Rongrong, JIANG Wenjing, GENG Weisong, CHEN Cen. Preparation of chitosan-chitosan oligosaccharide composite film and its application in strawberry preservation [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(8): 1785-1793. |
| [2] | LIU Pengfei, ZHANG Shuhan, HONG Kai, SHAO Yue, LOU Binggan. Isolation and identification of the pathogen causing tomato canker in Zhejiang Province of China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1293-1300. |
| [3] | MA Xian, YOU Yuwei, KANG Juan, WANG Guoqin, ZHENG Rui, SU Jianyu, YUE Sijun. Pathogen identification of post-harvest rotten Lycium barbarum and screening of natural fungicides [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(6): 1327-1335. |
| [4] | JI Mengting, CHEN Changjiang, ZHU Ling, ZHAN Menglin, XIAO Shun, CAI Xueqing. Identification of etiological bacterium causing leaf spot disease on Ficus carica [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(5): 1097-1106. |
| [5] | SHEN Lan, YANG Xiaofang, ZHANG Guofang. Identification and fungicide sensitivity of the pathogen causing root rot on strawberry [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 417-425. |
| [6] | GONG Xinxin, LIU Ruiling, HAN Yanchao, MENG Xianghong, GAO Haiyan, CHEN Hangjun. Isolation and identification of main postharvest pathogens of four edible fungi [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(2): 456-465. |
| [7] | DING Yingying, YANG Linping, YANG Qing, ZHANG Zichen, CAI Linying, YANG Kang, LI Chen, LIU Huiwen, BAO Guangbin, WANG Qing, WANG Guijun. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity of two novel goose astrovirus strains [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2458-2467. |
| [8] | BAO Mengnan, LI Jinbin, ZHANG Xian, YAN Jiahui. Identification of Meloidogyne spp. infecting tomato in Haidong City, Qinghai Province, China [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(12): 2545-2553. |
| [9] | QIU Yan, YE Ziran, TAN Xiangfeng, DAI Mengdi, GE Shihao, RUAN Yunjie, ZHAO Xianliang, KONG Dedong. Design and experiment of strawberry picking and grading robot based on YOLOv5-7.0 [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(11): 2364-2375. |
| [10] | LI Yani, CHEN Weiliang, MAO Bizeng. Pathogen identification of root rot of Curcuma wenyujin [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(5): 1086-1093. |
| [11] | YANG Lei, WANG Xiaofu, WEI Wei, CHEN Xiaoyun, PENG Cheng, XU Xiaoli, XU Junfeng. The antifungal responses of insects against an entomopathogenic fungi, Beauveria bassiana and their application potential in pest control [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(4): 825-836. |
| [12] | LUO Zhihan, LIU Pengfei, YU Jun, QI He, CHEN Xiaoguang, LOU Binggan. Identification and biological characteristics of pathogen causing branch dieback on Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(3): 579-588. |
| [13] | YE Tao, SUN Qinyu, CHEN Weili, SHAN Wenshu, LIAN Wenxu, NIU Tingting, ZHANG Jiaxia. Research progress of bZIP gene family in plant-pathogenic fungi [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(12): 2885-2894. |
| [14] | TANG Li, LI Linfeng, CUI Baofeng, LIU Zhenya, LI Yapeng, ZHANG Wangbin. Structural diversity and influencing factors of endophytes in the bark of Korla pear [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(11): 2546-2557. |
| [15] | MA Lijun, WU Nana, XU Bingliang, LIU Jia, ZHANG Shuwu. Determination of antifungal spectrum and evaluation of antifungal activity of Trichoderma viride B3 strain [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2024, 36(10): 2257-2263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||