浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 67-75.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250056
SlCHRC基因对高温环境下番茄花耐热性的影响
朱长松( ), 纳琦婷, 张梦卓, 曹慧, 刘诗颖, 张正科, 孟兰环(
), 纳琦婷, 张梦卓, 曹慧, 刘诗颖, 张正科, 孟兰环( )
)
- 海南大学 食品科学与工程学院,海南 海口 570228
-
收稿日期:2025-01-20出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:孟兰环,E-mail:huanhuanaini1012@126.com
朱长松,研究方向为采后果蔬贮藏分子生物学。E-mail:2539736122@qq.com -
通讯作者:孟兰环
Effect of SlCHRC gene on tomato floral thermotolerance under high-temperature environment
ZHU Changsong( ), NA Qiting, ZHANG Mengzhuo, CAO Hui, LIU Shiying, ZHANG Zhengke, MENG Lanhuan(
), NA Qiting, ZHANG Mengzhuo, CAO Hui, LIU Shiying, ZHANG Zhengke, MENG Lanhuan( )
)
- School of Food Science and Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
-
Received:2025-01-20Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:MENG Lanhuan
摘要:
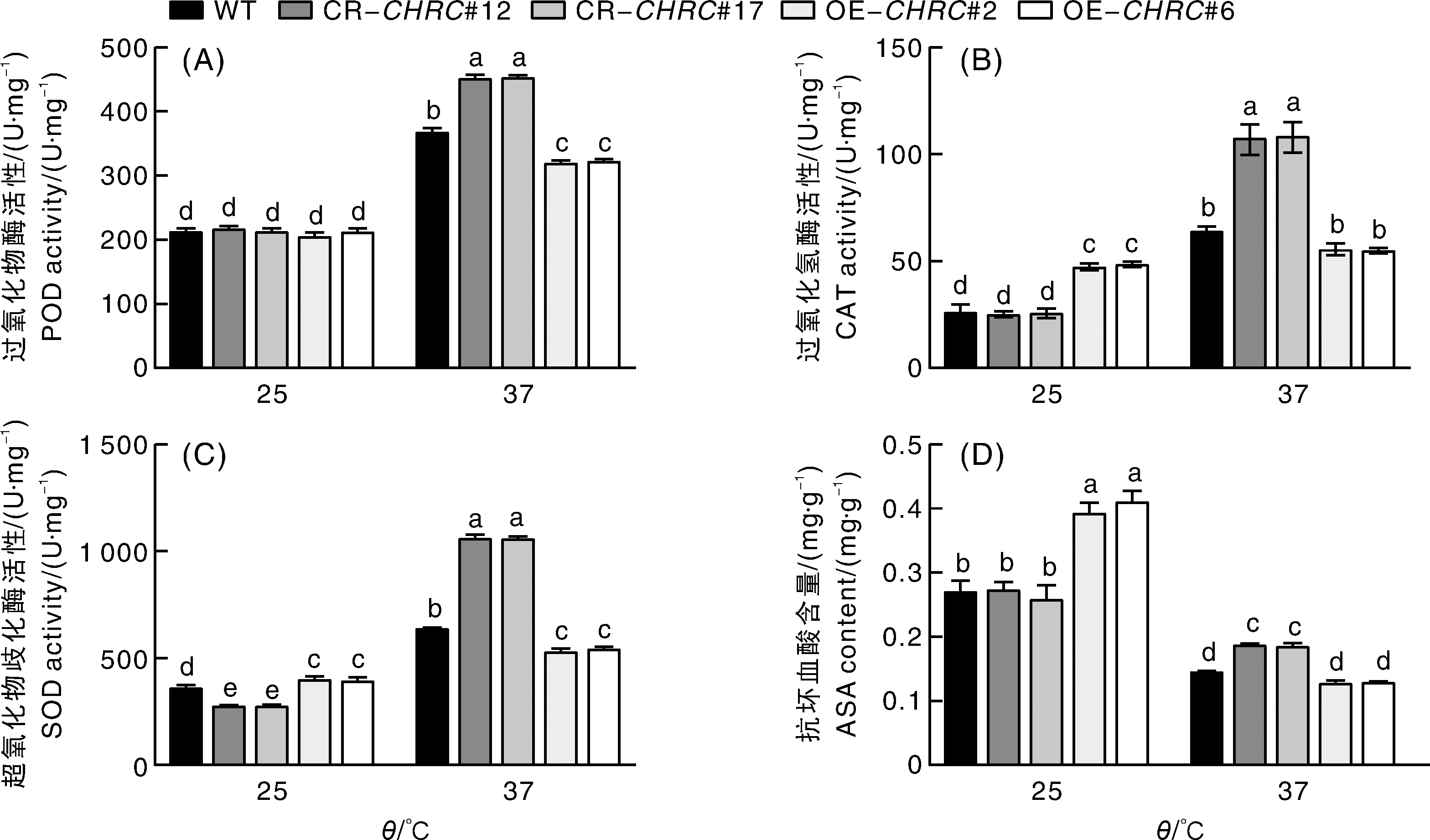
为探究番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)原纤维蛋白(fibrillin, FBN)家族成员番茄质体类胡萝卜素相关蛋白(chromoplast-associated carotenoid-binding protein, CHRC)基因SlCHRC在高温胁迫中的作用,本研究比较了野生型番茄Micro Tom、SlCHRC基因编辑株系和过表达株系在高温胁迫下花的电解质渗透率、丙二醛(malondialdehyde, MDA)含量、抗氧化酶活性、抗坏血酸含量和热响应相关基因的表达差异。 结果表明,与野生型相比,高温胁迫下SlCHRC基因编辑株系花的电解质渗透率和MDA含量显著降低;超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase, POD)和过氧化氢酶(catalase, CAT)活性,以及抗坏血酸含量显著升高;热响应相关基因SlsHSP、SlHsfA2、SlHSP20、SlHSP70和SlHSP90的转录水平也显著上调。SlCHRC过表达株系对高温的抗性显著低于野生型。以上结果表明,SlCHRC基因可能参与番茄高温胁迫响应的调控。
中图分类号:
引用本文
朱长松, 纳琦婷, 张梦卓, 曹慧, 刘诗颖, 张正科, 孟兰环. SlCHRC基因对高温环境下番茄花耐热性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 67-75.
ZHU Changsong, NA Qiting, ZHANG Mengzhuo, CAO Hui, LIU Shiying, ZHANG Zhengke, MENG Lanhuan. Effect of SlCHRC gene on tomato floral thermotolerance under high-temperature environment[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 67-75.
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene code | 正向引物序列(5'→3') Forward primer sequence(5'→3') | 反向引物序列(5'→3') Reverse primer sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| SlsHSP | Solyc11g020330 | CTGGAAAGAGACGGCGAAGGG | CTCTCCGCTCACTCTCAACACTC |
| SlHSP20 | Solyc09g015020 | GGTGGTCGGAGGAGCAATATCTTC | CAGGGGCAGAGTATGGAGTGTTG |
| SlHSP70 | Solyc04g009320 | CAAGCTGAAAGAGCTCAAGG | CTGTCCCAGCTGCATTACTT |
| SlHSP90 | Solyc05g010670 | TCAGCAATTCTTCCGATGCTCT | TCCTTGGTTCCTGACCTTGC |
| SlHsfA2 | Solyc08g062960 | TTCCAGTTTCATTCGGCAGCTTAAC | CTCTGACCAACATTCCTCCTCCTC |
| ACTIN | Solyc03g078400 | CAGCAGATGTGGATCTCAAA | CTGTGGACAATGGAAGGAC |
表1 qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 Primers used for quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene code | 正向引物序列(5'→3') Forward primer sequence(5'→3') | 反向引物序列(5'→3') Reverse primer sequence (5'→3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| SlsHSP | Solyc11g020330 | CTGGAAAGAGACGGCGAAGGG | CTCTCCGCTCACTCTCAACACTC |
| SlHSP20 | Solyc09g015020 | GGTGGTCGGAGGAGCAATATCTTC | CAGGGGCAGAGTATGGAGTGTTG |
| SlHSP70 | Solyc04g009320 | CAAGCTGAAAGAGCTCAAGG | CTGTCCCAGCTGCATTACTT |
| SlHSP90 | Solyc05g010670 | TCAGCAATTCTTCCGATGCTCT | TCCTTGGTTCCTGACCTTGC |
| SlHsfA2 | Solyc08g062960 | TTCCAGTTTCATTCGGCAGCTTAAC | CTCTGACCAACATTCCTCCTCCTC |
| ACTIN | Solyc03g078400 | CAGCAGATGTGGATCTCAAA | CTGTGGACAATGGAAGGAC |
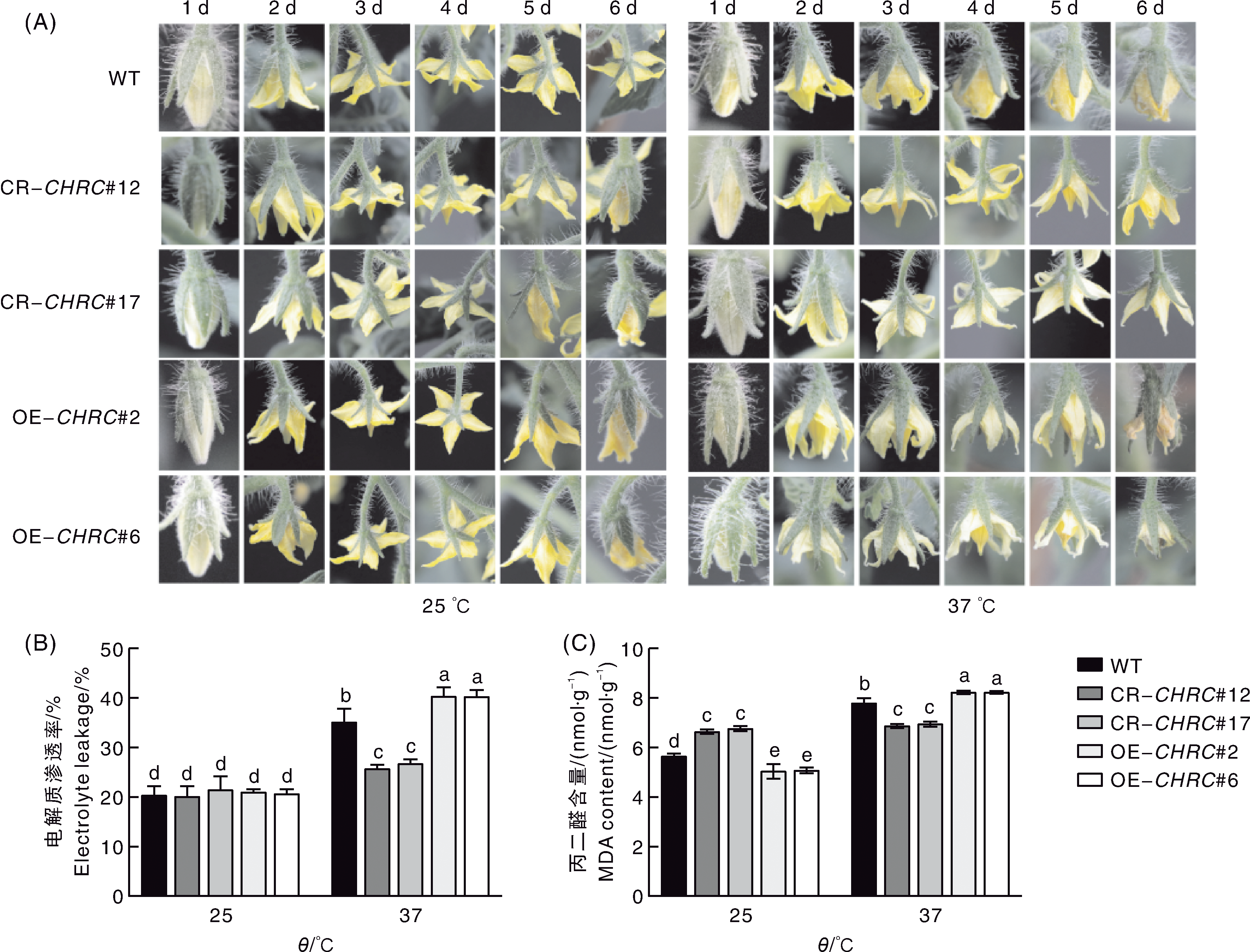
图1 高温胁迫下野生型、SlCHRC基因编辑植株和过表达植株花的表型、电解质渗透率和丙二醛含量 WT,野生型;CR-CHRC#12、CR-CHRC#17,SlCHRC基因编辑株系;OE-CHRC#2、OE-CHRC#6,SlCHRC基因过表达株系;柱上无相同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.1 Phenotypes, electrolyte leakage and malondialdehyde content of flowers in wild-type and SlCHRC gene-edited and SlCHRC overexpressing plants under high-temperature stress WT, Wild-type; CR-CHRC#12 and CR-CHRC#17, SlCHRC gene-edited lines; OE-CHRC#2 and OE-CHRC#6, SlCHRC gene overexpression lines; The bars marked without the same lowercase letter indicated significant differences at p<0.05. The same as below.
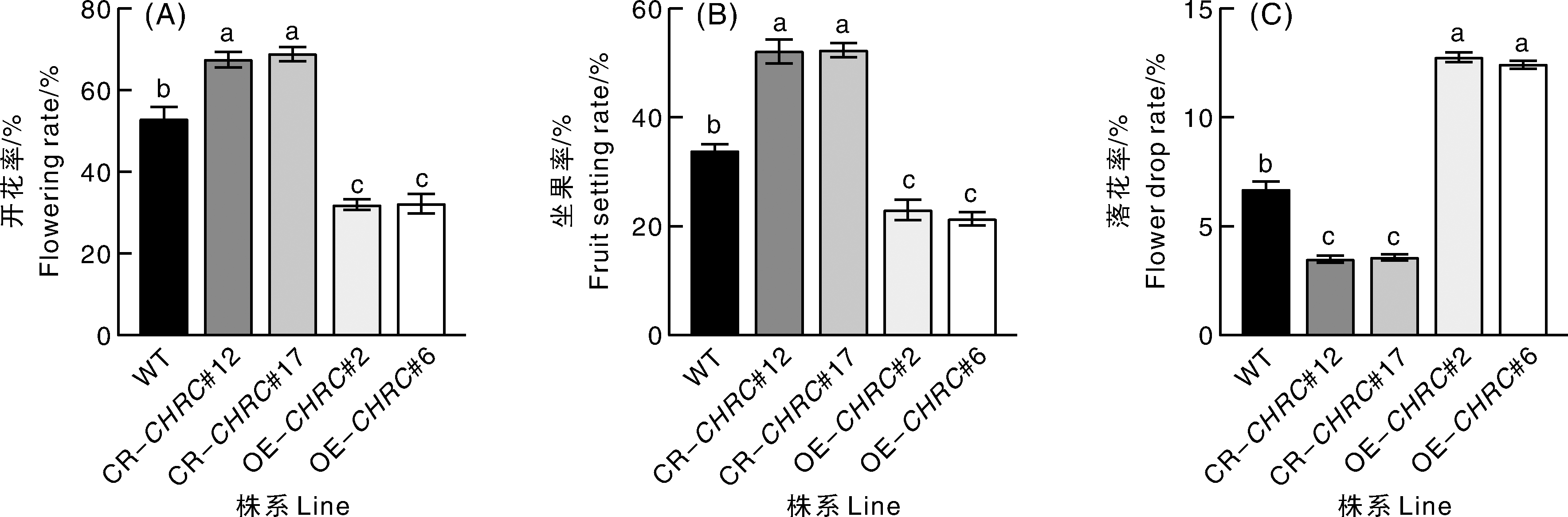
图2 高温处理后野生型、SlCHRC基因编辑株系和过表达株系的开花率、坐果率和落花率
Fig.2 Flowering rate, fruit setting rate and flower drop rate of wild-type, SlCHRC gene-edited lines and overexpression lines after high-temperature treatment
| [1] | 牛艳, 王晓静, 陈翔, 等. 中国番茄产业发展的现状问题和对策及宁夏番茄产业发展成效[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2022(12): 70-74. |
| NIU Y, WANG X J, CHEN X, et al. Current situation, problems and countermeasures of tomato industry development in China and achievements of tomato industry development in Ningxia[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022(12): 70-74. | |
| [2] | 孟兰环. 转录因子SlBEL11调控番茄果实叶绿素代谢和成熟的分子机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. |
| MENG L H. Research on the molecular mechanism of transcription factor SlBEL11 regulating chlorophyll metabolism and ripening of tomato fruits[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| [3] | 庄焜扬. 温度胁迫下番茄叶绿体与细胞核双定位WHIRLY1蛋白的功能分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2020. |
| ZHUANG K Y. Functional analysis of chloroplast-and nucleus-dual localized WHIRLY1 protein in tomato under temperature stress[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [4] | 苏应威, 刘海娇, 范云霞, 等. 高温对番茄幼苗叶片的损伤及外源氨基酸缓解高温下叶片伤害的效应评价[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2025, 30(03):120-130. |
| SU Y W, LIU H J, FAN Y X, et al. Evaluation of high temperature damage to tomato seedlingleaves and the effect of exogenous amino acid in alleviatingleaf damage under high temperature[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2025, 30(03):120-130. | |
| [5] | HOSHIKAWA K, PHAM D, EZURA H, et al. Genetic and molecular mechanisms conferring heat stress tolerance in tomato plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 786688. |
| [6] | 段玲. 番茄转录因子SlbZIP6在高温胁迫下的功能研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018. |
| DUAN L. Functional study of tomato transcription factor SlbZIP6 under high temperature stress[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2018. | |
| [7] | 李佳佳. 植物fibrillin家族蛋白的进化分析及其在水稻叶绿体中的功能鉴定[D]. 湖北: 华中农业大学, 2020. |
| LI J J. Evolution analysis and functional identifications of plant fibrillin family proteins in rice chloroplasts[D]. Hubei: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [8] | SUN H R, REN M, ZHANG J N. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of fibrillin (FBN) gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.)[J]. PeerJ, 2022, 10: e13414. |
| [9] | SINGH D K, MCNELLIS T W. Fibrillin protein function: the tip of the iceberg?[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2011, 16(8): 432-441. |
| [10] | REY P, GILLET B, RÖMER S, et al. Over-expression of a pepper plastid lipid-associated protein in tobacco leads to changes in plastid ultrastructure and plant development upon stress[J]. The Plant Journal, 2000, 21(5): 483-494. |
| [11] | LANGENKÄMPER G, MANAC’H N, BROIN M, et al. Accumulation of plastid lipid-associated proteins (fibrillin/CDSP34) upon oxidative stress, ageing and biotic stress in Solanaceae and in response to drought in other species[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2001, 52(360): 1545-1554. |
| [12] | EL-SAPPAH A H, LI J, YAN K, et al. Fibrillin gene family and its role in plant growth, development, and abiotic stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1453974. |
| [13] | KIM I, KIM E H, CHOI Y R, et al. Fibrillin2 in chloroplast plastoglobules participates in photoprotecti on and jasmonate-induced senescence[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 189(3): 1363-1397. |
| [14] | PANDEY A, SHARMAP, MISHRA D, et al. Genome-wide identification of the fibrillin gene family in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and its response to drought stress[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 234: 123757. |
| [15] | LIU J M, ZHANG Y, SHEN Q, et al. Identification of the FBN gene family in tomato and functional analysis of SlFBN11 in the electron transport under low night temperature[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 283(Pt 2): 137181. |
| [16] | VISHNEVETSKY M, OVADIS M, ITZHAKI H, et al. CHRC encoding a chromoplast-specific carotenoid-associated protein, is an early gibberellic acid-responsive gene[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(40): 24747-24750. |
| [17] | LIBAL-WEKSLER Y, VISHNEVETSKY M, OVADIS M, et al. Isolation and regulation of accumulation of a minor chromoplast-specific protein from cucumber corollas[J]. Plant Physiology, 1997, 113(1): 59-63. |
| [18] | SMIRRA I, HALEVY A H, VAINSTEIN A. Isolation and characterization of a chromoplast-specific carotenoid-associated protein from Cucumis sativus corollas[J]. Plant Physiology, 1993, 102(2): 491-496. |
| [19] | LEITNER-DAGAN Y, OVADIS M, SHKLARMAN E, et al. Expression and functional analyses of the plastid lipid-associated protein CHRC suggest its role in chromoplastogenesis and stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 142(1): 233-244. |
| [20] | AZARI R, TADMOR Y, MEIR A, et al. Light signaling genes and their manipulation towards modulation of phytonutrient content in tomato fruits[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2010, 28(1): 108-118. |
| [21] | KILAMBI H V, KUMAR R, SHARMA R, et al. Chromoplast-specific carotenoid-associated protein appears to be important for enhanced accumulation of carotenoids in hp1 tomato fruits[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 161(4): 2085-2101. |
| [22] | WANG Y, TIAN C, NA Q T, et al. The role of SlCHRC in carotenoid biosynthesis and plastid development in tomato fruit[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 281: 136354. |
| [23] | 朱丽云, 杨再强, 李军, 等. 花期低温寡照对番茄开花坐果特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 2017, 38(7): 456-465. |
| ZHU L Y, YANG Z Q, LI J, et al. Effect of low temperature and weak light at flowering stage on flower-fruit characteristics of tomato[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2017, 38(7): 456-465. | |
| [24] | 徐新娟, 李勇超. 2种植物相对电导率测定方法比较[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(7): 311-312. |
| XU X J, LI Y C. Comparison of two methods for determining the relative electrical conductivity of plants[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(7): 311-312. | |
| [25] | 张清航, 张永涛. 植物体内丙二醛(MDA)含量对干旱的响应[J]. 林业勘查设计, 2019, 48(1): 110-112. |
| ZHANG Q H, ZHANG Y T. Study on response to drought stress of MDA content in plants[J]. Forest Investigation Design, 2019, 48(1): 110-112. | |
| [26] | 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 211-217. |
| [27] | 刘冰珠, 张锋, 雷蕾, 等. 根区温度胁迫对番茄幼苗根系生长及蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2023(1): 68-77. |
| LIU B Z, ZHANG F, LEI L, et al. Effects of root-zone temperature stress on tomato seedling root system growth and sucrose metabolism[J]. China Vegetables, 2023(1): 68-77. | |
| [28] | 杜晨曦. 油菜素内酯受体SlBRI1磷酸化位点Ser-1040对番茄耐热性的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. |
| DU C X. Effects of the phosphorylation site ser-1040 of the brassinosteroid receptor SlBRI1 on the heat tolerance of tomatoes[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2020. | |
| [29] | 黄艳慧, 李亚灵, 温祥珍. 高温下不同空气湿度对温室番茄花粉活力和坐果率的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(11): 105-110. |
| HUANG Y H, LI Y L, WEN X Z. The effect of relative humidity on pollen vigor and fruit setting rate of greenhouse tomato under high temperature condition[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2011, 20(11): 105-110. | |
| [30] | ZAFAR M M, CHATTHA W S, KHAN A I, et al. Drought and heat stress on cotton genotypes suggested agro-physiological and biochemical features for climate resilience[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1265700. |
| [31] | AL-ZAHRANI H S, ALHARBY H F, FAHAD S. Antioxidative defense system, hormones, and metabolite accumulation in different plant parts of two contrasting rice cultivars as influenced by plant growth regulators under heat stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 911846. |
| [32] | 郭明欣, 刘佳佳, 侯琳琳, 等. 植物体内活性氧的产生及清除机制研究进展[J]. 科技视界, 2021(8): 104-106. |
| GUO M X, LIU J J, HOU L L, et al. Research progress on the generation and scavenging mechanism of reactive oxygen species in plants[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2021(8): 104-106. | |
| [33] | 张宇, 李亚灵. 自然高温对番茄内源激素及生殖生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2011(20): 27-29. |
| ZHANG Y, LI Y L. Effect of high temperature on the tomato growth[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2011(20): 27-29. | |
| [34] | 王冠玉, 贾平平, 靳娟, 等. 高温胁迫对枣花器官生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1485-1491. |
| WANG G Y, JIA P P, JIN J, et al. Effects of high temperature stress on physiological characteristics on jujube flower organs[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1485-1491. | |
| [35] | MUBAROK S, NURAINI A, HAMDANI J S, et al. Antioxidative response of parthenocarpic tomato, iaa9-3 and iaa9-5, under heat stress condition[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 207: 108333. |
| [36] | 伍国强, 张佳乐, 魏明. 热激转录因子HSF调控植物非生物胁迫响应的作用机制[J]. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(8): 123-136. |
| WU G Q, ZHANG J L, WEI M. The mechanisms of heat shock transcription factors(HSF)regulating plant response to abiotic stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(8): 123-136. | |
| [37] | FRAGKOSTEFANAKIS S, MESIHOVIC A, SIMM S, et al. HsfA2 controls the activity of developmentally and stress-regulated heat stress protection mechanisms in tomato male reproductive tissues[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(4): 2461-2477. |
| [38] | AHMAD M Z, SHAH Z, ULLAH A, et al. Genome wide and evolutionary analysis of heat shock protein 70 proteins in tomato and their role in response to heat and drought stress[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2022, 49(12): 11229-11241. |
| [39] | XU T, ZHOU H, FENG J, et al. Involvement of HSP70 in BAG9-mediated thermotolerance in Solanum lycopersicum[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2024, 207: 108353. |
| [40] | 刘云飞, 万红建, 杨悦俭, 等. 番茄热激蛋白90的全基因组鉴定及分析[J]. 遗传, 2014, 36(10): 1043-1052. |
| LIU Y F, WAN H J, YANG Y J, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of heat shock protein 90 in tomato[J]. Hereditas, 2014, 36(10): 1043-1052. | |
| [41] | YAO F W, SONG C H, WANG H T, et al. Genome-wide characterization of the HSP20 gene family identifies potential members involved in temperature stress response in apple[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 11: 609184. |
| [1] | 潘月云, 黄雨青, 丁正权, 施扬, 黄海祥, 李白. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制糯稻新种质[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 17-23. |
| [2] | 刘俊丽, 江建锋, 董祥伟, 杨海峻, 包晓琪, 付晨曦, 郭彬, 童文彬. 异形根孢囊霉对镉胁迫下番茄生长和基因表达的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 54-66. |
| [3] | 原增艳, 任欣欣, 宋小锋, 朱畇昊. 壳寡糖-纳米银的抗菌活性及其对红花种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 76-84. |
| [4] | 曹永庆, 姚小华, 王开良, 任华东. 普通油茶主要性状的年际稳定性[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1624-1633. |
| [5] | 王小慧, 贾赛男, 冯佳宇, 尹馨悦, 刘子萱, 刘雯洁, 赵帅滢, 王姝婧, 唐跃辉. 麻风树JcMYB27基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1658-1665. |
| [6] | 蒋明, 张胜, 陈孝赏, 张慧娟. 西兰花灰霉病响应基因BoWRKY15的克隆与功能鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1723-1732. |
| [7] | 缪百灵, 陈娟娟, 李亮杰, 楚宗丽, 董向向. 浙江红花油茶CchABCG5基因的功能[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(7): 1407-1416. |
| [8] | 周丹宁, 许姣, 白静, 刘湘楠, 朱畇昊. 内生真菌GG22蛋白质改善胁迫条件下红花幼苗的生长[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1193-1202. |
| [9] | 项缨, 丛建民, 潘丹红, 陶永刚. 春大棚有机种植不同品种番茄的生育进程分析和综合评价研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1252-1261. |
| [10] | 刘朋飞, 张舒涵, 洪凯, 邵越, 楼兵干. 浙江省番茄溃疡病病原菌分离与鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1293-1300. |
| [11] | 季梦婷, 陈长江, 朱玲, 詹梦琳, 肖顺, 蔡学清. 无花果细菌性叶斑病病原鉴定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(5): 1097-1106. |
| [12] | 狄延翠, 嵇泽琳, 王媛媛, 娄世浩, 张涛, 国志信, 申顺善, 朴凤植, 杜南山, 董晓星, 董韩. 番茄SlMYB52基因鉴定、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 808-819. |
| [13] | 周轶, 廖仪菲, 倪隽蓓, 钱敏杰, 周开兵, 滕元文. 疏花处理对台农一号杧果生理落果与果实成熟的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 831-838. |
| [14] | 秦宇坤, 陈俊英, 王玉萍, 张丽娟. 减氮增碳对长江流域棉花生产和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 869-879. |
| [15] | 张欢欢, 范挺秀, 高双成, 范丙友, 史国安. 2个牡丹切花品种核型、花药形态与花粉特性的比较[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(2): 329-337. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||