浙江农业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 126-135.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250027
沼液施用协同化肥减量在茭白生产和土壤改良上的效果
巴仕浩1,2( ), 童文彬3,*(
), 童文彬3,*( ), 杨海峻3, 江建锋3, 李子川1, 吴春艳2, 唐旭2, 柴彦君1, 李艳2,*(
), 杨海峻3, 江建锋3, 李子川1, 吴春艳2, 唐旭2, 柴彦君1, 李艳2,*( )
)
- 1.浙江科技大学 环境与资源学院,浙江省废弃生物质循环利用与生态处理技术重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310023
2.浙江省农业科学院 环境资源与土壤肥料研究所,浙江 杭州 310021
3.衢江区农业农村局,浙江 衢州 324022
-
收稿日期:2025-01-06出版日期:2026-01-25发布日期:2026-02-11 -
作者简介:李艳,E-mail: liyann0410@163.com
童文彬,E-mail: zjqztwb@163.com;
巴仕浩,研究方向为土壤改良和培肥。E-mail:bshqaq@163.com -
通讯作者:童文彬,李艳 -
基金资助:浙江省自然科学基金(LY23D010002)
Effect of biogas slurry application with chemical fertilizer reduction on water bamboo production and soil improvement
BA Shihao1,2( ), TONG Wenbin3,*(
), TONG Wenbin3,*( ), YANG Haijun3, JIANG Jianfeng3, LI Zichuan1, WU Chunyan2, TANG Xu2, CHAI Yanjun1, LI Yan2,*(
), YANG Haijun3, JIANG Jianfeng3, LI Zichuan1, WU Chunyan2, TANG Xu2, CHAI Yanjun1, LI Yan2,*( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Recycling and Ecotreatment of Waste Biomass of Zhejiang Province, School of Environment and Natural Resources, Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
2. Institute of Environment, Resource, Soil and Fertilizer, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hangzhou 310021, China
3. Qujiang District Agriculture and Rural Affairs Bureau, Quzhou 324022, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2025-01-06Online:2026-01-25Published:2026-02-11 -
Contact:TONG Wenbin,LI Yan
摘要:
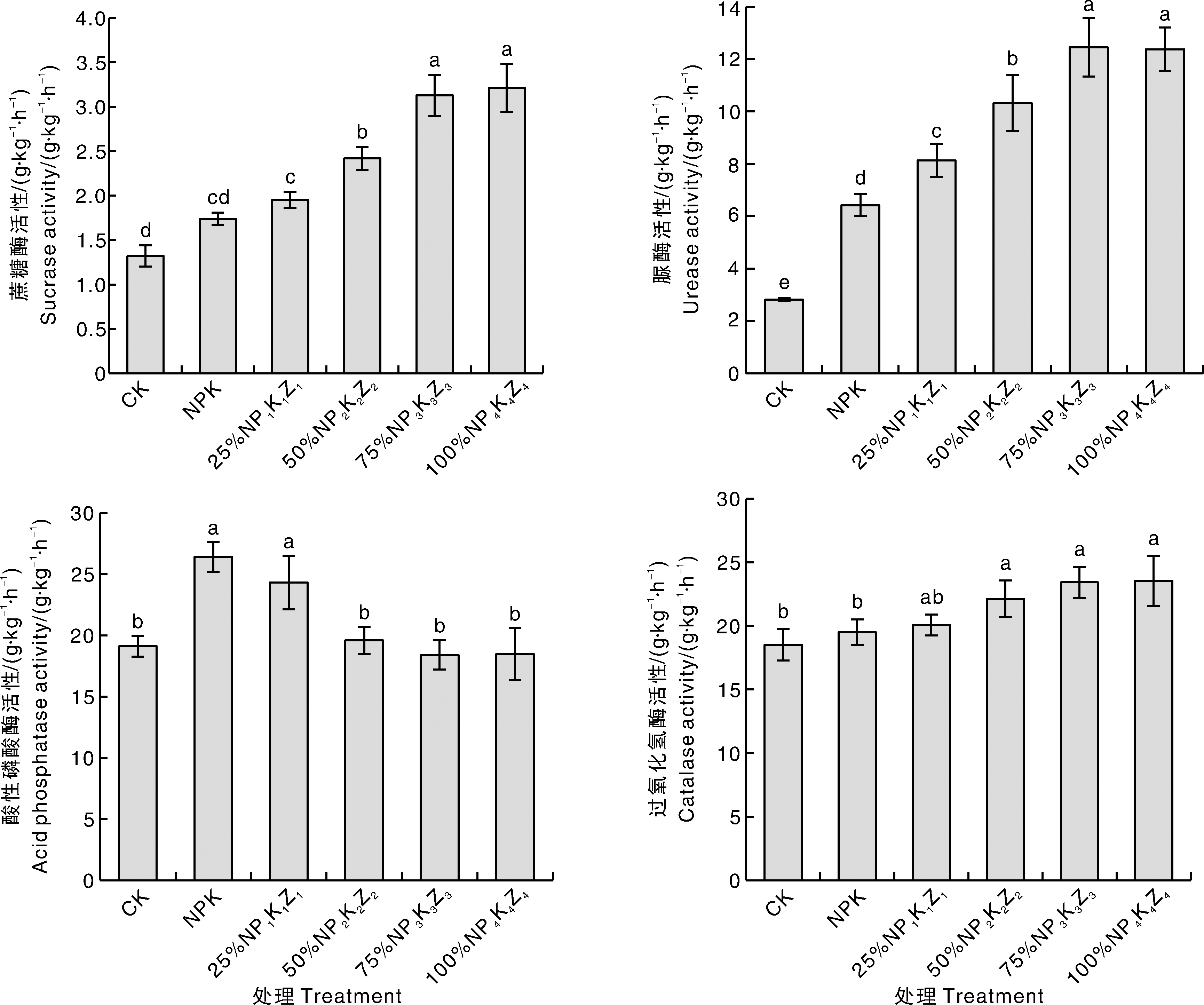
针对化肥施用过量导致农田养分流失和土壤退化等问题,探究沼液施用协同化肥减量技术在茭白田中的应用效果。试验共设置6个处理[CK,不施用任何肥料的空白对照;NPK,常规施肥(对照);25%NP1K1Z1、50%NP2K2Z2、75%NP3K3Z3、100%NP4K4Z4,沼液原液分别替代25%、50%、75%、100%的等当量氮肥],考察不同处理对茭白产量、品质,及土壤基本理化性质、土壤微生物量和土壤酶活性的影响。 结果表明: 与NPK相比,不同沼液替代处理下的茭白产量差异不显著。与NPK处理相比,75%NP3K3Z3、100%NP4K4Z4处理的茭白粗蛋白、维生素C含量显著(p<0.05)提升,硝酸盐含量显著降低,土壤有效磷、速效钾、微生物生物量碳和微生物量生物氮含量显著增加,土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶、过氧化氢酶活性显著增强。综合来看,75%NP3K3Z3在本试验条件下综合表现最好,在茭白不减产的前提下,不仅有效提升了茭白品质,还有效改良土壤,实现了茭白化肥减施增效和沼液资源化利用的目的。
中图分类号:
引用本文
巴仕浩, 童文彬, 杨海峻, 江建锋, 李子川, 吴春艳, 唐旭, 柴彦君, 李艳. 沼液施用协同化肥减量在茭白生产和土壤改良上的效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2026, 38(1): 126-135.
BA Shihao, TONG Wenbin, YANG Haijun, JIANG Jianfeng, LI Zichuan, WU Chunyan, TANG Xu, CHAI Yanjun, LI Yan. Effect of biogas slurry application with chemical fertilizer reduction on water bamboo production and soil improvement[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2026, 38(1): 126-135.
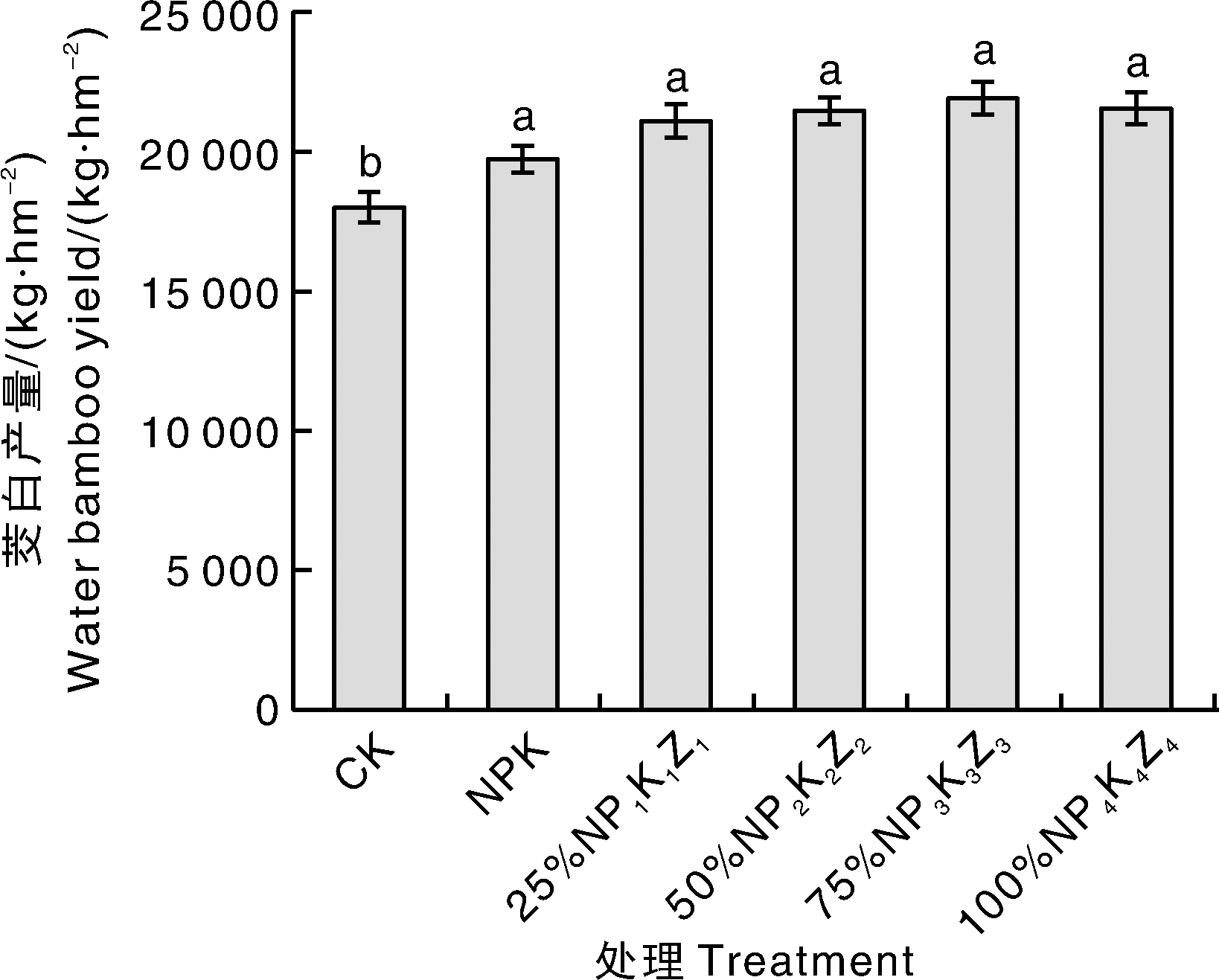
图1 不同处理下茭白的产量 柱上无相同字母的表示差异显著(p<0.05)。下同。
Fig.1 Yield of water bamboo under different treatments Bars marked without the same letters indicate significant difference at p<0.05 level. The same as below.
| 处理 Treatment | 茭长/cm Length of water bamboo shoot/cm | 茭宽/cm Width of water bamboo shoot/cm | 叶长/cm Length of leaf/cm | 叶宽/cm Width of leaf/cm | 壳茭重/g Gross weight of water bamboo shoot/g | 净茭重/g Net weight of water bamboo shoot/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.15±2.01 c | 4.25±1.11 a | 1.63±0.21 a | 2.76±0.15 c | 128.63±20.11 b | 96.02±9.89 b |
| NPK | 18.90±1.05 b | 4.44±0.56 a | 1.74±0.35 a | 3.65±0.99 b | 140.24±23.12 a | 105.48±15.23 ab |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 18.18±2.22 b | 4.46±0.86 a | 1.77±0.40 a | 3.66±0.81 b | 137.73±15.50 a | 112.66±8.96 a |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 20.09±3.15 a | 4.43±0.29 a | 1.79±0.11 a | 3.75±0.63 b | 141.65±29.91 a | 114.57±19.6 1a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 20.16±3.76 a | 4.43±0.25 a | 1.81±0.19 a | 3.69±0.89 b | 145.25±10.69 a | 115.12±20.11 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 20.50±2.56 a | 4.54±1.02 a | 1.87±0.26 a | 4.02±0.88 a | 148.63±12.22 a | 115.29±11.50 a |
表1 不同处理下茭白的经济性状
Table 1 Economic traits of water bamboo under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 茭长/cm Length of water bamboo shoot/cm | 茭宽/cm Width of water bamboo shoot/cm | 叶长/cm Length of leaf/cm | 叶宽/cm Width of leaf/cm | 壳茭重/g Gross weight of water bamboo shoot/g | 净茭重/g Net weight of water bamboo shoot/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.15±2.01 c | 4.25±1.11 a | 1.63±0.21 a | 2.76±0.15 c | 128.63±20.11 b | 96.02±9.89 b |
| NPK | 18.90±1.05 b | 4.44±0.56 a | 1.74±0.35 a | 3.65±0.99 b | 140.24±23.12 a | 105.48±15.23 ab |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 18.18±2.22 b | 4.46±0.86 a | 1.77±0.40 a | 3.66±0.81 b | 137.73±15.50 a | 112.66±8.96 a |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 20.09±3.15 a | 4.43±0.29 a | 1.79±0.11 a | 3.75±0.63 b | 141.65±29.91 a | 114.57±19.6 1a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 20.16±3.76 a | 4.43±0.25 a | 1.81±0.19 a | 3.69±0.89 b | 145.25±10.69 a | 115.12±20.11 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 20.50±2.56 a | 4.54±1.02 a | 1.87±0.26 a | 4.02±0.88 a | 148.63±12.22 a | 115.29±11.50 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 总糖含量/ (g·kg-1) Total sugar content/(g·kg-1) | 粗蛋白含量/ (g·kg-1) Crude protein content/(g·kg-1) | 膳食纤维含量/ (g·kg-1) Dietary fiber content/(g·kg-1) | 维生素C含量/ (mg·kg-1) Vitamin C content/(mg·kg-1) | 硝酸盐含量/ (mg·kg-1) Nitrate content/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 43.85±4.21 a | 10.15±0.42 c | 23.82±1.65 a | 179.16±7.40 c | 506.5±43.7 c |
| NPK | 45.60±2.69 a | 11.02±1.03 bc | 22.43±2.42 a | 209.78±13.42 b | 627.3±60.3 a |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 46.75±0.80 a | 11.67±0.91 bc | 23.28±2.46 a | 215.92±23.12 b | 578.9±48.9 b |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 47.11±5.14 a | 12.17±1.95 b | 23.05±2.20 a | 222.15±21.21 b | 564.3±55.2 b |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 47.17±3.47 a | 13.66±1.07 a | 22.51±1.39 a | 239.52±19.74 a | 512.9±1.29 c |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 48.90±2.41 a | 13.96±1.31 a | 22.43±2.41 a | 240.28±22.80 a | 524.3±26.7 c |
表2 不同处理下茭白的品质
Table 2 Quality of water bamboo under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 总糖含量/ (g·kg-1) Total sugar content/(g·kg-1) | 粗蛋白含量/ (g·kg-1) Crude protein content/(g·kg-1) | 膳食纤维含量/ (g·kg-1) Dietary fiber content/(g·kg-1) | 维生素C含量/ (mg·kg-1) Vitamin C content/(mg·kg-1) | 硝酸盐含量/ (mg·kg-1) Nitrate content/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 43.85±4.21 a | 10.15±0.42 c | 23.82±1.65 a | 179.16±7.40 c | 506.5±43.7 c |
| NPK | 45.60±2.69 a | 11.02±1.03 bc | 22.43±2.42 a | 209.78±13.42 b | 627.3±60.3 a |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 46.75±0.80 a | 11.67±0.91 bc | 23.28±2.46 a | 215.92±23.12 b | 578.9±48.9 b |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 47.11±5.14 a | 12.17±1.95 b | 23.05±2.20 a | 222.15±21.21 b | 564.3±55.2 b |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 47.17±3.47 a | 13.66±1.07 a | 22.51±1.39 a | 239.52±19.74 a | 512.9±1.29 c |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 48.90±2.41 a | 13.96±1.31 a | 22.43±2.41 a | 240.28±22.80 a | 524.3±26.7 c |
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量/ (g·kg-1) Organic matter content/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量/ (g·kg-1) Total nitrogen content/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷含量/ (g·kg-1) Total phosphorus content/ (g·kg-1) | 全钾含量/ (g·kg-1) Total potassium content/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮含量/ (mg·kg-1) Alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen content/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/ (mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/ (mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.17± 0.71 a | 18.24± 1.01 a | 1.02± 0.09 a | 0.71± 0.08 a | 13.6± 1.10 a | 120.9± 11.3 c | 31.29± 2.31 b | 78.72± 7.42 b |
| NPK | 5.20± 0.34 a | 19.96± 1.45 a | 1.18± 0.12 a | 0.74± 0.06 a | 14.5± 0.89 a | 149.5± 13.2 a | 32.08± 0.27 b | 73.87± 6.29 b |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 5.36± 0.42 a | 20.15± 2.14 a | 1.17± 0.04 a | 0.74± 0.03 a | 14.8± 0.72 a | 134.2± 10.5 b | 33.16± 1.19 b | 70.78± 4.41 b |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 5.38± 0.26 a | 20.36± 1.25 a | 1.20± 0.11 a | 0.76± 0.06 a | 15.0± 1.21 a | 142.4± 8.61 a | 33.10± 3.26 b | 87.24± 7.03 a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 5.37± 0.72 a | 21.02± 0.58 a | 1.25± 0.07 a | 0.83± 0.05 a | 15.8± 0.97 a | 151.2± 12.7 a | 43.34± 2.32 a | 90.55± 8.95 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 5.30± 0.52 a | 20.21± 1.42 a | 1.24± 0.13 a | 0.81± 0.07 a | 15.2± 0.47 a | 153.5± 14.2 a | 42.12± 3.37 a | 91.21± 7.95 a |
表3 不同处理下茭白田的表层(0~20 cm)土壤基本理化性质
Table 3 Basic physicochemical properties in surface (0-20 cm) soil of water bamboo fields under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | pH值 pH value | 有机质含量/ (g·kg-1) Organic matter content/ (g·kg-1) | 全氮含量/ (g·kg-1) Total nitrogen content/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷含量/ (g·kg-1) Total phosphorus content/ (g·kg-1) | 全钾含量/ (g·kg-1) Total potassium content/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮含量/ (mg·kg-1) Alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen content/ (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷含量/ (mg·kg-1) Available phosphorus content/ (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾含量/ (mg·kg-1) Available potassium content/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.17± 0.71 a | 18.24± 1.01 a | 1.02± 0.09 a | 0.71± 0.08 a | 13.6± 1.10 a | 120.9± 11.3 c | 31.29± 2.31 b | 78.72± 7.42 b |
| NPK | 5.20± 0.34 a | 19.96± 1.45 a | 1.18± 0.12 a | 0.74± 0.06 a | 14.5± 0.89 a | 149.5± 13.2 a | 32.08± 0.27 b | 73.87± 6.29 b |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 5.36± 0.42 a | 20.15± 2.14 a | 1.17± 0.04 a | 0.74± 0.03 a | 14.8± 0.72 a | 134.2± 10.5 b | 33.16± 1.19 b | 70.78± 4.41 b |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 5.38± 0.26 a | 20.36± 1.25 a | 1.20± 0.11 a | 0.76± 0.06 a | 15.0± 1.21 a | 142.4± 8.61 a | 33.10± 3.26 b | 87.24± 7.03 a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 5.37± 0.72 a | 21.02± 0.58 a | 1.25± 0.07 a | 0.83± 0.05 a | 15.8± 0.97 a | 151.2± 12.7 a | 43.34± 2.32 a | 90.55± 8.95 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 5.30± 0.52 a | 20.21± 1.42 a | 1.24± 0.13 a | 0.81± 0.07 a | 15.2± 0.47 a | 153.5± 14.2 a | 42.12± 3.37 a | 91.21± 7.95 a |
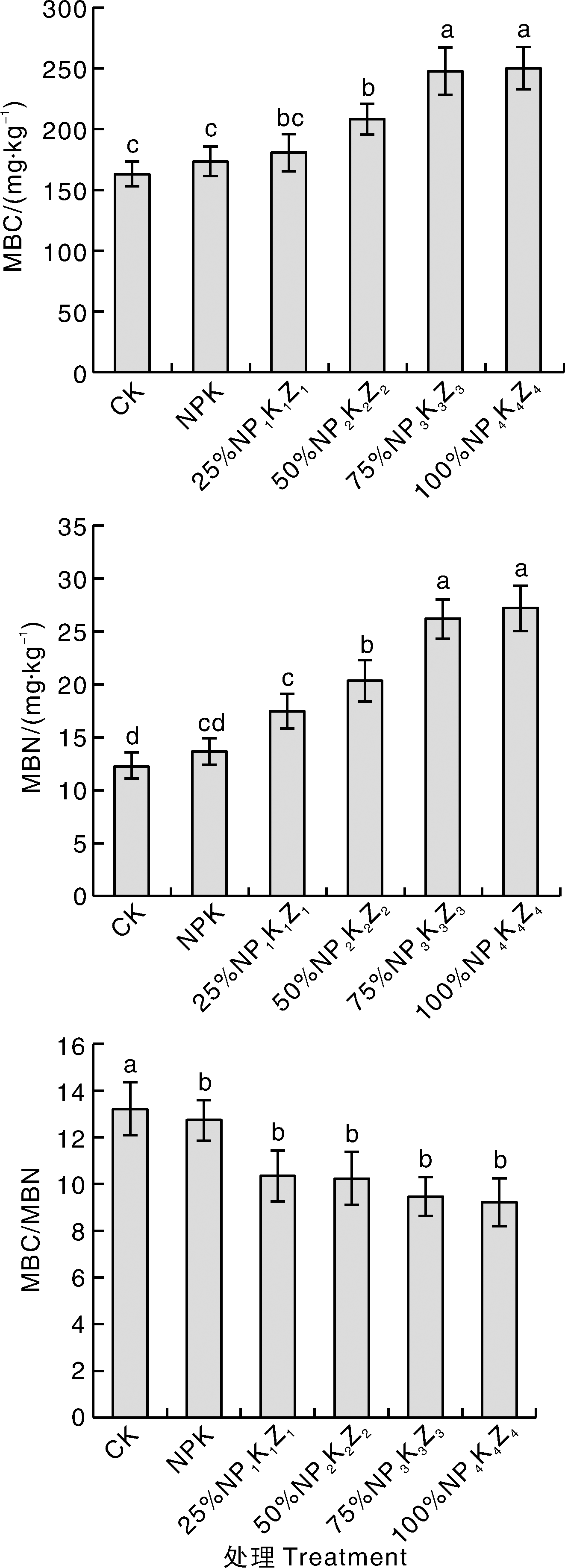
图2 不同处理下茭白田表层(0~20 cm)土壤的微生物生物量碳、氮含量 MBC,微生物生物量碳含量;MBN,微生物生物量氮含量;MBC/MBN,MBC与MBN的比值。
Fig.2 Microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content in surface (0-20 cm) soil of water bamboo field under different treatments MBC, Microbial biomass carbon content; MBN, Microbial biomass nitrogen content; MBC/MBN, Ratio of MBC to MBN.
| 处理 Treatment | Cu含量 Cu content | Cr含量 Cr content | Cd含量 Cd content | Ni含量 Ni content | Pb含量 Pb content | Zn含量 Zn content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 27.43±3.29 a | 16.71±1.84 a | 0.24±0.02 a | 26.02±1.41 a | 30.02±0.31 a | 68.24±6.99 a |
| NPK | 30.12±2.43 a | 19.01±1.21 a | 0.18±0.05 a | 25.14±2.75 a | 32.56±1.53 a | 68.80±9.21 a |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 26.47±2.26 a | 17.23±1.62 a | 0.23±0.04 a | 27.32±2.24 a | 32.39±1.42 a | 73.24±8.25 a |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 30.08±2.61 a | 20.12±1.86 a | 0.17±0.02 a | 24.98±2.23 a | 32.16±0.89 a | 73.16±6.43 a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 27.56±1.43 a | 18.48±1.31 a | 0.25±0.05 a | 26.56±1.76 a | 33.79±1.85 a | 73.42±5.68 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 30.74±3.01 a | 19.56±2.01 a | 0.19±0.08 a | 28.43±1.56 a | 32.58±1.49 a | 73.95±0.88 a |
表4 不同处理下茭白田表层(0~20 cm)土壤的重金属含量
Table 4 Heavy metals content in surface (0-20 cm) soil of water bamboo fields under different treatments mg·kg-1
| 处理 Treatment | Cu含量 Cu content | Cr含量 Cr content | Cd含量 Cd content | Ni含量 Ni content | Pb含量 Pb content | Zn含量 Zn content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 27.43±3.29 a | 16.71±1.84 a | 0.24±0.02 a | 26.02±1.41 a | 30.02±0.31 a | 68.24±6.99 a |
| NPK | 30.12±2.43 a | 19.01±1.21 a | 0.18±0.05 a | 25.14±2.75 a | 32.56±1.53 a | 68.80±9.21 a |
| 25%NP1K1Z1 | 26.47±2.26 a | 17.23±1.62 a | 0.23±0.04 a | 27.32±2.24 a | 32.39±1.42 a | 73.24±8.25 a |
| 50%NP2K2Z2 | 30.08±2.61 a | 20.12±1.86 a | 0.17±0.02 a | 24.98±2.23 a | 32.16±0.89 a | 73.16±6.43 a |
| 75%NP3K3Z3 | 27.56±1.43 a | 18.48±1.31 a | 0.25±0.05 a | 26.56±1.76 a | 33.79±1.85 a | 73.42±5.68 a |
| 100%NP4K4Z4 | 30.74±3.01 a | 19.56±2.01 a | 0.19±0.08 a | 28.43±1.56 a | 32.58±1.49 a | 73.95±0.88 a |
| [1] | 周佳燕. 基于SWOT分析的浙江茭白产业发展对策与建议[J]. 长江蔬菜, 2020(16): 34-37. |
| ZHOU J Y. Development countermeasures on Zizania aquatica industry of Zhejiang based on SWOT analysis[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2020(16): 34-37. | |
| [2] | 徐颖菲, 姚玉才, 章明奎. 全年淹水种植茭白对水田土壤性态的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(1): 15-21. |
| XU Y F, YAO Y C, ZHANG M K. Effects of Zizania latifolia plantation with the whole year water-logging on soil properties of paddy fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(1): 15-21. | |
| [3] | 石吕, 刘建, 魏亚凤, 等. 沼液在农业领域的资源化利用现状[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(35): 109-117. |
| SHI L, LIU J, WEI Y F, et al. Current status of resource utilization of biogas slurry in agriculture[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(35): 109-117. | |
| [4] | 王嘉鑫, 黄青, 赵小芳, 等. 沼液在水稻生产中的资源化利用及效益综述[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2019(9): 114-118. |
| WANG J X, HUANG Q, ZHAO X F, et al. Benefits and utilization of biogas slurry in rice production[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2019(9): 114-118. | |
| [5] | 张明慧, 高大文. 臭氧组合絮凝工艺处理牛粪沼液的研究[J]. 中国沼气, 2020, 38(1): 37-44. |
| ZHANG M H, GAO D W. Ozonation and flocculation combination treating biogas slurry of cow dung[J]. China Biogas, 2020, 38(1): 37-44. | |
| [6] | FERDOUS Z, ULLAH H, DATTA A, et al. Yield and profitability of tomato as influenced by integrated application of synthetic fertilizer and biogas slurry[J]. International Journal of Vegetable Science, 2018, 24(5): 445-455. |
| [7] | 刘银秀, 池永清, 董越勇, 等. 不同沼液施用年限土壤养分含量和微生物群落结构差异[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(3): 483-495. |
| LIU Y X, CHI Y Q, DONG Y Y, et al. Variation of nutrient content and microbial community in soils under different application years of biogas slurry[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(3): 483-495. | |
| [8] | 王德刚, 齐文, 王伟, 等. 沼液浇灌对双季茭白(秋茭)生长、产量及安全性的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2020, 61(4): 679-681. |
| WANG D G, QI W, WANG W, et al. Effects of biogas slurry application on growth, yield and safety of Zizania latifolia[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 61(4): 679-681. | |
| [9] | 叶巧丽, 姚光伟, 徐来源, 等. 不同用量沼液对茭白生长、产量及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 蔬菜, 2021(6): 35-38. |
| YE Q L, YAO G W, XU L Y, et al. Effects of different amount of biogas slurry on growth, yield of water bamboo and soil physicochemical properties[J]. Vegetables, 2021(6): 35-38. | |
| [10] | 陈艳. 沼液沼渣在番茄生产中的应用研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2013. |
| CHEN Y. Application research of biogas slurry and biogas residue in tomato production[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2013. | |
| [11] | 叶勇标, 杨梦飞, 杨新琴, 等. 沼液不同灌溉浓度对茭白生物学性状及田间水质的影响[J]. 长江蔬菜, 2017(18): 136-139. |
| YE Y B, YANG M F, YANG X Q, et al. Effect of different biogas slurry irrigation concentrations on biological traits and field water quality of Zizania latifolia[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2017(18): 136-139. | |
| [12] | TANG Y F, WANG L Y, CARSWELL A, et al. Fate and transfer of heavy metals following repeated biogas slurry application in a rice-wheat crop rotation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 270: 110938. |
| [13] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| [14] | FREY S D, KNORR M, PARRENT J L. Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004, 196: 159-171. |
| [15] | LIU Y L, WANG P, DING Y J, et al. Microbial activity promoted with organic carbon accumulation in macroaggregates of paddy soils under long-term rice cultivation[J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(24): 6565-6586. |
| [16] | 柴彦君, 张睿, 江建锋, 等. 沼液化肥配施对芦笋地土壤肥力及芦笋品质的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(5): 120-127. |
| CHAI Y J, ZHANG R, JIANG J F, et al. Effects of the combined biogas slurry with chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and Asparagus quality in field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(5): 120-127. | |
| [17] | 胡建林, 郭英, 董华林, 等. 沼液在水稻生产上的应用现状与展望[J]. 农业科技通讯, 2022(12): 197-199. |
| HU J L, GUO Y, DONG H L, et al. Application status and prospect of biogas slurry in rice production[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(12): 197-199. | |
| [18] | 刘庭付, 徐小燕, 王来亮, 等. 沼液部分替代化肥对茭白产量和生长发育的影响[J]. 长江蔬菜, 2020(6): 45-49. |
| LIU T F, XU X Y, WANG L L, et al. Effects of biogas slurry partly substituting for chemical fertilizers on yield and growth of Zizania latifolia[J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2020(6): 45-49. | |
| [19] | 黄旭. 沼液灌溉和秸秆还田对稻麦轮作生产的影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2020. |
| HUANG X. Effects of biogas slurry and straw returning on rice-wheat rotation production[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [20] | 张旭峰, 江郁菲, 王陆游, 等. 沼液与化肥配施对耕层土壤质量及水稻产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(1): 35-39. |
| ZHANG X F, JIANG Y F, WANG L Y, et al. Effects of combined application of biogas slurry and chemical fertilizer on soil quality and rice yield in tillage layer[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 66(1): 35-39. | |
| [21] | 韩晓飞, 李潇然, 王俊伟. 沼液替代化肥对露地萝卜产量、品质和土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(22): 34-39. |
| HAN X F, LI X R, WANG J W. Influences of biogas slurry instead of chemical fertilizer on yield and quality of radish in open field and soil physicochemical properties[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(22): 34-39. | |
| [22] | 罗伟. 沼液对马铃薯产量、品质及土壤环境质量的影响研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2020. |
| LUO W. Effect of biogas slurry on yield, quality of potato and environmental quality of soil[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [23] | 杜彩艳, 鲁海燕, 熊艳竹, 等. 连续两年沼液与化肥配施对桃生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. |
| DU C Y, LU H Y, XIONG Y Z, et al. Effects of combined application of biogas slurry and chemical fertilizer on peach growth and soil physical and chemical properties for two consecutive years[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(8): 165-175. | |
| [24] | 彭先进, 夏静, 石景涛, 等. 沼液施用对土壤质量的影响综述[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2023, 42(S1): 82-85. |
| PENG X J, XIA J, SHI J T, et al. Effects of biogas slurry application on soil: a review[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2023, 42(S1): 82-85. | |
| [25] | 杨诗贵, 洪宁, 李铸, 等. 沼液施用背景下稻田土壤养分的含量特征[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(2): 239-244. |
| YANG S G, HONG N, LI Z, et al. Characteristics of nutrient content in paddy soil under the background of biogas slurry application[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(2): 239-244. | |
| [26] | 郑学博, 樊剑波, 周静, 等. 沼液化肥配施对红壤旱地土壤养分和花生产量的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(3): 675-684. |
| ZHENG X B, FAN J B, ZHOU J, et al. Effects of combined application of biogas slurry and chemical fertilizer on soil nutrients and peanut yield in upland red soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(3): 675-684. | |
| [27] | 莫艳芳, 申云鑫, 贺彪, 等. 基于整合分析土壤微生物量碳、氮含量对有机肥施用的响应特征[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024(6): 89-101. |
| MO Y F, SHEN Y X, HE B, et al. The response characteristics of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen contents to organic fertilizer by Meta-analysis[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2024(6): 89-101. | |
| [28] | 杨铭. 免耕覆盖对小麦—花生轮作体系不同土层微生物量碳、氮含量及相关酶活性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(6): 216-222. |
| YANG M. Effects of no tillage and mulching on microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen contents and related enzyme activities in different soil layers of wheat-peanut rotation system[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(6): 216-222. | |
| [29] | 柴彦君, 黄利民, 董越勇, 等. 沼液施用量对毛竹林地土壤理化性质及碳储量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(8): 214-220. |
| CHAI Y J, HUANG L M, DONG Y Y, et al. Effects of biogas slurry application rates on soil physical and chemical properties and carbon storage of bamboo forest[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(8): 214-220. | |
| [30] | 张无敌, 尹芳, 徐锐, 等. 沼液对土壤生物学性质的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2009, 48(10): 2403-2407. |
| ZHANG W D, YIN F, XU R, et al. Effect of biogas liquid on biological properties of soil[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 48(10): 2403-2407. | |
| [31] | CHENG J B, CHEN Y C, HE T B, et al. Effects of biogas slurry irrigation DOC/N ratios on the fate of soil nitrogen and GHG emissions: a laboratory study[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 375: 114458. |
| [32] | 朱利霞, 陈居田, 徐思薇, 等. 生物炭施用下土壤微生物量碳氮的动态变化[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. |
| ZHU L X, CHEN J T, XU S W, et al. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen after biochar application[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 23(8): 193-200. | |
| [33] | 周伟, 徐莉, 俞元春, 等. 沼液施肥对杨树林地土壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 林业科技开发, 2015(1): 49-51. |
| ZHOU W, XU L, YU Y C, et al. Biogas slurry application influences on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen of poplar plantation[J]. China Forestry Science and Technology, 2015(1): 49-51. | |
| [34] | 王佩雯, 朱金峰, 任志广, 等. 不同土壤改良剂处理下连作植烟土壤化学性质及土壤酶活性的耦合分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2017, 19(4): 82-91. |
| WANG P W, ZHU J F, REN Z G, et al. Effects of different soil amendments on soil chemical properties and soil enzyme activities of continuous cropping tobacco[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(4): 82-91. | |
| [35] | 郝燕. 沼液对葡萄园土壤质量和葡萄产量品质的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2019. |
| HAO Y. Effect of biogas slurry applying on soil quality in vineyard and grape yield and quality[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [36] | 万海文, 贾亮亮, 赵京奇, 等. 追施沼液对小麦光合特性及土壤酶活性和养分含量的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(1): 35-44. |
| WAN H W, JIA L L, ZHAO J Q, et al. Effects of topdressing biogas slurry on photosynthesis characteristics of wheat and soil enzyme activities and nutrients[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(1): 35-44. | |
| [37] | 黄继川, 徐培智, 彭智平, 等. 基于稻田土壤肥力及生物学活性的沼液适宜用量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(2): 362-371. |
| HUANG J C, XU P Z, PENG Z P, et al. Biogas slurry use amount for suitable soil nutrition and biodiversity in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(2): 362-371. |
| [1] | 韦庆翠, 姜娜英, 沈骏扬, 张焕朝, 张衡锋. 化肥减量配施生物质炭对高沙土氮磷淋失及土壤性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 1943-1950. |
| [2] | 张敏, 张阳, 申婧, 虎陈霞. 化肥减量增效目标下配方肥补贴数字化转型的政企农三方演化博弈分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(7): 1567-1579. |
| [3] | 张智, 何豪豪, 郁妙, 许剑锋. 化肥减量配施土壤改良剂对土壤酸度、土壤养分和水稻产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(6): 1301-1308. |
| [4] | 应永飞, 韩东轩, 孟芳, 俞遴, 沈佳栾, 汪开英. 沼液替代化肥对水稻产量、品质和土壤特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(4): 880-891. |
| [5] | 沈佳瑜, 邓燕, 李贝, 王佳雨, 张姬雯, 彭国方, 吴群, 朱齐超, 张卫峰, 段志平. 优化施肥管理对常山胡柚产量、品质与温室气体排放的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(11): 2293-2307. |
| [6] | 王湘洁, 韩科峰, 马正波, 楼金, 王帅, 吴良欢. 四翅滨藜在浙江省的生长适应性及其影响因素[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(1): 134-144. |
| [7] | 孙鹂, 张淑文, 俞浙萍, 郑锡良, 梁森苗, 任海英, 戚行江. 腐殖酸钾对杨梅土壤改良和生长结实的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(8): 1878-1886. |
| [8] | 胡铁军. 化肥减量配施微生物肥对西蓝花产量品质与土壤性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(7): 1657-1665. |
| [9] | 岳宗伟, 李嘉骁, 孙向阳, 刘国梁, 李素艳, 王晨晨, 查贵超, 魏宁娴. 化肥有机肥配施对土壤性质、樱桃果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(9): 2192-2201. |
| [10] | 肖华, 徐杏, 谢传奇, 周昕, 周卫东, 唐文升. 鸟粪石沉淀预处理对猪场沼液双膜浓缩工艺的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(6): 1407-1415. |
| [11] | 茹朝, 郁继华, 武玥, 冯致, 缑兆辉, 金宁, 王舒亚, 刘泽慈, 吕剑. 化肥减量配施生物有机肥对露地大白菜产量及品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1626-1637. |
| [12] | 江涛, 王立国, 孙芳芳, 成剑波, 何腾兵, 秦松, 范成五, 阴文芳. 沼渣生物质炭对西南喀斯特山区沼液灌溉土壤氮淋溶和白菜产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(11): 2104-2115. |
| [13] | 韩科峰, 陈余平, 胡铁军, 张丰, 周飞, 陈剑秋, 吴良欢. 硅钙钾镁肥对浙江省酸性水稻土壤的改良效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(1): 117-122. |
| [14] | 程鹏飞, 王艳, 杨期勇, 刘德富, 刘天中. 微藻贴壁培养对沼液废水的处理效果[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(9): 1564-1569. |
| [15] | 刘芳, 韩丹, 赵铭钦, 李小勇, 管成伟. 微生物菌剂配施腐殖酸钾对植烟土壤改良及烤烟经济效益的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2017, 29(7): 1064-1069. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||