浙江农业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 2104-2115.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20250023
杨属植物HKT基因家族成员鉴定与盐胁迫下的表达模式分析
廖小龙1( ), 王兴胜1, 陈勇1, 李斌1, 洪思丹2, 梅利那2, 国颖2,*(
), 王兴胜1, 陈勇1, 李斌1, 洪思丹2, 梅利那2, 国颖2,*( )
)
- 1.伊犁哈萨克自治州林木良种繁育试验中心(伊犁哈萨克自治州平原林场),新疆 伊犁 835311
2.南京林业大学 林草学院,水土保持学院,江苏省杨树种质创新与品种改良重点实验室,南方现代林业协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210037
-
收稿日期:2025-01-09出版日期:2025-10-25发布日期:2025-11-13 -
作者简介:廖小龙(1972—),男,四川遂宁人,硕士研究生,高级工程师,研究方向为林木良种选育。E-mail:632771570@qq.com -
通讯作者:国颖,E-mail:yingguo@njfu.edu.cn -
基金资助:科技创新2030-重大项目课题(2023ZD0405601)
Identification of the HKT gene family members in Populus species and analysis of their expression patterns under salt stress
LIAO Xiaolong1( ), WANG Xingsheng1, CHEN Yong1, LI Bin1, HONG Sidan2, MEI Lina2, GUO Ying2,*(
), WANG Xingsheng1, CHEN Yong1, LI Bin1, HONG Sidan2, MEI Lina2, GUO Ying2,*( )
)
- 1. Ili Experimental Center of Tree Breeding for Improved Varieties(Plain Forestry Farm), Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture, Ili 835311, Xinjiang, China
2. Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Poplar Germplasm Enhancement and Variety Improvement, Co-Innovation Center for the Sustainable Forestry in Southern China, College of Forestry and Grassland, College of Soil and Water Conservation, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing 210037, China
-
Received:2025-01-09Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-11-13
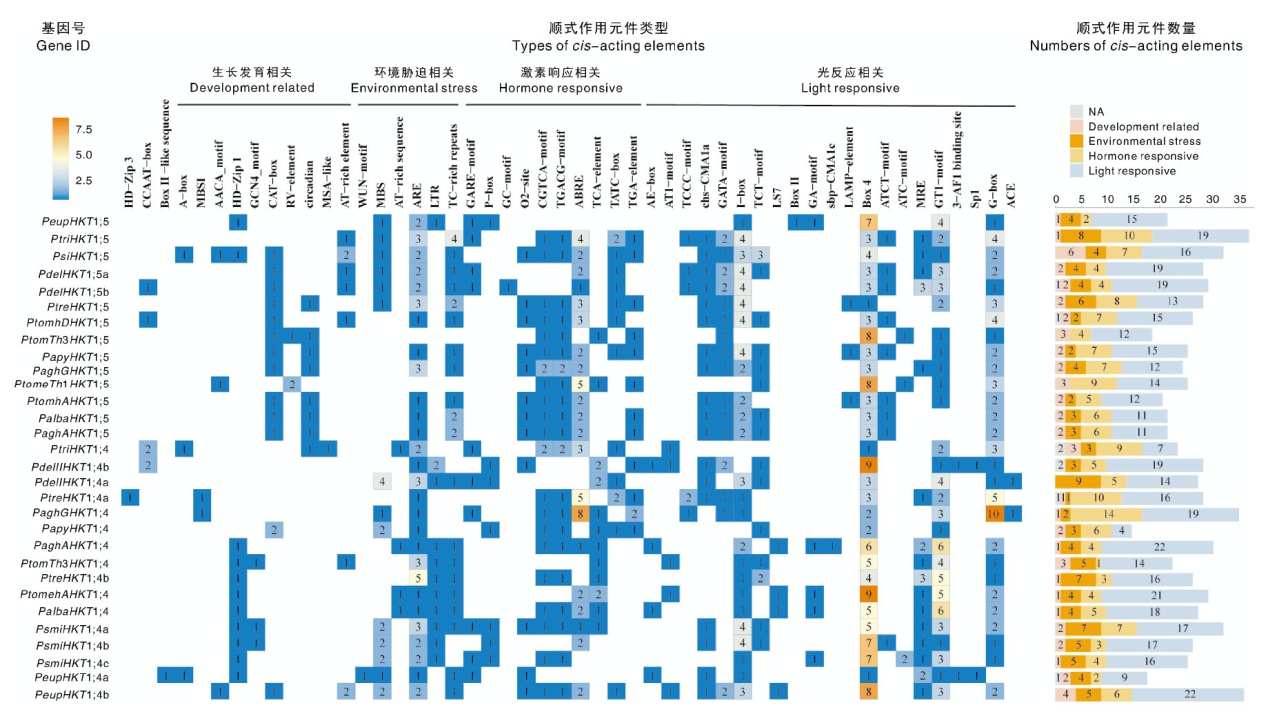
摘要: 为探究高亲和性K+转运蛋白(high-affinity K+ transporter, HKT)在杨属植物盐胁迫响应中的功能,并筛选耐盐育种关键基因,对包括银腺杨84K在内的11个杨属(Populus)物种开展全基因组水平的HKT基因家族成员鉴定,系统分析这些成员的保守结构域、蛋白质理化性质、保守基序(motif)、染色体定位和顺式作用元件等,并结合盐胁迫下银腺杨84K的实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和转录组测序(RNA-seq)数据解析HKT基因的时空表达谱。结果显示,共鉴定出30个HKT家族基因,其中29个基因定位于各物种的18号染色体。系统进化分析表明,这30个HKT基因均属于HKT1类,并划分为HKT1;4和HKT1;5两个亚组。顺式作用元件分析表明,启动子区域含有TC-rich repeats、MBS、G-box等重要的胁迫响应元件。PaghAHKT1;4在银腺杨84K中呈现出随着盐胁迫时间延长表达显著上调的趋势。综上,在杨属中共鉴定出30个HKT基因,这些基因在对盐胁迫的响应中发挥重要作用,其中PaghAHKT1;4可能是银腺杨84K耐盐育种的潜在靶基因。
中图分类号:
引用本文
廖小龙, 王兴胜, 陈勇, 李斌, 洪思丹, 梅利那, 国颖. 杨属植物HKT基因家族成员鉴定与盐胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(10): 2104-2115.
LIAO Xiaolong, WANG Xingsheng, CHEN Yong, LI Bin, HONG Sidan, MEI Lina, GUO Ying. Identification of the HKT gene family members in Populus species and analysis of their expression patterns under salt stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2025, 37(10): 2104-2115.
| 种/品种 Species/Cultivar | 单倍型 Haplotype | 组装方式 Assembly strategy |
|---|---|---|
| 欧洲山杨P. tremula | / | 基于参考基因组的基因组组装 |
| 毛果杨P. trichocarpa | / | Reference based assembly |
| 胡杨P. euphratica | / | 从头组装De novo assembly |
| 小叶杨P. simonii | / | |
| 银白杨P. alba | / | |
| 新疆杨P. alba var. pyramidalis | / | |
| 美洲黑杨I69 P. deltoides I69 | / | |
| 美洲黑杨2-2 P. deltoides 2-2 | / | |
| 银腺杨(银腺杨84K)P. alba×P. tremula var. glandulosa clone 84K | 单倍型A hapA | |
| 单倍型G hapG | ||
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型A hapA | |
| 单倍型D hapD | ||
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型1 hap1 | |
| 单倍型2 hap2 | ||
| 单倍型3 hap3 |
表1 杨属植物基因组信息统计表
Table 1 Statistical table of Populus plants genome information
| 种/品种 Species/Cultivar | 单倍型 Haplotype | 组装方式 Assembly strategy |
|---|---|---|
| 欧洲山杨P. tremula | / | 基于参考基因组的基因组组装 |
| 毛果杨P. trichocarpa | / | Reference based assembly |
| 胡杨P. euphratica | / | 从头组装De novo assembly |
| 小叶杨P. simonii | / | |
| 银白杨P. alba | / | |
| 新疆杨P. alba var. pyramidalis | / | |
| 美洲黑杨I69 P. deltoides I69 | / | |
| 美洲黑杨2-2 P. deltoides 2-2 | / | |
| 银腺杨(银腺杨84K)P. alba×P. tremula var. glandulosa clone 84K | 单倍型A hapA | |
| 单倍型G hapG | ||
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型A hapA | |
| 单倍型D hapD | ||
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型1 hap1 | |
| 单倍型2 hap2 | ||
| 单倍型3 hap3 |
| 基因名 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| PaghHKT1;5 | GGTGCTCTTCGTGGTTAT | CACAAAGATGGCTAAGGT |
| PaghAHKT1;4 | GCCAGCATTCTTCTTATT | TGACCACAAACAGCACCA |
| PaghGHKT1;4 | TCCCAACTCATTGTCTTC | CAAACAGCACCAAGATAG |
| UBQ | GTTGATTTTTGCTGGGAAGC | GATCTTGGCCTTCACGTTGT |
表2 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 2 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因名 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence(5'-3') | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| PaghHKT1;5 | GGTGCTCTTCGTGGTTAT | CACAAAGATGGCTAAGGT |
| PaghAHKT1;4 | GCCAGCATTCTTCTTATT | TGACCACAAACAGCACCA |
| PaghGHKT1;4 | TCCCAACTCATTGTCTTC | CAAACAGCACCAAGATAG |
| UBQ | GTTGATTTTTGCTGGGAAGC | GATCTTGGCCTTCACGTTGT |
| 蛋白质ID Protein ID | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度 Amino acid length/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/ku | 等电点 Isoelectric point | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaghAHKT1;5 | Pop_A18G018657 | 535 | 60.02 | 9.41 | |||
| PaghAHKT1;4 | Pop_A18G034182 | 470 | 52.95 | 9.01 | |||
| PaghGHKT1;5 | Pop_G18G019156 | 473 | 52.68 | 9.22 | |||
| PaghGHKT1;4 | Pop_G18G086088 | 206 | 23.22 | 9.49 | |||
| PalbaHKT1;5 | XP_034918867.1 | 535 | 60.02 | 9.41 | |||
| PalbaHKT1;4 | XP_034906209.1 | 521 | 58.94 | 9.02 | |||
| PapyHKT1;4 | GWHPACDA010899 | 621 | 69.63 | 9.03 | |||
| PapyHKT1;5 | GWHPACDA011033 | 451 | 50.37 | 9.04 | |||
| PtomTh1HKT1;5 | GWHPBJCQ043518 | 535 | 59.98 | 9.33 | |||
| PtomTh3HKT1;5 | GWHPBJCQ045429 | 535 | 59.79 | 9.26 | |||
| PtomTh3HKT1;4 | GWHPBJCQ045526 | 501 | 56.69 | 9.16 | |||
| PdelHKT1;5b | EVM0018125.1 | 516 | 58.11 | 9.51 | |||
| PdelHKT1;4b | EVM0019360.1 | 238 | 27.38 | 8.64 | |||
| PdelHKT1;5a | KAH8481580.1 | 473 | 52.73 | 9.27 | |||
| PdelHKT1;4a | KAH8481435.1 | 166 | 18.90 | 9.24 | |||
| PeupHKT1;5 | GWHPAAYU005564.1 | 535 | 59.96 | 9.29 | |||
| PeupHKT1;4b | GWHPAAYU005664.1 | 521 | 58.86 | 9.13 | |||
| PeupHKT1;4a | GWHPAAYU005662.1 | 422 | 47.86 | 8.85 | |||
| PsiHKT1;5 | Simonii00009649-RA | 535 | 59.94 | 9.39 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4c | Simonii00039973-RA | 521 | 58.81 | 9.15 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4b | Simonii00039952-RA | 521 | 59.00 | 9.13 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4a | Simonii00039964-RA | 498 | 56.32 | 9.07 | |||
| PtomhAHKT1;5 | KAG6741040.1 | 535 | 60.04 | 9.41 | |||
| PtomhAHKT1;4 | KAG6741120.1 | 500 | 56.53 | 9.16 | |||
| PtomhDHKT1;5 | KAG6740023.1 | 473 | 52.60 | 9.16 | |||
| PtreHKT1;5 | Potra2n18c32115.1 | 535 | 59.79 | 9.45 | |||
| PtreHKT1;4b | Potra2n8c18208.1 | 521 | 59.10 | 9.27 | |||
| PtreHKT1;4a | Potra2n18c32004.1 | 397 | 44.62 | 9.43 | |||
| PtriHKT1;5 | Potri.018G132200.1.p | 535 | 60.09 | 9.45 | |||
| PtriHKT1;4 | Potri.018G147501.2.p | 168 | 19.40 | 9.62 | |||
表3 杨属植物HKT蛋白的理化性质
Table 3 Physicochemical properties of HKT protein in Populus plants
| 蛋白质ID Protein ID | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸长度 Amino acid length/aa | 分子量 Molecular weight/ku | 等电点 Isoelectric point | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaghAHKT1;5 | Pop_A18G018657 | 535 | 60.02 | 9.41 | |||
| PaghAHKT1;4 | Pop_A18G034182 | 470 | 52.95 | 9.01 | |||
| PaghGHKT1;5 | Pop_G18G019156 | 473 | 52.68 | 9.22 | |||
| PaghGHKT1;4 | Pop_G18G086088 | 206 | 23.22 | 9.49 | |||
| PalbaHKT1;5 | XP_034918867.1 | 535 | 60.02 | 9.41 | |||
| PalbaHKT1;4 | XP_034906209.1 | 521 | 58.94 | 9.02 | |||
| PapyHKT1;4 | GWHPACDA010899 | 621 | 69.63 | 9.03 | |||
| PapyHKT1;5 | GWHPACDA011033 | 451 | 50.37 | 9.04 | |||
| PtomTh1HKT1;5 | GWHPBJCQ043518 | 535 | 59.98 | 9.33 | |||
| PtomTh3HKT1;5 | GWHPBJCQ045429 | 535 | 59.79 | 9.26 | |||
| PtomTh3HKT1;4 | GWHPBJCQ045526 | 501 | 56.69 | 9.16 | |||
| PdelHKT1;5b | EVM0018125.1 | 516 | 58.11 | 9.51 | |||
| PdelHKT1;4b | EVM0019360.1 | 238 | 27.38 | 8.64 | |||
| PdelHKT1;5a | KAH8481580.1 | 473 | 52.73 | 9.27 | |||
| PdelHKT1;4a | KAH8481435.1 | 166 | 18.90 | 9.24 | |||
| PeupHKT1;5 | GWHPAAYU005564.1 | 535 | 59.96 | 9.29 | |||
| PeupHKT1;4b | GWHPAAYU005664.1 | 521 | 58.86 | 9.13 | |||
| PeupHKT1;4a | GWHPAAYU005662.1 | 422 | 47.86 | 8.85 | |||
| PsiHKT1;5 | Simonii00009649-RA | 535 | 59.94 | 9.39 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4c | Simonii00039973-RA | 521 | 58.81 | 9.15 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4b | Simonii00039952-RA | 521 | 59.00 | 9.13 | |||
| PsiHKT1;4a | Simonii00039964-RA | 498 | 56.32 | 9.07 | |||
| PtomhAHKT1;5 | KAG6741040.1 | 535 | 60.04 | 9.41 | |||
| PtomhAHKT1;4 | KAG6741120.1 | 500 | 56.53 | 9.16 | |||
| PtomhDHKT1;5 | KAG6740023.1 | 473 | 52.60 | 9.16 | |||
| PtreHKT1;5 | Potra2n18c32115.1 | 535 | 59.79 | 9.45 | |||
| PtreHKT1;4b | Potra2n8c18208.1 | 521 | 59.10 | 9.27 | |||
| PtreHKT1;4a | Potra2n18c32004.1 | 397 | 44.62 | 9.43 | |||
| PtriHKT1;5 | Potri.018G132200.1.p | 535 | 60.09 | 9.45 | |||
| PtriHKT1;4 | Potri.018G147501.2.p | 168 | 19.40 | 9.62 | |||
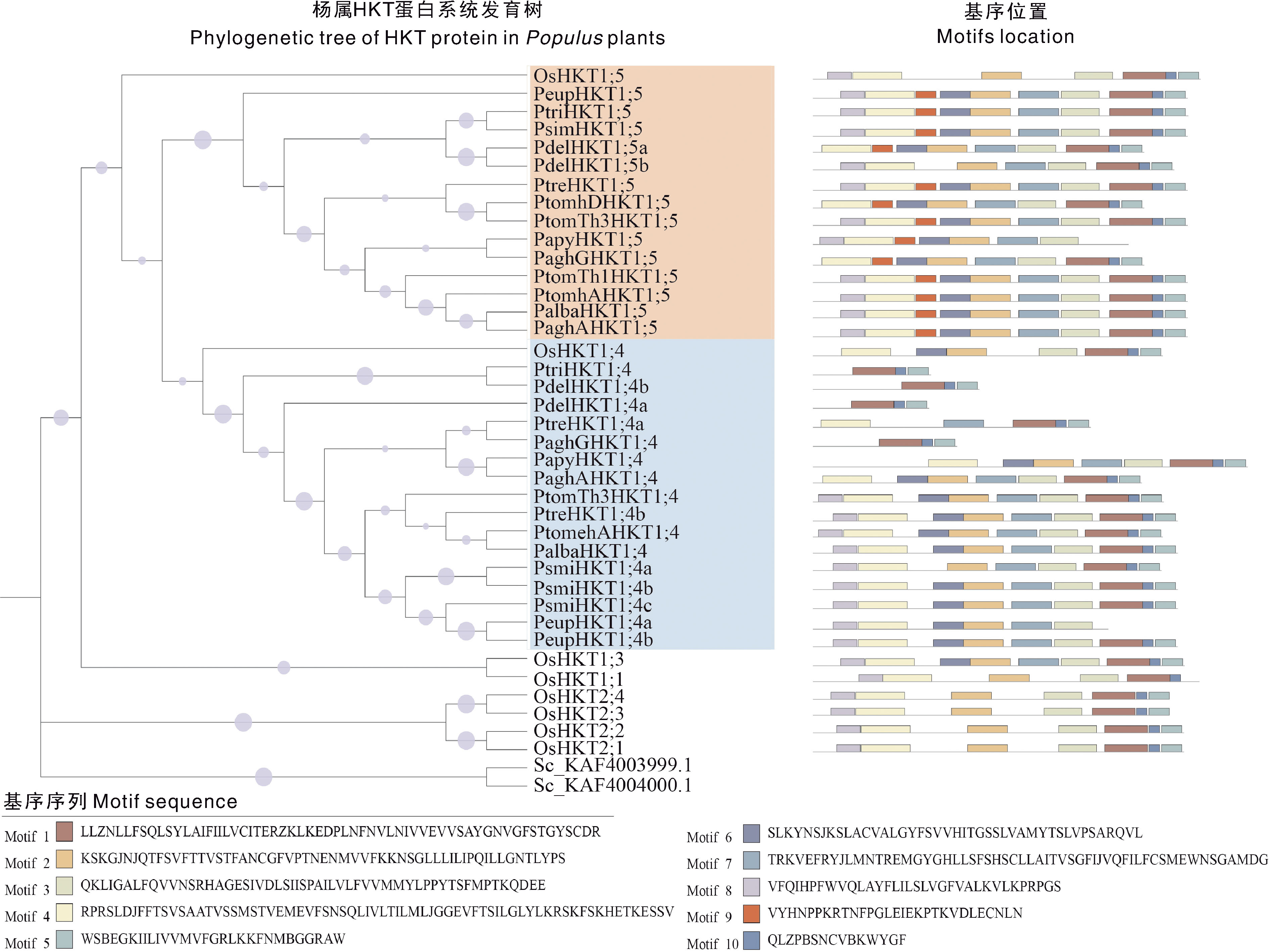
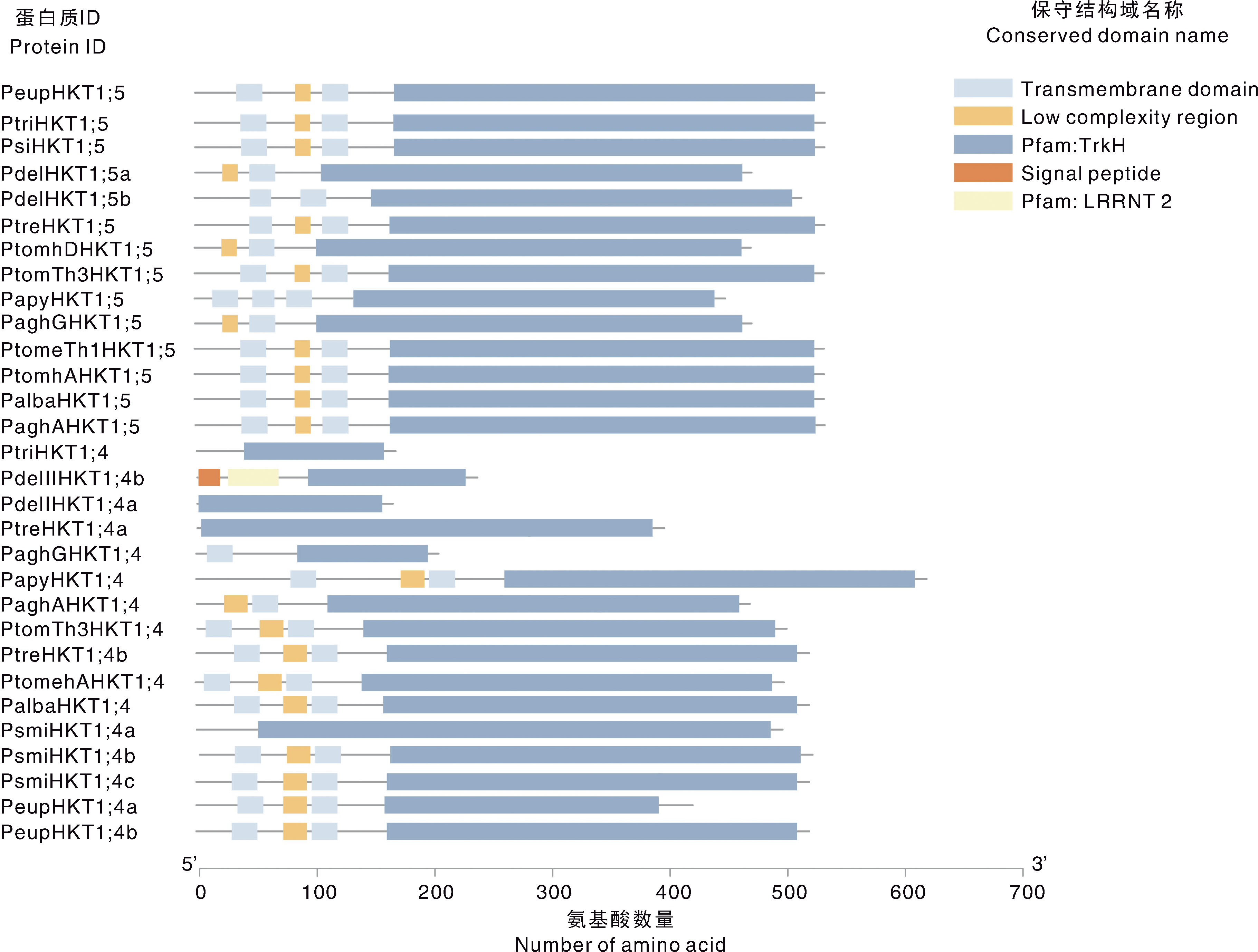
图2 杨属植物HKT基因家族成员的系统进化树和保守基序 紫色圆点表示bootstrap,范围在0.315~1.000。不同彩色方块表示不同保守基序。
Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree and conserved motifs of HKT gene family members in Populus plants The purple dots indicate the nodes of the bootstrap between 0.315-1.000. Different coloured cubes represent different conserved motifs.
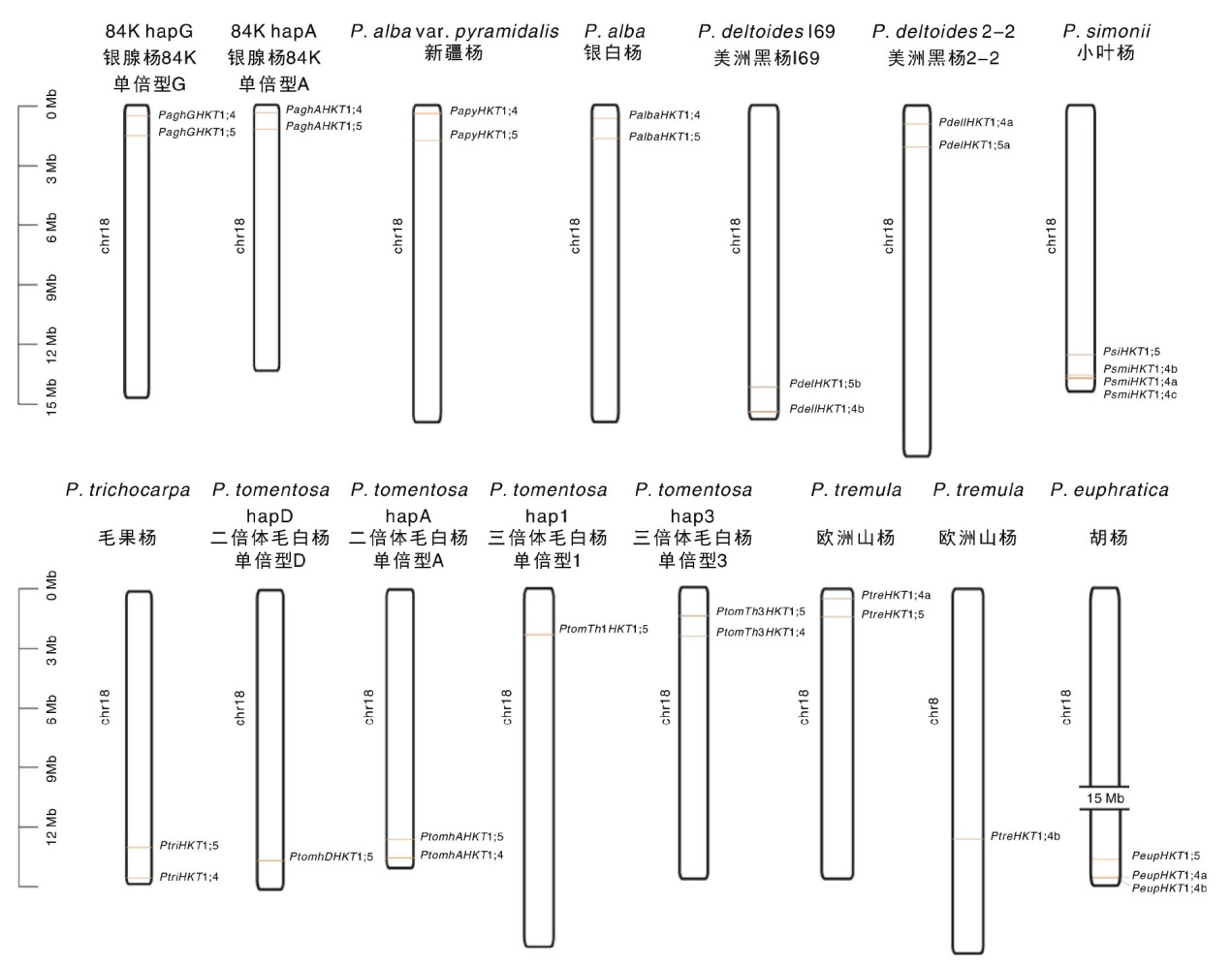
| 种/品种 Species/Cultivar | 单倍型 Haplotype | 同源组1 OG01 | 同源组2 OG02 | 同源组3 OG03 | 同源组4 OG04 | 同源组5 OG05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 银腺杨84K P. alba×P. tremula var. glandulosa clone 84K | 单倍型A hapA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 单倍型G hapG | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 银白杨P. alba | / | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 新疆杨P. alba var. pyramidalis | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型1 hap 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型3 hap 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 美洲黑杨2-2 P. deltoides 2-2 | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 美洲黑杨Ⅰ69 P. deltoides I69 | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 胡杨P. euphratica | / | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 小叶杨P. simonii | / | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型A hap A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型D hap D | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 欧洲山杨P. tremula | / | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 毛果杨P. trichocarpa | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 水稻Oryza sativa | / | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 总计Total | / | 14 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
表4 杨属植物HKT家族成员的同源性
Table 4 Homology of HKT family members in Populus plants
| 种/品种 Species/Cultivar | 单倍型 Haplotype | 同源组1 OG01 | 同源组2 OG02 | 同源组3 OG03 | 同源组4 OG04 | 同源组5 OG05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 银腺杨84K P. alba×P. tremula var. glandulosa clone 84K | 单倍型A hapA | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 单倍型G hapG | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 银白杨P. alba | / | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 新疆杨P. alba var. pyramidalis | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型1 hap 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 三倍体毛白杨P.×tomentosa Carr. clone 741 | 单倍型3 hap 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 美洲黑杨2-2 P. deltoides 2-2 | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 美洲黑杨Ⅰ69 P. deltoides I69 | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 胡杨P. euphratica | / | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 小叶杨P. simonii | / | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型A hap A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 二倍体毛白杨P. tomentosa | 单倍型D hap D | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 欧洲山杨P. tremula | / | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 毛果杨P. trichocarpa | / | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 水稻Oryza sativa | / | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 总计Total | / | 14 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
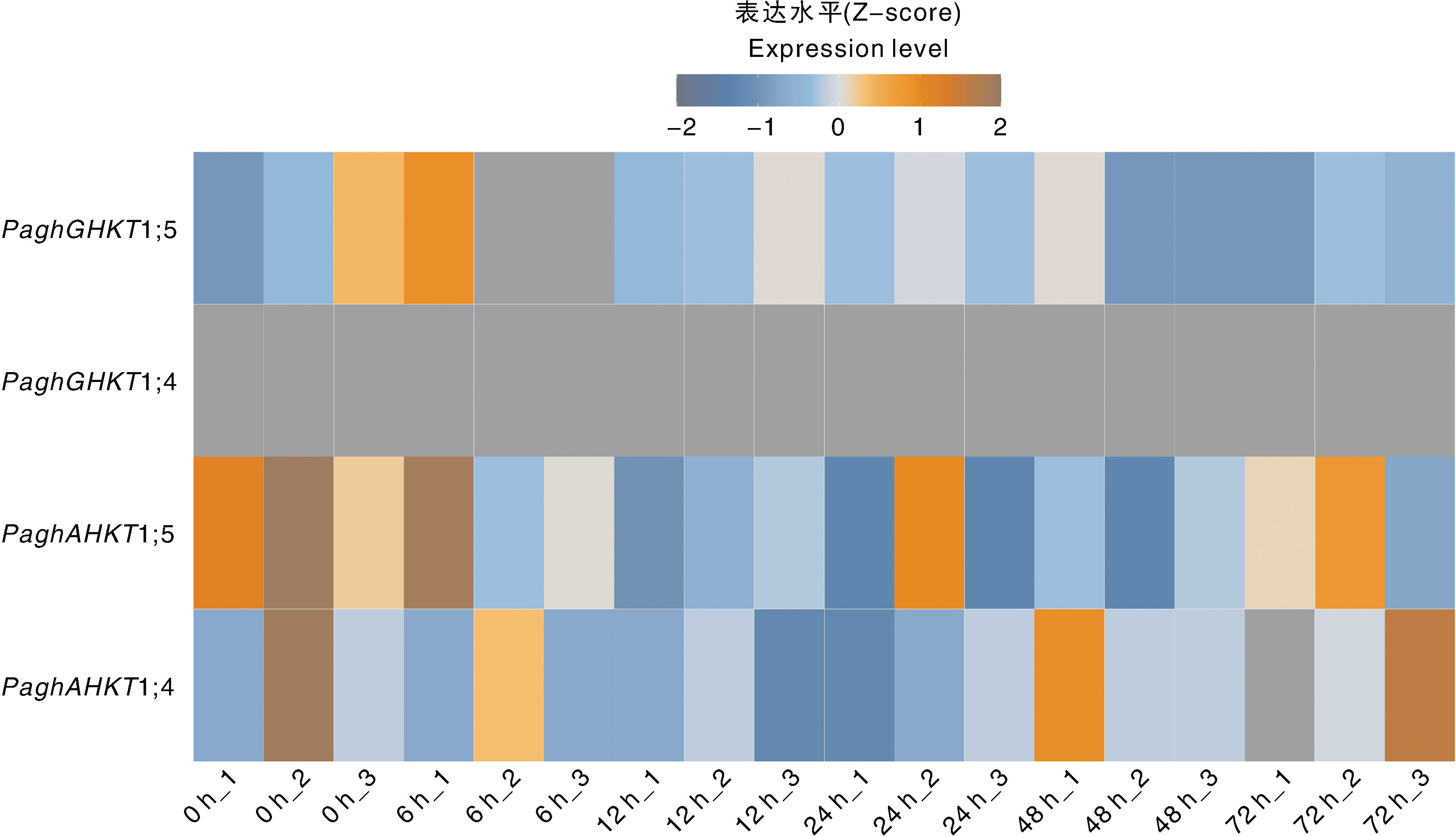
图5 100 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下银腺杨84K叶片中HKT基因的表达水平 图中横坐标下方的1、2、3分别表示100 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理各时间点(0、6、12、24、48、72 h)的3个生物学重复。表达量采用Z-score方法进行均一化。
Fig.5 Expression level of HKT genes in the leaves of poplar clone 84K under 100 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatment The labels 1, 2, and 3 below the x-axis indicate the three biological replicates for each time point(0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h) under 100 mmol·L 1 NaCl treatment. The expression levels were normalized using the Z-score method.
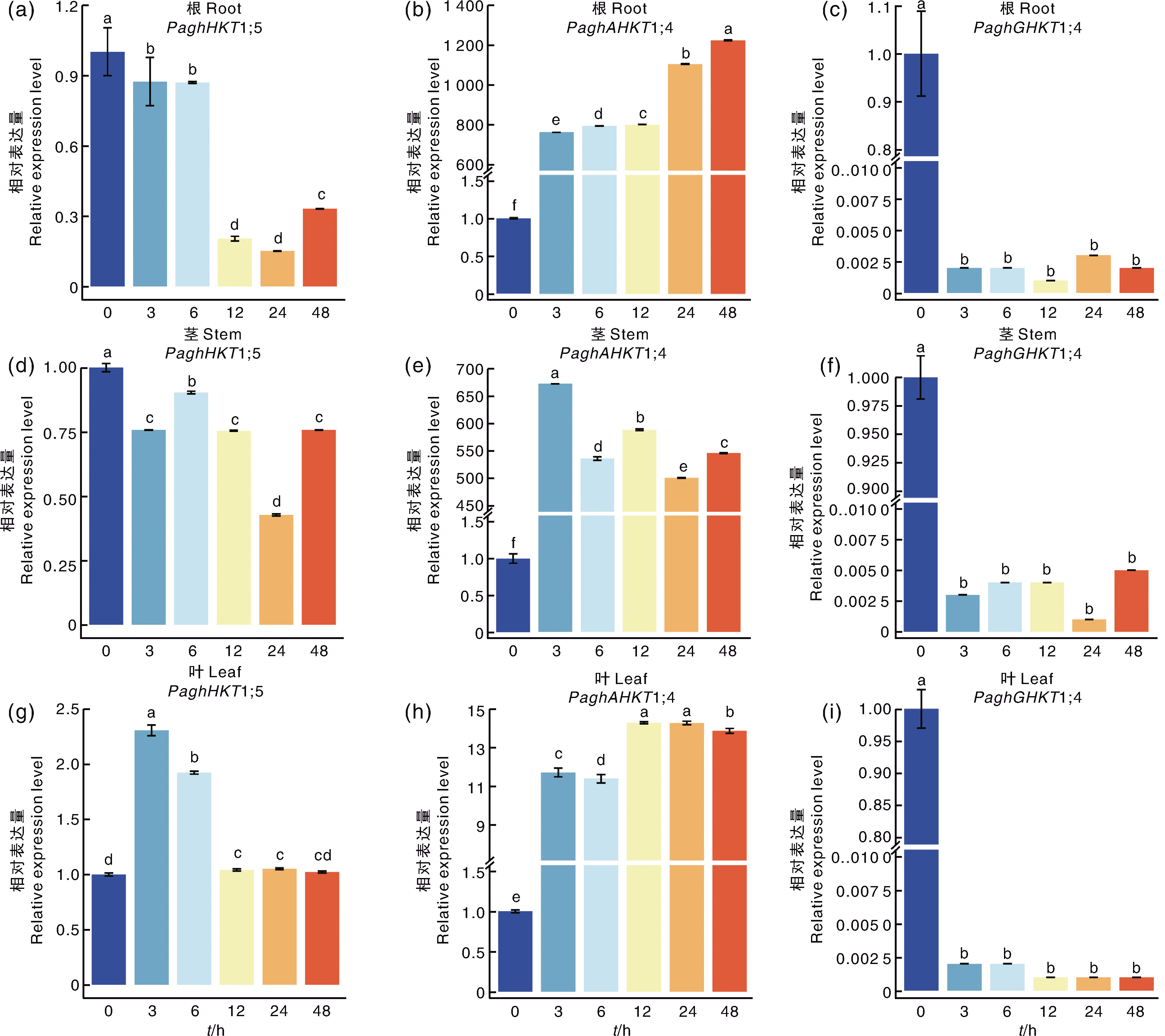
图6 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下银腺杨84K不同组织中HKT基因的表达水平 柱上无相同小写字母表示差异显著(p<0.05)。
Fig.6 Expression level of HKT genes in different tissues in poplar clone 84K under 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatment Data marked without the same lowercase letter in each column indicated significant differences at p<0.05.
| [1] | 欧阳易佳. 唤醒“沉睡”耕地资源让盐碱沙荒变“大国粮仓”[EB/OL]. (2024-01-13)[2024-06-30]. https://news.sina.com.cn/zx/gj/2024-01-14/doc-inacmkcr9735840.shtml. |
| [2] | 杜建辉. 重度盐碱化耕地治理的N种新模式[EB/OL]. (2023-11-15)[2024-06-30]. https://www.btzx.com.cn/web/2023/11/15/ARTI1700035965497340.html. |
| [3] | 梅隆, 刘自艰, 赵倩倩. 从“治理”到“适应”,重新认识盐碱地的价值[EB/OL]. (2022-07-29)[2024-06-30]. https://szb.farmer.com.cn/2022/20220729/20220729_008/20220729_008_1.htm. |
| [4] | 刘钰, 张艳华, 方升佐. 株行距配置和无性系对杨树人工林碳储量的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 2024, 44(3): 242-249. |
| LIU Y, ZHANG Y H, FANG S Z. Effects of planting spacing configurations and clones on carbon storage in poplar plantations[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 2024, 44(3): 242-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 姚诗雨, 王杰, 黄文娟, 等. 不同展叶物候期胡杨离子分布、吸收和运输特征及其与土壤盐分关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 2023, 43(12): 2118-2129. |
| YAO S Y, WANG J, HUANG W J, et al. Distribution, uptake and transport characteristics of Populus euphratica ions at different leaf phenological stages and their relationship with soil salinity[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2023, 43(12): 2118-2129. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 左照江, 张汝民, 高岩. 盐胁迫下植物细胞离子流变化的研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(5): 805-811. |
| ZUO Z J, ZHANG R M, GAO Y. Advances in plant cell ion flux with salt stress: a review[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2014, 31(5): 805-811. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | SHABALA S. Ionic and osmotic components of salt stress specifically modulate net ion fluxes from bean leaf mesophyll[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2000, 23(8): 825-837. |
| [8] | SHI H Z, LEE B H, WU S J, et al. Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2002, 21(1): 81-85. |
| [9] | MUNNS R, TESTER M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 651-681. |
| [10] | VERA-ESTRELLA R, BARKLA B J, BOHNERT H J, et al. Salt stress in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. cell suspensions activates adaptive mechanisms similar to those observed in the whole plant[J]. Planta, 1999, 207(3): 426-435. |
| [11] | BEILBY M J, SHEPHERD V A. Modeling the current-voltage characteristics of charophyte membranes. II. the effect of salinity on membranes of Lamprothamnium papulosum[J]. The Journal of Membrane Biology, 2001, 181(2): 77-89. |
| [12] | SHABALA L, CUIN T A, NEWMAN I A, et al. Salinity-induced ion flux patterns from the excised roots of Arabidopsis sos mutants[J]. Planta, 2005, 222(6): 1041-1050. |
| [13] | RIEDELSBERGER J, MILLER J K, VALDEBENITO-MATURANA B, et al. Plant HKT channels: an updated view on structure, function and gene regulation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(4): 1892. |
| [14] | BYRT C S, XU B, KRISHNAN M, et al. The Na+ transporter, TaHKT1;5-D, limits shoot Na+ accumulation in bread wheat[J]. The Plant Journal, 2014, 80(3): 516-526. |
| [15] | HAMAMOTO S, HORIE T, HAUSER F, et al. HKT transporters mediate salt stress resistance in plants: from structure and function to the field[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2015, 32: 113-120. |
| [16] | XIAO L Y, SHI Y Y, WANG R, et al. The transcription factor OsMYBc and an E3 ligase regulate expression of a K+ transporter during salt stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 190(1): 843-859. |
| [17] | HUA Y P, PEI M N, SONG H L, et al. Boron confers salt tolerance through facilitating BnaA2.HKT1-mediated root xylem Na+ unloading in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)[J]. The Plant Journal, 2024, 120(4): 1326-1342. |
| [18] | UCHIYAMA T, SAITO S, YAMANASHI T, et al. The HKT1 Na+ transporter protects plant fertility by decreasing Na+ content in stamen filaments[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(22): eadg5495. |
| [19] | 徐文君, 刘兆普, 隆小华, 等. 农杆菌介导转AtNHX1基因杨树的获得[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2007, 43(3): 413-416. |
| XU W J, LIU Z P, LONG X H, et al. Transformation of populus x euramericana with AtNHX1 gene mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2007, 43(3): 413-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | SUN J, CHEN S L, DAI S X, et al. NaCl-induced alternations of cellular and tissue ion fluxes in roots of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive poplar species[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 149(2): 1141-1153. |
| [21] | ZHANG Z Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Improved genome assembly provides new insights into genome evolution in a desert poplar (Populus euphratica)[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2020, 20(3): 781-794. |
| [22] | LIU Y J, WANG X R, ZENG Q Y. De novo assembly of white poplar genome and genetic diversity of white poplar population in Irtysh River basin in China[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2019, 62(5): 609-618. |
| [23] | ZHANG L, ZHAO J T, BI H, et al. Bioinformatic analysis of chromatin organization and biased expression of duplicated genes between two poplars with a common whole-genome duplication[J]. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8: 62. |
| [24] | WU H N, YAO D, CHEN Y H, et al. De novo genome assembly of Populus simonii further supports that Populus simonii and Populus trichocarpa belong to different sections[J]. G3 Genes Genomes Genetics, 2020, 10(2): 455-466. |
| [25] | WANG J, DING J H, TAN B Y, et al. A major locus controls local adaptation and adaptive life history variation in a perennial plant[J]. Genome Biology, 2018, 19(1): 72. |
| [26] | EVANS L M, SLAVOV G T, RODGERS-MELNICK E, et al. Population genomics of Populus trichocarpa identifies signatures of selection and adaptive trait associations[J]. Nature Genetics, 2014, 46(10): 1089-1096. |
| [27] | XUE L J, WU H T, CHEN Y N, et al. Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex determination in Populus deltoides[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5893. |
| [28] | BAI S J, WU H N, ZHANG J P, et al. Genome assembly of salicaceae Populus deltoides(eastern cottonwood) I-69 based on nanopore sequencing and Hi-C technologies[J]. Journal of Heredity, 2021, 112(3): 303-310. |
| [29] | QIU D Y, BAI S L, MA J C, et al. The genome of Populus alba×Populus tremula var. glandulosa clone 84K[J]. DNA Research, 2019, 26(5): 423-431. |
| [30] | AN X M, GAO K, CHEN Z, et al. High quality haplotype-resolved genome assemblies of Populus tomentosa Carr., a stabilized interspecific hybrid species widespread in Asia[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2022, 22(2): 786-802. |
| [31] | TONG S F, WANG Y B, CHEN N N, et al. PtoNF-YC9-SRMT-PtoRD26 module regulates the high saline tolerance of a triploid poplar[J]. Genome Biology, 2022, 23(1): 148. |
| [32] | 李建国, 濮励杰, 朱明, 等. 土壤盐渍化研究现状及未来研究热点[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(9): 1233-1245. |
| LI J G, PU L J, ZHU M, et al. The present situation and hot issues in the salt-affected soil research[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(9): 1233-1245. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [33] | 储陈辰. 杨属和柳属泛基因组构建与基因组变异分析[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2023. |
| CHU C C. Pan-genome and genomic variation analysis of genera Populus and Salix[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [34] | XU Z S, NI Z Y, LIU L, et al. Characterization of the TaAIDFa gene encoding a CRT/DRE-binding factor responsive to drought, high-salt, and cold stress in wheat[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2008, 280(6): 497-508. |
| [35] | ERPEN L, DEVI H S, GROSSER J W, et al. Potential use of the DREB/ERF, MYB, NAC and WRKY transcription factors to improve abiotic and biotic stress in transgenic plants[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2018, 132(1): 1-25. |
| [36] | HENDERSON S W, DUNLEVY J D, WU Y, et al. Functional differences in transport properties of natural HKT1;1 variants influence shoot Na+ exclusion in grapevine rootstocks[J]. New Phytologist, 2018, 217(3): 1113-1127. |
| [37] | WU Y, HENDERSON S W, WEGE S, et al. The grapevine NaE sodium exclusion locus encodes sodium transporters with diverse transport properties and localisation[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 246: 153113. |
| [38] | ZHANG M, CAO Y B, WANG Z P, et al. A retrotransposon in an HKT1 family sodium transporter causes variation of leaf Na+ exclusion and salt tolerance in maize[J]. New Phytologist, 2018, 217(3): 1161-1176. |
| [39] | ALNAYEF M, SOLIS C, SHABALA L, et al. Changes in expression level of OsHKT1;5 alters activity of membrane transporters involved in K+ and Ca2+ acquisition and homeostasis in salinized rice roots[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(14): 4882. |
| [1] | 胡莹洁, 杜晨琪, 王鎏帆, 寿建昕, 王超, 徐梅, 严旭. 囊泡运输调控植物盐胁迫响应的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(9): 2003-2011. |
| [2] | 关秀生, 刘铁山, 王娟, 张茂林, 刘春晓, 董瑞, 关海英, 刘强, 徐扬, 何春梅. 玉米NF-YA家族基因的生物信息学分析与克隆[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2025, 37(8): 1605-1614. |
| [3] | 吴国江, 周伟, 李艳肖, 侯杰, 杨志强, 周亚星. 高粱ZF-HD基因家族鉴定与盐碱胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(6): 1217-1231. |
| [4] | 宛燕, 周晓春, 房海灵, 林沂, 亓希武, 于盱, 陈泽群, 梁呈元. 金银花光形态建成因子LjCOP1基因克隆及表达模式分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(6): 1290-1299. |
| [5] | 李亚萍, 金福来, 黄宗贵, 张涛, 段晓婧, 姜武, 陶正明, 陈家栋. 铁皮石斛糖苷水解酶GH3基因家族鉴定及表达模式分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(4): 790-799. |
| [6] | 高憬, 陆玲鸿, 古咸彬, 范飞, 宋根华, 张慧琴. 猕猴桃AcWRKY94基因的克隆及其在盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(11): 2501-2509. |
| [7] | 唐跃辉, 陈淑颖, 何文琼, 王涵瑾, 包欣欣, 贾赛男, 王瑶瑶, 陈宇阳, 杨同文. 麻风树JcERF22基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2024, 36(10): 2219-2228. |
| [8] | 梁成刚, 汪燕, 关志秀, 韦春玉, 邓娇, 黄娟, 孟子烨, 石桃雄. 苦荞蔗糖转运体家族FtSUCs的鉴定与生物信息学分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(8): 1591-1598. |
| [9] | 麻仲花, 吴娜, 陈娟, 赵匆, 闫承宏, 刘吉利. 盐胁迫与供磷水平对柳枝稷苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(6): 1205-1216. |
| [10] | 李丽艳, 谭海霞, 李婧, 王连龙, 杜迎辉, 徐志文. 耐盐促生芽孢杆菌的筛选及其对盐胁迫下燕麦生长的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(6): 1268-1276. |
| [11] | 刘晨, 徐浩博, 斯钰阳, 李亚鹏, 郭玉婷, 杜长霞. 基于转录组学的植物响应盐胁迫调控机制研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(4): 870-878. |
| [12] | 杨昕霞, 唐满生, 张斌. 大豆PP2C家族基因鉴定与响应盐胁迫的转录组分析[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(2): 207-220. |
| [13] | 刘涛, 陈海荣, 汪成忠, 任丽, 张荻. 干旱和盐胁迫下百子莲的抗逆生理研究[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(12): 2669-2681. |
| [14] | 孟娜, 薛辉, 魏明, 魏胜华. 氯通道抑制剂缓解栽培大豆盐伤害的离子特征[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(10): 2095-2104. |
| [15] | 周贝宁, 毛恋, 花壮壮, 芦建国. 碱性盐胁迫对夏蜡梅生长与离子分布的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(1): 79-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||